Abstract
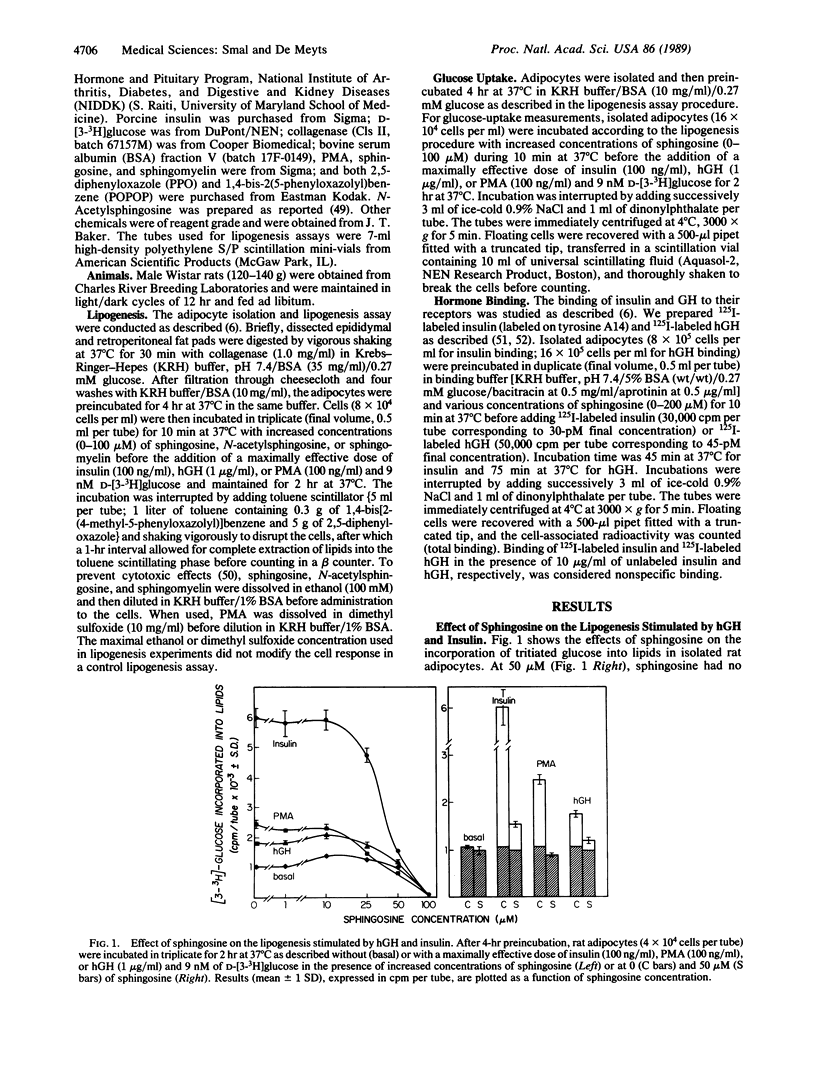
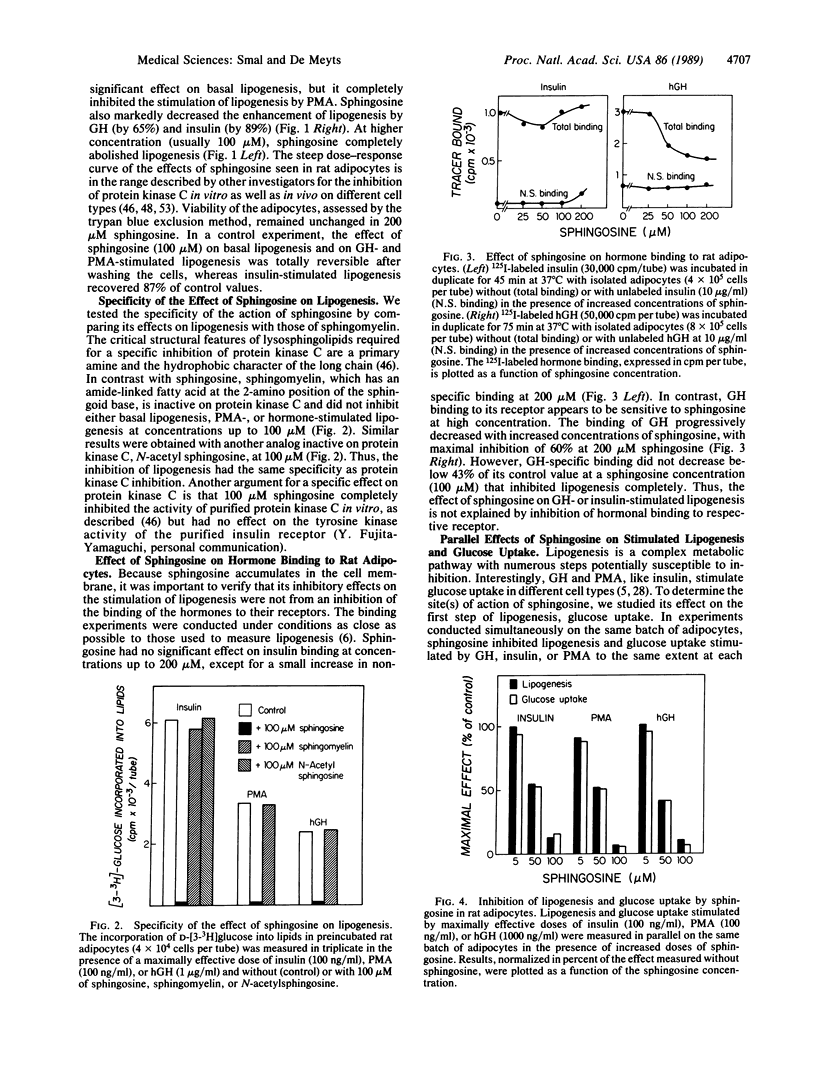
Insulin, human growth hormone (hGH), and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate all stimulate lipogenesis in rat adipocytes preincubated without hGH for 4 hr. As previous data suggested that protein kinase C plays an important role in the action of insulin and in the insulin-like effects of hGH in rat adipocytes, we tested the effects of sphingosine, a potent inhibitor of protein kinase C, on the lipogenic activity of both hormones. At 50 microM, sphingosine had no effect on basal lipogenesis but completely abolished the action of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate and decreased by 65% and 89%, respectively, the effects of hGH and insulin. At higher concentrations (100 microM), sphingosine abolished both basal and hormone-stimulated lipogenesis; this effect was partially reversible after washing the cells. Similar effects of sphingosine on basal and stimulated glucose uptake were seen in parallel, suggesting that sphingosine inhibits lipogenesis at the glucose-uptake step in rat adipocytes. N-Acetylsphingosine and sphingomyelin, two analogs of sphingosine that are inactive on protein kinase C, did not inhibit lipogenesis induced by hGH, insulin, or phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. Sphingosine did not inhibit insulin binding to rat adipocytes at concentrations up to 200 microM but decreased hGH binding to its receptors by 44% at 50 microM. These data suggest a direct link between the inhibition of protein kinase C and that of lipogenesis and provide new evidence for the involvement of protein kinase C in the mechanism of action of growth hormone and insulin in rat adipocytes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Augert G., Exton J. H. Insulin and oxytocin effects on phosphoinositide metabolism in adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3600–3609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackshear P. J., Witters L. A., Girard P. R., Kuo J. F., Quamo S. N. Growth factor-stimulated protein phosphorylation in 3T3-L1 cells. Evidence for protein kinase C-dependent and -independent pathways. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13304–13315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosca L., Rousseau G. G., Hue L. Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate and insulin increase the concentration of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate and stimulate glycolysis in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6440–6444. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boutin J. M., Jolicoeur C., Okamura H., Gagnon J., Edery M., Shirota M., Banville D., Dusanter-Fourt I., Djiane J., Kelly P. A. Cloning and expression of the rat prolactin receptor, a member of the growth hormone/prolactin receptor gene family. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):69–77. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90488-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherqui G., Caron M., Wicek D., Lascols O., Capeau J., Picard J. Decreased insulin responsiveness in fat cells rendered protein kinase C-deficient by a treatment with a phorbol ester. Endocrinology. 1987 May;120(5):2192–2194. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-5-2192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherqui G., Caron M., Wicek D., Lascols O., Capeau J., Picard J. Insulin stimulation of glucose metabolism in rat adipocytes: possible implication of protein kinase C. Endocrinology. 1986 May;118(5):1759–1769. