Abstract
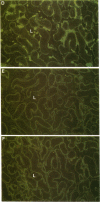
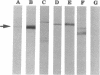
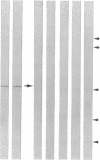
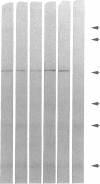
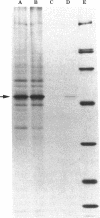
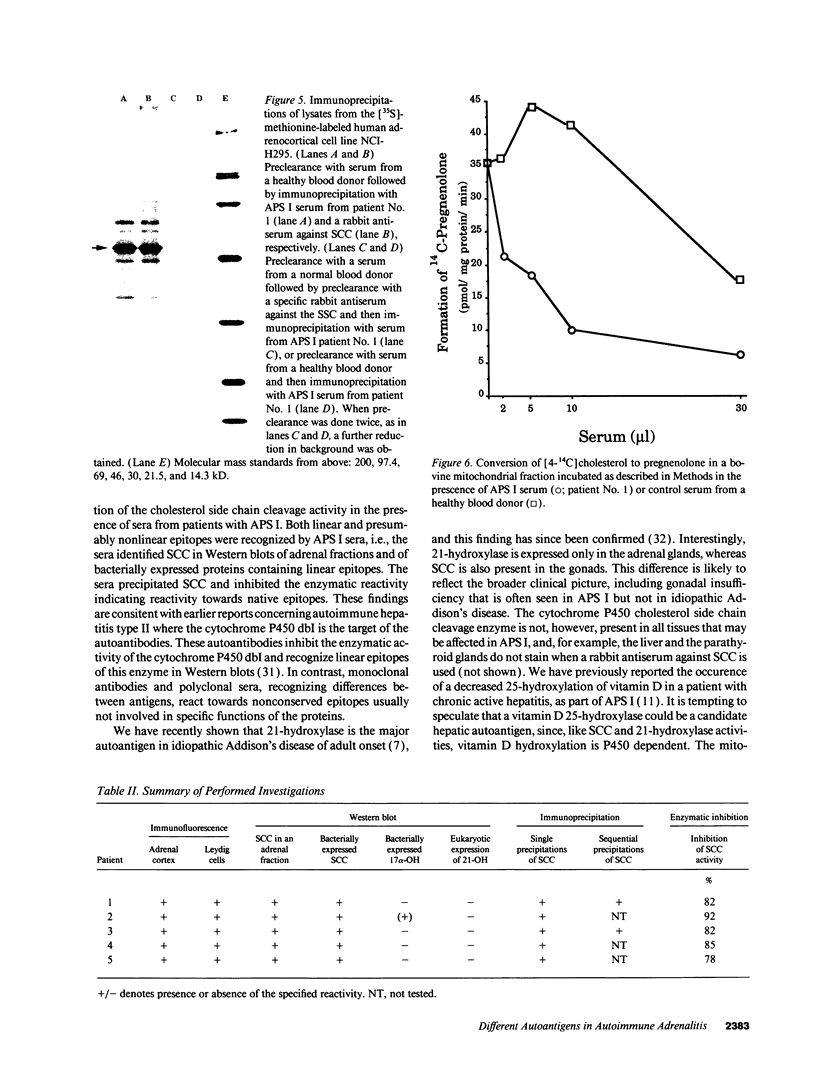
Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type I (APS I) and idiopathic Addison's disease are both disorders with adrenal insufficiency but with differences in genetic background, clinical presentation, and extent of extraadrenal manifestations. In this study the major adrenal autoantigen identified with sera from patients with APS I was characterized by analyses using indirect immunofluorescence, Western blots of adrenal subcellular fractions and of recombinant proteins, immunoprecipitations of [35S]methionine-labeled lysates of a human steroid-producing cell line, and studies of enzymatic activity. Sera from patients with APS I, identifying cells in adrenal glands and testes involved in steroid synthesis, reacted in Western blots with a 53-kD antigen, which comigrated with the cytochrome P450 cholesterol side chain cleavage enzyme (SCC). The sera also immunoprecipitated this protein from lysates of radiolabeled adrenal cells. The enzymatic activity of SCC was inhibited by the APS I sera but not by control sera. Sera from patients with idiopathic Addison's disease did not react with the SCC. The results show that the autoimmune responses towards adrenal tissue in patients suffering from APS I and Addison's disease are remarkably selective and suggest that a determination of the antigen involved in a patient with autoimmune adrenal insufficiency will have diagnostic as well as prognostic implications.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahonen P., Koskimies S., Lokki M. L., Tiilikainen A., Perheentupa J. The expression of autoimmune polyglandular disease type I appears associated with several HLA-A antigens but not with HLA-DR. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Jun;66(6):1152–1157. doi: 10.1210/jcem-66-6-1152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahonen P., Myllärniemi S., Sipilä I., Perheentupa J. Clinical variation of autoimmune polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy (APECED) in a series of 68 patients. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jun 28;322(26):1829–1836. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199006283222601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arulanantham K., Dwyer J. M., Genel M. Evidence for defective immunoregulation in the syndrome of familial candidiasis endocrinopathy. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jan 25;300(4):164–168. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197901253000403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIZZARD R. M., CHANDLER R. W., KYLE M. A., HUNG W. Adrenal antibodies in Addison's disease. Lancet. 1962 Nov 3;2(7262):901–903. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(62)90681-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIZZARD R. M., KYLE M. STUDIES OF THE ADRENAL ANTIGENS AND ANTIBODIES IN ADDISON'S DISEASE. J Clin Invest. 1963 Oct;42:1653–1660. doi: 10.1172/JCI104851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baekkeskov S., Aanstoot H. J., Christgau S., Reetz A., Solimena M., Cascalho M., Folli F., Richter-Olesen H., De Camilli P., Camilli P. D. Identification of the 64K autoantigen in insulin-dependent diabetes as the GABA-synthesizing enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):151–156. doi: 10.1038/347151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banga J. P., McGregor A. M. Enzymes as targets for autoantibodies in human autoimmune disease: relevance to pathogenesis? Autoimmunity. 