Abstract
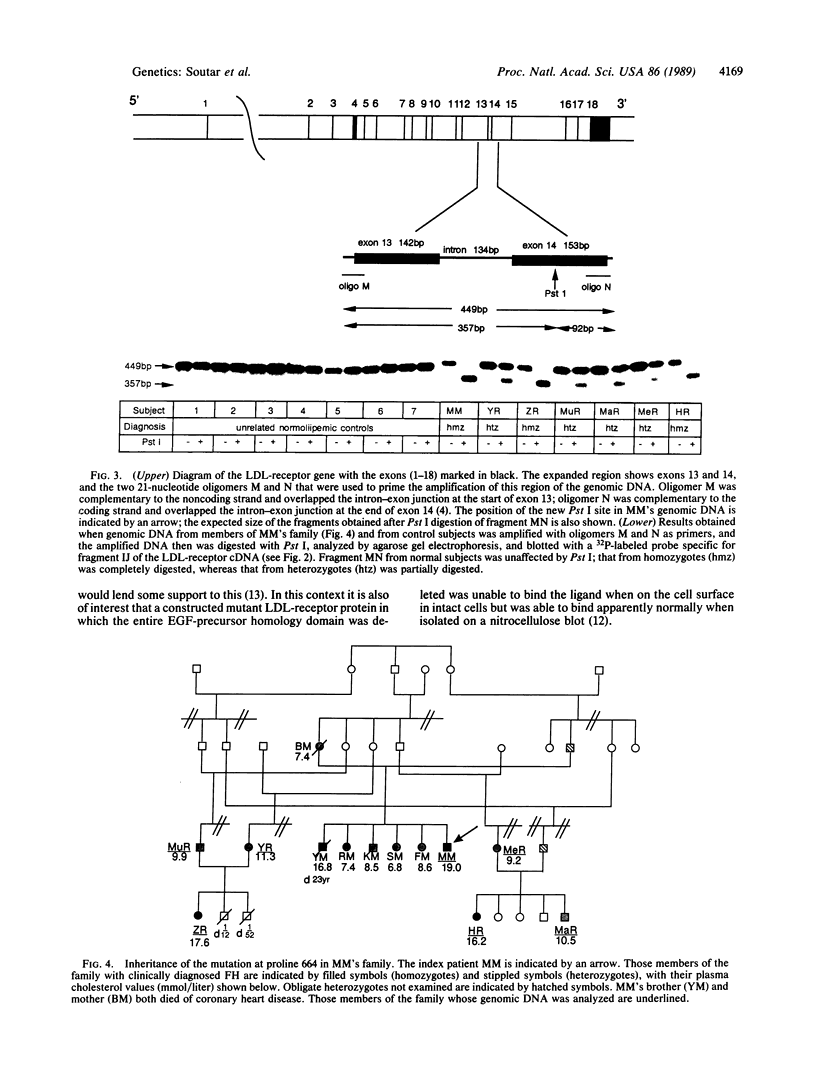
The coding region of the low density lipoprotein (LDL)-receptor gene from a patient (MM) with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) has been sequenced from six overlapping 500-base-pair amplified fragments of the cDNA from cultured skin fibroblasts. Two separate single nucleotide base changes from the normal sequence were detected. The first involved substitution of guanine for adenine in the third position of the codon for amino acid residue Cys-27 and did not affect the protein sequence. The second mutation was substitution of thymine for cytosine in the DNA for the codon for amino acid residue 664, changing the codon from CCG (proline) to CTG (leucine) and introducing a new site for the restriction enzyme PstI. MM is a true homozygote with two identical genes, and the mutation cosegregated with clinically diagnosed FH in his family in which first cousin marriages occurred frequently. The amino acid change occurs in the center of growth factor repeat C in the epidermal growth factor precursor-homology domain of the protein, a region of highly conserved sequence between bovine and human LDL receptors, and results in slowed, but complete, maturation of the precursor to the mature form of the receptor and, despite its remoteness from the ligand-binding domain, in impaired binding of LDL. LDL receptors in MM's skin fibroblasts bind less LDL than normal and with reduced affinity. Thus this naturally occurring single point mutation affects both intracellular transport of the protein and ligand binding and occurs in growth factor-like repeat C, a region that has not previously been found to influence LDL binding.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alber T., Bell J. A., Sun D. P., Nicholson H., Wozniak J. A., Cook S., Matthews B. W. Replacements of Pro86 in phage T4 lysozyme extend an alpha-helix but do not alter protein stability. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):631–635. doi: 10.1126/science.3277275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. M., Thompson G. R., Myant N. B., Steiner R., Oakley C. M. Cadiovascular complications of homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia. Br Heart J. 1980 Oct;44(4):361–368. doi: 10.1136/hrt.44.4.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):34–47. doi: 10.1126/science.3513311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. G., Goldstein J. L., Südhof T. C., Anderson R. G., Russell D. W., Brown M. S. Acid-dependent ligand dissociation and recycling of LDL receptor mediated by growth factor homology region. Nature. 1987 Apr 23;326(6115):760–765. doi: 10.1038/326760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Feng D. F., Johnson M. S. Computer-based characterization of epidermal growth factor precursor. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):558–560. doi: 10.1038/307558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esser V., Limbird L. E., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. Mutational analysis of the ligand binding domain of the low density lipoprotein receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13282–13290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esser V., Russell D. W. Transport-deficient mutations in the low density lipoprotein receptor. Alterations in the cysteine-rich and cysteine-poor regions of the protein block intracellular transport. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13276–13281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes N. S., Pandolfi de Rinaldis P. P., Macdonnell J., Cross N. C., Luzzatto L. Polymerase chain reaction automated at low cost. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 24;16(12):5687–5688. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.12.5687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavigan S. J., Patel D. D., Soutar A. K., Knight B. L. An antibody to the low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor that partially inhibits the binding of LDL to cultured human fibroblasts. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 15;171(1-2):355–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Anderson R. G., Russell D. W., Schneider W. J. Receptor-mediated endocytosis: concepts emerging from the LDL receptor system. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:1–39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht M. H., Sturtevant J. M., Sauer R. T. Effect of single amino acid replacements on the thermal stability of the NH2-terminal domain of phage lambda repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5685–5689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs H. H., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. Deletion of exon encoding cysteine-rich repeat of low density lipoprotein receptor alters its binding specificity in a subject with familial hypercholesterolemia. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13114–13120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight B. L., Gavigan S. J., Soutar A. K., Patel D. D. Defective processing and binding of low-density lipoprotein receptors in fibroblasts from a familial hypercholesterolaemic subject. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Feb 15;179(3):693–698. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14602.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight B. L., Patel D. D., Gavigan S. J., Soutar A. K. Low-density-lipoprotein-receptor mRNA content of fibroblasts from normal and familial hypercholesterolaemic subjects. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Dec 15;178(2):555–561. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14482.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight B. L., Soutar A. K. Degradation by cultured fibroblasts and macrophages of unmodified and 1,2-cyclohexanedione-modified low-density lipoprotein from normal and homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemic subjects. Biochem J. 1982 Jan 15;202(1):145–152. doi: 10.1042/bj2020145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Smith K. D., Boyer S. H., Borgaonkar D. S., Wachtel S. S., Miller O. J., Breg W. R., Jones H. W., Jr, Rary J. M. Analysis of human Y-chromosome-specific reiterated DNA in chromosome variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1245–1249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrman M. A., Schneider W. J., Brown M. S., Davis C. G., Elhammer A., Russell D. W., Goldstein J. L. The Lebanese allele at the low density lipoprotein receptor locus. Nonsense mutation produces truncated receptor that is retained in endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):401–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. W., Nicholson H., Becktel W. J. Enhanced protein thermostability from site-directed mutations that decrease the entropy of unfolding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6663–6667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. W., Schneider W. J., Yamamoto T., Luskey K. L., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Domain map of the LDL receptor: sequence homology with the epidermal growth factor precursor. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):577–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90388-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Russell D. W. The LDL receptor gene: a mosaic of exons shared with different proteins. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):815–822. doi: 10.1126/science.2988123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Bishop R. W., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. Deletion in cysteine-rich region of LDL receptor impedes transport to cell surface in WHHL rabbit. Science. 1986 Jun 6;232(4755):1230–1237. doi: 10.1126/science.3010466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Davis C. G., Brown M. S., Schneider W. J., Casey M. L., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. The human LDL receptor: a cysteine-rich protein with multiple Alu sequences in its mRNA. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yutani K., Ogasahara K., Tsujita T., Sugino Y. Dependence of conformational stability on hydrophobicity of the amino acid residue in a series of variant proteins substituted at a unique position of tryptophan synthase alpha subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4441–4444. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Driel I. R., Goldstein J. L., Südhof T. C., Brown M. S. First cysteine-rich repeat in ligand-binding domain of low density lipoprotein receptor binds Ca2+ and monoclonal antibodies, but not lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17443–17449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]