Abstract
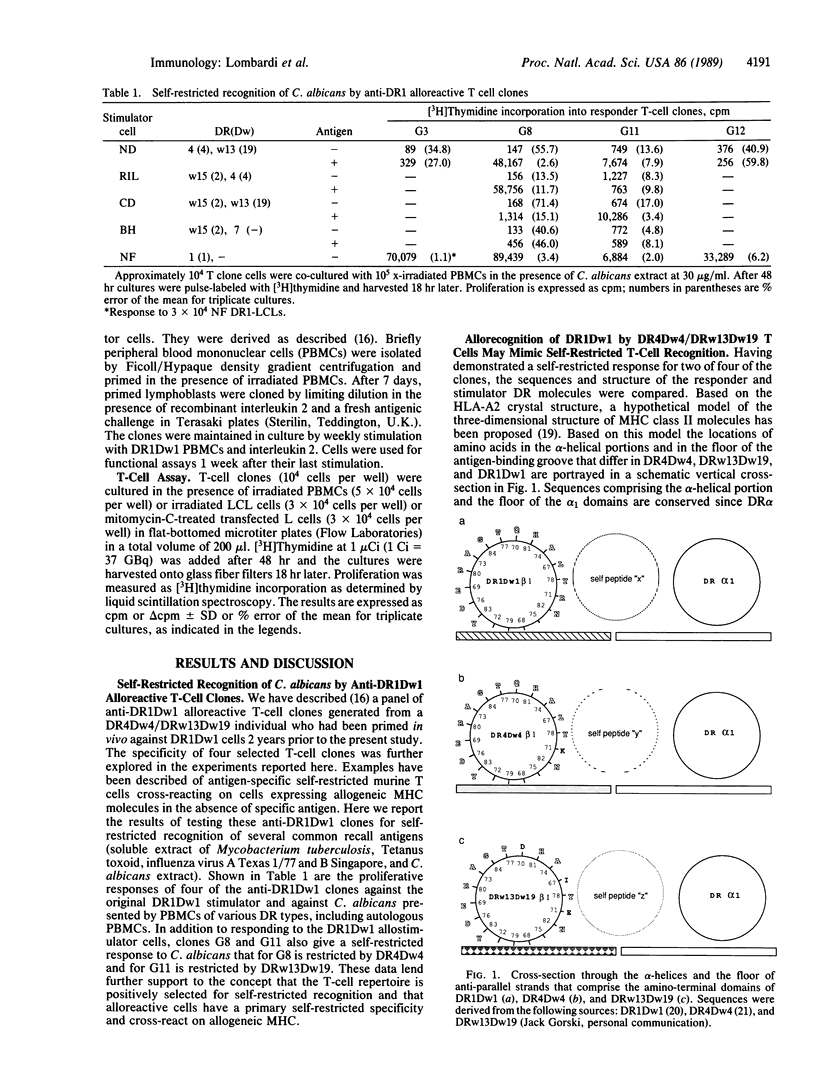
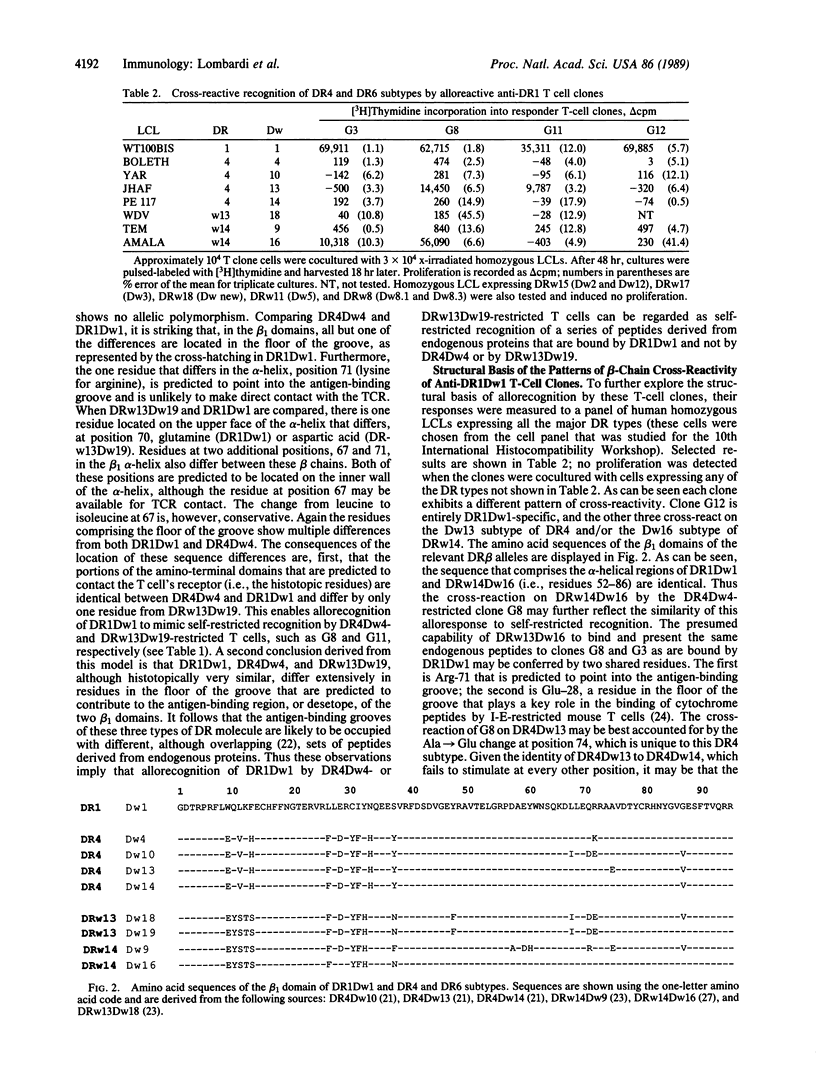
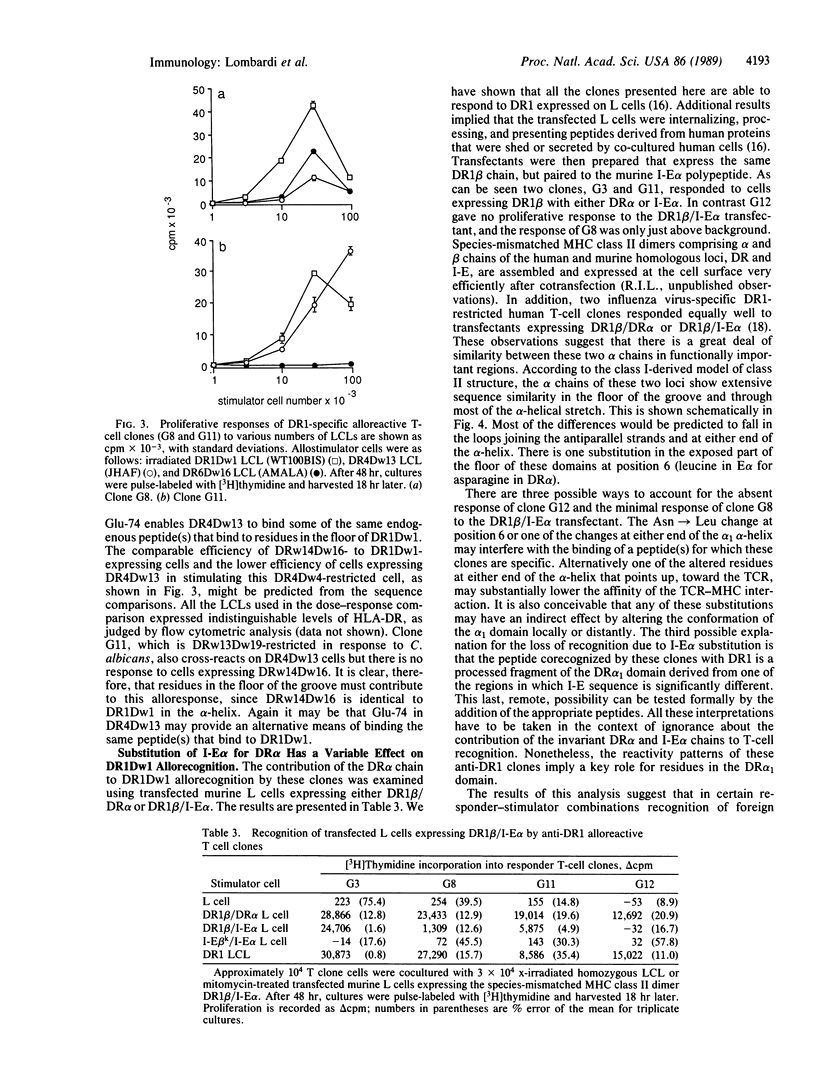
Coculture of a series of anti-DR1Dw1 alloreactive human T-cell clones with autologous (DR4Dw4/DRw13Dw19) antigen-presenting cells and a series of recall antigens revealed that two of four clones tested proliferated in response to Candida albicans. One was restricted by DR4Dw4 and the other was restricted by DRw13Dw19. These results provide further evidence that many alloreactive T cells have a primary self-restricted specificity and cross-react on allogeneic major histocompatibility complex products. Structural comparison of the responder and stimulator DR molecules for these clones revealed that the regions predicted to contact the T cells' receptor, and thereby to determine self-restriction, are identical in sequence for DR4Dw4 and DR1Dw1 and differ by one residue between DRw13Dw19 and DR1Dw1. The DR beta residues that differ between responder, DR4Dw4 and DR13Dw19, and stimulator, DR1Dw1, are predicted to contribute to antigen binding. This implies that these anti-DR1 T cells may be specific for endogenous peptides that are bound by DR1 and not by the responder DR products, seen in a self-restricted manner. These T-cell clones also cross-reacted on DR4Dw13 and DRw14Dw16 molecules and on a human/murine hybrid class II dimer DR1 beta/I-E alpha. These reactions are discussed in terms of self-restricted peptide recognition. Thus these data suggest that in certain responder/stimulator combinations allorecognition may resemble self-restricted recognition of fragments of endogenous antigens that are bound by stimulator but not by responder major histocompatibility complex products.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babbitt B. P., Allen P. M., Matsueda G., Haber E., Unanue E. R. Binding of immunogenic peptides to Ia histocompatibility molecules. 1985 Sep 26-Oct 2Nature. 317(6035):359–361. doi: 10.1038/317359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C. O., Mathis D. J., Kanter M. R., Williams V. E., 2nd, McDevitt H. O. The murine Ia alpha chains, E alpha and A alpha, show a surprising degree of sequence homology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):534–538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhard E. J., Le A. X., Barbosa J. A., Lacy E., Engelhard V. H. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes from HLA-A2 transgenic mice specific for HLA-A2 expressed on human cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Sep 1;168(3):1157–1162. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.3.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkman P. J., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bennett W. S., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. Structure of the human class I histocompatibility antigen, HLA-A2. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):506–512. doi: 10.1038/329506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. H., Jardetzky T., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bjorkman P. J., Wiley D. C. A hypothetical model of the foreign antigen binding site of class II histocompatibility molecules. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):845–850. doi: 10.1038/332845a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buus S., Sette A., Colon S. M., Jenis D. M., Grey H. M. Isolation and characterization of antigen-Ia complexes involved in T cell recognition. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1071–1077. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90822-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buus S., Sette A., Grey H. M. The interaction between protein-derived immunogenic peptides and Ia. Immunol Rev. 1987 Aug;98:115–141. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00522.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayberger C., Parham P., Rothbard J., Ludwig D. S., Schoolnik G. K., Krensky A. M. HLA-A2 peptides can regulate cytolysis by human allogeneic T lymphocytes. Nature. 1987 Dec 24;330(6150):763–765. doi: 10.1038/330763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finberg R., Burakoff S. J., Cantor H., Benacerraf B. Biological significance of alloreactivity: T cells stimulated by Sendai virus-coated syngeneic cells specifically lyse allogeneic target cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5145–5149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski J. First domain sequence of the HLA-DRB1 chain from two HLA-DRw14 homozygous typing cell lines: TEM (Dw9) and AMALA (Dw16). Hum Immunol. 