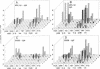
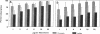Abstract
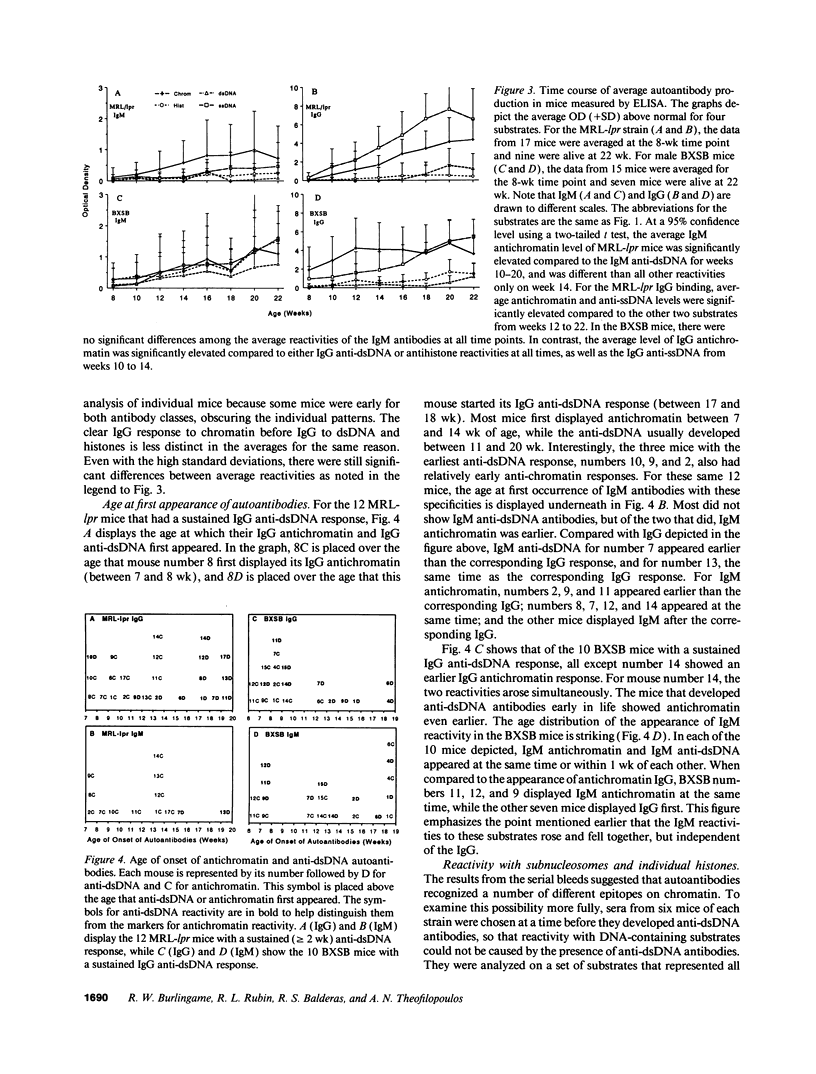
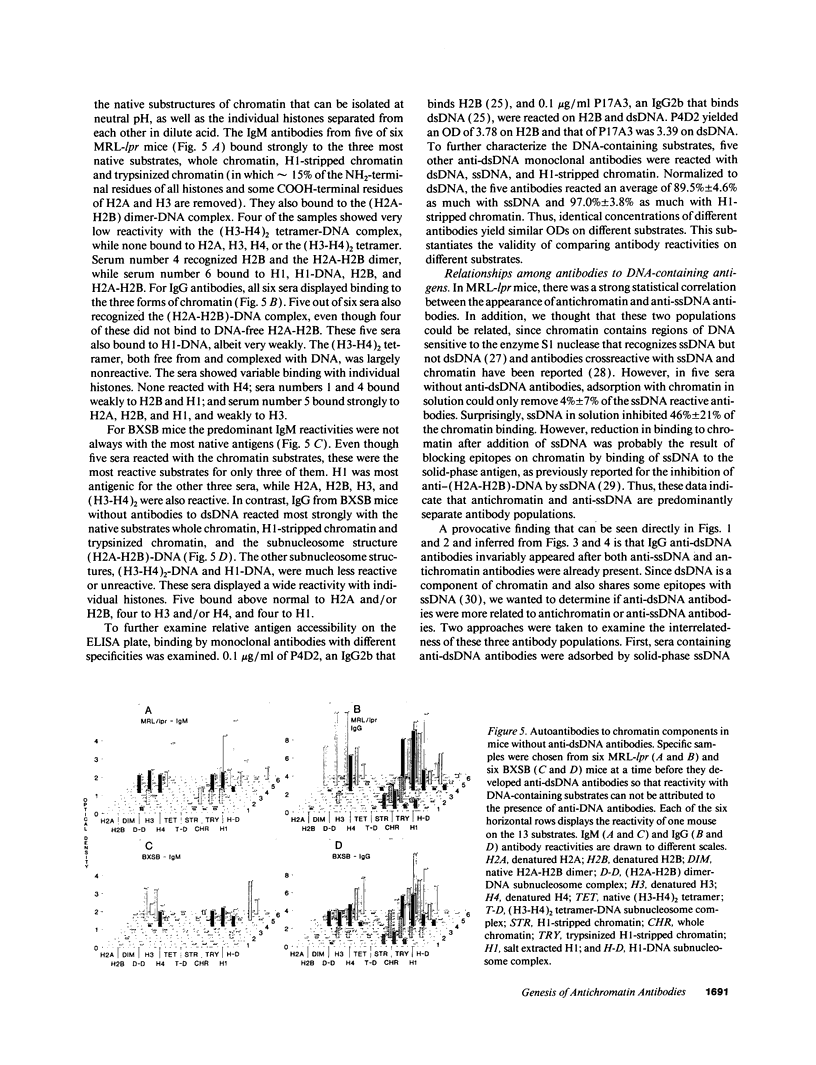
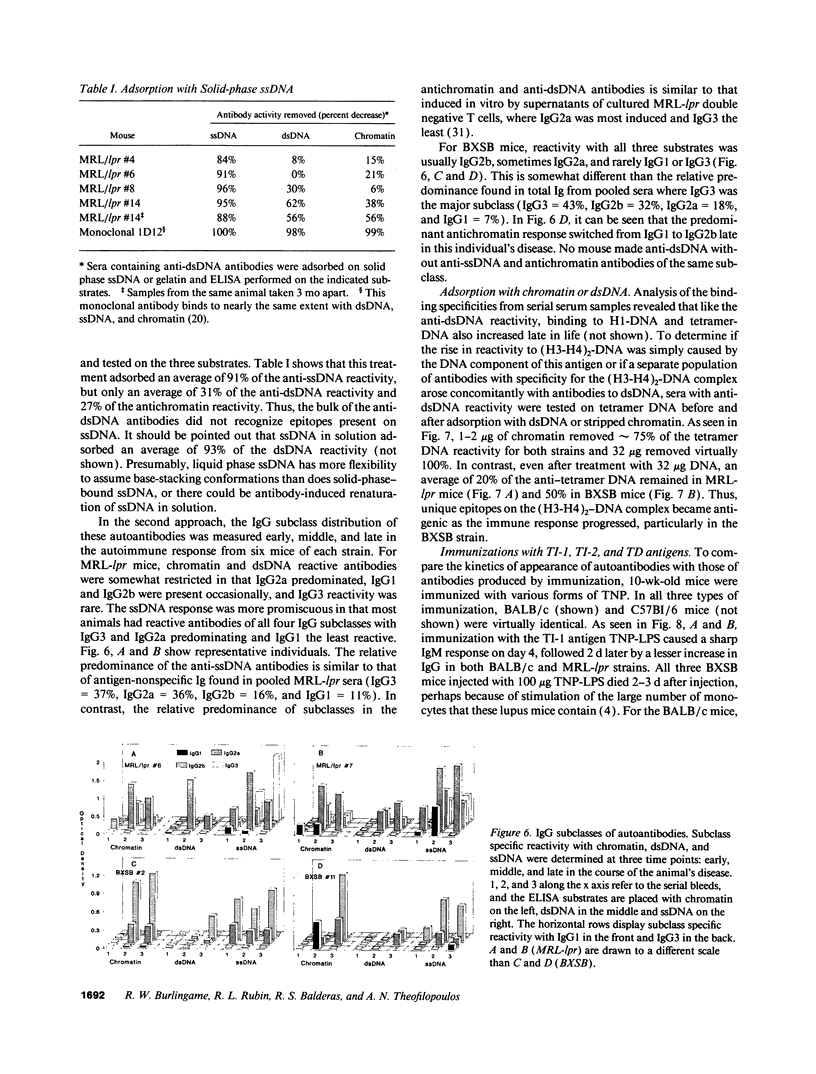
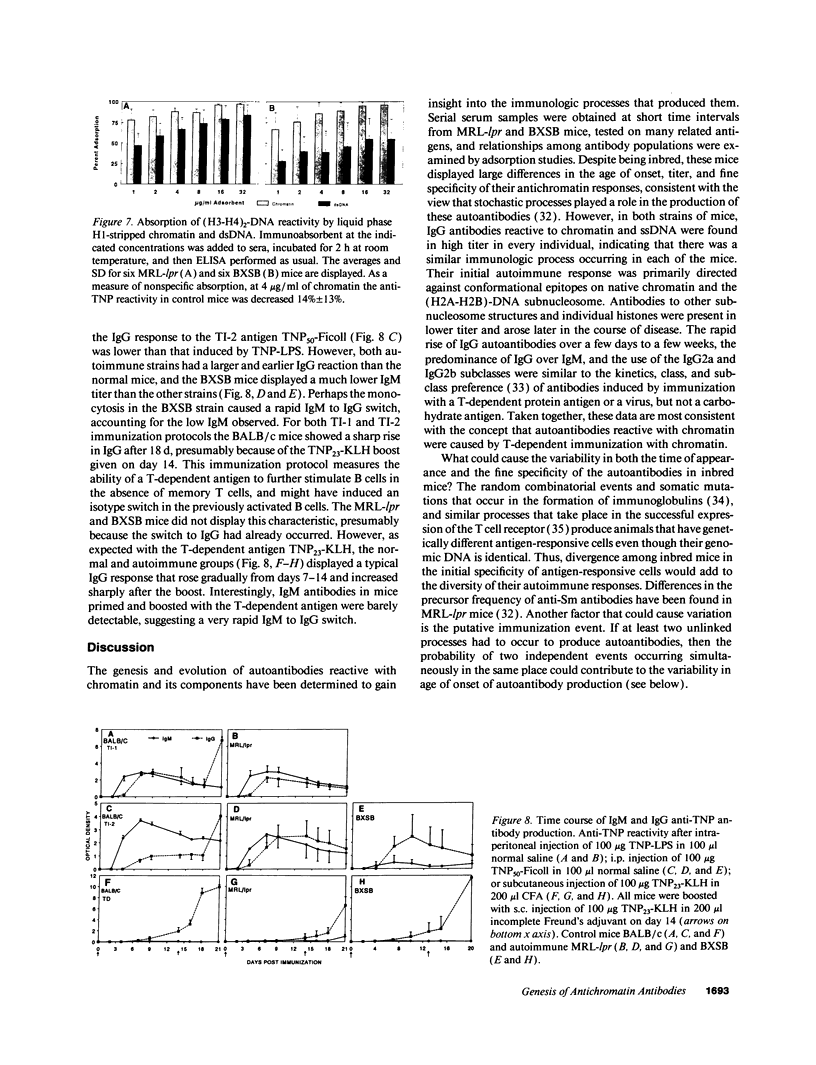
Autoantibodies reacting with chromatin and its components, histones and DNA, are characteristic of the human autoimmune disease SLE and drug-induced lupus, but the mechanisms of their induction remain unknown. Serial serum samples collected over short intervals from lupus-prone MRL/MP-lpr/lpr and BXSB mice were tested by ELISA on chromatin and its substructures to characterize the initial autoimmune response to these antigens. Direct binding studies demonstrated that the early autoantibodies recognized discontinuous epitopes on native chromatin and the (H2A-H2B)-DNA subnucleosome. As the immune response progressed, native DNA and other chromatin constituents generally became antigenic. Based on adsorption studies and IgG subclass restriction, antibodies to native DNA were more related to chromatin than to denatured DNA. The kinetics of autoantibody appearance and the Ig class distribution were similar to the kinetics and distribution seen in antibodies induced by immunization with an exogenous T-dependent antigen. These results are most consistent with the view that autoantibodies reacting with chromatin are generated by autoimmunization with chromatin, and antibodies to native DNA are a subset of the wide spectrum of antichromatin autoantibodies.
