Abstract
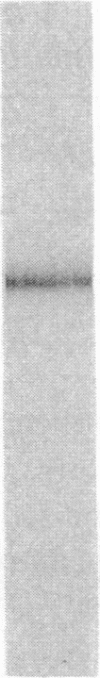
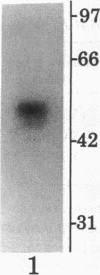
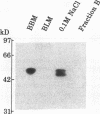
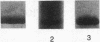
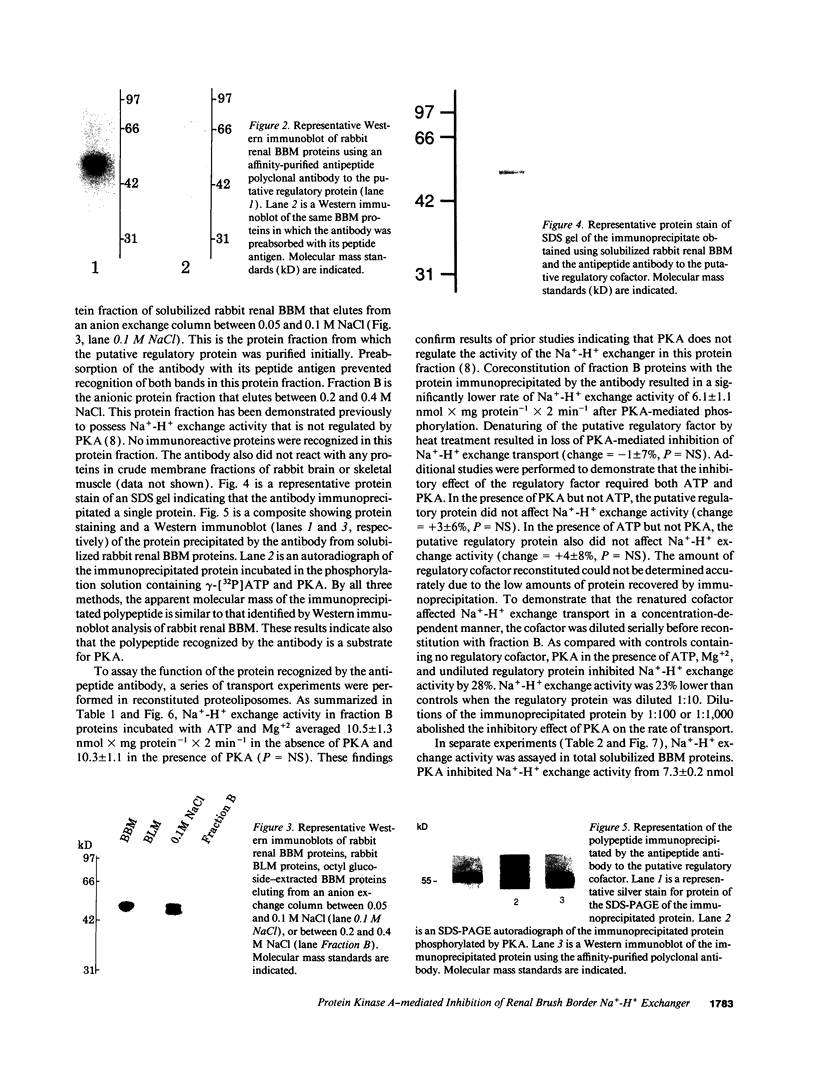
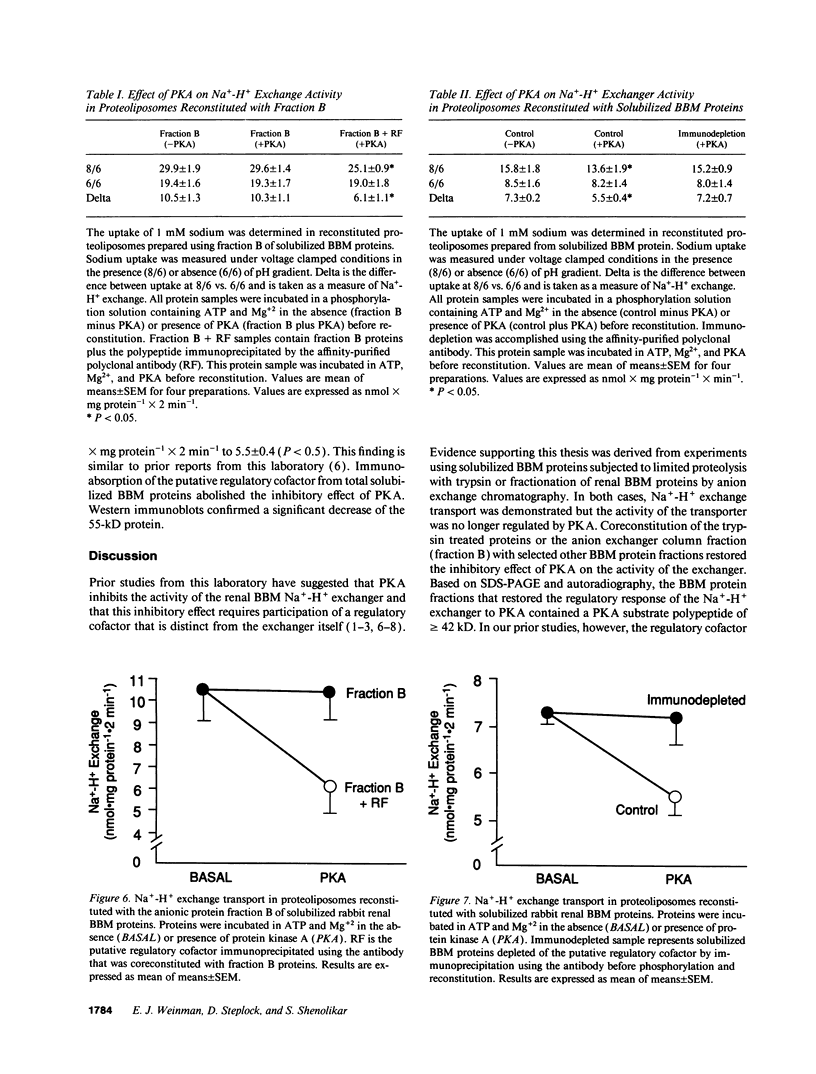
Prior studies have suggested that protein kinase A (PKA)-mediated inhibition of the rabbit renal brush border membrane (BBM) Na(+)-H+ exchanger involves a regulatory protein that is distinct from the transporter. This putative regulatory protein was purified by column chromatography and SDS-PAGE, and a partial primary amino acid sequence was determined. An affinity-purified polyclonal antibody to a synthetic peptide representing a sequence of the protein recognized a polypeptide of 55 kD in BBM but not in basolateral membrane. The antibody immunoprecipitated a PKA substrate of a similar molecular mass from detergent-solubilized BBM proteins. When assayed after reconstitution, PKA in the presence of ATP and Mg2+ did not inhibit Na(+)-H+ exchange transport in a fraction of solubilized BBM proteins eluting from an anion exchange column between 0.2 and 0.4 M NaCl (fraction B). Coreconstitution of fraction B with the immunoprecipitated 55-kD protein restored the inhibitory effect of PKA (change = 42%, P < 0.05). By contrast, Na(+)-H+ exchange transport in total solubilized BBM proteins was inhibited 25% (P < 0.05) by PKA, ATP, and Mg2+. This effect was abolished by immunodepletion of the cAMP regulatory protein (change = +5%, P = NS). These findings provide evidence that the regulation of renal BBM Na(+)-H+ exchange transport by PKA is affected by repletion and depletion of a specific protein. This suggests that PKA-mediated inhibition of the renal BBM Na(+)-H+ exchanger requires participation of a regulatory protein that is distinct from the transporter itself.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beavo J. A., Bechtel P. J., Krebs E. G. Preparation of homogeneous cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase(s) and its subunits from rabbit skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1974;38:299–308. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)38046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolson G. M., Hise M. K., Weinman E. J. Relationship among parathyroid hormone, cAMP, and calcium on proximal tubule sodium transport. Am J Physiol. 1985 Sep;249(3 Pt 2):F409–F416. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.249.3.F409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. F. Peritz' F test: basic program of a robust multiple comparison test for statistical analysis of all differences among group means. Comput Biol Med. 1984;14(4):437–445. doi: 10.1016/0010-4825(84)90044-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensley C. B., Bradley M. E., Mircheff A. K. Parathyroid hormone-induced translocation of Na-H antiporters in rat proximal tubules. Am J Physiol. 1989 Oct;257(4 Pt 1):C637–C645. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.4.C637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn A. M., Dolson G. M., Hise M. K., Bennett S. C., Weinman E. J. Parathyroid hormone and dibutyryl cAMP inhibit Na+/H+ exchange in renal brush border vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1985 Feb;248(2 Pt 2):F212–F218. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.2.F212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell G., Steplock D., Shenolikar S., Weinman E. J. Identification of a putative Na(+)-H+ exchanger regulatory cofactor in rabbit renal BBM. Am J Physiol. 1990 Dec;259(6 Pt 2):F867–F871. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.6.F867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider C., Newman R. A., Sutherland D. R., Asser U., Greaves M. F. A one-step purification of membrane proteins using a high efficiency immunomatrix. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10766–10769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenolikar S., Foulkes J. G., Cohen P. Isolation of an active fragment of protein phosphatase inhibitor-I from rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochem Soc Trans. 1978;6(5):935–937. doi: 10.1042/bst0060935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse C. M., Brant S. R., Walker M. S., Pouyssegur J., Donowitz M. Cloning and sequencing of a rabbit cDNA encoding an intestinal and kidney-specific Na+/H+ exchanger isoform (NHE-3). J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):9340–9346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Updyke T. V., Nicolson G. L. Immunoaffinity isolation of membrane antigens with biotinylated monoclonal antibodies and streptavidin-agarose. Methods Enzymol. 1986;121:717–725. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)21070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinman E. J., Dubinsky W. P., Dinh Q., Steplock D., Shenolikar S. Effect of limited trypsin digestion on the renal Na+-H+ exchanger and its regulation by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Membr Biol. 1989 Aug;109(3):233–241. doi: 10.1007/BF01870280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinman E. J., Dubinsky W. P., Shenolikar S. Reconstitution of cAMP-dependent protein kinase regulated renal Na+-H+ exchanger. J Membr Biol. 1988;101(1):11–18. doi: 10.1007/BF01872815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinman E. J., Shenolikar S., Kahn A. M. cAMP-associated inhibition of Na+-H+ exchanger in rabbit kidney brush-border membranes. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jan;252(1 Pt 2):F19–F25. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.252.1.F19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinman E. J., Steplock D., Bui G., Yuan N., Shenolikar S. Regulation of renal Na(+)-H+ exchanger by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 2):F1254–F1258. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.5.F1254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinman E., Hanley R., Morell G., Yuan N., Steplock D., Bui G., Shenolikar S. Regulation of the renal Na(+)-H+ exchanger by calcium calmodulin-dependent multifunctional protein kinase II. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1992;18(1):35–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]