Abstract
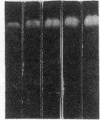
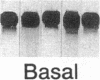
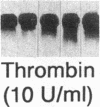
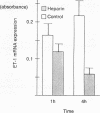
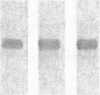
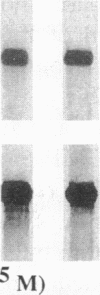
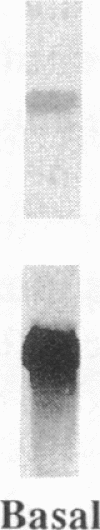
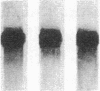
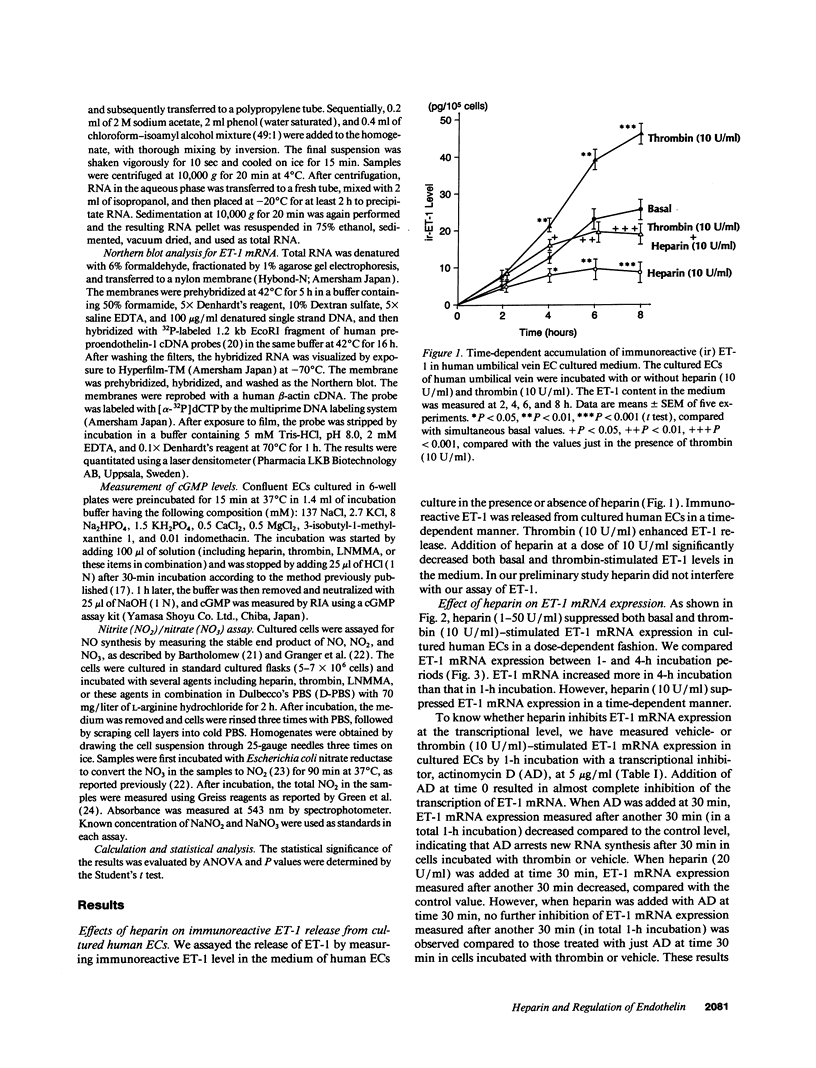
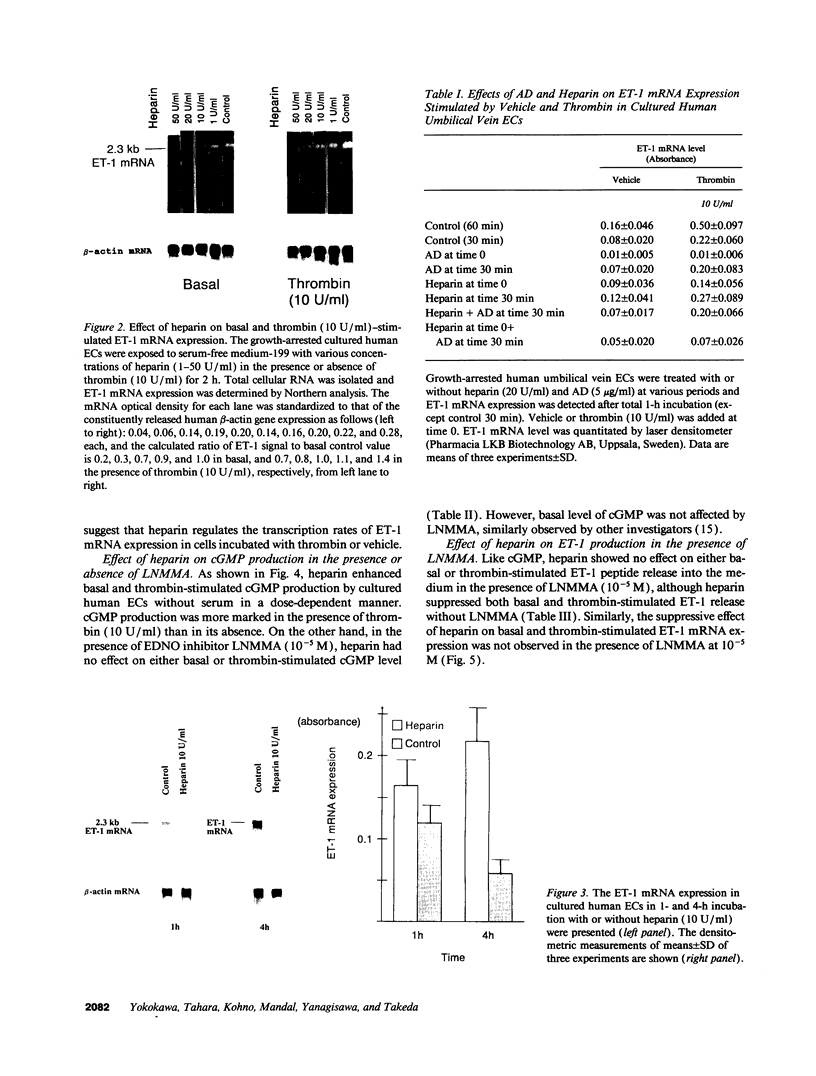
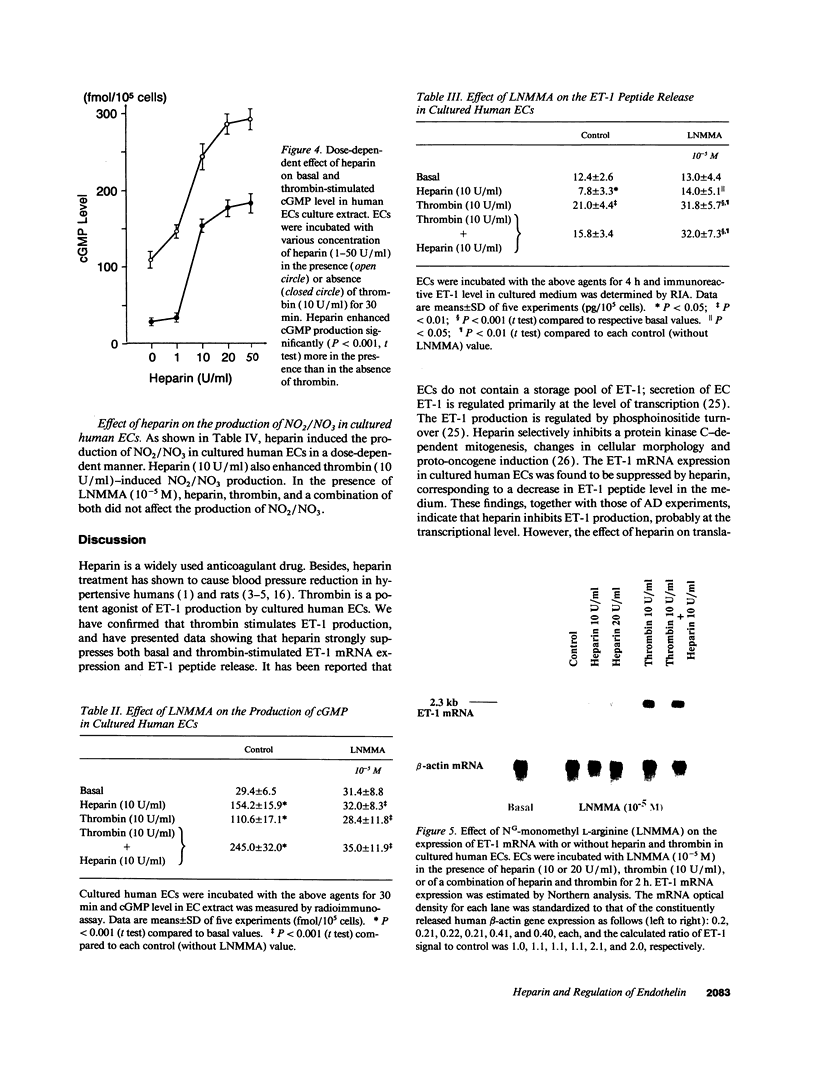
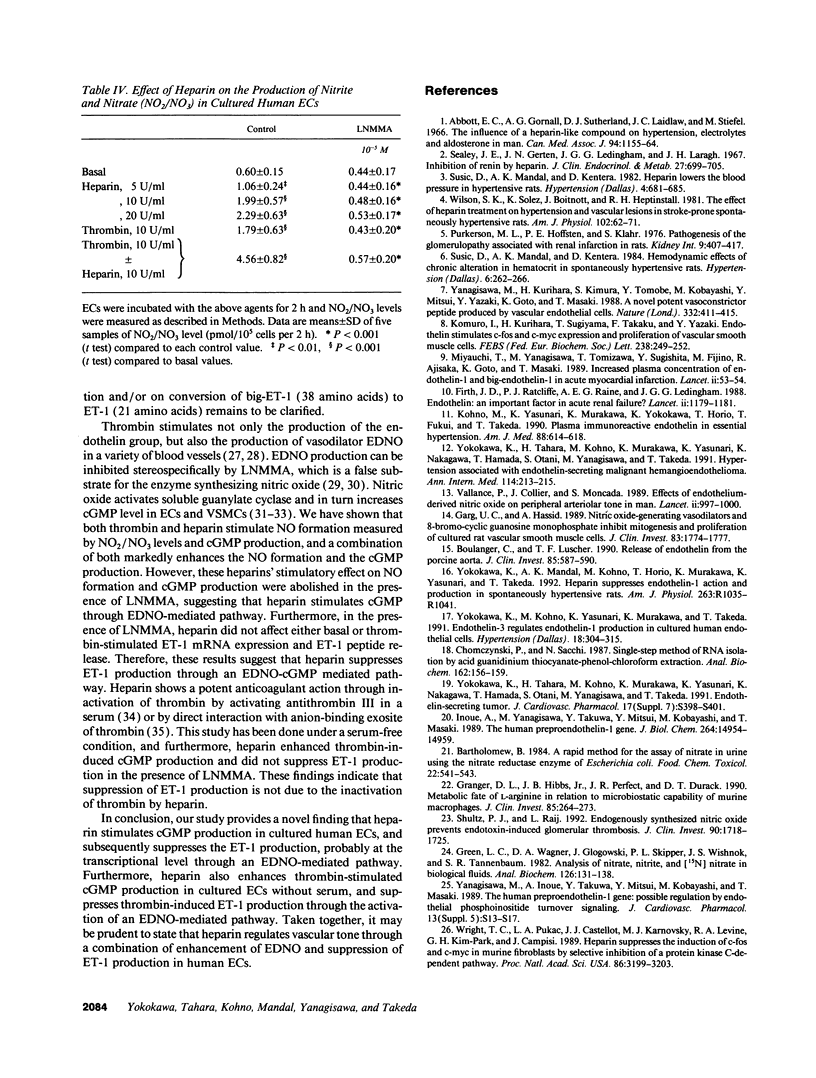
Heparin shows blood pressure lowering effect in hypertensive patients and animal models. The present study examined the effect of heparin on vasoconstrictor endothelin-1 (ET-1) production in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells (ECs) to elucidate the mechanism of antihypertensive effect of heparin. Heparin suppressed both basal and thrombin-stimulated ET-1 mRNA expression paralleled with a decrease in ET-1 peptide release in a dose-dependent manner. Heparin concomitantly enhanced nitric oxide (NO) formation measured by NO2/NO3 levels and cGMP production in ECs. These enhancements were more marked when ECs were stimulated by thrombin. However, these heparin's effects were blunted in the presence of endothelium-derived nitric oxide (EDNO) synthesizing inhibitor NG-monomethyl L-arginine. Therefore, these results suggest that suppression of ET-1 production by heparin is EDNO mediated.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbott E. C., Gornall A. G., Sutherland D. J., Laidlaw J. C., Stiefel M. The influence of a heparin-like compound on hypertension, electrolytes and aldosterone in man. Can Med Assoc J. 1966 May 28;94(22):1155–1164. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold W. P., Mittal C. K., Katsuki S., Murad F. Nitric oxide activates guanylate cyclase and increases guanosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate levels in various tissue preparations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3203–3207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomew B. A rapid method for the assay of nitrate in urine using the nitrate reductase enzyme of Escherichia coli. Food Chem Toxicol. 