Abstract
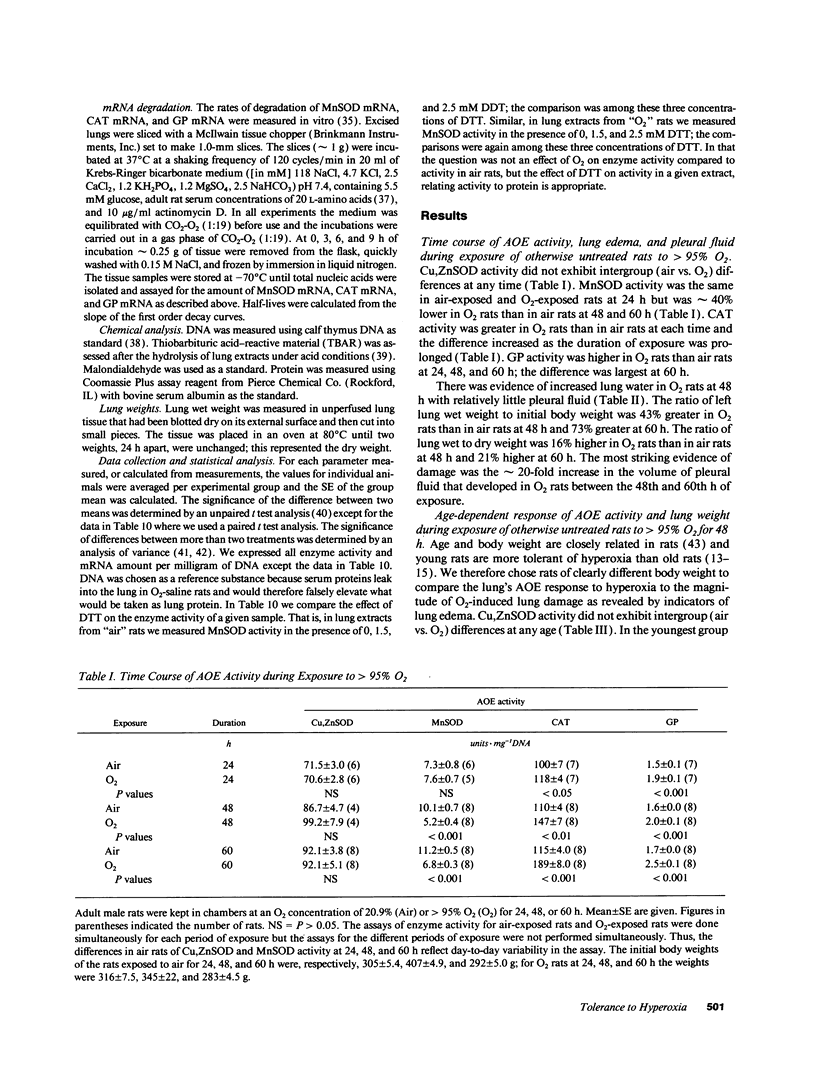
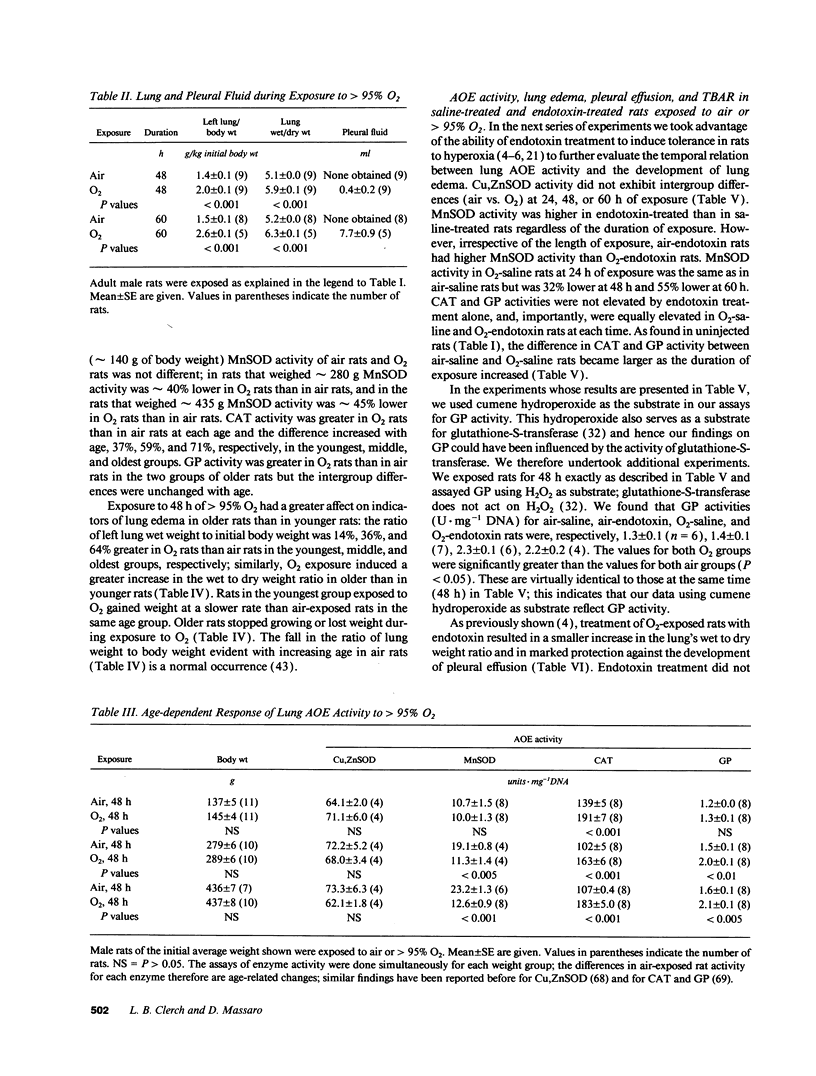
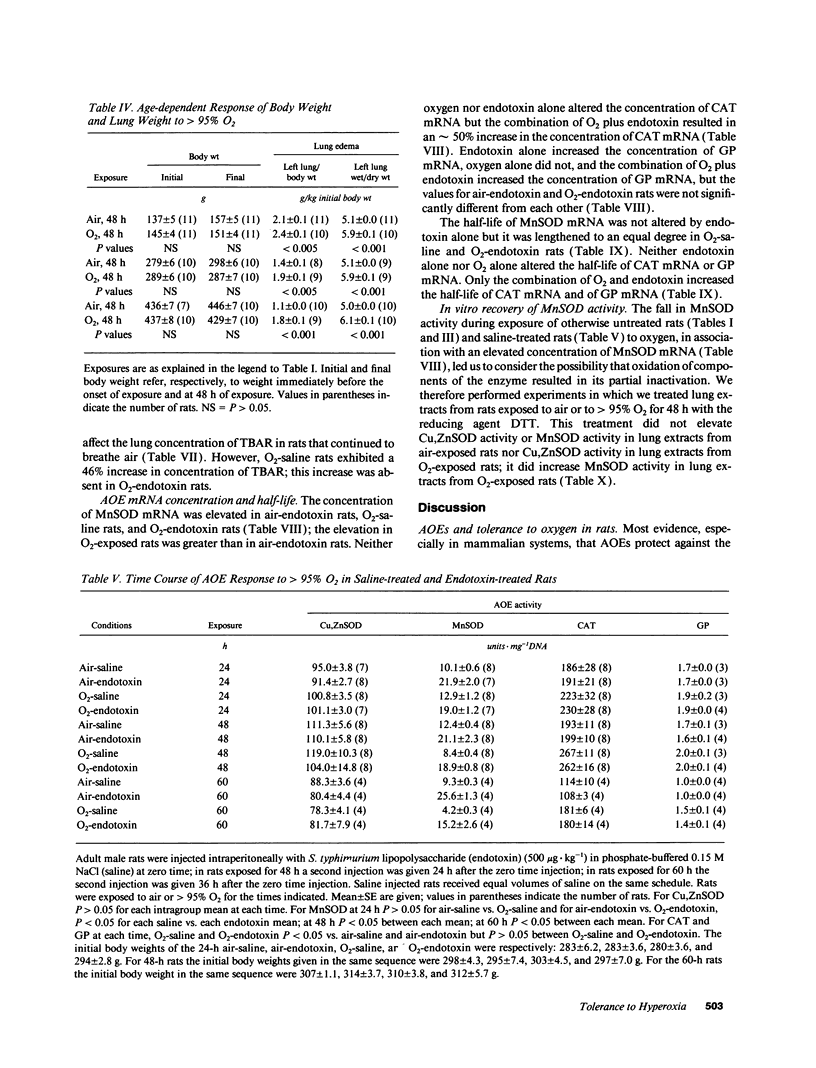
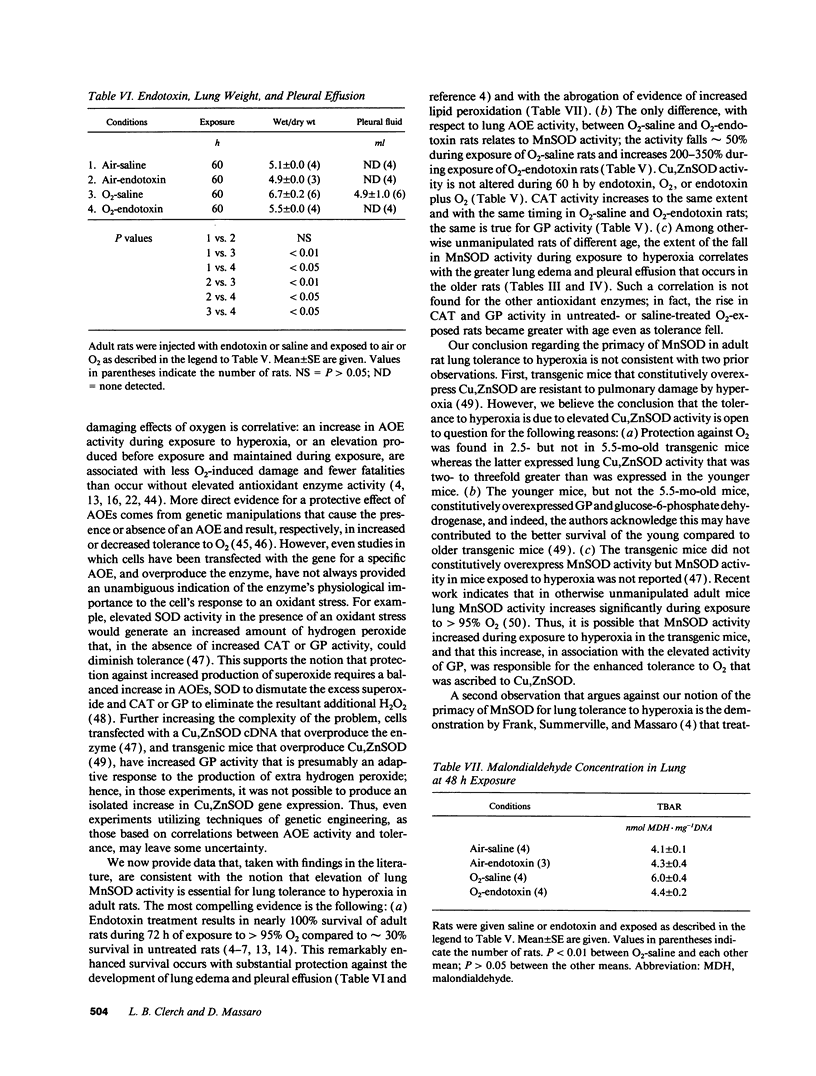
Tolerance to hyperoxia usually requires an increase of lung antioxidant enzyme (AOE) activity. We used rats with different degrees of tolerance to > 95% O2 to evaluate the importance of individual AOEs for tolerance; we also explored the regulation of AOE gene expression. During exposure of adult rats to > 95% O2, lung manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) activity fell approximately 50% despite a threefold increase of MnSOD mRNA concentration; addition of a reducing agent to lung extracts from O2-exposed rats partially restored MnSOD activity. Endotoxin induced tolerance to O2 (a) without elevating Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase activity, (b) with increases of catalase and glutathione peroxidase (GP) activity of the same magnitude as occurred in O2-saline rats, but (c) with MnSOD activity 1.5-1.9-fold higher than in air-saline rats and 1.4-3.6-fold higher than in O2-saline rats. Endotoxin elevated the concentration of MnSOD and GP mRNAs without increasing their stability. O2 elevated MnSOD mRNA concentration, and increased its stability. O2 plus endotoxin increased the concentration and stability of MnSOD, catalase, and GP mRNAs. These data suggest that in adult rats tolerance to hyperoxia requires increased MnSOD activity; the data show gene expression and regulation vary among the AOEs, and that increased stability of the AOEs' mRNAs plays an important role in AOE gene expression and in tolerance to hyperoxia.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEERS R. F., Jr, SIZER I. W. A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):133–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barra D., Schinina M. E., Simmaco M., Bannister J. V., Bannister W. H., Rotilio G., Bossa F. The primary structure of human liver manganese superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12595–12601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boveris A., Chance B. The mitochondrial generation of hydrogen peroxide. General properties and effect of hyperbaric oxygen. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;134(3):707–716. doi: 10.1042/bj1340707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boveris A. Mitochondrial production of superoxide radical and hydrogen peroxide. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1977;78:67–82. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9035-4_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brashear R. E., Sharma H. M., DeAtley R. E. Prolonged survival breathing oxygen at ambient pressure. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Sep;108(3):701–704. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.108.3.701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brauer R. W., Parrish D. E., Way R. O., Pratt P. C., Pessotti R. L. Protection by altitude acclimatization against lung damage from exposure to oxygen at 825 mm Hg. J Appl Physiol. 1970 Apr;28(4):474–481. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1970.28.4.474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. M., Lambertsen C. J. Pulmonary oxygen toxicity: a review. Pharmacol Rev. 1971 Jun;23(2):37–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerch L. B., Iqbal J., Massaro D. Perinatal rat lung catalase gene expression: influence of corticosteroid and hyperoxia. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jun;260(6 Pt 1):L428–L433. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1991.260.6.L428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerch L. B., Massaro D. Oxidation-reduction-sensitive binding of lung protein to rat catalase mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):2853–2855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerch L. B., Massaro D. Rat lung antioxidant enzymes: differences in perinatal gene expression and regulation. Am J Physiol. 1992 Oct;263(4 Pt 1):L466–L470. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1992.263.4.L466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crapo J. D., McCord J. M., Fridovich I. Preparation and assay of superoxide dismutases. Methods Enzymol. 1978;53:382–393. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)53044-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crapo J. D., Tierney D. F. Superoxide dismutase and pulmonary oxygen toxicity. Am J Physiol. 1974 Jun;226(6):1401–1407. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.226.6.1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross C. E., Last J. A. Lack of correlation between glutathione peroxidase activities and slsceptibility to O2 toxicity in rat lungs. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1977 Jul;17(3):433–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durnam D. M., Palmiter R. D. A practical approach for quantitating specific mRNAs by solution hybridization. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jun;131(2):385–393. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90188-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A. B., Diamond S., Mellen S. Effect of O2 exposure on metabolism of the rabbit alveolar macrophage. J Appl Physiol. 1974 Sep;37(3):341–345. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1974.37.3.