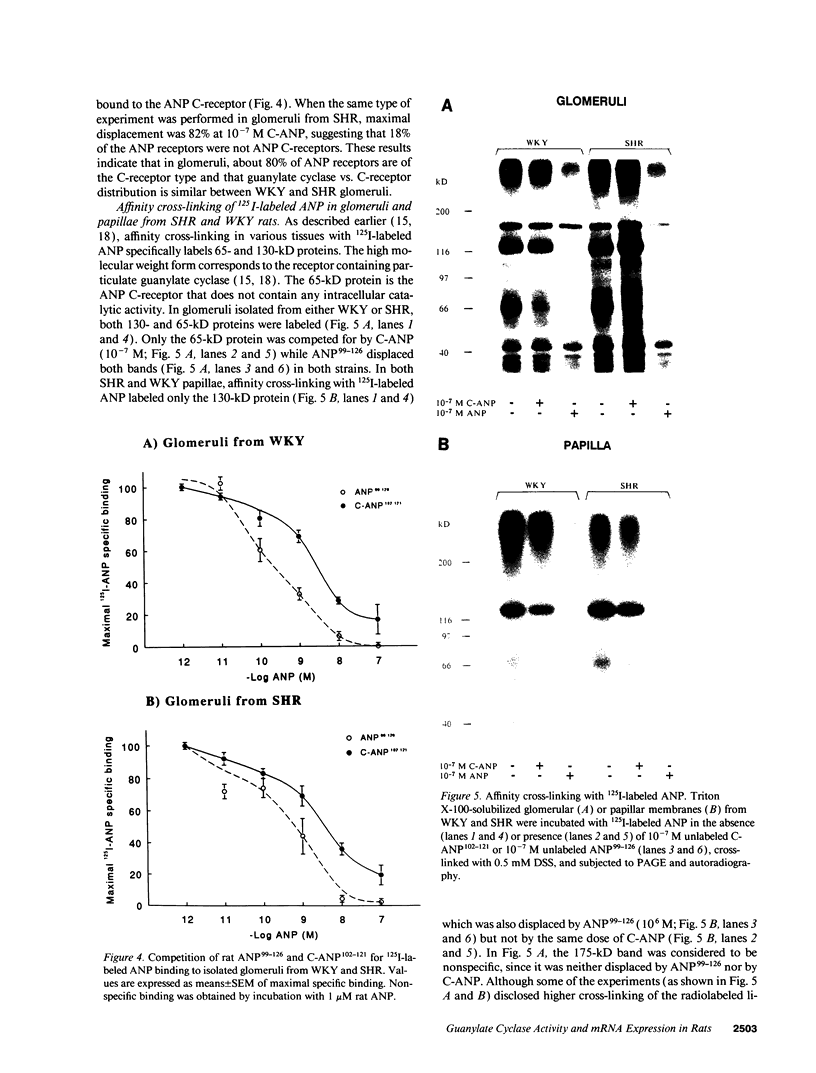
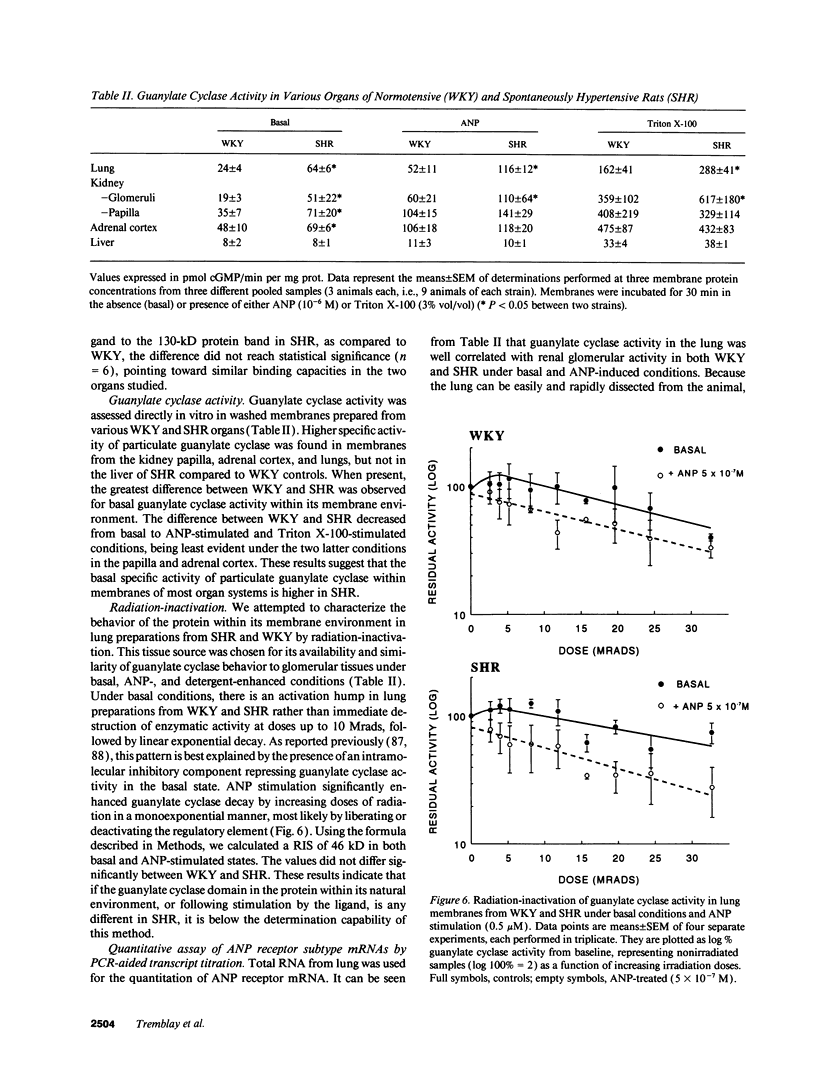