Full text
PDF
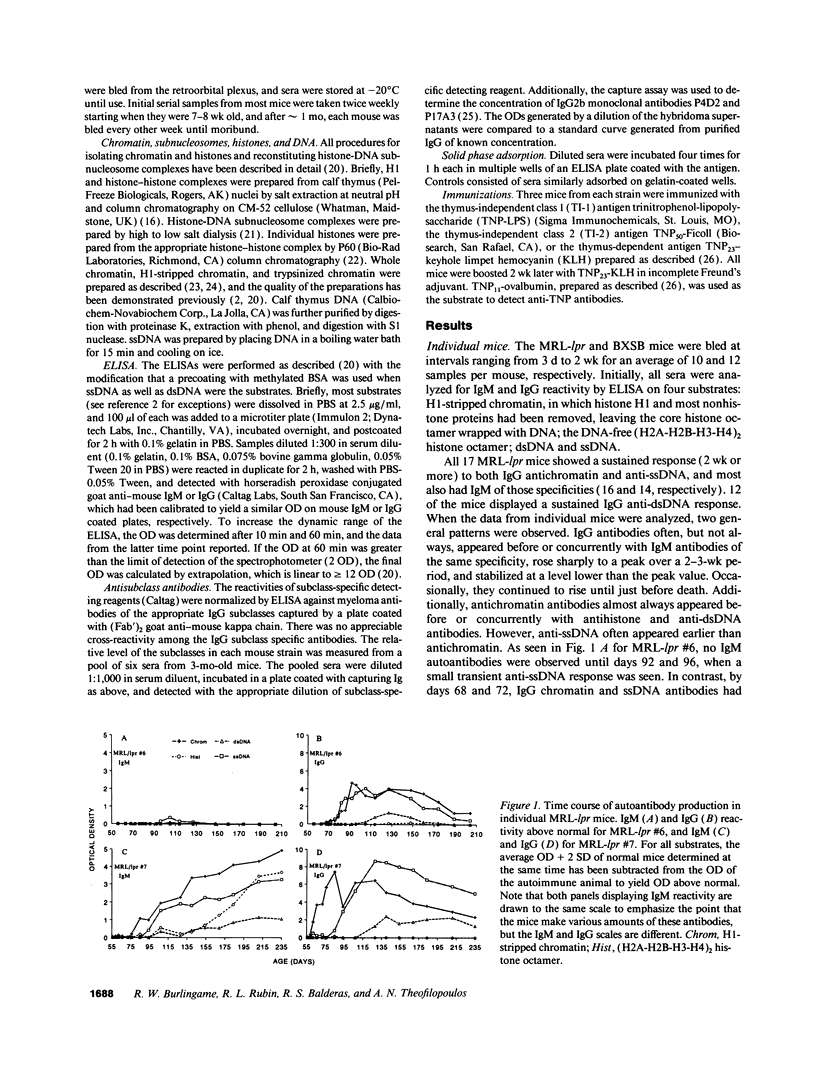
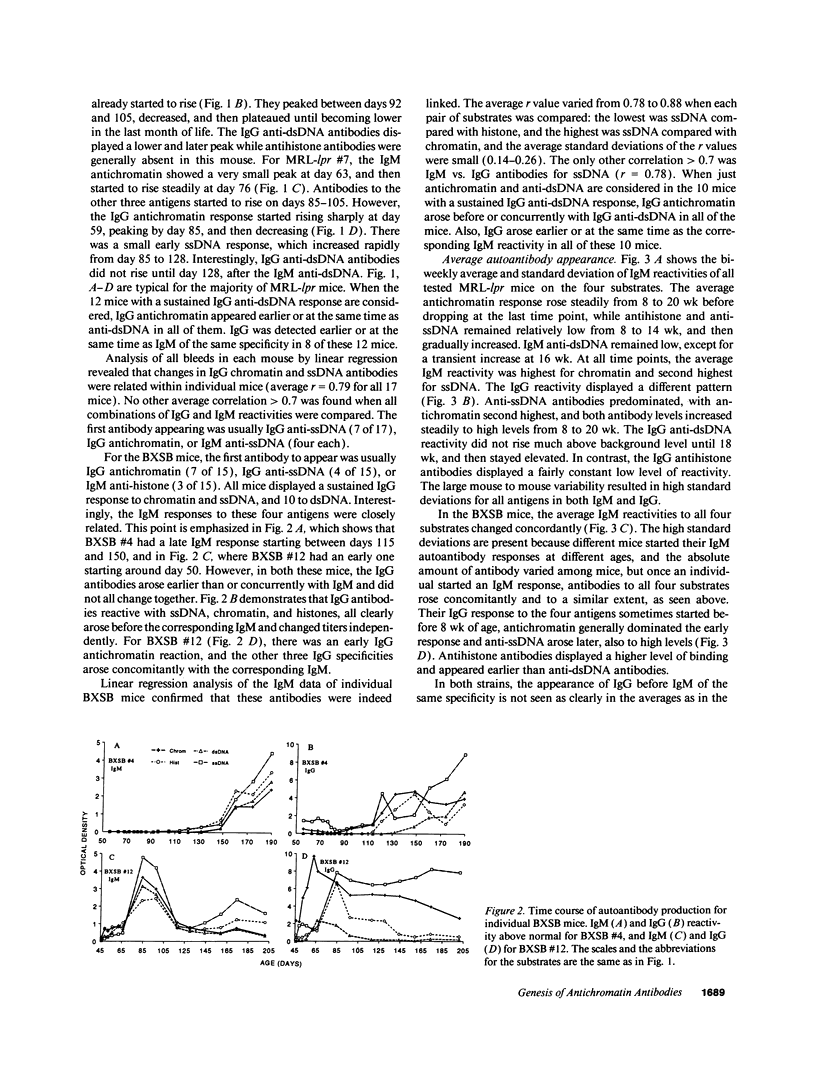



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews B. S., Eisenberg R. A., Theofilopoulos A. N., Izui S., Wilson C. B., McConahey P. J., Murphy E. D., Roths J. B., Dixon F. J. Spontaneous murine lupus-like syndromes. Clinical and immunopathological manifestations in several strains. J Exp Med. 1978 Nov 1;148(5):1198–1215. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.5.1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arents G., Burlingame R. W., Wang B. C., Love W. E., Moudrianakis E. N. The nucleosomal core histone octamer at 3.1 A resolution: a tripartite protein assembly and a left-handed superhelix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10148–10152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boire G., Lopez-Longo F. J., Lapointe S., Ménard H. A. Sera from patients with autoimmune disease recognize conformational determinants on the 60-kd Ro/SS-A protein. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Jun;34(6):722–730. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burlingame R. W., Rubin R. L. Drug-induced anti-histone autoantibodies display two patterns of reactivity with substructures of chromatin. J Clin Invest. 1991 Aug;88(2):680–690. doi: 10.1172/JCI115353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burlingame R. W., Rubin R. L. Subnucleosome structures as substrates in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Dec 5;134(2):187–199. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90380-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. L., Shores E. W., Rapoport R., Caster S., Eisenberg R. A., Pisetsky D. S. Anti-Sm autoantibodies in MRL mice: analysis of precursor frequency. Cell Immunol. 1985 Dec;96(2):448–454. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90376-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa O., Monier J. C. Antihistone antibodies detected by micro-ELISA and immunoblotting in mice with lupus-like syndrome (MRL/1, MRL/n, PN, and NZB strains). Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Aug;40(2):276–282. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(86)90031-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond B., Scharff M. D. Somatic mutation of the T15 heavy chain gives rise to an antibody with autoantibody specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5841–5844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. A., Craven S. Y., Cohen P. L. Isotype progression and clonality of anti-Sm autoantibodies in MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr mice. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):728–733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esser C., Radbruch A. Immunoglobulin class switching: molecular and cellular analysis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:717–735. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.003441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faiferman I., Koffler D. Reaction of antipolynucleotide antibody from systemic lupus erythematosus patient serum with double-stranded DNA complexed to protein. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Jul;30(7):814–818. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher C. L., Eisenberg R. A., Cohen P. L. Quantitation and IgG subclass distribution of antichromatin autoantibodies in SLE mice. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Feb;46(2):205–213. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(88)90183-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French D. L., Laskov R., Scharff M. D. The role of somatic hypermutation in the generation of antibody diversity. Science. 