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flohé L., Schlegel W. Glutathion-Peroxidase. IV. Intrazelluläre Verteilung des Glutathion-Peroxidase-Systems in der Rattenleber. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1971 Oct;352(10):1401–1410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank L., Bucher J. R., Roberts R. J. Oxygen toxicity in neonatal and adult animals of various species. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1978 Nov;45(5):699–704. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1978.45.5.699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank L. Endotoxin reverses the decreased tolerance of rats to greater than 95% O2 after preexposure to lower O2. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Sep;51(3):577–583. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.51.3.577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank L., Iqbal J., Hass M., Massaro D. New "rest period" protocol for inducing tolerance to high O2 exposure in adult rats. Am J Physiol. 1989 Oct;257(4 Pt 1):L226–L231. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1989.257.4.L226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank L., Neriishi K. Endotoxin treatment protects vitamin E-deficient rats from pulmonary O2 toxicity. Am J Physiol. 1984 Sep;247(3 Pt 2):R520–R526. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1984.247.3.R520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank L. Protection from O2 toxicity by preexposure to hypoxia: lung antioxidant enzyme role. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Aug;53(2):475–482. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.53.2.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank L., Summerville J., Massaro D. Potection from oxygen toxicity with endotoxin. Role of the endogenous antioxidant enzymes of the lung. J Clin Invest. 1980 May;65(5):1104–1110. doi: 10.1172/JCI109763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank L., Yam J., Roberts R. J. The role of endotoxin in protection of adult rats from oxygen-induced lung toxicity. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):269–275. doi: 10.1172/JCI108936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman B. A., Crapo J. D. Hyperoxia increases oxygen radical production in rat lungs and lung mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):10986–10992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutases. An adaptation to a paramagnetic gas. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):7761–7764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gail D. B., Massaro D. Oxygen consumption by rat lung after in vivo hyperoxia. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Jun;113(6):889–892. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.113.6.889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargrove J. L., Schmidt F. H. The role of mRNA and protein stability in gene expression. FASEB J. 1989 Oct;3(12):2360–2370. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.12.2676679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hass M. A., Frank L., Massaro D. The effect of bacterial endotoxin on synthesis of (Cu,Zn)superoxide dismutase in lungs of oxygen-exposed rats. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9379–9383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hass M. A., Iqbal J., Clerch L. B., Frank L., Massaro D. Rat lung Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase. Isolation and sequence of a full-length cDNA and studies of enzyme induction. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1241–1246. doi: 10.1172/JCI114007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hass M. A., Massaro D. Developmental regulation of rat lung Cu,Zn-superoxide dismutase. Biochem J. 1987 Sep 15;246(3):697–703. doi: 10.1042/bj2460697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugaard N. Cellular mechanisms of oxygen toxicity. Physiol Rev. 1968 Apr;48(2):311–373. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1968.48.2.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. S., Masters C. J. Epigenetic interconversions of the multiple forms of mouse liver catalase. FEBS Lett. 1970 Nov 9;11(1):45–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80488-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal J., Whitney P. Use of cyanide and diethyldithiocarbamate in the assay of superoxide dismutases. Free Radic Biol Med. 1991;10(1):69–77. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(91)90023-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapanci Y., Weibel E. R., Kaplan H. P., Robinson F. R. Pathogenesis and reversibility of the pulmonary lesions of oxygen toxicity in monkeys. II. Ultrastructural and morphometric studies. Lab Invest. 1969 Jan;20(1):101–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelner M. J., Alexander N. M. Inhibition of erythrocyte superoxide dismutase by diethyldithiocarbamate also results in oxyhemoglobin-catalyzed glutathione depletion and methemoglobin production. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1636–1641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kistler G. S., Caldwell P. R., Weibel E. R. Development of fine structural damage to alveolar and capillary lining cells in oxygen-poisoned rat lungs. J Cell Biol. 1967 Mar;32(3):605–628. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.3.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi M., Frank L., Massaro D. Oxygen toxicity in rats. Varied effect of dexamethasone treatment depending on duration of hyperoxia. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Jun;131(6):907–911. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.6.907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence R. A., Burk R. F. Glutathione peroxidase activity in selenium-deficient rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Aug 23;71(4):952–958. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90747-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcillat O., Zhang Y., Lin S. W., Davies K. J. Mitochondria contain a proteolytic system which can recognize and degrade oxidatively-denatured proteins. Biochem J. 1988 Sep 15;254(3):677–683. doi: 10.1042/bj2540677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda A., Longo D. L., Kobayashi Y., Appella E., Oppenheim J. J., Matsushima K. Induction of mitochondrial manganese superoxide dismutase by interleukin 1. FASEB J. 1988 Dec;2(15):3087–3091. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.15.3263930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan H. E., Earl D. C., Broadus A., Wolpert E. B., Giger K. E., Jefferson L. S. Regulation of protein synthesis in heart muscle. I. Effect of amino acid levels on protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):2152–2162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell M. J., Snape S. D., Nunn J. F. An early marker of hyperoxic lung injury in the rat and its pharmacological modulation. Br J Anaesth. 1991 Jun;66(6):697–702. doi: 10.1093/bja/66.6.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkawa H., Ohishi N., Yagi K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jun;95(2):351–358. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90738-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ospital J. J., Kasuyama R. S., Tierney D. F. Poor correlation between oxygen toxicity and activity of glutathione peroxidase. Exp Lung Res. 1983 Nov;5(3):193–199. doi: 10.3109/01902148309061514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paglia D. E., Valentine W. N. Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Jul;70(1):158–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. D., Meshnick S. R., Eaton J. W. Superoxide dismutase-rich bacteria. Paradoxical increase in oxidant toxicity. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3640–3645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touati D. Molecular genetics of superoxide dismutases. Free Radic Biol Med. 1988;5(5-6):393–402. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(88)90113-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touati D. The molecular genetics of superoxide dismutase in E. coli. An approach to understanding the biological role and regulation of SODS in relation to other elements of the defence system against oxygen toxicity. Free Radic Res Commun. 1989;8(1):1–9. doi: 10.3109/10715768909087967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visner G. A., Dougall W. C., Wilson J. M., Burr I. A., Nick H. S. Regulation of manganese superoxide dismutase by lipopolysaccharide, interleukin-1, and tumor necrosis factor. Role in the acute inflammatory response. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2856–2864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner B. B., Burhans M. S., Clark J. C., Wispé J. R. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha increases Mn-SOD expression: protection against oxidant injury. Am J Physiol. 1991 Apr;260(4 Pt 1):L296–L301. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1991.260.4.L296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisiger R. A., Fridovich I. Mitochondrial superoxide simutase. Site of synthesis and intramitochondrial localization. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 10;248(13):4793–4796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White C. W., Avraham K. B., Shanley P. F., Groner Y. Transgenic mice with expression of elevated levels of copper-zinc superoxide dismutase in the lungs are resistant to pulmonary oxygen toxicity. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):2162–2168. doi: 10.1172/JCI115249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Goeddel D. V. Induction of manganous superoxide dismutase by tumor necrosis factor: possible protective mechanism. Science. 1988 Nov 11;242(4880):941–944. doi: 10.1126/science.3263703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yam J., Frank L., Roberts R. J. Age-related development of pulmonary antioxidant enzymes in the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1978 Feb;157(2):293–296. doi: 10.3181/00379727-157-40040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yam J., Frank L., Roberts R. J. Oxygen toxicity: comparison of lung biochemical responses in neonatal and adult rats. Pediatr Res. 1978 Feb;12(2):115–119. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197802000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yam J., Frank L., Roberts R. J. Oxygen toxicity: comparison of lung biochemical responses in neonatal and adult rats. Pediatr Res. 1978 Feb;12(2):115–119. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197802000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