1989 Feb;24(2):145–149. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(89)90054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski J., Mach B. Polymorphism of human Ia antigens: gene conversion between two DR beta loci results in a new HLA-D/DR specificity. Nature. 1986 Jul 3;322(6074):67–70. doi: 10.1038/322067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregersen P. K., Shen M., Song Q. L., Merryman P., Degar S., Seki T., Maccari J., Goldberg D., Murphy H., Schwenzer J. Molecular diversity of HLA-DR4 haplotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2642–2646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hünig T., Bevan M. J. Specificity of T-cell cones illustrates altered self hypothesis. Nature. 1981 Dec 3;294(5840):460–462. doi: 10.1038/294460a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechler R. I., Bal V., Rothbard J. B., Germain R. N., Sekaly R., Long E. O., Lamb J. Structural and functional studies of HLA-DR restricted antigen recognition by human helper T lymphocyte clones by using transfected murine cell lines. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 1;141(9):3003–3009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Trowsdale J., Travers P. J., Carey J., Grosveld F., Jenkins J., Bodmer W. F. Sequence of an HLA-DR alpha-chain cDNA clone and intron-exon organization of the corresponding gene. Nature. 1982 Oct 21;299(5885):750–752. doi: 10.1038/299750a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone A. M., Fathman C. G. The structure of T-cell epitopes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:477–501. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.002401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo D., Sprent J. Identity of cells that imprint H-2-restricted T-cell specificity in the thymus. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):672–675. doi: 10.1038/319672a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi G., Sidhu S., Lamb J. R., Batchelor J. R., Lechler R. I. Co-recognition of endogenous antigens with HLA-DR1 by alloreactive human T cell clones. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 1;142(3):753–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrack P., Kappler J. T cells can distinguish between allogeneic major histocompatibility complex products on different cell types. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):840–843. doi: 10.1038/332840a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrack P., Kushnir E., Born W., McDuffie M., Kappler J. The development of helper T cell precursors in mouse thymus. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2508–2514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzinger P., Bevan M. J. Hypothesis: why do so many lymphocytes respond to major histocompatibility antigens? Cell Immunol. 1977 Mar 1;29(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90269-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronchese F., Schwartz R. H., Germain R. N. Functionally distinct subsites on a class II major histocompatibility complex molecule. Nature. 1987 Sep 17;329(6136):254–256. doi: 10.1038/329254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teh H. S., Kisielow P., Scott B., Kishi H., Uematsu Y., Blüthmann H., von Boehmer H. Thymic major histocompatibility complex antigens and the alpha beta T-cell receptor determine the CD4/CD8 phenotype of T cells. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):229–233. doi: 10.1038/335229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonnelle C., DeMars R., Long E. O. DO beta: a new beta chain gene in HLA-D with a distinct regulation of expression. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2839–2847. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04012.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umetsu D. T., Yunis E. J., Matsui Y., Jabara H. H., Geha R. S. HLA-DR-4-associated alloreactivity of an HLA-DR-3-restricted human tetanus toxoid-specific T cell clone: inhibition of both reactivities by an alloantiserum. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Apr;15(4):356–361. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Callahan G. N., Althage A., Cooper S., Klein P. A., Klein J. On the thymus in the differentiation of "H-2 self-recognition" by T cells: evidence for dual recognition? J Exp Med. 1978 Mar 1;147(3):882–896. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.3.882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


