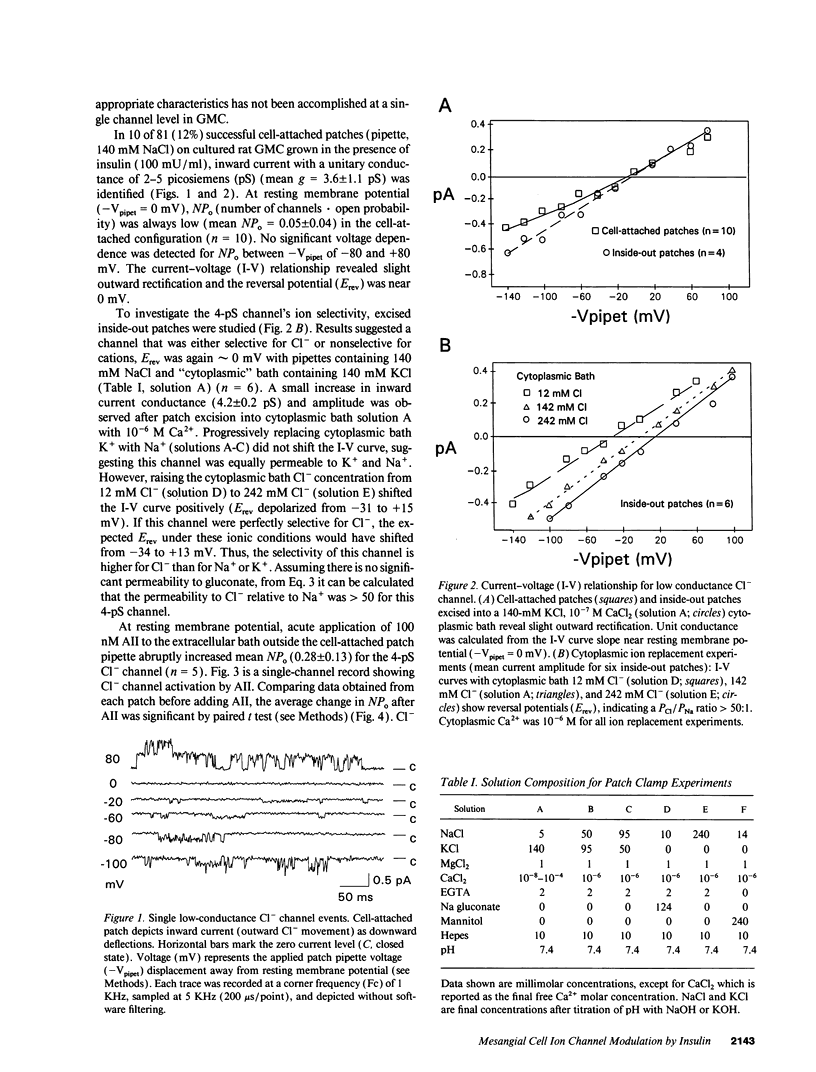
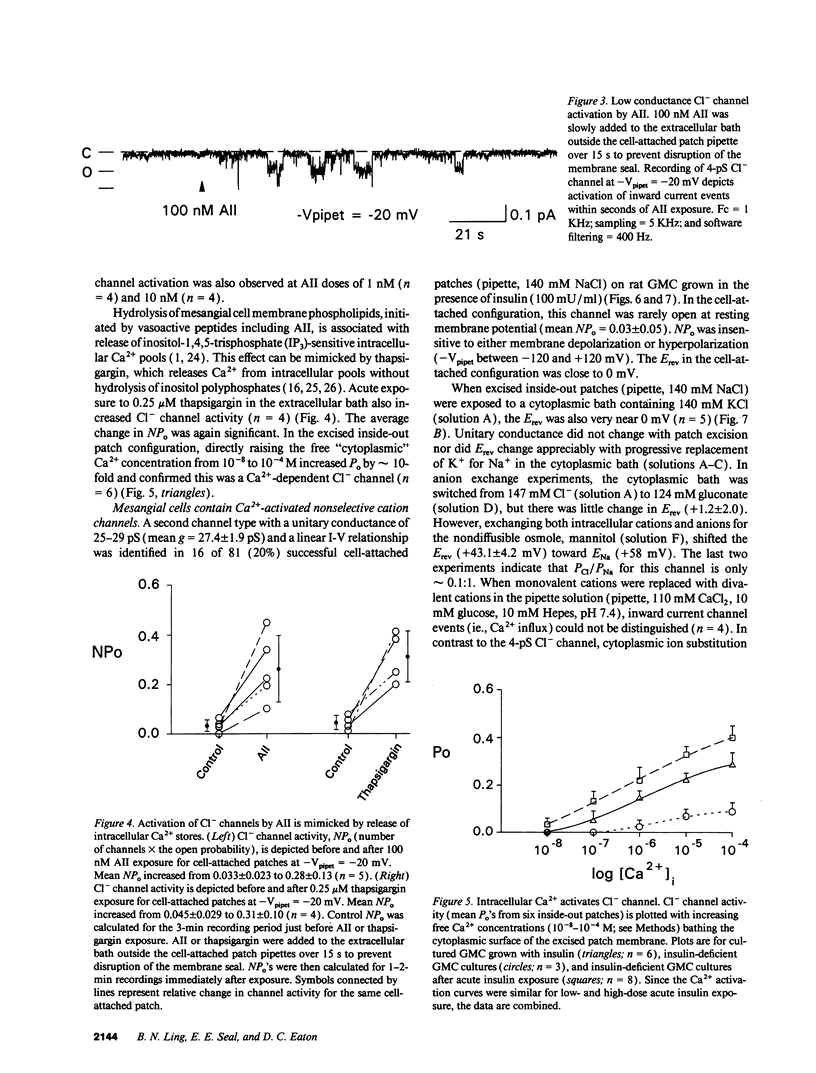
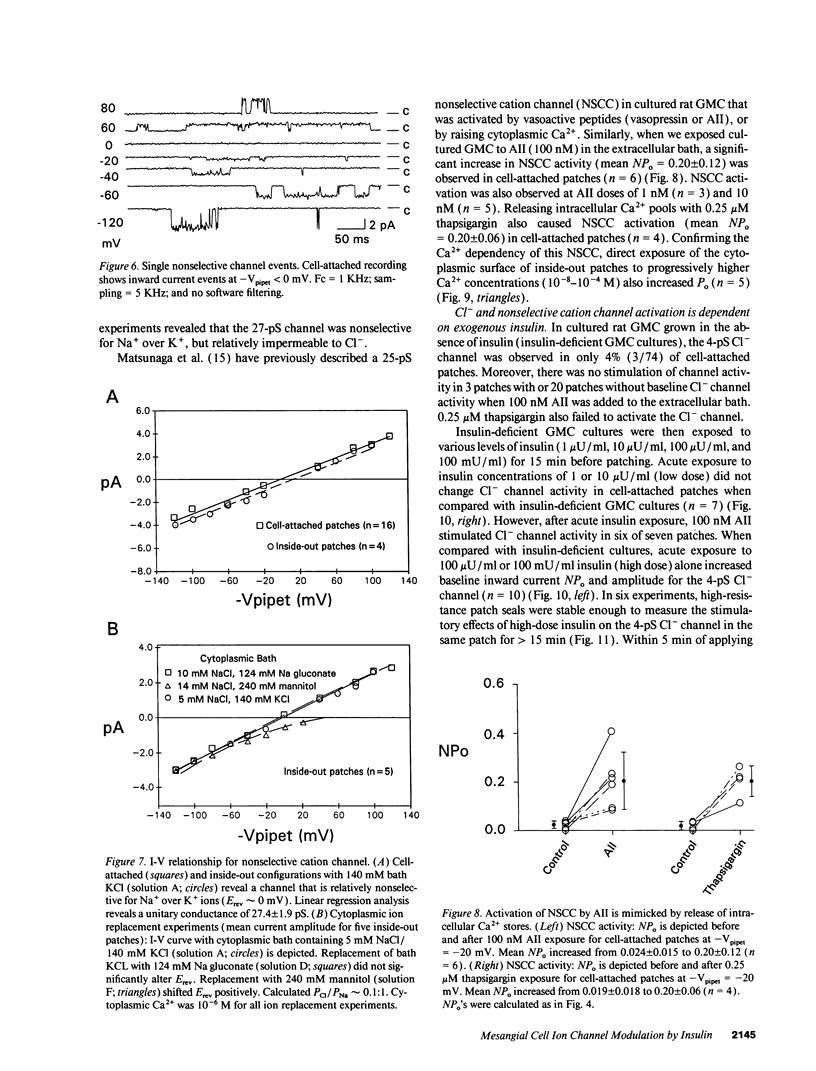
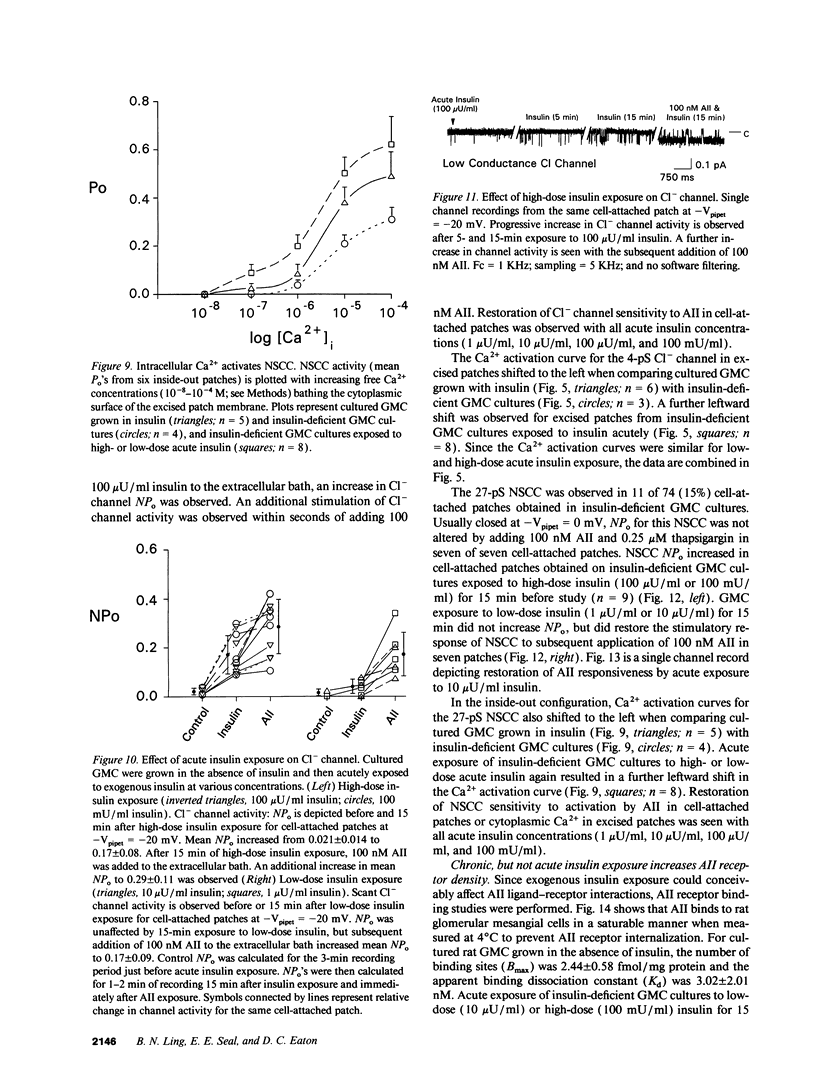
Abstract
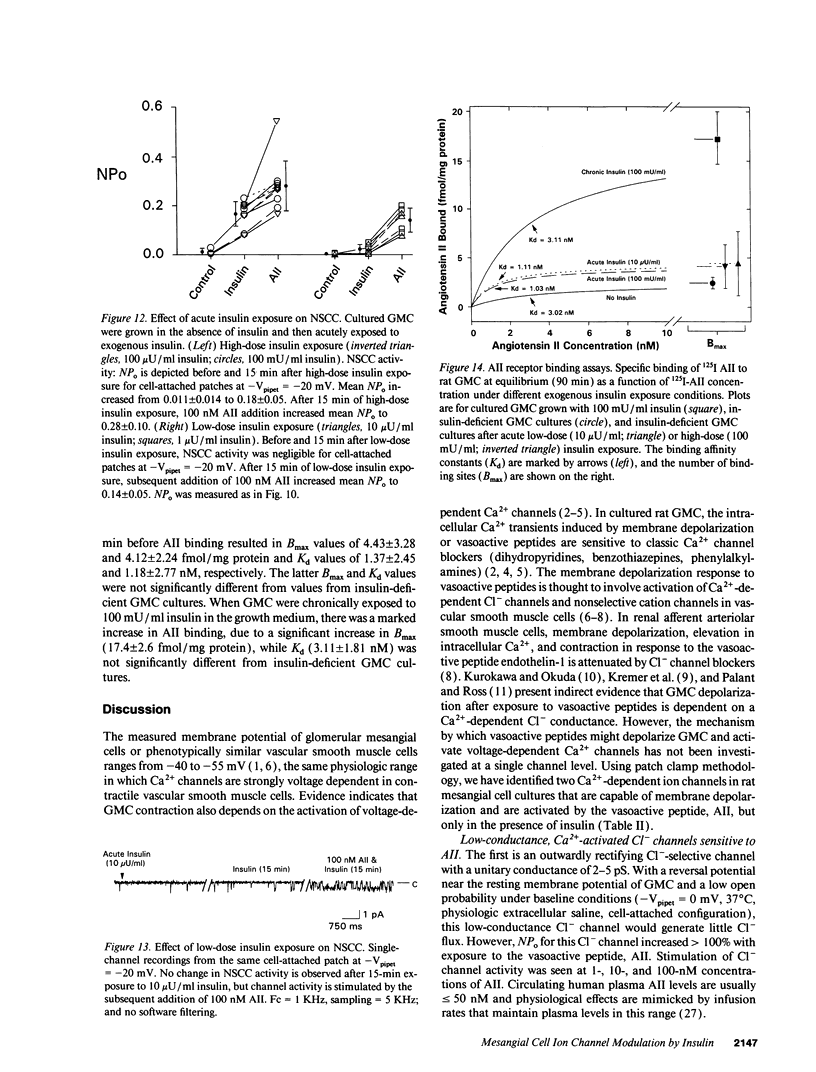
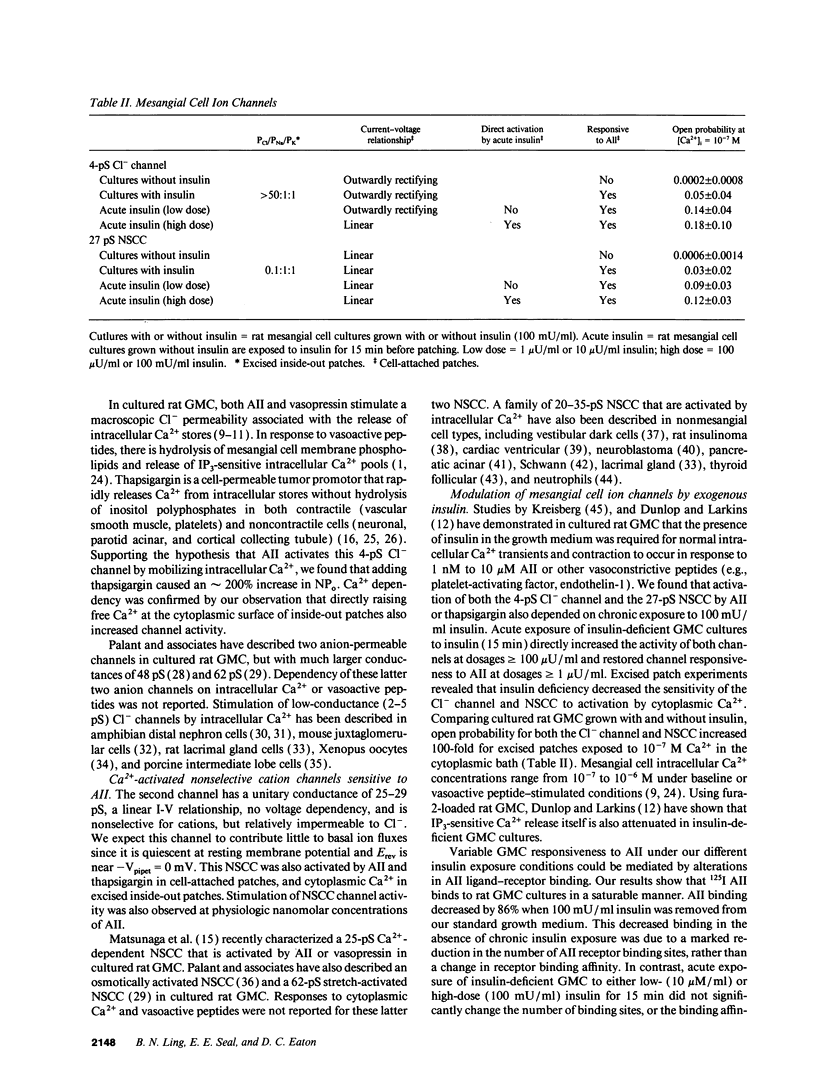
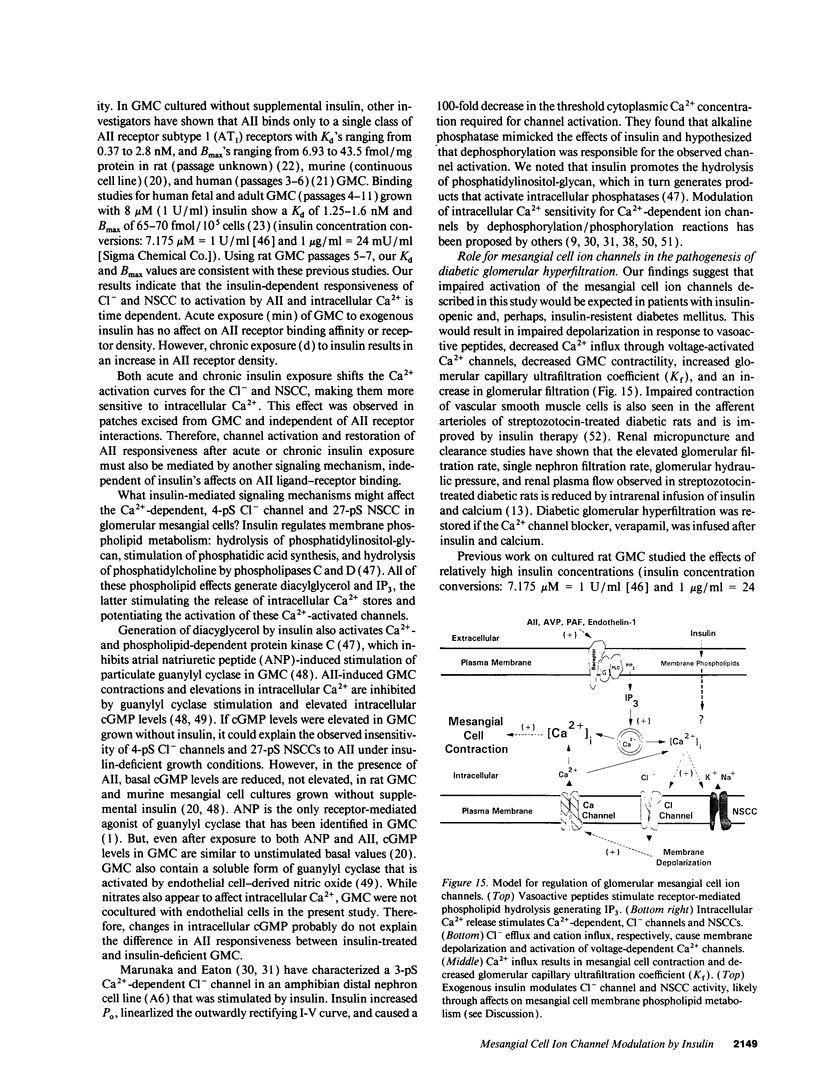
We used patch clamp methodology to investigate how glomerular mesangial cells (GMC) depolarize, thus stimulating voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels and GMC contraction. In rat GMC cultures grown in 100 mU/ml insulin, 12% of cell-attached patches contained a Ca(2+)-dependent, 4-picosiemens Cl- channel. Basal NPo (number of channels times open probability) was < 0.1 at resting membrane potential. Acute application of 1-100 nM angiotensin II (AII) or 0.25 microM thapsigargin (to release [Ca2+]i stores) increased NPo. In GMC grown without insulin, Cl- channels were rare (4%) and unresponsive to AII or thapsigargin in cell-attached patches, and less sensitive to [Ca2+]i in excised patches. GMC also contained 27-pS nonselective cation channels (NSCC) stimulated by AII, thapsigargin, or [Ca2+]i, but again only when insulin was present. In GMC grown without insulin, 15 min of insulin exposure increased NPo (insulin > or = 100 microU/ml) and restored AII and [Ca2+]i responsiveness (insulin > or = 1 microU/ml) to both Cl- and NSCC. GMC AII receptor binding studies showed a Bmax (binding sites) of 2.44 +/- 0.58 fmol/mg protein and a Kd (binding dissociation constant) of 3.02 +/- 2.01 nM in the absence of insulin. Bmax increased by 86% and Kd was unchanged after chronic (days) insulin exposure. In contrast, neither Kd nor Bmax was significantly affected by acute (15-min) exposure. Therefore, we concluded that: (a) rat GMC cultures contain Ca(2+)-dependent Cl- and NSCC, both