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-5-1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu D. T., Granner D. K. The effect of phorbol esters and diacylglycerol on expression of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) gene in rat hepatoma H4IIE cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):16848–16853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Civan M. M., Peterson-Yantorno K., O'Brien T. G. Insulin and phorbol ester stimulate conductive Na+ transport through a common pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):963–967. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Closset J., Smal J., Gomez F., Hennen G. Purification of the 22000- and 20000-mol.wt. forms of human somatotropin and characterization of their binding to liver and mammary binding sites. Biochem J. 1983 Sep 15;214(3):885–892. doi: 10.1042/bj2140885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. R., Konda T. S., Standaert M. L., Davis J. S., Pollet R. J., Farese R. V. Insulin increases membrane and cytosolic protein kinase C activity in BC3H-1 myocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3633–3639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Torrontegui G., Berthet J. The action of insulin on the incorporation of [32P]phosphate in the phospholipids of rat adipose tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jun 1;116(3):477–481. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(66)90117-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doglio A., Dani C., Grimaldi P., Ailhaud G. Growth hormone stimulates c-fos gene expression by means of protein kinase C without increasing inositol lipid turnover. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1148–1152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Ellis L., Jarnagin K., Edery M., Graf L., Clauser E., Ou J. H., Masiarz F., Kan Y. W., Goldfine I. D. The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Barnes D. E., Davis J. S., Standaert M. L., Pollet R. J. Effects of insulin and protein synthesis inhibitors on phospholipid metabolism, diacylglycerol levels, and pyruvate dehydrogenase activity in BC3H-1 cultured myocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7094–7100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Davis J. S., Barnes D. E., Standaert M. L., Babischkin J. S., Hock R., Rosic N. K., Pollet R. J. The de novo phospholipid effect of insulin is associated with increases in diacylglycerol, but not inositol phosphates or cytosolic Ca2+. Biochem J. 1985 Oct 15;231(2):269–278. doi: 10.1042/bj2310269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Konda T. S., Davis J. S., Standaert M. L., Pollet R. J., Cooper D. R. Insulin rapidly increases diacylglycerol by activating de novo phosphatidic acid synthesis. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):586–589. doi: 10.1126/science.3107122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Kuo J. Y., Babischkin J. S., Davis J. S. Insulin provokes a transient activation of phospholipase C in the rat epididymal fat pad. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8589–8592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Larson R. E., Sabir M. A. Insulin acutely increases phospholipids in the phosphatidate-inositide cycle in rat adipose tissue. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4042–4045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Sabir M. A., Larson R. E., Trudeau W. L., 3rd Insulin treatment acutely increases the concentration of phosphatidylserine in rat adipose tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jan 7;750(1):200–202. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90221-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Sabir M. A., Larson R. E., Trudeau W., 3rd Further observations on the increases in inositide phospholipids after stimulation by ACTH, cAMP and insulin, and on discrepancies in phosphatidylinositol mass and 32PO4-labeling during inhibition of hormonal effects by cycloheximide. Cell Calcium. 