Abstract
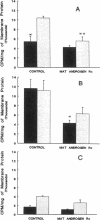
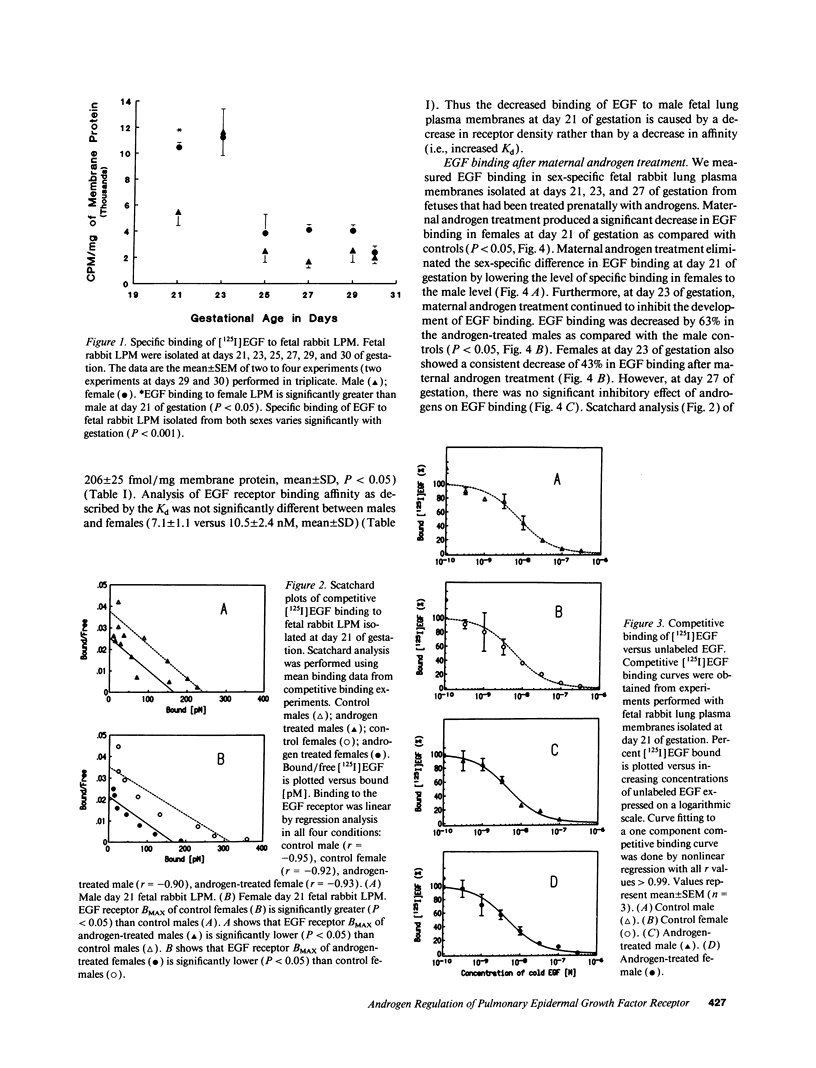
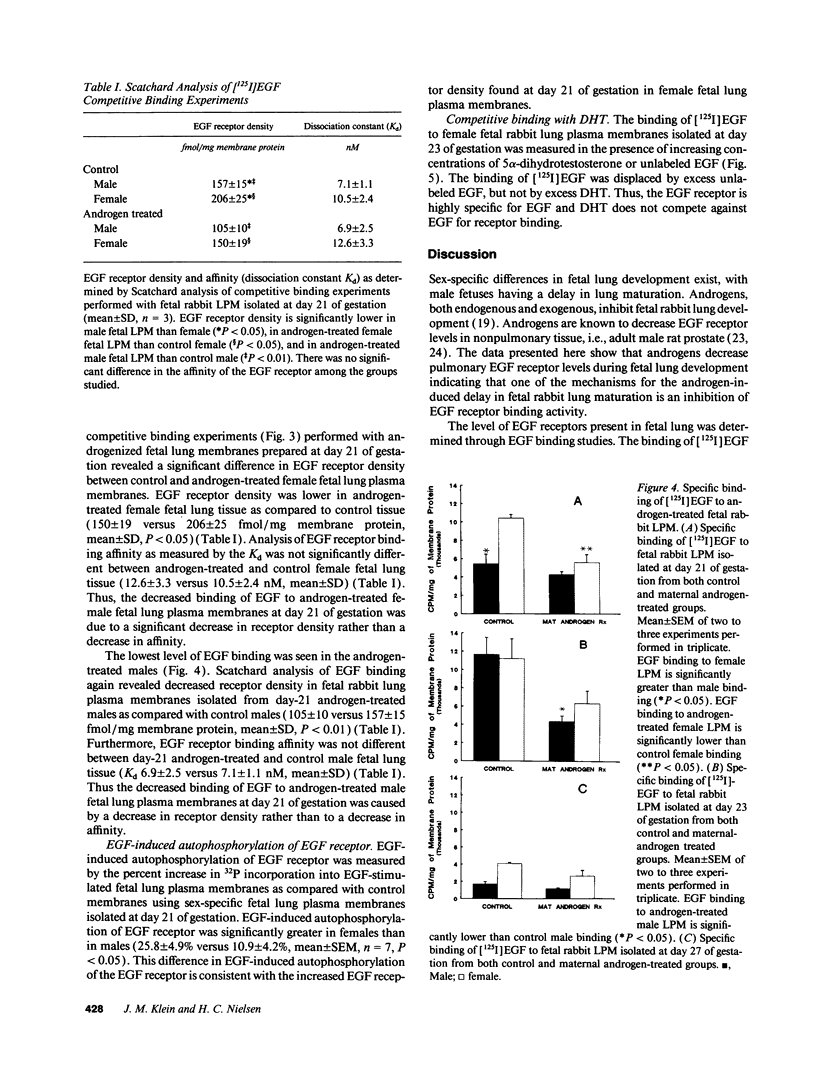
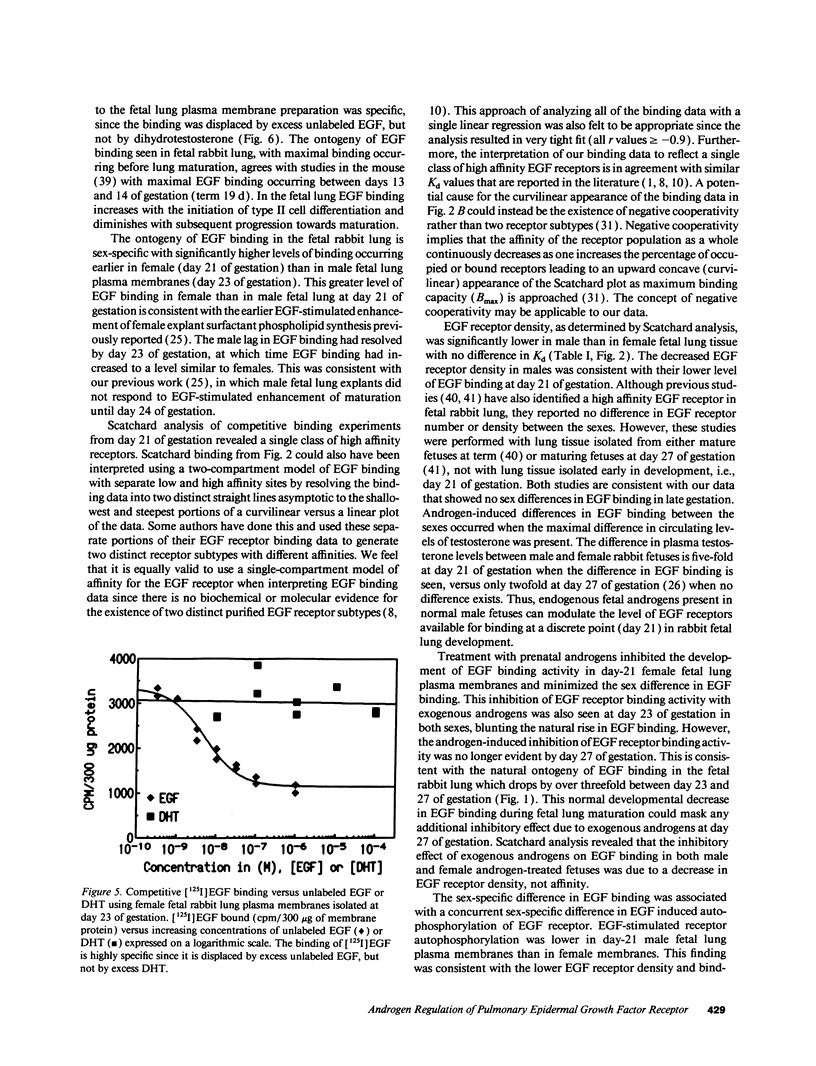
Fetal lung development progresses in a sex-specific manner with male fetuses exhibiting delayed maturation. Androgens, both exogenous and endogenous, inhibit while epidermal growth factor (EGF) enhances fetal lung development. We hypothesized that one mechanism responsible for the delay in male fetal lung development is an androgen-induced delay in EGF receptor binding activity. We measured EGF binding in sex-specific fetal rabbit lung plasma membranes isolated from control fetuses (days 21, 23, 25, 27, 29, and 30 of gestation) and from androgen-treated fetuses (days 21, 23, and 27 of gestation) that had been continuously exposed in vivo to exogenous 5 alpha-dihydrotestosterone from day 12 through 27 of gestation. Specific binding of EGF was significantly lower in male than in female fetal lung tissue isolated from controls at day 21 of gestation. Scatchard analysis revealed that this decrease in EGF binding was associated with decreased EGF receptor density without any significant change in affinity. Prenatal exogenous androgen treatment led to decreased EGF binding in fetal rabbit lung tissue from both sexes secondary to a decrease in EGF receptor density. These findings suggest that one mechanism responsible for the delay in male fetal lung maturation is an androgen-induced delay in EGF receptor binding activity during fetal lung development.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AVERY M. E., MEAD J. Surface properties in relation to atelectasis and hyaline membrane disease. AMA J Dis Child. 1959 May;97(5 Pt 1):517–523. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1959.02070010519001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adamson E. D., Deller M. J., Warshaw J. B. Functional EGF receptors are present on mouse embryo tissues. Nature. 1981 Jun 25;291(5817):656–659. doi: 10.1038/291656a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alm J., Scott S., Fisher D. A. Epidermal growth factor receptor ontogeny in mice with congenital hypothyroidism. J Dev Physiol. 1986 Oct;8(5):377–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:193–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G. Properties of the receptor for epidermal growth factor. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):357–358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90365-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterton W. Z., Escobedo M. B., Sexson W. R., Gray M. E., Sundell H. W., Stahlman M. T. Effect of epidermal growth factor on lung maturation in fetal rabbits. Pediatr Res. 1979 Feb;13(2):104–108. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197902000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. S., Lazar C. S., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y., Gill G. N., Rosenfeld M. G. Requirement for intrinsic protein tyrosine kinase in the immediate and late actions of the EGF receptor. