Abstract
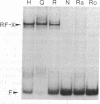
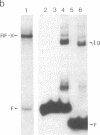
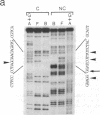
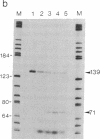
The regulation of major histocompatibility complex class II gene expression is directly involved in the control of normal and abnormal immune responses. In humans, HLA-DR, -DQ, and -DP class II heterodimers are encoded by a family of alpha- and beta-chain genes clustered in the major histocompatibility complex. Their expression is developmentally controlled and normally restricted to certain cell types. This control is mediated by cis-acting sequences in class II promoters and by trans-acting regulatory factors. Several nuclear proteins bind to class II promoter sequences. In a form of hereditary immunodeficiency characterized by a defect in a trans-acting regulatory factor controlling class II gene transcription, we have observed that one of these nuclear factors (RF-X) does not bind to its target sequence (the class II X box). A cDNA encoding RF-X was isolated by screening a phage expression library with an X-box binding-site probe. The recombinant protein has the binding specificity of RF-X, including a characteristic gradient of affinity for the X boxes of HLA-DR, -DP, and -DQ promoters. RF-X mRNA is present in the regulatory mutants, indicating a defect in the synthesis of a functional form of the RF-X protein.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellocq C., Kolakofsky D. Translational requirement for La Crosse virus S-mRNA synthesis: a possible mechanism. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3960–3967. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3960-3967.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benacerraf B. Role of MHC gene products in immune regulation. Science. 1981 Jun 12;212(4500):1229–1238. doi: 10.1126/science.6165083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanar M. A., Boettger E. C., Flavell R. A. Transcriptional activation of HLA-DR alpha by interferon gamma requires a trans-acting protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4672–4676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottazzo G. F., Todd I., Mirakian R., Belfiore A., Pujol-Borrell R. Organ-specific autoimmunity: a 1986 overview. Immunol Rev. 1986 Dec;94:137–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.1986.tb01168.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins T., Korman A. J., Wake C. T., Boss J. M., Kappes D. J., Fiers W., Ault K. A., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Strominger J. L., Pober J. S. Immune interferon activates multiple class II major histocompatibility complex genes and the associated invariant chain gene in human endothelial cells and dermal fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4917–4921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Bollekens J., Staub A., Benoist C., Mathis D. A multiplicity of CCAAT box-binding proteins. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):863–872. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90513-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Durand B., Marfing C., Le Meur M., Benoist C., Mathis D. Conserved major histocompatibility complex class II boxes--X and Y--are transcriptional control elements and specifically bind nuclear proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6249–6253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly A., Trowsdale J. Complete nucleotide sequence of a functional HLA-DP beta gene and the region between the DP beta 1 and DP alpha 1 genes: comparison of the 5' ends of HLA class II genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1607–1621. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W., Candeias S., Guardiola J., Accolla R., Benoist C., Mathis D. An enhancer factor defect in a mutant Burkitt lymphoma cell line. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1781–1790. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liou H. C., Boothby M. R., Glimcher L. H. Distinct cloned class II MHC DNA binding proteins recognize the X box transcription element. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):69–71. doi: 10.1126/science.3140376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mach B., Gorski J., Rollini P., Berte C., Amaldi I., Berdoz J., Ucla C. Polymorphism and regulation of HLA class II genes of the major histocompatibility complex. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):67–74. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massa P. T., ter Meulen V., Fontana A. Hyperinducibility of Ia antigen on astrocytes correlates with strain-specific susceptibility to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4219–4223. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matis L. A., Glimcher L. H., Paul W. E., Schwartz R. H. Magnitude of response of histocompatibility-restricted T-cell clones is a function of the product of the concentrations of antigen and Ia molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):6019–6023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.6019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa K., Doyle C., Strominger J. L. Sequence-specific interactions of nuclear factors with conserved sequences of human class II major histocompatibility complex genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4939–4943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polla B. S., Poljak A., Geier S. G., Nathenson S. G., Ohara J., Paul W. E., Glimcher L. H. Three distinct signals can induce class II gene expression in a murine pre-B-cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4878–4882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reith W., Satola S., Sanchez C. H., Amaldi I., Lisowska-Grospierre B., Griscelli C., Hadam M. R., Mach B. Congenital immunodeficiency with a regulatory defect in MHC class II gene expression lacks a specific HLA-DR promoter binding protein, RF-X. Cell. 1988 Jun 17;53(6):897–906. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)90389-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Maki R. A., Clayton L. K., Tonegawa S. Complete primary structures of the E beta chain and gene of the mouse major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5520–5524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai M., Strominger J. L. B-cell-specific enhancer activity of conserved upstream elements of the class II major histocompatibility complex DQB gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6909–6913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. H. T-lymphocyte recognition of antigen in association with gene products of the major histocompatibility complex. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:237–261. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P. A., Basta P. V., Ting J. P. Upstream DNA sequences required for tissue-specific expression of the HLA-DR alpha gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4254–4258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., LeBowitz J. H., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Molecular cloning of an enhancer binding protein: isolation by screening of an expression library with a recognition site DNA. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):415–423. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., LaMarco K. L., Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. In situ detection of sequence-specific DNA binding activity specified by a recombinant bacteriophage. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):801–806. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Préval C., Hadam M. R., Mach B. Regulation of genes for HLA class II antigens in cell lines from patients with severe combined immunodeficiency. N Engl J Med. 1988 May 19;318(20):1295–1300. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198805193182003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Préval C., Lisowska-Grospierre B., Loche M., Griscelli C., Mach B. A trans-acting class II regulatory gene unlinked to the MHC controls expression of HLA class II genes. Nature. 1985 Nov 21;318(6043):291–293. doi: 10.1038/318291a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]