1983 Jul;4(3):195–218. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(83)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Standaert M. L., Barnes D. E., Davis J. S., Pollet R. J. Phorbol ester provokes insulin-like effects on glucose transport, amino acid uptake, and pyruvate dehydrogenase activity in BC3H-1 cultured myocytes. Endocrinology. 1985 Jun;116(6):2650–2655. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-6-2650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster C. M., Shafer J. A., Rozsa F. W., Wang X. Y., Lewis S. D., Renken D. A., Natale J. E., Schwartz J., Carter-Su C. Growth hormone promoted tyrosyl phosphorylation of growth hormone receptors in murine 3T3-F442A fibroblasts and adipocytes. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 12;27(1):326–334. doi: 10.1021/bi00401a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaver R. C., Sweeley C. C. Chemistry and metabolism of sphingolipids. 3-Oxo derivatives of N-acetylsphingosine and N-acetyldihydrosphingosine. J Am Chem Soc. 1966 Aug 5;88(15):3643–3647. doi: 10.1021/ja00967a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn B. P., Colliton J. W., McDermott J. M., Witters L. A. Phorbol esters, but not insulin, promote depletion of cytosolic protein kinase C in rat adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 28;135(3):1119–1125. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91044-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman H. M. Growth hormone and the metabolism of carbohydrate and lipid in adipose tissue. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1968 Feb 5;148(2):419–440. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1968.tb20367.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves C. B., McDonald J. M. Insulin and phorbol ester stimulate phosphorylation of a 40-kDa protein in adipocyte plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11286–11292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Bell R. M. Aminoacridines, potent inhibitors of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5124–5131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Bell R. M. Lysosphingolipids inhibit protein kinase C: implications for the sphingolipidoses. Science. 1987 Feb 6;235(4789):670–674. doi: 10.1126/science.3101176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Greenberg C. S., Bell R. M. Sphingosine inhibition of agonist-dependent secretion and activation of human platelets implies that protein kinase C is a necessary and common event of the signal transduction pathways. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13620–13626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Loomis C. R., Merrill A. H., Jr, Bell R. M. Sphingosine inhibition of protein kinase C activity and of phorbol dibutyrate binding in vitro and in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12604–12609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyworth C. M., Whetton A. D., Kinsella A. R., Houslay M. D. The phorbol ester, TPA inhibits glucagon-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity. FEBS Lett. 1984 May 7;170(1):38–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81364-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaksson O. G., Edén S., Jansson J. O. Mode of action of pituitary growth hormone on target cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:483–499. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson A. B., Schulman H. Sphingosine inhibits calmodulin-dependent enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15241–15244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R. The molecular mechanism of insulin action. Annu Rev Med. 1985;36:429–451. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.36.020185.002241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch D., Obermaier B., Häring H. U. Phorbolesters enhance basal D-glucose transport but inhibit insulin stimulation of D-glucose transport and insulin binding in isolated rat adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 30;128(2):824–832. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90121-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klip A., Ramlal T. Protein kinase C is not required for insulin stimulation of hexose uptake in muscle cells in culture. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 15;242(1):131–136. doi: 10.1042/bj2420131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambeth J. D., Burnham D. N., Tyagi S. R. Sphinganine effects on chemoattractant-induced diacylglycerol generation, calcium fluxes, superoxide production, and on cell viability in the human neutrophil. Delivery of sphinganine with bovine serum albumin minimizes cytotoxicity without affecting inhibition of the respiratory burst. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3818–3822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. S., Weinstein I. B. Membrane effects of tumor promoters: stimulation of sugar uptake in mammalian cell cultures. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Jun;99(3):451–460. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040990319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. W., Spencer S. A., Cachianes G., Hammonds R. G., Collins C., Henzel W. J., Barnard R., Waters M. J., Wood W. I. Growth hormone receptor and serum binding protein: purification, cloning and expression. Nature. 1987 Dec 10;330(6148):537–543. doi: 10.1038/330537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill A. H., Jr, Sereni A. M., Stevens V. L., Hannun Y. A., Bell R. M., Kinkade J. M., Jr Inhibition of phorbol ester-dependent differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemic (HL-60) cells by sphinganine and other long-chain bases. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12610–12615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. H., Murray D. K. Sphingolipids inhibit insulin and phorbol ester stimulated uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jul 16;138(1):463–467. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90303-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien T. G., Saladik D. Regulation of hexose transport in BALB/c 3T3 preadipose cells: effects of glucose concentration and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Sep;112(3):376–384. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041120311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington S. R., Martin B. R. Insulin-stimulated phosphoinositide metabolism in isolated fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11039–11045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Pena A., Rozengurt E. Vasopressin rapidly stimulates protein kinase C in quiescent Swiss 3T3 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Oct;129(1):124–130. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041290117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R., Fox J. A., Sherline P., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin-stimulated hydrolysis of a novel glycolipid generates modulators of cAMP phosphodiesterase. Science. 1986 Aug 29;233(4767):967–972. doi: 10.1126/science.3016898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R., Sherline P., Fox J. A. Insulin-stimulated diacylglycerol production results from the hydrolysis of a novel phosphatidylinositol glycan. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1116–1121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J., Foster C. M., Satin M. S. Growth hormone and insulin-like growth factors I and II produce distinct alterations in glucose metabolism in 3T3-F442A adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8724–8728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skoglund G., Hansson A., Ingelman-Sundberg M. Rapid effects of phorbol esters on isolated rat adipocytes. Relationship to the action of protein kinase C. Eur J Biochem. 1985 May 2;148(3):407–412. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08854.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smal J., Closset J., Hennen G., De Meyts P. Receptor binding properties and insulin-like effects of human growth hormone and its 20 kDa-variant in rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11071–11079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smal J., De Meyts P. Role of kinase C in the insulin-like effects of human growth hormone in rat adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Sep 30;147(3):1232–1240. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80202-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smal J., Kathuria S., De Meyts P. Acridine orange, an inhibitor of protein kinase C, abolishes insulin and growth hormone stimulation of lipogenesis in rat adipocytes. FEBS Lett. 1989 Feb 27;244(2):465–468. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabarini D., Heinrich J., Rosen O. M. Activation of S6 kinase activity in 3T3-L1 cells by insulin and phorbol ester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4369–4373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama S., White M. F., Kahn C. R. Phorbol ester-induced serine phosphorylation of the insulin receptor decreases its tyrosine kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3440–3447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama S., White M. F., Lauris V., Kahn C. R. Phorbol esters modulate insulin receptor phosphorylation and insulin action in cultured hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7797–7801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trevillyan J. M., Perisic O., Traugh J. A., Byus C. V. Insulin- and phorbol ester-stimulated phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):3041–3044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Riedel H., Yarden Y., Coussens L., Gray A., Dull T., Schlessinger J., Waterfield M. D., Parker P. J. Protein kinases in cellular signal transduction: tyrosine kinase growth factor receptors and protein kinase C. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 2):713–724. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walaas S. I., Horn R. S., Adler A., Albert K. A., Walaas O. Insulin increases membrane protein kinase C activity in rat diaphragm. FEBS Lett. 1987 Aug 17;220(2):311–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80837-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson E., Olcott M. C., Bell R. M., Merrill A. H., Jr, Lambeth J. D. Inhibition of the oxidative burst in human neutrophils by sphingoid long-chain bases. Role of protein kinase C in activation of the burst. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12616–12623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Werve G., Proietto J., Jeanrenaud B. Tumour-promoting phorbol esters increase basal and inhibit insulin-stimulated lipogenesis in rat adipocytes without decreasing insulin binding. Biochem J. 1985 Jan 15;225(2):523–527. doi: 10.1042/bj2250523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


