Abstract
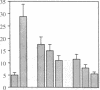
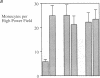
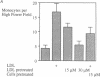
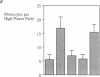
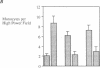
Addition of leumedin, N-[9H-(2,7-dimethylfluorenyl-9-methoxy) carbon]-L-leucine at 30-60 microM together with LDL almost completely prevented the induction of monocyte chemotactic protein mRNA, reduced monocyte chemotactic protein 1 levels by 84%, and inhibited monocyte migration into the subendothelial space of cocultures of human aortic wall cells by < or = 98%. LDL incubated with leumedin formed a stable complex that remained intact even after refloating in an ultracentrifuge. Leumedin at 50 microM did not change conjugated diene formation during coculture modification of LDL or Cu++ catalyzed oxidation of LDL. Unlike LDL from control rabbits, LDL isolated from rabbits that were injected with 20 mg/kg leumedin was remarkably resistant to modification by the coculture and did not induce monocyte migration to a significant degree. Moreover, HDL isolated from rabbits injected with leumedin was far more effective in protecting against LDL modification by the artery wall cocultures than HDL from control rabbits. We conclude that leumedins can associate with lipoproteins in vivo, rendering LDL resistant to biological modification and markedly amplifying the protective capacity of HDL against in vitro LDL oxidation by artery wall cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berliner J. A., Territo M. C., Sevanian A., Ramin S., Kim J. A., Bamshad B., Esterson M., Fogelman A. M. Minimally modified low density lipoprotein stimulates monocyte endothelial interactions. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1260–1266. doi: 10.1172/JCI114562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch R. M., Weitzberg M., Blok N., Muhlhauser R., Martin D., Farmer S. G., Bator J. M., Connor J. R., Green M., Ko C. N-(fluorenyl-9-methoxycarbonyl) amino acids, a class of antiinflammatory agents with a different mechanism of action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):355–359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carew T. E., Schwenke D. C., Steinberg D. Antiatherogenic effect of probucol unrelated to its hypocholesterolemic effect: evidence that antioxidants in vivo can selectively inhibit low density lipoprotein degradation in macrophage-rich fatty streaks and slow the progression of atherosclerosis in the Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic rabbit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7725–7729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisolm G. M., 3rd, Morel D. W. Lipoprotein oxidation and cytotoxicity: effect of probucol on streptozotocin-treated rats. Am J Cardiol. 1988 Jul 25;62(3):20B–26B. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(88)80046-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushing S. D., Berliner J. A., Valente A. J., Territo M. C., Navab M., Parhami F., Gerrity R., Schwartz C. J., Fogelman A. M. Minimally modified low density lipoprotein induces monocyte chemotactic protein 1 in human endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5134–5138. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esterbauer H., Jürgens G., Quehenberger O., Koller E. Autoxidation of human low density lipoprotein: loss of polyunsaturated fatty acids and vitamin E and generation of aldehydes. J Lipid Res. 1987 May;28(5):495–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esterbauer H., Striegl G., Puhl H., Rotheneder M. Continuous monitoring of in vitro oxidation of human low density lipoprotein. Free Radic Res Commun. 1989;6(1):67–75. doi: 10.3109/10715768909073429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogelman A. M., Elahi F., Sykes K., Van Lenten B. J., Territo M. C., Berliner J. A. Modification of the Recalde method for the isolation of human monocytes. J Lipid Res. 1988 Sep;29(9):1243–1247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank J. S., Fogelman A. M. Ultrastructure of the intima in WHHL and cholesterol-fed rabbit aortas prepared by ultra-rapid freezing and freeze-etching. J Lipid Res. 1989 Jul;30(7):967–978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haberland M. E., Fong D., Cheng L. Malondialdehyde-altered protein occurs in atheroma of Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic rabbits. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):215–218. doi: 10.1126/science.2455346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell B. How to characterize a biological antioxidant. Free Radic Res Commun. 1990;9(1):1–32. doi: 10.3109/10715769009148569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita T., Nagano Y., Yokode M., Ishii K., Kume N., Ooshima A., Yoshida H., Kawai C. Probucol prevents the progression of atherosclerosis in Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic rabbit, an animal model for familial hypercholesterolemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5928–5931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao F., Berliner J. A., Mehrabian M., Navab M., Demer L. L., Lusis A. J., Fogelman A. M. Minimally modified low density lipoprotein is biologically active in vivo in mice. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):2253–2257. doi: 10.1172/JCI115261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo S. K., Detmers P. A., Levin S. M., Wright S. D. Transient adhesion of neutrophils to endothelium. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1779–1793. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehrabian M., Demer L. L., Lusis A. J. Differential accumulation of intimal monocyte-macrophages relative to lipoproteins and lipofuscin corresponds to hemodynamic forces on cardiac valves in mice. Arterioscler Thromb. 1991 Jul-Aug;11(4):947–957. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.11.4.947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrilees M. J., Scott L. Interaction of aortic endothelial and smooth muscle cells in culture. Effect on glycosaminoglycan levels. Atherosclerosis. 1981 May;39(2):147–161. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(81)90064-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navab M., Hough G. P., Stevenson L. W., Drinkwater D. C., Laks H., Fogelman A. M. Monocyte migration into the subendothelial space of a coculture of adult human aortic endothelial and smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;82(6):1853–1863. doi: 10.1172/JCI113802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navab M., Imes S. S., Hama S. Y., Hough G. P., Ross L. A., Bork R. W., Valente A. J., Berliner J. A., Drinkwater D. C., Laks H. Monocyte transmigration induced by modification of low density lipoprotein in cocultures of human aortic wall cells is due to induction of monocyte chemotactic protein 1 synthesis and is abolished by high density lipoprotein. J Clin Invest. 1991 Dec;88(6):2039–2046. doi: 10.1172/JCI115532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navab M., Liao F., Hough G. P., Ross L. A., Van Lenten B. J., Rajavashisth T. B., Lusis A. J., Laks H., Drinkwater D. C., Fogelman A. M. Interaction of monocytes with cocultures of human aortic wall cells involves interleukins 1 and 6 with marked increases in connexin43 message. J Clin Invest. 1991 May;87(5):1763–1772. doi: 10.1172/JCI115195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noronha-Blob L., Lowe V. C., Weitzberg M., Burch R. M. NPC 15669 enhances survival and reverses leukopenia in endotoxin-treated mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jul 9;199(3):387–388. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90507-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajavashisth T. B., Andalibi A., Territo M. C., Berliner J. A., Navab M., Fogelman A. M., Lusis A. J. Induction of endothelial cell expression of granulocyte and macrophage colony-stimulating factors by modified low-density lipoproteins. Nature. 1990 Mar 15;344(6263):254–257. doi: 10.1038/344254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg D. Antioxidants and atherosclerosis. A current assessment. Circulation. 1991 Sep;84(3):1420–1425. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.3.1420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg D., Parthasarathy S., Carew T. E., Khoo J. C., Witztum J. L. Beyond cholesterol. Modifications of low-density lipoprotein that increase its atherogenicity. N Engl J Med. 1989 Apr 6;320(14):915–924. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198904063201407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valente A. J., Graves D. T., Vialle-Valentin C. E., Delgado R., Schwartz C. J. Purification of a monocyte chemotactic factor secreted by nonhuman primate vascular cells in culture. Biochemistry. 1988 May 31;27(11):4162–4168. doi: 10.1021/bi00411a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witztum J. L., Steinberg D. Role of oxidized low density lipoprotein in atherogenesis. J Clin Invest. 1991 Dec;88(6):1785–1792. doi: 10.1172/JCI115499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]