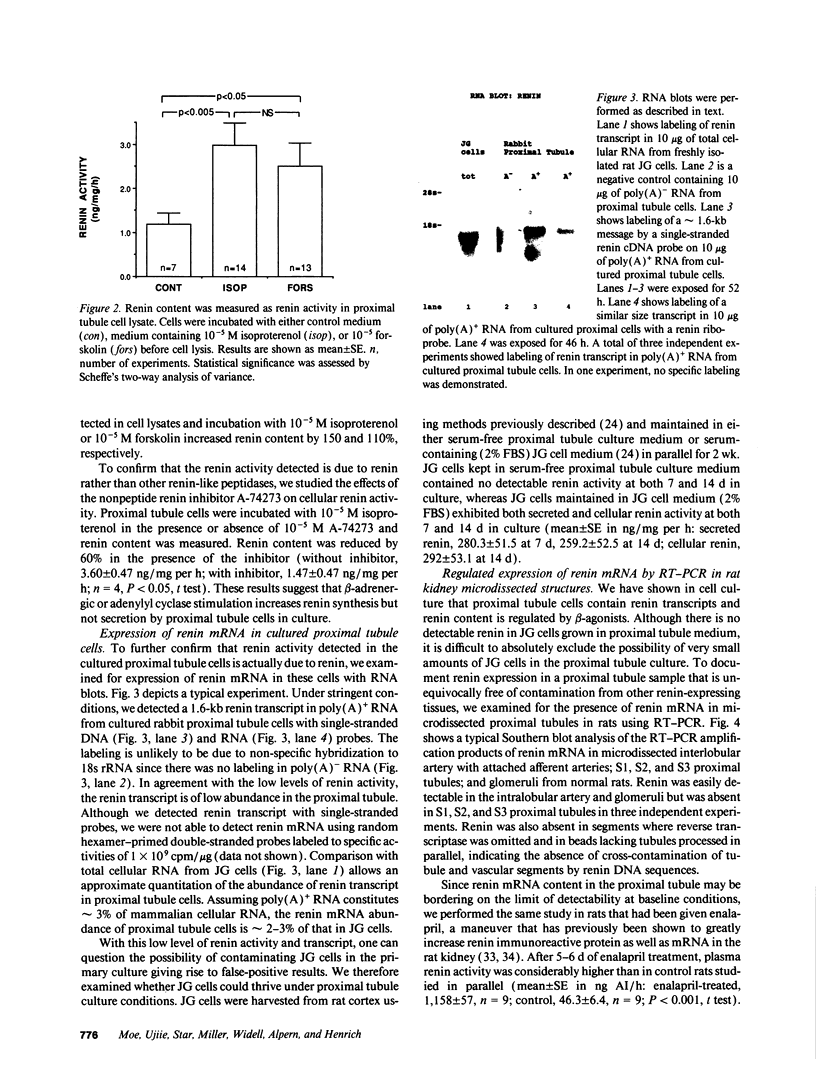
Abstract
Angiotensinogen, angiotensin-converting enzyme, and renin constitute the components of the renin-angiotensin system. The mammalian renal proximal tubule contains angiotensinogen, angiotensin-converting enzyme, and angiotensin receptors. Previous immunohistochemical studies describing the presence of renin in the proximal tubule could not distinguish synthesized renin from renin trapped from the glomerular filtrate. In the present study, we examined the presence of renin activity and mRNA in rabbit proximal tubule cells in primary culture and renin mRNA in microdissected proximal tubules. Renin activity was present in lysates of proximal tubule cells in primary culture. Cellular renin content in cultured proximal tubule cells was increased by incubation with 10(-5) M isoproterenol and 10(-5) M forskolin by 150 and 110%, respectively. In addition, renin transcripts were detected in poly(A)+ RNA from cultured proximal tubule cells by RNA blots under high stringency conditions. In microdissected tubules from normal rats, renin mRNA was not detectable with reverse transcription and polymerase chain reaction. However, in tubules from rats administered the angiotensinogen-converting-enzyme inhibitor, enalapril, renin was easily detected in the S2 segment of the proximal tubule. We postulate the existence of a local renin-angiotensin system that enables the proximal tubule to generate angiotensin II, thereby providing an autocrine system that could locally modulate NaHCO3 and NaCl absorption.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailie M. D., Rector F. C., Jr, Seldin D. W. Angiotensin II in arterial and renal venous plasma and renal lymph in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jan;50(1):119–126. doi: 10.1172/JCI106465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bello-Reuss E. Effect of catecholamines on fluid reabsorption by the isolated proximal convoluted tubule. Am J Physiol. 1980 May;238(5):F347–F352. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.238.5.F347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. P., Douglas J. G. Angiotensin II binding sites on isolated rat renal brush border membranes. Endocrinology. 1982 Dec;111(6):1830–1836. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-6-1830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. P., Douglas J. G. Angiotensin II-binding sites in rat and primate isolated renal tubular basolateral membranes. Endocrinology. 1983 Jun;112(6):2007–2014. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-6-2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruneval P., Hinglais N., Alhenc-Gelas F., Tricottet V., Corvol P., Menard J., Camilleri J. P., Bariety J. Angiotensin I converting enzyme in human intestine and kidney. Ultrastructural immunohistochemical localization. Histochemistry. 1986;85(1):73–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00508656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnham C. E., Hawelu-Johnson C. L., Frank B. M., Lynch K. R. Molecular cloning of rat renin cDNA and its gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5605–5609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens D. L., Clauser E., Celio M. R., Inagami T. Generation of angiotensinogen by cultured neuroblastoma and glioma cells. Brain Res. 1986 Feb 5;364(2):205–211. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90832-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschepper C. F., Mellon S. H., Cumin F., Baxter J. D., Ganong W. F. Analysis by immunocytochemistry and in situ hybridization of renin and its mRNA in kidney, testis, adrenal, and pituitary of the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7552–7556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas J. G. Angiotensin receptor subtypes of the kidney cortex. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jul;253(1 Pt 2):F1–F7. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.1.F1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzau V. J., Ellison K. E., Brody T., Ingelfinger J., Pratt R. E. A comparative study of the distributions of renin and angiotensinogen messenger ribonucleic acids in rat and mouse tissues. Endocrinology. 1987 Jun;120(6):2334–2338. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-6-2334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Perez A., Martin B., Murphy H. R., Uchida S., Murer H., Cowley B. D., Jr, Handler J. S., Burg M. B. Molecular cloning of cDNA coding for kidney aldose reductase. Regulation of specific mRNA accumulation by NaCl-mediated osmotic stress. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16815–16821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geibel J., Giebisch G., Boron W. F. Angiotensin II stimulates both Na(+)-H+ exchange and Na+/HCO3- cotransport in the rabbit proximal tubule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7917–7920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez R. A., Chevalier R. L., Everett A. D., Elwood J. P., Peach M. J., Lynch K. R., Carey R. M. Recruitment of renin gene-expressing cells in adult rat kidneys. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 2):F660–F665. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.4.F660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez R. A., Lynch K. R., Chevalier R. L., Everett A. D., Johns D. W., Wilfong N., Peach M. J., Carey R. M. Renin and angiotensinogen gene expression and intrarenal renin distribution during ACE inhibition. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jun;254(6 Pt 2):F900–F906. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.254.6.F900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez R. A., Lynch K. R., Sturgill B. C., Elwood J. P., Chevalier R. L., Carey R. M., Peach M. J. Distribution of renin mRNA and its protein in the developing kidney. Am J Physiol. 1989 Nov;257(5 Pt 2):F850–F858. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.257.5.F850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris P. J., Young J. A. Dose-dependent stimulation and inhibition of proximal tubular sodium reabsorption by angiotensin II in the rat kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Jan 17;367(3):295–297. doi: 10.1007/BF00581370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrich W. L., McAllister E. A., Smith P. B., Campbell W. B. Guanosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate as a mediator of inhibition of renin release. Am J Physiol. 1988 Sep;255(3 Pt 2):F474–F478. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.3.F474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horie S., Moe O., Tejedor A., Alpern R. J. Preincubation in acid medium increases Na/H antiporter activity in cultured renal proximal tubule cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4742–4745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingelfinger J. R., Pratt R. E., Ellison K., Dzau V. J. Sodium regulation of angiotensinogen mRNA expression in rat kidney cortex and medulla. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1311–1315. doi: 10.1172/JCI112716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingelfinger J. R., Zuo W. M., Fon E. A., Ellison K. E., Dzau V. J. In situ hybridization evidence for angiotensinogen messenger RNA in the rat proximal tubule. An hypothesis for the intrarenal renin angiotensin system. J Clin Invest. 1990 Feb;85(2):417–423. doi: 10.1172/JCI114454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kifor I., Dzau V. J. Endothelial renin-angiotensin pathway: evidence for intracellular synthesis and secretion of angiotensins. Circ Res. 1987 Mar;60(3):422–428. doi: 10.1161/01.res.60.3.422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz A., Della Bruna R., Pfeilschifter J., Taugner R., Bauer C. Atrial natriuretic peptide inhibits renin release from juxtaglomerular cells by a cGMP-mediated process. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4769–4773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. Y., Cogan M. G. Angiotensin II stimulation of hydrogen ion secretion in the rat early proximal tubule. Modes of action, mechanism, and kinetics. J Clin Invest. 1988 Aug;82(2):601–607. doi: 10.1172/JCI113638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. Y., Cogan M. G. Angiotensin II: a potent regulator of acidification in the rat early proximal convoluted tubule. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jul;80(1):272–275. doi: 10.1172/JCI113059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchetti J., Roseau S., Alhenc-Gelas F. Angiotensin I converting enzyme and kinin-hydrolyzing enzymes along the rabbit nephron. Kidney Int. 1987 Mar;31(3):744–751. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moe O. W., Miller R. T., Horie S., Cano A., Preisig P. A., Alpern R. J. Differential regulation of Na/H antiporter by acid in renal epithelial cells and fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1991 Nov;88(5):1703–1708. doi: 10.1172/JCI115487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moe O. W., Tejedor A., Levi M., Seldin D. W., Preisig P. A., Alpern R. J. Dietary NaCl modulates Na(+)-H+ antiporter activity in renal cortical apical membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jan;260(1 Pt 2):F130–F137. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.260.1.F130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyama T., Murphy H. R., Martin B. M., Garcia-Perez A. Detection of specific mRNAs in single nephron segments by use of the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 2):F1470–F1474. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.5.F1470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naruse M., Shizume K., Inagami T. Renin and angiotensins in cultured mouse adrenocortical tumour cells. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1985 Apr;108(4):545–549. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1080545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura T., Clemens D. L., Inagami T. Renin, angiotensins, and angiotensin-converting enzyme in neuroblastoma cells: evidence for intracellular formation of angiotensins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6940–6943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen K., Jorgensen J. An easy radioimmunological microassay of renin activity, concentration and substrate in human and animal plasma and tissues based on angiotensin I trapping by antibody. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Nov;39(5):816–825. doi: 10.1210/jcem-39-5-816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proud D., Nakamura S., Carone F. A., Herring P. L., Kawamura M., Inagami T., Pisano J. J. Kallikrein-kinin and renin-angiotensin systems in rat renal lymph. Kidney Int. 1984 Jun;25(6):880–885. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richoux J. P., Cordonnier J. L., Bouhnik J., Clauser E., Corvol P., Menard J., Grignon G. Immunocytochemical localization of angiotensinogen in rat liver and kidney. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;233(2):439–451. doi: 10.1007/BF00238309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rightsel W. A., Okamura T., Inagami T., Pitcock J. A., Takii Y., Brooks B., Brown P., Muirhead E. E. Juxtaglomerular cells grown as monolayer cell culture contain renin, angiotensin I-converting enzyme, and angiotensin I and II/III. Circ Res. 1982 Jun;50(6):822–829. doi: 10.1161/01.res.50.6.822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rix E., Ganten D., Schüll B., Unger T., Taugner R. Converting-enzyme in the choroid plexus, brain, and kidney: immunocytochemical and biochemical studies in rats. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Mar 10;22(2):125–130. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90075-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster V. L., Kokko J. P., Jacobson H. R. Angiotensin II directly stimulates sodium transport in rabbit proximal convoluted tubules. J Clin Invest. 1984 Feb;73(2):507–515. doi: 10.1172/JCI111237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seikaly M. G., Arant B. S., Jr, Seney F. D., Jr Endogenous angiotensin concentrations in specific intrarenal fluid compartments of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1990 Oct;86(4):1352–1357. doi: 10.1172/JCI114846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Star R. A., Nonoguchi H., Balaban R., Knepper M. A. Calcium and cyclic adenosine monophosphate as second messengers for vasopressin in the rat inner medullary collecting duct. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1879–1888. doi: 10.1172/JCI113534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner R. W., Tucker B. J., Blantz R. C. Glomerular hemodynamics in rats with chronic sodium depletion. Effect of saralasin. J Clin Invest. 1979 Aug;64(2):503–512. doi: 10.1172/JCI109488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinay P., Gougoux A., Lemieux G. Isolation of a pure suspension of rat proximal tubules. Am J Physiol. 1981 Oct;241(4):F403–F411. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.4.F403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. E., Erdös E. G., Gedney C. D., Dowben R. M., Reynolds R. C. Isolation of membrane-bound renal enzymes that metabolize kinins and angiotensins. Biochem J. 1976 Sep 1;157(3):643–650. doi: 10.1042/bj1570643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinman E. J., Sansom S. C., Knight T. F., Senekjian H. O. Alpha and beta adrenergic agonists stimulate water absorption in the rat proximal tubule. J Membr Biol. 1982;69(2):107–111. doi: 10.1007/BF01872270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagawa N., Capparelli A. W., Jo O. D., Friedal A., Barrett J. D., Eggena P. Production of angiotensinogen and renin-like activity by rabbit proximal tubular cells in culture. Kidney Int. 1991 May;39(5):938–941. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]