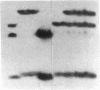
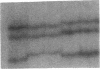
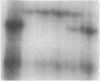
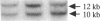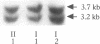Abstract
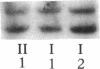
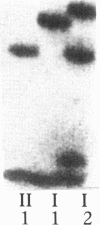
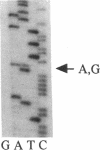
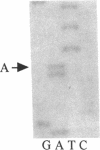
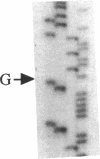
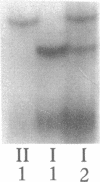
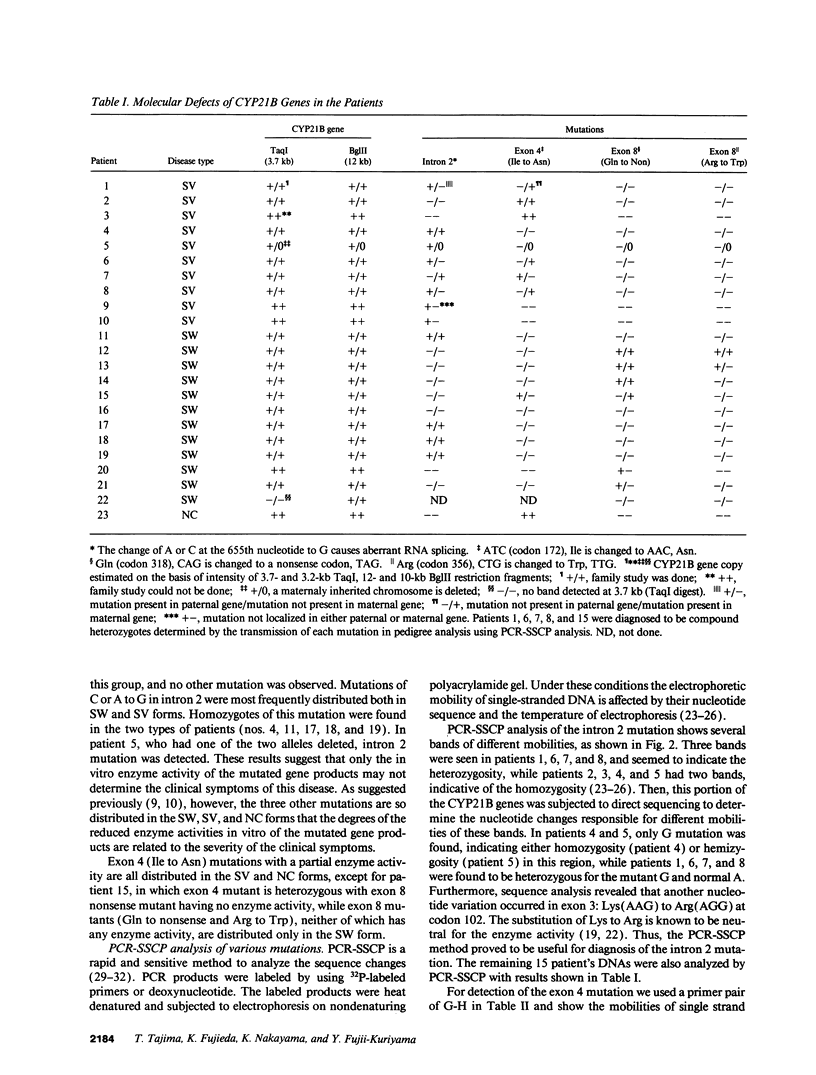
Steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency is a major cause of congenital adrenal hyperplasia and is caused by genetic impairment of this enzyme. Since approximately 80% of cases are caused by point mutations of the CYP21B (CYP21A2) gene, whereas the remaining 20% are due to deletion of this gene, we used the polymerase chain reaction single strand conformation polymorphism technique for rapid and accurate diagnosis of this disease. Of 23 patients examined, 1 had a hemizygous CYP21B gene. 18 patient's genes localized their harmful mutations or deletion on both the alleles, while 4 of them found their causative mutations on one of the two alleles, and 1 failed to find any responsible mutation. All the mutations (four nucleotide substitutions) detected are also found in the CYP21A (CYP21A1) pseudogene. A mutation at the intron 2 site is most prevalent in both salt-wasting and simple virilizing forms of the disease, and accounts for 37% of the patient's genes (17/46). Pedigree analysis of these mutations revealed that the mutations (at least four of them) occurred de novo at a considerable frequency on both the paternally and maternally inherited chromosomes. This result could explain occasional discordance of the diagnosis using HLA typing with the clinical symptoms.