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):820–823. doi: 10.1038/328820a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devaskar U. P. Epidermal growth factor receptors in fetal and maternal rabbit lung. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jul 30;107(2):714–720. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91549-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. A. Hormone epidermal growth factor interactions in development. Horm Res. 1990;33(2-4):69–75. doi: 10.1159/000181487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freidenberg G. R., Klein H. H., Kladde M. P., Cordera R., Olefsky J. M. Regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor number and phosphorylation by fasting in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):752–757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannopoulos G., Smith S. K. Androgen receptors in fetal rabbit lung and the effect of fetal sex on the levels of circulating hormones and pulmonary hormone receptors. J Steroid Biochem. 1982 Nov;17(5):461–465. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(82)90002-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross I., Dynia D. W., Rooney S. A., Smart D. A., Warshaw J. B., Sissom J. F., Hoath S. B. Influence of epidermal growth factor on fetal rat lung development in vitro. Pediatr Res. 1986 May;20(5):473–477. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198605000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi M., Hirano H., Maki M. Effect of human epidermal growth factor on lung surfactant production in fetal rabbit. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1989 Sep;159(1):15–22. doi: 10.1620/tjem.159.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjalmarson O. Epidemiology and classification of acute, neonatal respiratory disorders. A prospective study. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1981 Nov;70(6):773–783. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1981.tb06228.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. D., Gray M. E., Carpenter G., Pepinsky R. B., Stahlman M. T. Ontogeny of epidermal growth factor receptor and lipocortin-1 in fetal and neonatal human lungs. Hum Pathol. 1990 Feb;21(2):182–191. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(90)90127-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. D., Gray M. E., Carpenter G., Pepinsky R. B., Sundell H., Stahlman M. T. Ontogeny of epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase and of lipocortin-1 in the ovine lung. Pediatr Res. 1989 May;25(5):535–541. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198905000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury M. J., Marks J. S., McCarthy B. J., Zaro S. M. Factors affecting the sex differential in neonatal mortality: the role of respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1985 Mar 15;151(6):777–782. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(85)90518-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J. M., Nielsen H. C. Sex-specific differences in rabbit fetal lung maturation in response to epidermal growth factor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jan 13;1133(2):121–126. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90058-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz I. M. Numbers of receptor sites from Scatchard graphs: facts and fantasies. Science. 1982 Sep 24;217(4566):1247–1249. doi: 10.1126/science.6287580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingham R. B., Stancel G. M., Loose-Mitchell D. S. Estrogen regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor messenger ribonucleic acid. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Mar;2(3):230–235. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-3-230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. C., Futrakul P. Birth weight, gestational age, and sex as determining factors in the incidence of respiratory distress syndrome of prematurely born infants. J Pediatr. 1968 May;72(5):628–635. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(68)80005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishige W. K., Uetake C. A., Greenwood F. C., Akaka J. Pulmonary insulin responsivitiy: in vivo effects of insulin on the diabetic rat lung and specific insulin binding to lung receptors in normal rats. Endocrinology. 1977 Jun;100(6):1710–1722. doi: 10.1210/endo-100-6-1710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naeye R. L., Burt L. S., Wright D. L., Blanc W. A., Tatter D. Neonatal mortality, the male disadvantage. Pediatrics. 1971 Dec;48(6):902–906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen H. C. Androgen receptors influence the production of pulmonary surfactant in the testicular feminization mouse fetus. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):177–181. doi: 10.1172/JCI111943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen H. C. Epidermal growth factor influences the developmental clock regulating maturation of the fetal lung fibroblast. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 11;1012(2):201–206. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(89)90097-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen H. C., Torday J. S. Anatomy of fetal rabbit gonads and the sexing of fetal rabbits. Lab Anim. 1983 Apr;17(2):148–150. doi: 10.1258/002367783780959411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen H. C., Zinman H. M., Torday J. S. Dihydrotestosterone inhibits fetal rabbit pulmonary surfactant production. J Clin Invest. 1982 Mar;69(3):611–616. doi: 10.1172/JCI110488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver A. M. Epidermal growth factor receptor expression in human foetal tissues is age-dependent. Br J Cancer. 1988 Oct;58(4):461–463. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perelman R. H., Palta M., Kirby R., Farrell P. M. Discordance between male and female deaths due to the respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatrics. 1986 Aug;78(2):238–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raaberg L., Nexø E., Buckley S., Luo W., Snead M. L., Warburton D. Epidermal growth factor transcription, translation, and signal transduction by rat type II pneumocytes in culture. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1992 Jan;6(1):44–49. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/6.1.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadiq H. F., Devaskar U. P. Glucocorticoids increase pulmonary epidermal growth factor receptors in female and male fetal rabbit. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Feb 29;119(1):408–414. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91667-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St-Arnaud R., Poyet P., Walker P., Labrie F. Androgens modulate epidermal growth factor receptor levels in the rat ventral prostate. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1988 Mar;56(1-2):21–27. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(88)90004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultan C., Migeon B. R., Rothwell S. W., Maes M., Zerhouni N., Migeon C. J. Androgen receptors and metabolism in cultured human fetal fibroblasts. Pediatr Res. 1980 Jan;14(1):67–69. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198001000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundell H. W., Gray M. E., Serenius F. S., Escobedo M. B., Stahlman M. T. Effects of epidermal growth factor on lung maturation in fetal lambs. Am J Pathol. 1980 Sep;100(3):707–726. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F. Specific receptors for epidermal growth factor in rat intestinal microvillus membranes. Am J Physiol. 1988 Mar;254(3 Pt 1):G429–G435. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.254.3.G429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todderud G., Carpenter G. Epidermal growth factor: the receptor and its function. Biofactors. 1989 Mar;2(1):11–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torday J. S. Androgens delay human fetal lung maturation in vitro. Endocrinology. 1990 Jun;126(6):3240–3244. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-6-3240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torday J. S., Nielsen H. C. The sex difference in fetal lung surfactant production. Exp Lung Res. 1987;12(1):1–19. doi: 10.3109/01902148709068811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traish A. M., Wotiz H. H. Prostatic epidermal growth factor receptors and their regulation by androgens. Endocrinology. 1987 Oct;121(4):1461–1467. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-4-1461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veyssiere G., Berger M., Jean-Faucher C., De Turckheim M., Jean C. Levels of testosterone in the plasma, gonads, and adrenals during fetal development of the rabbit. Endocrinology. 1976 Nov;99(5):1263–1268. doi: 10.1210/endo-99-5-1263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitsett J. A., Weaver T. E., Lieberman M. A., Clark J. C., Daugherty C. Differential effects of epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor-beta on synthesis of Mr = 35,000 surfactant-associated protein in fetal lung. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7908–7913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]