stimulated by AII. (b) Cl- efflux and cation influx, respectively, would promote GMC depolarization, leading to voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel activation and GMC contraction. (c) Responsiveness of Cl- and NSCC to AII is dependent on insulin exposure; AII receptor density increases with chronic, but not acute insulin, and channel sensitivity to [Ca2+]i increases with both acute and chronic insulin. (d) Decreased GMC contractility may contribute to the glomerular hyperfiltration seen in insulinopenic or insulin-resistant diabetic patients.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagdade J. D., Bierman E. L., Porte D., Jr The significance of basal insulin levels in the evaluation of the insulin response to glucose in diabetic and nondiabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1967 Oct;46(10):1549–1557. doi: 10.1172/JCI105646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bank N. Mechanisms of diabetic hyperfiltration. Kidney Int. 1991 Oct;40(4):792–807. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baró I., Eisner D. A. The effects of thapsigargin on [Ca2+]i in isolated rat mesenteric artery vascular smooth muscle cells. Pflugers Arch. 1992 Jan;420(1):115–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00378652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan S., Gray P. T., Ritchie J. M. A calcium-activated cation-selective channel in rat cultured Schwann cells. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Sep 22;222(1228):349–355. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1984.0068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chansel D., Czekalski S., Pham P., Ardaillou R. Characterization of angiotensin II receptor subtypes in human glomeruli and mesangial cells. Am J Physiol. 