1991;9(2):177–182. doi: 10.3109/08916939109006755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes H. J., Arlotto M. P., Waterman M. R. Expression and enzymatic activity of recombinant cytochrome P450 17 alpha-hydroxylase in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5597–5601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann-Antczak A., Wedlock N., Bednarek J., Kiso Y., Krishnan H., Fowler S., Smith B. R., Furmaniak J. Autoimmune Addison's disease and 21-hydroxylase. Lancet. 1992 Aug 15;340(8816):429–430. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91513-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkhem I., Gustafsson J. Mitochondrial omega-hydroxylation of cholesterol side chain. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 25;249(8):2528–2535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkhem I., Karlmar K. E. A novel technique for assay of side-chain cleavage of exogenous and endogenous cholesterol in adrenal mitochondrial and submitochondrial preparations. Anal Biochem. 1975 Oct;68(2):404–414. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90636-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blizzard R. M., Gibbs J. H. Candidiasis: studies pertaining to its association with endocrinopathies and pernicious anemia. Pediatrics. 1968 Aug;42(2):231–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung B. C., Matteson K. J., Voutilainen R., Mohandas T. K., Miller W. L. Human cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme, P450scc: cDNA cloning, assignment of the gene to chromosome 15, and expression in the placenta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8962–8966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarnocka B., Ruf J., Ferrand M., Carayon P., Lissitzky S. Purification of the human thyroid peroxidase and its identification as the microsomal antigen involved in autoimmune thyroid diseases. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 7;190(1):147–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80446-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder M., Maclaren N., Riley W. Gonadal autoantibodies in patients with hypogonadism and/or Addison's disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Jun;52(6):1137–1142. doi: 10.1210/jcem-52-6-1137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazdar A. F., Oie H. K., Shackleton C. H., Chen T. R., Triche T. J., Myers C. E., Chrousos G. P., Brennan M. F., Stein C. A., La Rocca R. V. Establishment and characterization of a human adrenocortical carcinoma cell line that expresses multiple pathways of steroid biosynthesis. Cancer Res. 1990 Sep 1;50(17):5488–5496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson J., Holmberg I., Hardell L. I., Foucard T. Hypoparathyroidism and liver disease--evidence for a vitamin D hydroxylation defect. A case report. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1984 Feb;105(2):211–214. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1050211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harkins J. B., Nelson E. B., Masters B. S., Bryan G. T. Preparation and properties of microsomal membranes from isozonal cells of beef adrenal cortex. Endocrinology. 1974 Mar;94(3):897–902. doi: 10.1210/endo-94-3-897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu M. C., Guo I. C., Lin J. H., Chung B. C. Regulated expression of cytochrome P-450scc (cholesterol-side-chain cleavage enzyme) in cultured cell lines detected by antibody against bacterially expressed human protein. Biochem J. 1991 Mar 15;274(Pt 3):813–817. doi: 10.1042/bj2740813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine W. J., Stewart A. G., Scarth L. A clinical and immunological study of adrenocortical insufficiency (Addison's disease). Clin Exp Immunol. 1967 Jan;2(1):31–70. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson F. A., Burman P., Löf L., Mårdh S. Major parietal cell antigen in autoimmune gastritis with pernicious anemia is the acid-producing H+,K+-adenosine triphosphatase of the stomach. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):475–479. doi: 10.1172/JCI113344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krohn K., Uibo R., Aavik E., Peterson P., Savilahti K. Identification by molecular cloning of an autoantigen associated with Addison's disease as steroid 17 alpha-hydroxylase. Lancet. 