Abstract
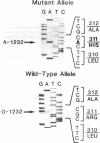
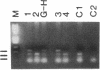
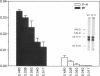
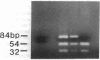
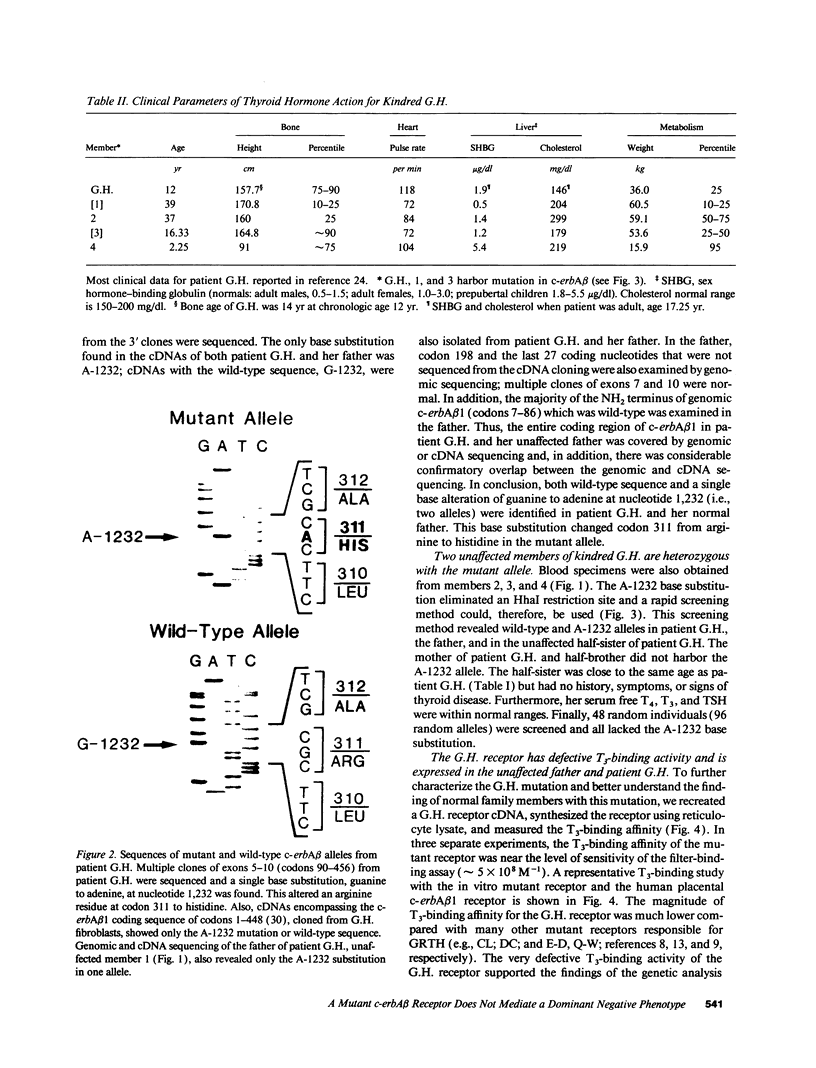
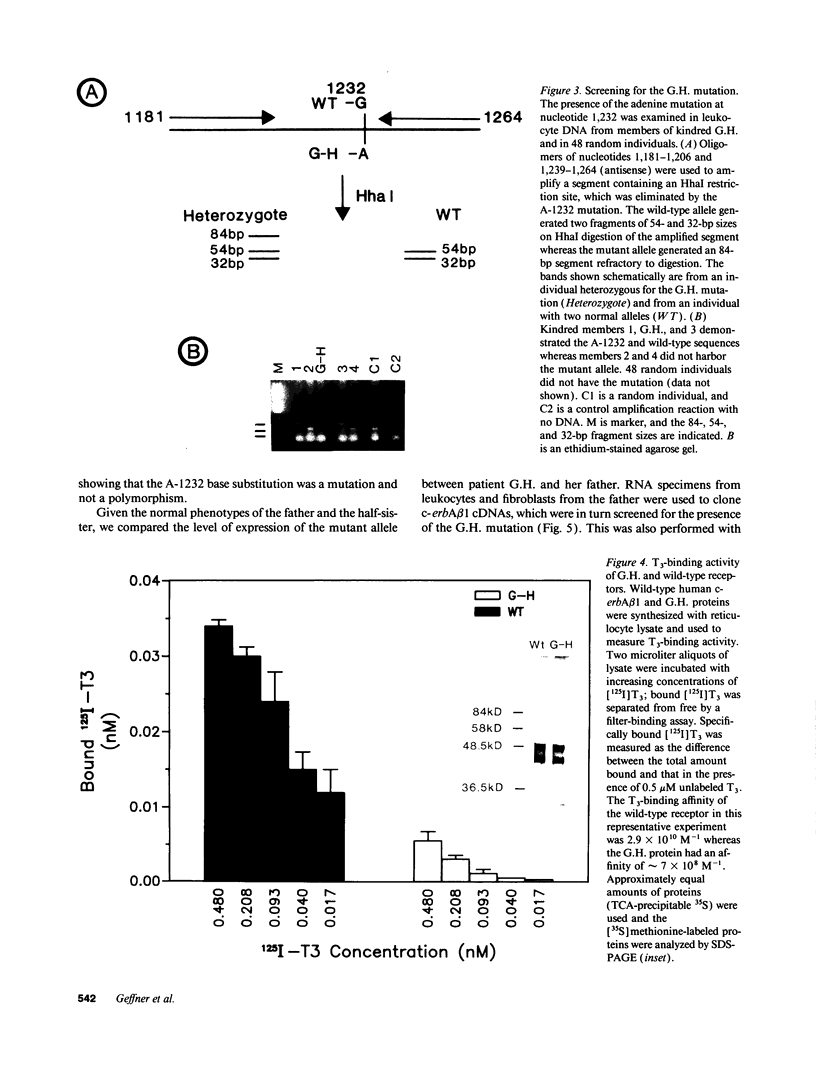
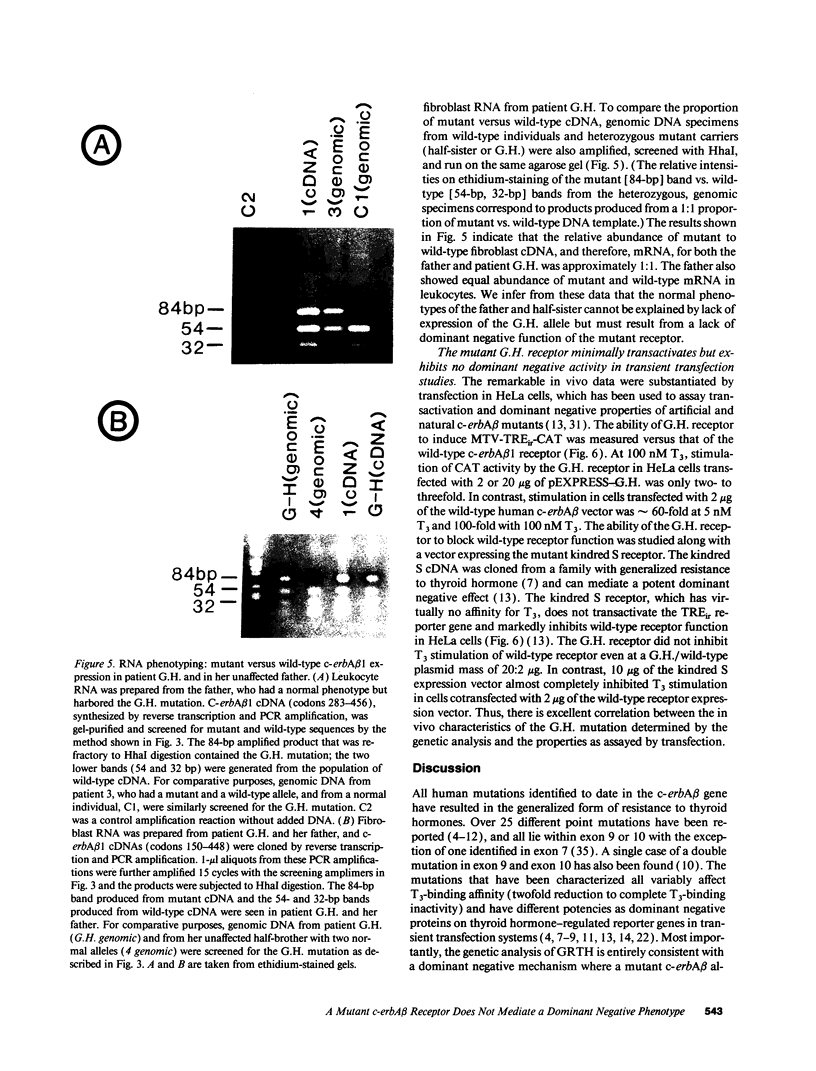
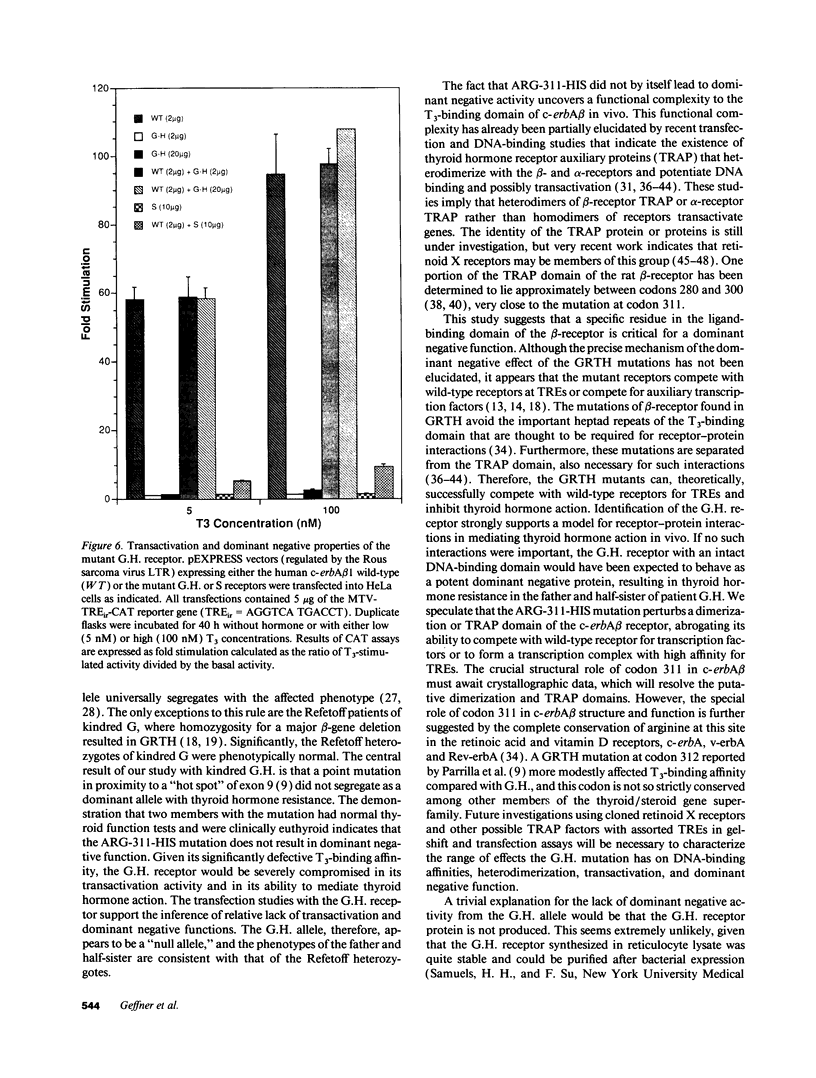
We have examined the c-erbA beta thyroid hormone receptor gene in a kindred, G.H., with a member, patient G.H., who had a severe form of selective pituitary resistance to thyroid hormones (PRTH). This patient manifested inappropriately normal thyrotropin-stimulating hormone, markedly elevated serum free thyroxine (T4) and total triiodothyronine (T3), and clinical hyperthyroidism. The complete c-erbA beta 1 coding sequence was examined by a combination of genomic and cDNA cloning for patient G.H. and her unaffected father. A single mutation, a guanine to adenine transition at nucleotide 1,232, was found in one allele of both these members, altering codon 311 from arginine to histidine. In addition, a half-sister of patient G.H. also harbored this mutant allele and, like the father, was clinically normal. The G.H. receptor, synthesized with reticulocyte lysate, had significantly defective T3-binding activity with a Ka of approximately 5 x 10(8) M-1. RNA phenotyping using leukocytes and fibroblasts demonstrated an equal level of expression of wild-type and mutant alleles in patient G.H. and her unaffected father. Finally, the G.H. receptor had no detectable dominant negative activity in a transfection assay. Thus, in contrast to the many other beta-receptor mutants responsible for the generalized form of thyroid hormone resistance, the G.H. receptor appeared unable to antagonize normal receptor function. These results suggest that the arginine at codon 311 in c-erbA beta is crucial for the structural integrity required for dominant negative function. The ARG-311-HIS mutation may contribute to PRTH in patient G.H. by inactivating a beta-receptor allele, but it cannot be the sole cause of the disease.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck-Peccoz P., Mariotti S., Guillausseau P. J., Medri G., Piscitelli G., Bertoli A., Barbarino A., Rondena M., Chanson P., Pinchera A. Treatment of hyperthyroidism due to inappropriate secretion of thyrotropin with the somatostatin analog SMS 201-995. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989 Jan;68(1):208–214. doi: 10.1210/jcem-68-1-208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behr M., Loos U. A point mutation (Ala229 to Thr) in the hinge domain of the c-erbA beta thyroid hormone receptor gene in a family with generalized thyroid hormone resistance. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Jul;6(7):1119–1126. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.7.1324420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnside J., Darling D. S., Chin W. W. A nuclear factor that enhances binding of thyroid hormone receptors to thyroid hormone response elements. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2500–2504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee V. K., Nagaya T., Madison L. D., Datta S., Rentoumis A., Jameson J. L. Thyroid hormone resistance syndrome. Inhibition of normal receptor function by mutant thyroid hormone receptors. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):1977–1984. doi: 10.1172/JCI115225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cugini C. D., Jr, Leidy J. W., Jr, Chertow B. S., Bérard J., Bradley W. E., Menke J. B., Hao E. H., Usala S. J. An arginine to histidine mutation in codon 315 of the c-erbA beta thyroid hormone receptor in a kindred with generalized resistance to thyroid hormones results in a receptor with significant 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine binding activity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 May;74(5):1164–1170. doi: 10.1210/jcem.74.5.1314846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darling D. S., Beebe J. S., Burnside J., Winslow E. R., Chin W. W. 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine (T3) receptor-auxiliary protein (TRAP) binds DNA and forms heterodimers with the T3 receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jan;5(1):73–84. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-1-73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulgeroff A. J., Geffner M. E., Koyal S. N., Wong M., Hershman J. M. Bromocriptine and Triac therapy for hyperthyroidism due to pituitary resistance to thyroid hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 Oct;75(4):1071–1075. doi: 10.1210/jcem.75.4.1400873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman B. M., Casanova J., Raaka B. M., Ghysdael J., Samuels H. H. Half-site spacing and orientation determines whether thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors and related factors bind to DNA response elements as monomers, homodimers, or heterodimers. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Mar;6(3):429–442. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.3.1316541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman B. M., Samuels H. H. pEXPRESS: a family of expression vectors containing a single transcription unit active in prokaryotes, eukaryotes and in vitro. Gene. 1991 Aug 30;105(1):9–15. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90507-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman B. M., Yang C. R., Au M., Casanova J., Ghysdael J., Samuels H. H. A domain containing leucine-zipper-like motifs mediate novel in vivo interactions between the thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Oct;3(10):1610–1626. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-10-1610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershengorn M. C., Weintraub B. D. Thyrotropin-induced hyperthyroidism caused by selective pituitary resistance to thyroid hormone. A new syndrome of "inappropriate secretion of TSH". J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):633–642. doi: 10.1172/JCI108133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer S. A., Umesono K., Mangelsdorf D. J., Evans R. M. Retinoid X receptor interacts with nuclear receptors in retinoic acid, thyroid hormone and vitamin D3 signalling. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):446–449. doi: 10.1038/355446a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunitake J. M., Hartman N., Henson L. C., Lieberman J., Williams D. E., Wong M., Hershman J. M. 3,5,3'-triiodothyroacetic acid therapy for thyroid hormone resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989 Aug;69(2):461–466. doi: 10.1210/jcem-69-2-461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazar M. A., Berrodin T. J., Harding H. P. Differential DNA binding by monomeric, homodimeric, and potentially heteromeric forms of the thyroid hormone receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5005–5015. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazar M. A., Berrodin T. J. Thyroid hormone receptors form distinct nuclear protein-dependent and independent complexes with a thyroid hormone response element. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Nov;4(11):1627–1635. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-11-1627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid M., Kastner P., Lyons R., Nakshatri H., Saunders M., Zacharewski T., Chen J. Y., Staub A., Garnier J. M., Mader S. Purification, cloning, and RXR identity of the HeLa cell factor with which RAR or TR heterodimerizes to bind target sequences efficiently. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):377–395. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90478-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier C. A., Dickstein B. M., Ashizawa K., McClaskey J. H., Muchmore P., Ransom S. C., Menke J. B., Hao E. H., Usala S. J., Bercu B. B. Variable transcriptional activity and ligand binding of mutant beta 1 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine receptors from four families with generalized resistance to thyroid hormone. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Feb;6(2):248–258. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.2.1569968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mixson A. J., Parrilla R., Ransom S. C., Wiggs E. A., McClaskey J. H., Hauser P., Weintraub B. D. Correlations of language abnormalities with localization of mutations in the beta-thyroid hormone receptor in 13 kindreds with generalized resistance to thyroid hormone: identification of four new mutations. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 Oct;75(4):1039–1045. doi: 10.1210/jcem.75.4.1400869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. B., Towle H. C. Identification of nuclear factors that enhance binding of the thyroid hormone receptor to a thyroid hormone response element. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Sep;3(9):1434–1442. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-9-1434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell A. L., Koenig R. J. Mutational analysis identifies a new functional domain of the thyroid hormone receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 May;4(5):715–720. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-5-715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell A. L., Rosen E. D., Darling D. S., Koenig R. J. Thyroid hormone receptor mutations that interfere with transcriptional activation also interfere with receptor interaction with a nuclear protein. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jan;5(1):94–99. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-1-94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono S., Schwartz I. D., Mueller O. T., Root A. W., Usala S. J., Bercu B. B. Homozygosity for a dominant negative thyroid hormone receptor gene responsible for generalized resistance to thyroid hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 Nov;73(5):990–994. doi: 10.1210/jcem-73-5-990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrilla R., Mixson A. J., McPherson J. A., McClaskey J. H., Weintraub B. D. Characterization of seven novel mutations of the c-erbA beta gene in unrelated kindreds with generalized thyroid hormone resistance. Evidence for two "hot spot" regions of the ligand binding domain. J Clin Invest. 1991 Dec;88(6):2123–2130. doi: 10.1172/JCI115542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Refetoff S., DeGroot L. J., Benard B., DeWind L. T. Studies of a sibship with apparent hereditary resistance to the intracellular action of thyroid hormone. Metabolism. 1972 Aug;21(8):723–756. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(72)90121-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Refetoff S., DeWind L. T., DeGroot L. J. Familial syndrome combining deaf-mutism, stuppled epiphyses, goiter and abnormally high PBI: possible target organ refractoriness to thyroid hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Feb;27(2):279–294. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-2-279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Refetoff S. Syndromes of thyroid hormone resistance. Am J Physiol. 1982 Aug;243(2):E88–E98. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1982.243.2.E88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai A., Miyamoto T., Refetoff S., DeGroot L. J. Dominant negative transcriptional regulation by a mutant thyroid hormone receptor-beta in a family with generalized resistance to thyroid hormone. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Dec;4(12):1988–1994. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-12-1988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai A., Nakai A., DeGroot L. J. Structural analysis of human thyroid hormone receptor beta gene. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1990 Jun 18;71(2):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(90)90245-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai A., Takeda K., Ain K., Ceccarelli P., Nakai A., Seino S., Bell G. I., Refetoff S., DeGroot L. J. Generalized resistance to thyroid hormone associated with a mutation in the ligand-binding domain of the human thyroid hormone receptor beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8977–8981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sap J., Muñoz A., Damm K., Goldberg Y., Ghysdael J., Leutz A., Beug H., Vennström B. The c-erb-A protein is a high-affinity receptor for thyroid hormone. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):635–640. doi: 10.1038/324635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spanjaard R. A., Darling D. S., Chin W. W. Ligand-binding and heterodimerization activities of a conserved region in the ligand-binding domain of the thyroid hormone receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8587–8591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda K., Balzano S., Sakurai A., DeGroot L. J., Refetoff S. Screening of nineteen unrelated families with generalized resistance to thyroid hormone for known point mutations in the thyroid hormone receptor beta gene and the detection of a new mutation. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):496–502. doi: 10.1172/JCI115023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda K., Sakurai A., DeGroot L. J., Refetoff S. Recessive inheritance of thyroid hormone resistance caused by complete deletion of the protein-coding region of the thyroid hormone receptor-beta gene. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 Jan;74(1):49–55. doi: 10.1210/jcem.74.1.1727829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda K., Weiss R. E., Refetoff S. Rapid localization of mutations in the thyroid hormone receptor-beta gene by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis in 18 families with thyroid hormone resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 Apr;74(4):712–719. doi: 10.1210/jcem.74.4.1548332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Giguere V., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Retinoic acid and thyroid hormone induce gene expression through a common responsive element. Nature. 1988 Nov 17;336(6196):262–265. doi: 10.1038/336262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usala S. J., Bale A. E., Gesundheit N., Weinberger C., Lash R. W., Wondisford F. E., McBride O. W., Weintraub B. D. Tight linkage between the syndrome of generalized thyroid hormone resistance and the human c-erbA beta gene. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Dec;2(12):1217–1220. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-12-1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usala S. J., Bercu B. B., Refetoff S. Diverse abnormalities of the c-erbA beta thyroid hormone receptor gene in generalized thyroid hormone resistance. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1991;299:251–258. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5973-9_15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usala S. J., Menke J. B., Watson T. L., Bérard W. E., Bradley C., Bale A. E., Lash R. W., Weintraub B. D. A new point mutation in the 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine-binding domain of the c-erbA beta thyroid hormone receptor is tightly linked to generalized thyroid hormone resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 Jan;72(1):32–38. doi: 10.1210/jcem-72-1-32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usala S. J., Menke J. B., Watson T. L., Wondisford F. E., Weintraub B. D., Bérard J., Bradley W. E., Ono S., Mueller O. T., Bercu B. B. A homozygous deletion in the c-erbA beta thyroid hormone receptor gene in a patient with generalized thyroid hormone resistance: isolation and characterization of the mutant receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Mar;5(3):327–335. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-3-327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usala S. J. Molecular diagnosis and characterization of thyroid hormone resistance syndromes. Thyroid. 1991 Winter;1(4):361–367. doi: 10.1089/thy.1991.1.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usala S. J., Tennyson G. E., Bale A. E., Lash R. W., Gesundheit N., Wondisford F. E., Accili D., Hauser P., Weintraub B. D. A base mutation of the C-erbA beta thyroid hormone receptor in a kindred with generalized thyroid hormone resistance. Molecular heterogeneity in two other kindreds. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jan;85(1):93–100. doi: 10.1172/JCI114438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger C., Thompson C. C., Ong E. S., Lebo R., Gruol D. J., Evans R. M. The c-erb-A gene encodes a thyroid hormone receptor. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):641–646. doi: 10.1038/324641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wondisford F. E., Farr E. A., Radovick S., Steinfelder H. J., Moates J. M., McClaskey J. H., Weintraub B. D. Thyroid hormone inhibition of human thyrotropin beta-subunit gene expression is mediated by a cis-acting element located in the first exon. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14601–14604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynne A. G., Gharib H., Scheithauer B. W., Davis D. H., Freeman S. L., Horvath E. Hyperthyroidism due to inappropriate secretion of thyrotropin in 10 patients. Am J Med. 1992 Jan;92(1):15–24. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(92)90009-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen P. M., Darling D. S., Chin W. W. Basal and thyroid hormone receptor auxiliary protein-enhanced binding of thyroid hormone receptor isoforms to native thyroid hormone response elements. Endocrinology. 1991 Dec;129(6):3331–3336. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-6-3331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. C., Delsert C., Andersen B., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., När A. M., Kim S. Y., Boutin J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. RXR beta: a coregulator that enhances binding of retinoic acid, thyroid hormone, and vitamin D receptors to their cognate response elements. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1251–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90301-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Hoffmann B., Tran P. B., Graupner G., Pfahl M. Retinoid X receptor is an auxiliary protein for thyroid hormone and retinoic acid receptors. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):441–446. doi: 10.1038/355441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]