1992 Mar;262(3 Pt 2):F432–F441. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.262.3.F432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Neher E., Reuter H., Stevens C. F. Inward current channels activated by intracellular Ca in cultured cardiac cells. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):752–754. doi: 10.1038/294752a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craelius W., el-Sherif N., Palant C. E. Stretch-activated ion channels in cultured mesangial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 15;159(2):516–521. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90023-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop M. E., Larkins R. G. Insulin-dependent contractility of glomerular mesangial cells in response to angiotensin II, platelet-activating factor and endothelin is attenuated by prostaglandin E2. Biochem J. 1990 Dec 15;272(3):561–568. doi: 10.1042/bj2720561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Computer programs for calculating total from specified free or free from specified total ionic concentrations in aqueous solutions containing multiple metals and ligands. Methods Enzymol. 1988;157:378–417. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)57093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V. Phospholipid signaling systems in insulin action. Am J Med. 1988 Nov 28;85(5A):36–43. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90396-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foidart J., Sraer J., Delarue F., Mahieu P., Ardaillou R. Evidence for mesangial glomerular receptors for angiotensin II linked to mesangial cell contractility. FEBS Lett. 1980 Dec 1;121(2):333–339. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80375-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haneda M., Kikkawa R., Maeda S., Togawa M., Koya D., Horide N., Kajiwara N., Shigeta Y. Dual mechanism of angiotensin II inhibits ANP-induced mesangial cGMP accumulation. Kidney Int. 1991 Aug;40(2):188–194. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassid A., Pidikiti N., Gamero D. Effects of vasoactive peptides on cytosolic calcium in cultured mesangial cells. Am J Physiol. 1986 Dec;251(6 Pt 2):F1018–F1028. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.251.6.F1018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi K., Epstein M., Loutzenhiser R., Forster H. Impaired myogenic responsiveness of the afferent arteriole in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: role of eicosanoid derangements. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1992 May;2(11):1578–1586. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V2111578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisberg J. I. Insulin requirement for contraction of cultured rat glomerular mesangial cells in response to angiotensin II: possible role for insulin in modulating glomerular hemodynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4190–4192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremer S. G., Zeng W., Sridhara S., Skorecki K. L. Multiple signaling pathways for Cl(-)-dependent depolarization of mesangial cells: role of Ca2+, PKC, and G proteins. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 2):F668–F678. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.262.4.F668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurokawa K., Okuda T. Calcium-activated chloride conductance of mesangial cells. Kidney Int Suppl. 