Full text
PDF

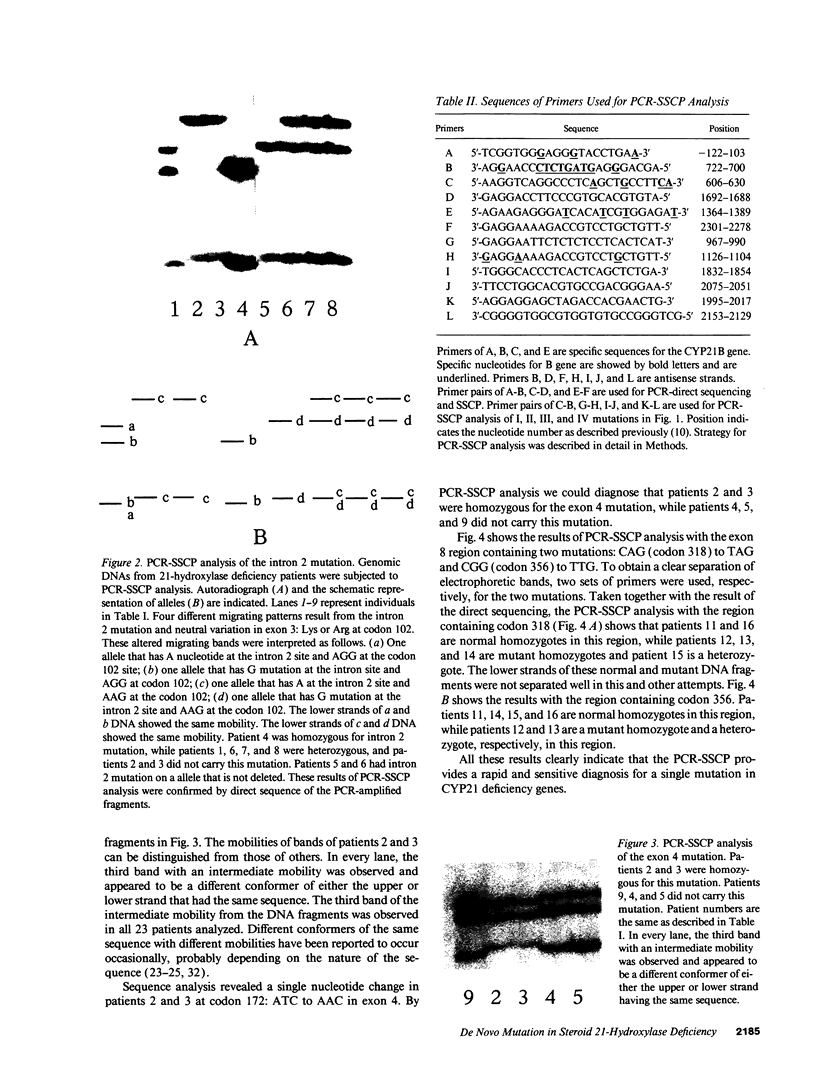

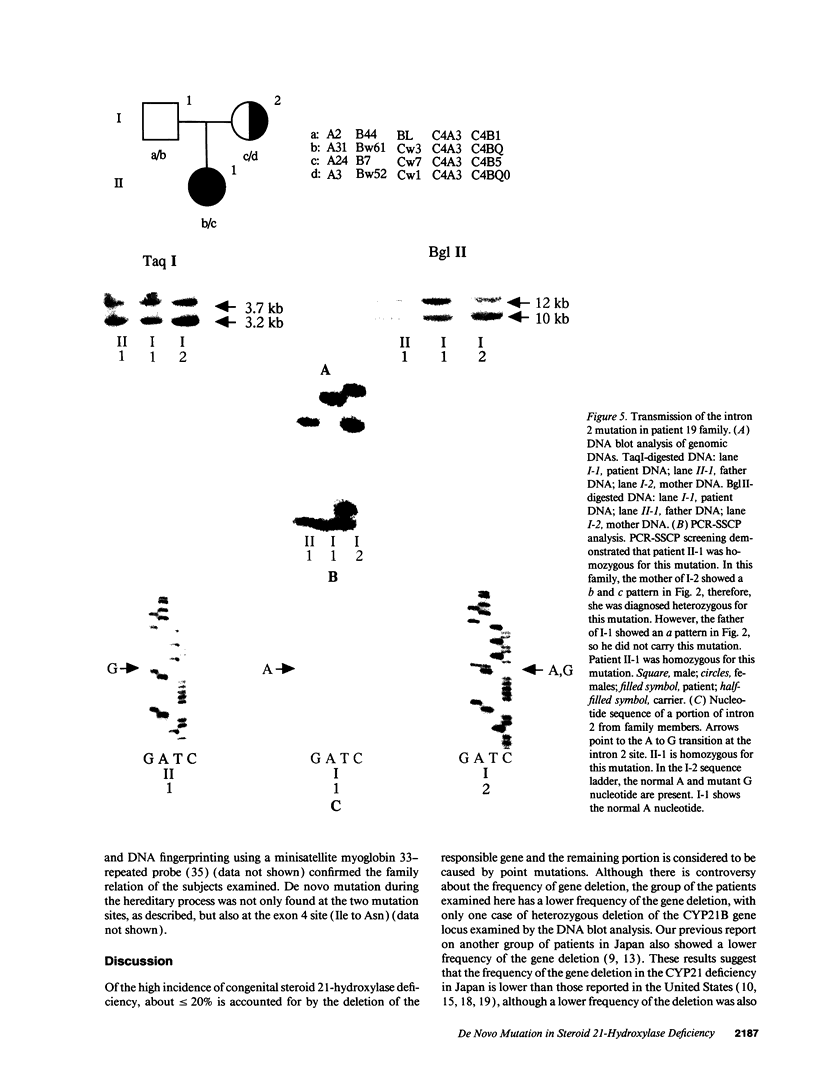
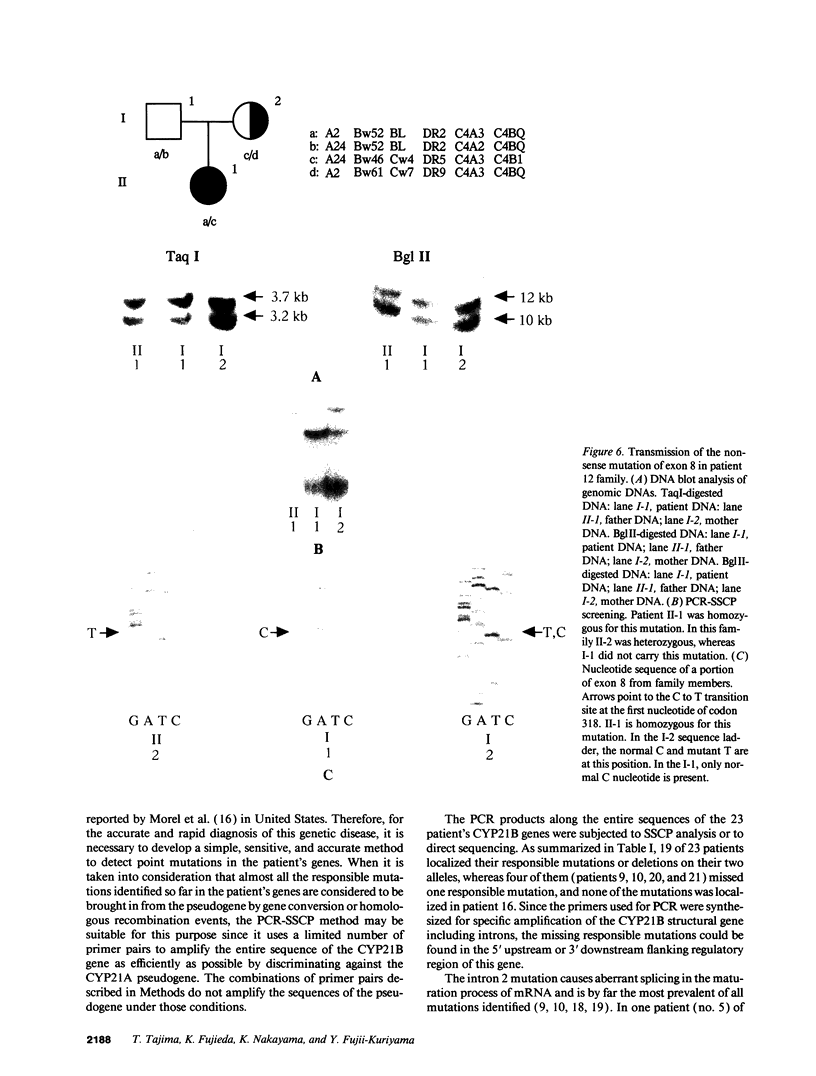


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amor M., Parker K. L., Globerman H., New M. I., White P. C. Mutation in the CYP21B gene (Ile-172----Asn) causes steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1600–1604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berta P., Hawkins J. R., Sinclair A. H., Taylor A., Griffiths B. L., Goodfellow P. N., Fellous M. Genetic evidence equating SRY and the testis-determining factor. Nature. 1990 Nov 29;348(6300):448–450. doi: 10.1038/348448A0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawthon R. M., Weiss R., Xu G. F., Viskochil D., Culver M., Stevens J., Robertson M., Dunn D., Gesteland R., O'Connell P. A major segment of the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene: cDNA sequence, genomic structure, and point mutations. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):193–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90253-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiou S. H., Hu M. C., Chung B. C. A missense mutation at Ile172----Asn or Arg356----Trp causes steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3549–3552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier S., Sinnott P. J., Dyer P. A., Price D. A., Harris R., Strachan T. Pulsed field gel electrophoresis identifies a high degree of variability in the number of tandem 21-hydroxylase and complement C4 gene repeats in 21-hydroxylase deficiency haplotypes. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1393–1402. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03520.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier S., Tassabehji M., Sinnott P., Strachan T. A de novo pathological point mutation at the 21-hydroxylase locus: implications for gene conversion in the human genome. Nat Genet. 1993 Mar;3(3):260–265. doi: 10.1038/ng0393-260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean M., White M. B., Amos J., Gerrard B., Stewart C., Khaw K. T., Leppert M. Multiple mutations in highly conserved residues are found in mildly affected cystic fibrosis patients. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):863–870. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90196-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada F., Kimura A., Iwanaga T., Shimozawa K., Yata J., Sasazuki T. Gene conversion-like events cause steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency in congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8091–8094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmberg A., Tusie-Luna M. T., Tabarelli M., Kofler R., White P. C. R339H and P453S: CYP21 mutations associated with nonclassic steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency that are not apparent gene conversions. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Aug;6(8):1318–1322. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.8.1406709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi Y., Hiromasa T., Tanae A., Miki T., Nakura J., Kondo T., Ohura T., Ogawa E., Nakayama K., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Effects of individual mutations in the P-450(C21) pseudogene on the P-450(C21) activity and their distribution in the patient genomes of congenital steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency. J Biochem. 1991 Apr;109(4):638–644. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi Y., Tanae A., Inoue H., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Evidence for frequent gene conversion in the steroid 21-hydroxylase P-450(C21) gene: implications for steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Jan;42(1):17–25. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi Y., Tanae A., Inoue H., Hiromasa T., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Aberrant splicing and missense mutations cause steroid 21-hydroxylase [P-450(C21)] deficiency in humans: possible gene conversion products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7486–7490. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi Y., Yoshioka H., Yamane M., Gotoh O., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Complete nucleotide sequence of two steroid 21-hydroxylase genes tandemly arranged in human chromosome: a pseudogene and a genuine gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2841–2845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Thein S. L. Individual-specific 'fingerprints' of human DNA. Nature. 1985 Jul 4;316(6023):76–79. doi: 10.1038/316076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. L., Levine L. S. Molecular and clinical advances in congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Pediatr. 1987 Jul;111(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80334-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. L., Morel Y. The molecular genetics of 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:371–393. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.002103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel Y., André J., Uring-Lambert B., Hauptmann G., Bétuel H., Tossi M., Forest M. G., David M., Bertrand J., Miller W. L. Rearrangements and point mutations of P450c21 genes are distinguished by five restriction endonuclease haplotypes identified by a new probing strategy in 57 families with congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):527–536. doi: 10.1172/JCI113914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet E., Crété P., Kuttenn F., Raux-Demay M. C., Boué J., White P. C., Boué A. Distribution of deletions and seven point mutations on CYP21B genes in three clinical forms of steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jan;48(1):79–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