1984 Jul;22(7):541–543. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(84)90224-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulanger C., Lüscher T. F. Release of endothelin from the porcine aorta. Inhibition by endothelium-derived nitric oxide. J Clin Invest. 1990 Feb;85(2):587–590. doi: 10.1172/JCI114477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulanger C., Schini V. B., Moncada S., Vanhoutte P. M. Stimulation of cyclic GMP production in cultured endothelial cells of the pig by bradykinin, adenosine diphosphate, calcium ionophore A23187 and nitric oxide. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Sep;101(1):152–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12105.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Mey J. G., Claeys M., Vanhoutte P. M. Endothelium-dependent inhibitory effects of acetylcholine, adenosine triphosphate, thrombin and arachidonic acid in the canine femoral artery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Jul;222(1):166–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd, Witting J. I., Pouliott C., Fareed J. Thrombin anion-binding exosite interactions with heparin and various polyanions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;556:158–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb22499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garg U. C., Hassid A. Nitric oxide-generating vasodilators and 8-bromo-cyclic guanosine monophosphate inhibit mitogenesis and proliferation of cultured rat vascular smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 May;83(5):1774–1777. doi: 10.1172/JCI114081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger D. L., Hibbs J. B., Jr, Perfect J. R., Durack D. T. Metabolic fate of L-arginine in relation to microbiostatic capability of murine macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jan;85(1):264–273. doi: 10.1172/JCI114422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L. C., Wagner D. A., Glogowski J., Skipper P. L., Wishnok J. S., Tannenbaum S. R. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem. 1982 Oct;126(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Harbison R. G., Wood K. S., Kadowitz P. J. Activation of purified soluble guanylate cyclase by endothelium-derived relaxing factor from intrapulmonary artery and vein: stimulation by acetylcholine, bradykinin and arachidonic acid. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Jun;237(3):893–900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue A., Yanagisawa M., Takuwa Y., Mitsui Y., Kobayashi M., Masaki T. The human preproendothelin-1 gene. Complete nucleotide sequence and regulation of expression. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14954–14959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno M., Yasunari K., Murakawa K., Yokokawa K., Horio T., Fukui T., Takeda T. Plasma immunoreactive endothelin in essential hypertension. Am J Med. 1990 Jun;88(6):614–618. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(90)90527-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyauchi T., Yanagisawa M., Tomizawa T., Sugishita Y., Suzuki N., Fujino M., Ajisaka R., Goto K., Masaki T. Increased plasma concentrations of endothelin-1 and big endothelin-1 in acute myocardial infarction. Lancet. 1989 Jul 1;2(8653):53–54. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90303-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purkerson M. L., Hoffsten P. E., Klahr S. Pathogenesis of the glomerulopathy associated with renal infarction in rats. Kidney Int. 1976 May;9(5):407–417. doi: 10.1038/ki.1976.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport R. M., Draznin M. B., Murad F. Mechanisms of adenosine triphosphate-, thrombin-, and trypsin-induced relaxation of rat thoracic aorta. Circ Res. 1984 Oct;55(4):468–479. doi: 10.1161/01.res.55.4.468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Palmer R. M., Hodson H. F., Moncada S. A specific inhibitor of nitric oxide formation from L-arginine attenuates endothelium-dependent relaxation. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Feb;96(2):418–424. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11833.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. D., Damus P. S. The purification and mechanism of action of human antithrombin-heparin cofactor. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6490–6505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakuma I., Stuehr D. J., Gross S. S., Nathan C., Levi R. Identification of arginine as a precursor of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8664–8667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealey J. E., Gerten J. N., Ledingham J. G., Laragh J. H. Inhibition of renin by heparin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 May;27(5):699–705. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-5-699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shultz P. J., Raij L. Endogenously synthesized nitric oxide prevents endotoxin-induced glomerular thrombosis. J Clin Invest. 1992 Nov;90(5):1718–1725. doi: 10.1172/JCI116045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Susic D., Mandal A. K., Kentera D. Hemodynamic effects of chronic alteration in hematocrit in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 1984 Mar-Apr;6(2 Pt 1):262–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Susic D., Mandal A. K., Kentera D. Heparin lowers the blood pressure in hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 1982 Sep-Oct;4(5):681–685. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.4.5.681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallance P., Collier J., Moncada S. Effects of endothelium-derived nitric oxide on peripheral arteriolar tone in man. Lancet. 1989 Oct 28;2(8670):997–1000. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. K., Solez K., Boitnott J. K., Heptinstall R. H. The effects of heparin treatment on hypertension and vascular lesions in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Pathol. 1981 Jan;102(1):62–71. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright T. C., Jr, Pukac L. A., Castellot J. J., Jr, Karnovsky M. J., Levine R. A., Kim-Park H. Y., Campisi J. Heparin suppresses the induction of c-fos and c-myc mRNA in murine fibroblasts by selective inhibition of a protein kinase C-dependent pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3199–3203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Inoue A., Takuwa Y., Mitsui Y., Kobayashi M., Masaki T. The human preproendothelin-1 gene: possible regulation by endothelial phosphoinositide turnover signaling. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1989;13 (Suppl 5):S13–S18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Kurihara H., Kimura S., Tomobe Y., Kobayashi M., Mitsui Y., Yazaki Y., Goto K., Masaki T. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):411–415. doi: 10.1038/332411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokokawa K., Kohno M., Yasunari K., Murakawa K., Takeda T. Endothelin-3 regulates endothelin-1 production in cultured human endothelial cells. Hypertension. 1991 Sep;18(3):304–315. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.18.3.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokokawa K., Mandal A. K., Kohno M., Horio T., Murakawa K., Yasunari K., Takeda T. Heparin suppresses endothelin-1 action and production in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol. 1992 Nov;263(5 Pt 2):R1035–R1041. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1992.263.5.R1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokokawa K., Tahara H., Kohno M., Murakawa K., Yasunari K., Nakagawa K., Hamada T., Otani S., Yanagisawa M., Takeda T. Endothelin-secreting tumor. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1991;17 (Suppl 7):S398–S401. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199100177-00111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokokawa K., Tahara H., Kohno M., Murakawa K., Yasunari K., Nakagawa K., Hamada T., Otani S., Yanagisawa M., Takeda T. Hypertension associated with endothelin-secreting malignant hemangioendothelioma. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Feb 1;114(3):213–215. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-114-3-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]