1989 Jun 9;244(4909):1152–1157. doi: 10.1126/science.2658060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahring L. C., Weigle W. O. The regulatory effects of cytokines on the induction of a peripheral immunologic tolerance in mice. J Immunol. 1990 Sep 1;145(5):1318–1323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey J. E., Baxevanis A. D., Moudrianakis E. N. Spectropolarimetric analysis of the core histone octamer and its subunits. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 30;29(4):965–972. doi: 10.1021/bi00456a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodnow C. C., Crosbie J., Jorgensen H., Brink R. A., Basten A. Induction of self-tolerance in mature peripheral B lymphocytes. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):385–391. doi: 10.1038/342385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habets W. J., Hoet M. H., van Venrooij W. J. Epitope patterns of anti-RNP antibodies in rheumatic diseases. Evidence for an antigen-driven autoimmune response. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Jun;33(6):834–841. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hang L. M., Aguado M. T., Dixon F. J., Theofilopoulos A. N. Induction of severe autoimmune disease in normal mice by simultaneous action of multiple immunostimulators. J Exp Med. 1985 Feb 1;161(2):423–428. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.2.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley S. B., Crosbie J., Brink R., Kantor A. B., Basten A., Goodnow C. C. Elimination from peripheral lymphoid tissues of self-reactive B lymphocytes recognizing membrane-bound antigens. Nature. 1991 Oct 24;353(6346):765–769. doi: 10.1038/353765a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt D. F., Michel H., Dickinson T. A., Shabanowitz J., Cox A. L., Sakaguchi K., Appella E., Grey H. M., Sette A. Peptides presented to the immune system by the murine class II major histocompatibility complex molecule I-Ad. Science. 1992 Jun 26;256(5065):1817–1820. doi: 10.1126/science.1319610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg D., Williams W., Axford J., Bakimer R., Bell D., Casaseca-Grayson T., Diamond B., Ebling F., Hahn B., Harkiss G. Comparison of DNA antibody idiotypes in human sera: an international collaborative study of 19 idiotypes from 11 different laboratories. J Autoimmun. 1990 Aug;3(4):393–414. doi: 10.1016/s0896-8411(05)80008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardetzky T. S., Lane W. S., Robinson R. A., Madden D. R., Wiley D. C. Identification of self peptides bound to purified HLA-B27. Nature. 1991 Sep 26;353(6342):326–329. doi: 10.1038/353326a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney J. S., Hughes B. W., Masada M. P., Allison A. C. Influence of adjuvants on the quantity, affinity, isotype and epitope specificity of murine antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Jul 26;121(2):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90156-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinman D. M., Eisenberg R. A., Steinberg A. D. Development of the autoimmune B cell repertoire in MRL-lpr/lpr mice. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 15;144(2):506–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losman M. J., Fasy T. M., Novick K. E., Monestier M. Monoclonal autoantibodies to subnucleosomes from a MRL/Mp(-)+/+ mouse. Oligoclonality of the antibody response and recognition of a determinant composed of histones H2A, H2B, and DNA. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 1;148(5):1561–1569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutter L. C. Kinetic analysis of deoxyribonuclease I cleavages in the nucleosome core: evidence for a DNA superhelix. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 15;124(2):391–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90306-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madaio M. P., Hodder S., Schwartz R. S., Stollar B. D. Responsiveness of autoimmune and normal mice to nucleic acid antigens. J Immunol. 1984 Feb;132(2):872–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matis L. A. The molecular basis of T-cell specificity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:65–82. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.000433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mencke A. J., Rill R. L. Circular dichroism and thermal denaturation studies of subnucleosomes and their relationships to nucleosome structure. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 31;21(18):4362–4370. doi: 10.1021/bi00261a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merino R., Fossati L., Lacour M., Izui S. Selective autoantibody production by Yaa+ B cells in autoimmune Yaa(+)-Yaa- bone marrow chimeric mice. J Exp Med. 1991 Nov 1;174(5):1023–1029. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.5.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller F. W., Twitty S. A., Biswas T., Plotz P. H. Origin and regulation of a disease-specific autoantibody response. Antigenic epitopes, spectrotype stability, and isotype restriction of anti-Jo-1 autoantibodies. J Clin Invest. 1990 Feb;85(2):468–475. doi: 10.1172/JCI114461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller F. W., Waite K. A., Biswas T., Plotz P. H. The role of an autoantigen, histidyl-tRNA synthetase, in the induction and maintenance of autoimmunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9933–9937. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J. Immunologic tolerance: collaboration between antigen and lymphokines. Science. 1989 Jul 14;245(4914):147–153. doi: 10.1126/science.2526369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oohara I., Wada A. Spectroscopic studies on histone-DNA interactions. I. The interaction of histone (H2A, H2B) dimer with DNA: DNA sequence dependence. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):389–397. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90699-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papalian M., Lafer E., Wong R., Stollar B. D. Reaction of systemic lupus erythematosus antinative DNA antibodies with native DNA fragments from 20 to 1,200 base pairs. J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;65(2):469–477. doi: 10.1172/JCI109690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisetsky D. S., Grudier J. P., Gilkeson G. S. A role for immunogenic DNA in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Feb;33(2):153–159. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portanova J. P., Arndt R. E., Kotzin B. L. Selective production of autoantibodies in graft-vs-host-induced and spontaneous murine lupus. Predominant reactivity with histone regions accessible in chromatin. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 1;140(3):755–760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prud'Homme G. J., Park C. L., Fieser T. M., Kofler R., Dixon F. J., Theofilopoulos A. N. Identification of a B cell differentiation factor(s) spontaneously produced by proliferating T cells in murine lupus strains of the lpr/lpr genotype. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):730–742. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichlin M., Reichlin M. W. Autoantibodies to the Ro/SS-A particle react preferentially with the human antigen. J Autoimmun. 1989 Aug;2(4):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(89)90164-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond T. J., Finch J. T., Rushton B., Rhodes D., Klug A. Structure of the nucleosome core particle at 7 A resolution. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):532–537. doi: 10.1038/311532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenberg M. B., Amkraut A. A. Immunogenicity of trinitrophenyl-hemocyanin: production of primary and secondary anti-hapten precipitins. J Immunol. 1966 Sep;97(3):421–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. L., Bell S. A., Burlingame R. W. Autoantibodies associated with lupus induced by diverse drugs target a similar epitope in the (H2A-H2B)-DNA complex. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jul;90(1):165–173. doi: 10.1172/JCI115832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. L., Tang F. L., Tsay G., Pollard K. M. Pseudoautoimmunity in normal mice: anti-histone antibodies elicited by immunization versus induction during graft-versus-host reaction. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1990 Feb;54(2):320–332. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(90)90093-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. L., Theofilopoulos A. N. Monoclonal autoantibodies reacting with multiple structurally related and unrelated macromolecules. Int Rev Immunol. 1988 Mar;3(1-2):71–95. doi: 10.3109/08830188809051183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. S., Stollar B. D. Origins of anti-DNA autoantibodies. J Clin Invest. 1985 Feb;75(2):321–327. doi: 10.1172/JCI111704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shefner R., Kleiner G., Turken A., Papazian L., Diamond B. A novel class of anti-DNA antibodies identified in BALB/c mice. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):287–296. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlomchik M., Mascelli M., Shan H., Radic M. Z., Pisetsky D., Marshak-Rothstein A., Weigert M. Anti-DNA antibodies from autoimmune mice arise by clonal expansion and somatic mutation. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):265–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair E. W., Burch J. A., Jr, Ward M. M., Keene J. D., Pisetsky D. S. Temporal correlation of antibody responses to different epitopes of the human La autoantigen. J Clin Invest. 1990 Feb;85(2):515–521. doi: 10.1172/JCI114467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahourdin C. S., Bustin M. Chromatin subunits elicit species-specific antibodies against nucleoprotein antigenic determinants. Biochemistry. 1980 Sep 16;19(19):4387–4394. doi: 10.1021/bi00560a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Dixon F. J. Murine models of systemic lupus erythematosus. Adv Immunol. 1985;37:269–390. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60342-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrigiani G. Quantitative estimation of antibodies in the immunoglobulin classes of the mouse. I. Effect of adjuvants on the antibody response to human serum albumin and keyhole limpet haemocyanin. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 May;11(1):125–135. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varela F., Andersson A., Dietrich G., Sundblad A., Holmberg D., Kazatchkine M., Coutinho A. Population dynamics of natural antibodies in normal and autoimmune individuals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5917–5921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. High-resolution mapping of S1- and DNase I-hypersensitive sites in chromatin. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1538–1539. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Van Lente F. Dissection of chromosome structure with trypsin and nucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4249–4253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Westhuyzen D. R., von Holt C. A new procedure for the isolation and fractionation of histones. FEBS Lett. 1971 May 20;14(5):333–337. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80294-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]