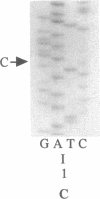
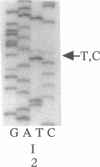
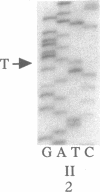
- Orita M., Iwahana H., Kanazawa H., Hayashi K., Sekiya T. Detection of polymorphisms of human DNA by gel electrophoresis as single-strand conformation polymorphisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2766–2770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orita M., Sekiya T., Hayashi K. DNA sequence polymorphisms in Alu repeats. Genomics. 1990 Oct;8(2):271–278. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90282-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orita M., Suzuki Y., Sekiya T., Hayashi K. Rapid and sensitive detection of point mutations and DNA polymorphisms using the polymerase chain reaction. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):874–879. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owerbach D., Crawford Y. M., Draznin M. B. Direct analysis of CYP21B genes in 21-hydroxylase deficiency using polymerase chain reaction amplification. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Jan;4(1):125–131. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-1-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owerbach D., Sherman L., Ballard A. L., Azziz R. Pro-453 to Ser mutation in CYP21 is associated with nonclassic steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Aug;6(8):1211–1215. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.8.1406699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang S. Y., Wallace M. A., Hofman L., Thuline H. C., Dorche C., Lyon I. C., Dobbins R. H., Kling S., Fujieda K., Suwa S. Worldwide experience in newborn screening for classical congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Pediatrics. 1988 Jun;81(6):866–874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues N. R., Dunham I., Yu C. Y., Carroll M. C., Porter R. R., Campbell R. D. Molecular characterization of the HLA-linked steroid 21-hydroxylase B gene from an individual with congenital adrenal hyperplasia. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1653–1661. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02414.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Bugawan T. L., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Analysis of enzymatically amplified beta-globin and HLA-DQ alpha DNA with allele-specific oligonucleotide probes. Nature. 1986 Nov 13;324(6093):163–166. doi: 10.1038/324163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinnott P. J., Dyer P. A., Price D. A., Harris R., Strachan T. 21-hydroxylase deficiency families with HLA identical affected and unaffected sibs. J Med Genet. 