1992 Mar 28;339(8796):770–773. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91894-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kämpe O., Andersson A., Björk E., Hallberg A., Karlsson F. A. High-glucose stimulation of 64,000-Mr islet cell autoantigen expression. Diabetes. 1989 Oct;38(10):1326–1328. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.10.1326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maclaren N. K., Riley W. J. Inherited susceptibility to autoimmune Addison's disease is linked to human leukocyte antigens-DR3 and/or DR4, except when associated with type I autoimmune polyglandular syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Mar;62(3):455–459. doi: 10.1210/jcem-62-3-455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manns M. Autoantibodies and antigens in liver diseases--updated. J Hepatol. 1989 Sep;9(2):272–280. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(89)90063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. L. Molecular biology of steroid hormone synthesis. Endocr Rev. 1988 Aug;9(3):295–318. doi: 10.1210/edrv-9-3-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morohashi K., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Okada Y., Sogawa K., Hirose T., Inayama S., Omura T. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of cDNA for mRNA of mitochondrial cytochrome P-450(SCC) of bovine adrenal cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4647–4651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld M., Maclaren N., Blizzard R. Autoimmune polyglandular syndromes. Pediatr Ann. 1980 Apr;9(4):154–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley W. J., Maclaren N. K., Neufeld M. Adrenal autoantibodies and Addison disease in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Pediatr. 1980 Aug;97(2):191–195. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasano H., Mason J. I., Sasano N. Immunohistochemical analysis of cytochrome P-450 17 alpha-hydroxylase in pig adrenal cortex, testis and ovary. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1989 Apr;62(2):197–202. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(89)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinner M. W., Blizzard R. M., Childs B. Clinical and genetic heterogeneity in idiopathic Addison's disease and hypoparathyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Jun;28(6):795–804. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-6-795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takikawa O., Gomi T., Suhara K., Itagaki E., Takemori S., Katagiri M. Properties of an adrenal cytochrome P-450 (P-450SCC) for the side chain cleavage of cholesterol. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Sep;190(1):300–306. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90279-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M. Autoantibodies in pathology and cell biology. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):841–842. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90356-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trence D. L., Morley J. E., Handwerger B. S. Polyglandular autoimmune syndromes. Am J Med. 1984 Jul;77(1):107–116. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90444-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tusie-Luna M. T., Traktman P., White P. C. Determination of functional effects of mutations in the steroid 21-hydroxylase gene (CYP21) using recombinant vaccinia virus. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):20916–20922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winqvist O., Karlsson F. A., Kämpe O. 21-Hydroxylase, a major autoantigen in idiopathic Addison's disease. Lancet. 1992 Jun 27;339(8809):1559–1562. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91829-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]