Abstract
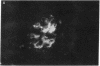
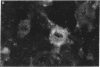
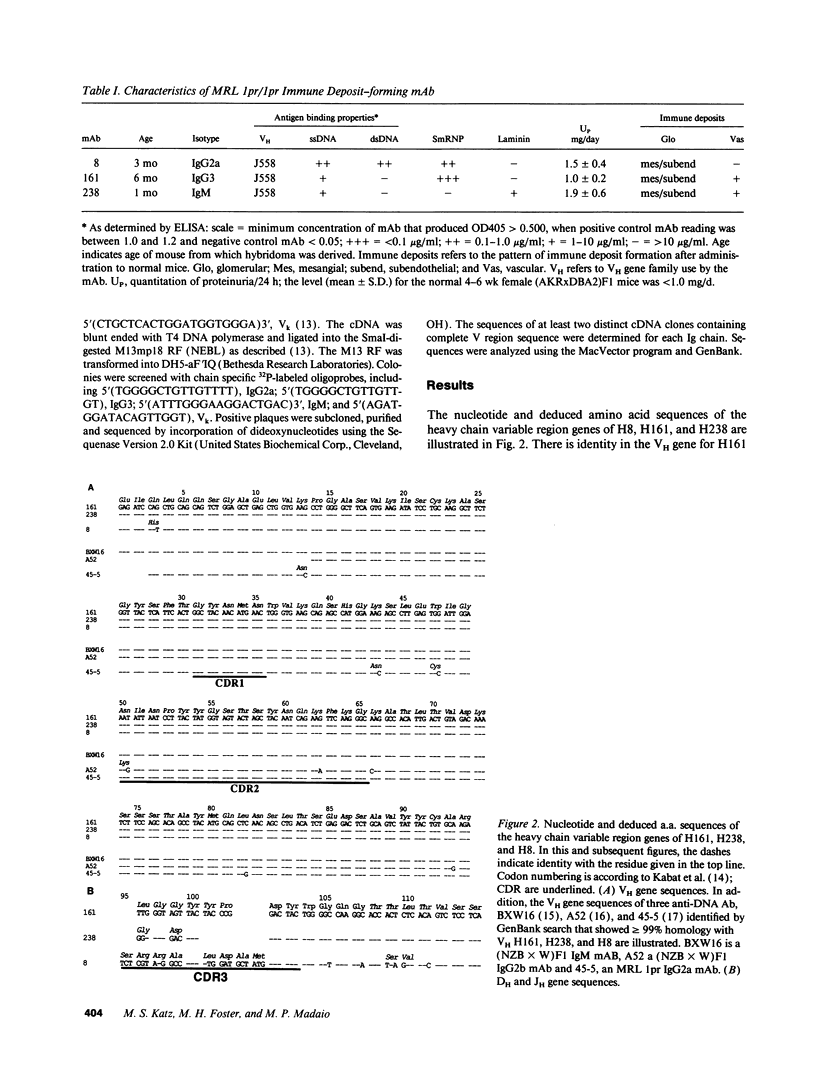
To examine the influence of variable region sequences on the capacity of individual lupus autoantibodies (autoAb) to form glomerular immune deposits, the complete VH and VL region sequences of three anti-DNA mAb that produced morphologically similar immune deposits after administration to normal mice were determined. The Ig were independently derived from 1-mo-old (H238, IgM), 3-mo-old (H8, IgG2a), and 6-mo-old (H161, IgG3) MRL-lpr/lpr mice, and they all produced subendothelial and mesangial immune deposits after passive transfer to normal mice. In addition, H238 and H161 produced granular deposits in small extraglomerular vessels. The mAb had nearly identical VH gene sequences; H8 differed from H238 and H161 by a single nucleotide in FR1 that resulted in a histidine for glutamine substitution. This VH gene sequence was also > 99% homologous to another anti-DNA Ab (termed H241), that we previously reported to produce glomerular immune deposits in a similar morphologic pattern. H161 and H238 were encoded by DFL16 and JH2 genes, whereas H8 was encoded by a JH4 gene. Different Vk family genes were used to encode the three mAb, however H161 and H238 both used a Jk5 gene. The results indicate that an identical or highly related VH gene is used to encode a subgroup of murine lupus autoAb that share immune deposit forming properties. Furthermore, they raise the possibility that amino acid residues independent from those encoded by VH genes may be influential in immune deposit formation at extraglomerular sites.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Admetlla M., Cequier A., Amer R., Javaloyas M., Sabaté X., Gausí C. Pericarditis aguda idiopática: clínica, evolución y complicaciones. Estudio prospectivo de 101 casos. Med Clin (Barc) 1985 Nov 2;85(14):563–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey N. C., Fidanza V., Mayer R., Mazza G., Fougereau M., Bona C. Activation of clones producing self-reactive antibodies by foreign antigen and antiidiotype antibody carrying the internal image of the antigen. J Clin Invest. 1989 Sep;84(3):744–756. doi: 10.1172/JCI114232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busto P., Gerstein R., Dupre L., Giorgetti C. A., Selsing E., Press J. L. Molecular analysis of heavy and light chains used by primary and secondary anti-(T,G)-A--L antibodies produced by normal and xid mice. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 15;139(2):608–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. A. The specificity of anti-DNA antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):1–2. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claflin J. L., Berry J., Flaherty D., Dunnick W. Somatic evolution of diversity among anti-phosphocholine antibodies induced with Proteus morganii. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):3060–3068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S. H., Staudt L. M., Kavaler J., Schwartz D., Gerhard W. U., Weigert M. G. V region gene usage and somatic mutation in the primary and secondary responses to influenza virus hemagglutinin. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2795–2801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebling F., Hahn B. H. Restricted subpopulations of DNA antibodies in kidneys of mice with systemic lupus. Comparison of antibodies in serum and renal eluates. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Apr;23(4):392–403. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilat D., Webster D. M., Rees A. R. V region sequences of anti-DNA and anti-RNA autoantibodies from NZB/NZW F1 mice. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1745–1753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faaber P., Capel P. J., Rijke G. P., Vierwinden G., van de Putte L. B., Koene R. A. Cross-reactivity of anti-DNA antibodies with proteoglycans. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Mar;55(3):502–508. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster M. H., MacDonald M., Barrett K. J., Madaio M. P. VH gene analysis of spontaneously activated B cells in adult MRL-lpr/lpr mice. J558 bias is not limited to classic lupus autoantibodies. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 1;147(5):1504–1511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster M. H., Madaio M. P., Barrett K. J. Variable region sequence analysis of anti-DNA antibodies: evidence for a family of closely related germ-line VH genes encoding lupus autoantibodies. DNA Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;11(3):175–182. doi: 10.1089/dna.1992.11.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavalchin J., Datta S. K. The NZB X SWR model of lupus nephritis. II. Autoantibodies deposited in renal lesions show a distinctive and restricted idiotypic diversity. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 1;138(1):138–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavalchin J., Seder R. A., Datta S. K. The NZB X SWR model of lupus nephritis. I. Cross-reactive idiotypes of monoclonal anti-DNA antibodies in relation to antigenic specificity, charge, and allotype. Identification of interconnected idiotype families inherited from the normal SWR and the autoimmune NZB parents. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 1;138(1):128–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn B. H., Ebling F. M. Idiotype restriction in murine lupus; high frequency of three public idiotypes on serum IgG in nephritic NZB/NZW F1 mice. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2110–2118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg D. A., Collins C. Detection of cross-reactive anti-DNA antibody idiotypes on renal tissue-bound immunoglobulins from lupus patients. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):287–294. doi: 10.1172/JCI111959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley D. E., Wiedemann L. M., Pittet A. C., Strauss S., Nelson K. J., Davis J., Van Ness B., Perry R. P. Nonproductive kappa immunoglobulin genes: recombinational abnormalities and other lesions affecting transcription, RNA processing, turnover, and translation. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1660–1675. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinman D. M., Steinberg A. D. Systemic autoimmune disease arises from polyclonal B cell activation. J Exp Med. 1987 Jun 1;165(6):1755–1760. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.6.1755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffler D., Schur P. H., Kunkel H. G. Immunological studies concerning the nephritis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. 1967 Oct 1;126(4):607–624. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.4.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kofler R., Strohal R., Balderas R. S., Johnson M. E., Noonan D. J., Duchosal M. A., Dixon F. J., Theofilopoulos A. N. Immunoglobulin kappa light chain variable region gene complex organization and immunoglobulin genes encoding anti-DNA autoantibodies in lupus mice. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):852–860. doi: 10.1172/JCI113689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komisar J. L., Leung K. Y., Crawley R. R., Talal N., Teale J. M. Ig VH gene family repertoire of plasma cells derived from lupus-prone MRL/lpr and MRL/++ mice. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 1;143(1):340–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leahy D. J., Rule G. S., Whittaker M. M., McConnell H. M. Sequences of 12 monoclonal anti-dinitrophenyl spin-label antibodies for NMR studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3661–3665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livant D., Blatt C., Hood L. One heavy chain variable region gene segment subfamily in the BALB/c mouse contains 500-1000 or more members. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):461–470. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90603-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madaio M. P., Carlson J., Cataldo J., Ucci A., Migliorini P., Pankewycz O. Murine monoclonal anti-DNA antibodies bind directly to glomerular antigens and form immune deposits. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):2883–2889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion T. N., Tillman D. M., Jou N. T. Interclonal and intraclonal diversity among anti-DNA antibodies from an (NZB x NZW)F1 mouse. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 1;145(7):2322–2332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng K. H., Lavigueur A., Ricard L., Boivrette M., Maclean S., Cloutier D., Gibson D. M. Characterization of allelic V kappa-1 region genes in inbred strains of mice. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 15;143(2):638–648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Keefe T. L., Bandyopadhyay S., Datta S. K., Imanishi-Kari T. V region sequences of an idiotypically connected family of pathogenic anti-DNA autoantibodies. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 1;144(11):4275–4283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pankewycz O. G., Migliorini P., Madaio M. P. Polyreactive autoantibodies are nephritogenic in murine lupus nephritis. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3287–3294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panosian-Sahakian N., Klotz J. L., Ebling F., Kronenberg M., Hahn B. Diversity of Ig V gene segments found in anti-DNA autoantibodies from a single (NZB x NZW)F1 mouse. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4500–4506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radic M. Z., Mascelli M. A., Erikson J., Shan H., Weigert M. Ig H and L chain contributions to autoimmune specificities. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):176–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reininger L., Berney T., Shibata T., Spertini F., Merino R., Izui S. Cryoglobulinemia induced by a murine IgG3 rheumatoid factor: skin vasculitis and glomerulonephritis arise from distinct pathogenic mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):10038–10042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.10038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabbaga J., Pankewycz O. G., Lufft V., Schwartz R. S., Madaio M. P. Cross-reactivity distinguishes serum and nephritogenic anti-DNA antibodies in human lupus from their natural counterparts in normal serum. J Autoimmun. 1990 Apr;3(2):215–235. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(90)90142-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Hatakeyama A., Shibata S., Osaki H., Suzuki M., Horie K., Kitagawa Y., Yoshinaga K. Heterogeneity of immune complex-derived anti-DNA antibodies associated with lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 1991 Apr;39(4):746–753. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlomchik M., Mascelli M., Shan H., Radic M. Z., Pisetsky D., Marshak-Rothstein A., Weigert M. Anti-DNA antibodies from autoimmune mice arise by clonal expansion and somatic mutation. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):265–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trepicchio W., Jr, Barrett K. J. Eleven MRL-lpr/lpr anti-DNA autoantibodies are encoded by genes from four VH gene families: a potentially biased usage of VH genes. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2323–2331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trepicchio W., Jr, Maruya A., Barrett K. J. The heavy chain genes of a lupus anti-DNA autoantibody are encoded in the germ line of a nonautoimmune strain of mouse and conserved in strains of mice polymorphic for this gene locus. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 1;139(9):3139–3145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao B. P., Ebling F. M., Roman C., Panosian-Sahakian N., Calame K., Hahn B. H. Structural characteristics of the variable regions of immunoglobulin genes encoding a pathogenic autoantibody in murine lupus. J Clin Invest. 1990 Feb;85(2):530–540. doi: 10.1172/JCI114469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlahakos D. V., Foster M. H., Adams S., Katz M., Ucci A. A., Barrett K. J., Datta S. K., Madaio M. P. Anti-DNA antibodies form immune deposits at distinct glomerular and vascular sites. Kidney Int. 1992 Jun;41(6):1690–1700. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlahakos D., Foster M. H., Ucci A. A., Barrett K. J., Datta S. K., Madaio M. P. Murine monoclonal anti-DNA antibodies penetrate cells, bind to nuclei, and induce glomerular proliferation and proteinuria in vivo. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1992 Feb;2(8):1345–1354. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V281345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida H., Yoshida M., Izui S., Lambert P. H. Distinct clonotypes of anti-DNA antibodies in mice with lupus nephritis. J Clin Invest. 1985 Aug;76(2):685–694. doi: 10.1172/JCI112022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]