1989 Jan;26(1):10–17. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.1.10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinnott P., Collier S., Costigan C., Dyer P. A., Harris R., Strachan T. Genesis by meiotic unequal crossover of a de novo deletion that contributes to steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2107–2111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speiser P. W., Dupont B., Rubinstein P., Piazza A., Kastelan A., New M. I. High frequency of nonclassical steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Jul;37(4):650–667. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speiser P. W., Dupont J., Zhu D., Serrat J., Buegeleisen M., Tusie-Luna M. T., Lesser M., New M. I., White P. C. Disease expression and molecular genotype in congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1992 Aug;90(2):584–595. doi: 10.1172/JCI115897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speiser P. W., New M. I., White P. C. Molecular genetic analysis of nonclassic steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency associated with HLA-B14,DR1. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jul 7;319(1):19–23. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198807073190104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Orita M., Shiraishi M., Hayashi K., Sekiya T. Detection of ras gene mutations in human lung cancers by single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis of polymerase chain reaction products. Oncogene. 1990 Jul;5(7):1037–1043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tajima T., Fujieda K., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. de novo mutation causes steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency in one family of HLA-identical affected and unaffected siblings. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993 Jul;77(1):86–89. doi: 10.1210/jcem.77.1.8325964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., Grossberger D., Onufer B. J., Chaplin D. D., New M. I., Dupont B., Strominger J. L. Two genes encoding steroid 21-hydroxylase are located near the genes encoding the fourth component of complement in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1089–1093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., New M. I., Dupont B. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (2). N Engl J Med. 1987 Jun 18;316(25):1580–1586. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198706183162506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., Vitek A., Dupont B., New M. I. Characterization of frequent deletions causing steroid 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4436–4440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]