1990 Nov;30:S48–S50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitan I. B. Phosphorylation of ion channels. J Membr Biol. 1985;87(3):177–190. doi: 10.1007/BF01871217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling B. N., Kokko K. E., Eaton D. C. Inhibition of apical Na+ channels in rabbit cortical collecting tubules by basolateral prostaglandin E2 is modulated by protein kinase C. J Clin Invest. 1992 Oct;90(4):1328–1334. doi: 10.1172/JCI115998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus D. C., Takeuchi S., Wangemann P. Ca(2+)-activated nonselective cation channel in apical membrane of vestibular dark cells. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jun;262(6 Pt 1):C1423–C1429. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.6.C1423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden P. A., Brenner B. M. Nitric oxide and endothelins: novel autocrine/paracrine regulators of the circulation. Semin Nephrol. 1991 Mar;11(2):169–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A., Tan Y. P., Trautmann A. Three types of calcium-dependent channel in rat lacrimal glands. J Physiol. 1984 Dec;357:293–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marunaka Y., Eaton D. C. Chloride channels in the apical membrane of a distal nephron A6 cell line. Am J Physiol. 1990 Feb;258(2 Pt 1):C352–C368. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.2.C352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marunaka Y., Eaton D. C. Effects of insulin and phosphatase on a Ca2(+)-dependent Cl- channel in a distal nephron cell line (A6). J Gen Physiol. 1990 May;95(5):773–789. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.5.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marunaka Y., Eaton D. C. Effects of vasopressin and cAMP on single amiloride-blockable Na channels. Am J Physiol. 1991 May;260(5 Pt 1):C1071–C1084. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.260.5.C1071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama Y., Moore D., Petersen O. H. Calcium-activated cation channel in rat thyroid follicular cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 5;821(2):229–232. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90091-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama Y., Peterson O. H. Single-channel currents in isolated patches of plasma membrane from basal surface of pancreatic acini. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):159–161. doi: 10.1038/299159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga H., Yamashita N., Miyajima Y., Okuda T., Chang H., Ogata E., Kurokawa K. Ion channel activities of cultured rat mesangial cells. Am J Physiol. 1991 Nov;261(5 Pt 2):F808–F814. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.261.5.F808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menè P., Cinotti G. A., Pugliese F. Signal transduction in mesangial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1992 Apr;2(10 Suppl):S100–S106. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V210s100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mené P., Simonson M. S., Dunn M. J. Phospholipids in signal transduction of mesangial cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Mar;256(3 Pt 2):F375–F386. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.3.F375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mené P., Simonson M. S., Dunn M. J. Physiology of the mesangial cell. Physiol Rev. 1989 Oct;69(4):1347–1424. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.4.1347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. T., Patlak J. B., Worley J. F., Standen N. B. Calcium channels, potassium channels, and voltage dependence of arterial smooth muscle tone. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jul;259(1 Pt 1):C3–18. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.1.C3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishio M., Tsukahara H., Hiraoka M., Sudo M., Kigoshi S., Muramatsu I. Calcium channel current in cultured rat mesangial cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Jan;43(1):96–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palant C. E., Ross M. J. Role of ionic currents in the physiological response to angiotensin II. Ren Physiol Biochem. 1991 Jul-Oct;14(4-5):186–198. doi: 10.1159/000173404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray P. E., Aguilera G., Kopp J. B., Horikoshi S., Klotman P. E. Angiotensin II receptor-mediated proliferation of cultured human fetal mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 1991 Oct;40(4):764–771. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgess N. C., Hales C. N., Ashford M. L. Calcium and ATP regulate the activity of a non-selective cation channel in a rat insulinoma cell line. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Aug;409(6):607–615. doi: 10.1007/BF00584661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Neher E., Sakmann B. Rat brain serotonin receptors in Xenopus oocytes are coupled by intracellular calcium to endogenous channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):5063–5067. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.5063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takenaka T., Epstein M., Forster H., Landry D. W., Iijima K., Goligorsky M. S. Attenuation of endothelin effects by a chloride channel inhibitor, indanyloxyacetic acid. Am J Physiol. 1992 May;262(5 Pt 2):F799–F806. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.262.5.F799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taleb O., Feltz P., Bossu J. L., Feltz A. Small-conductance chloride channels activated by calcium on cultured endocrine cells from mammalian pars intermedia. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Oct;412(6):641–646. doi: 10.1007/BF00583766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf G., Thaiss F., Schoeppe W., Stahl R. A. Angiotensin II-induced proliferation of cultured murine mesangial cells: inhibitory role of atrial natriuretic peptide. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1992 Dec;3(6):1270–1278. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V361270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xuan Y. T., Wang O. L., Whorton A. R. Thapsigargin stimulates Ca2+ entry in vascular smooth muscle cells: nicardipine-sensitive and -insensitive pathways. Am J Physiol. 1992 May;262(5 Pt 1):C1258–C1265. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.5.C1258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellen G. Single Ca2+-activated nonselective cation channels in neuroblastoma. Nature. 1982 Mar 25;296(5855):357–359. doi: 10.1038/296357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Y. M., Lermioglu F., Hassid A. Modulation of Ca by agents affecting voltage-sensitive Ca channels in mesangial cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Dec;257(6 Pt 2):F1094–F1099. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.257.6.F1094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Tscharner V., Prod'hom B., Baggiolini M., Reuter H. Ion channels in human neutrophils activated by a rise in free cytosolic calcium concentration. 1986 Nov 27-Dec 3Nature. 324(6095):369–372. doi: 10.1038/324369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