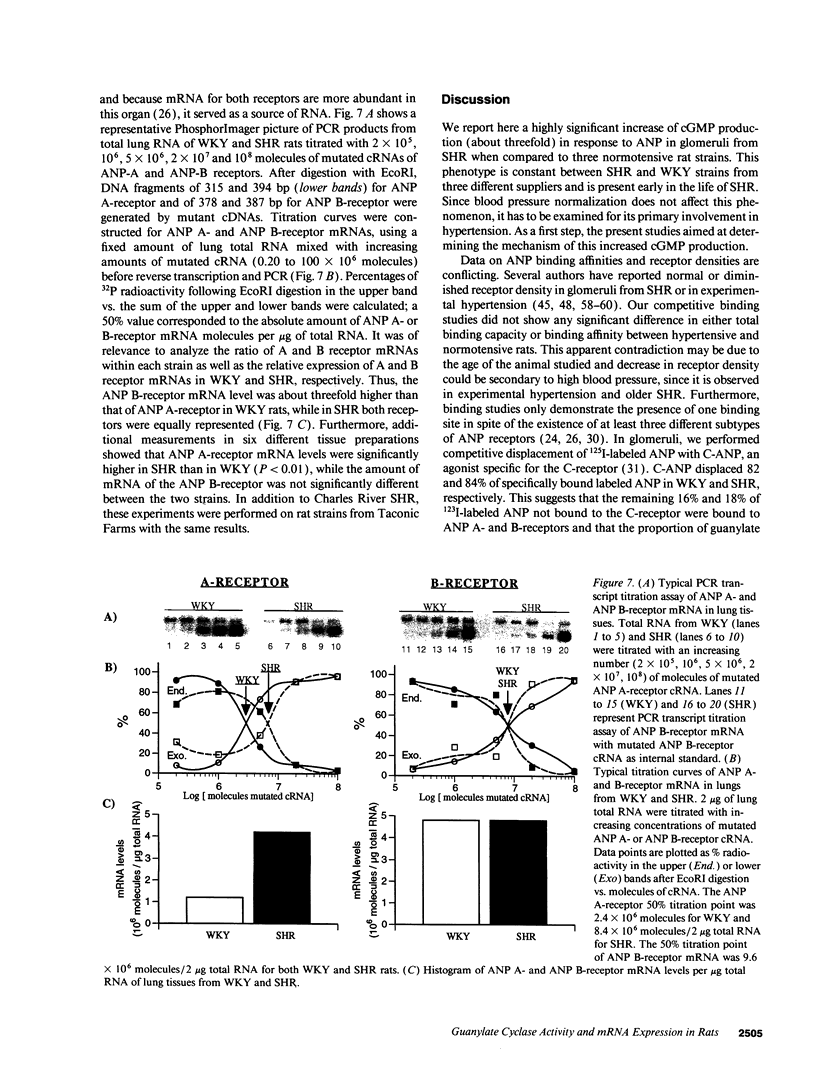
Abstract
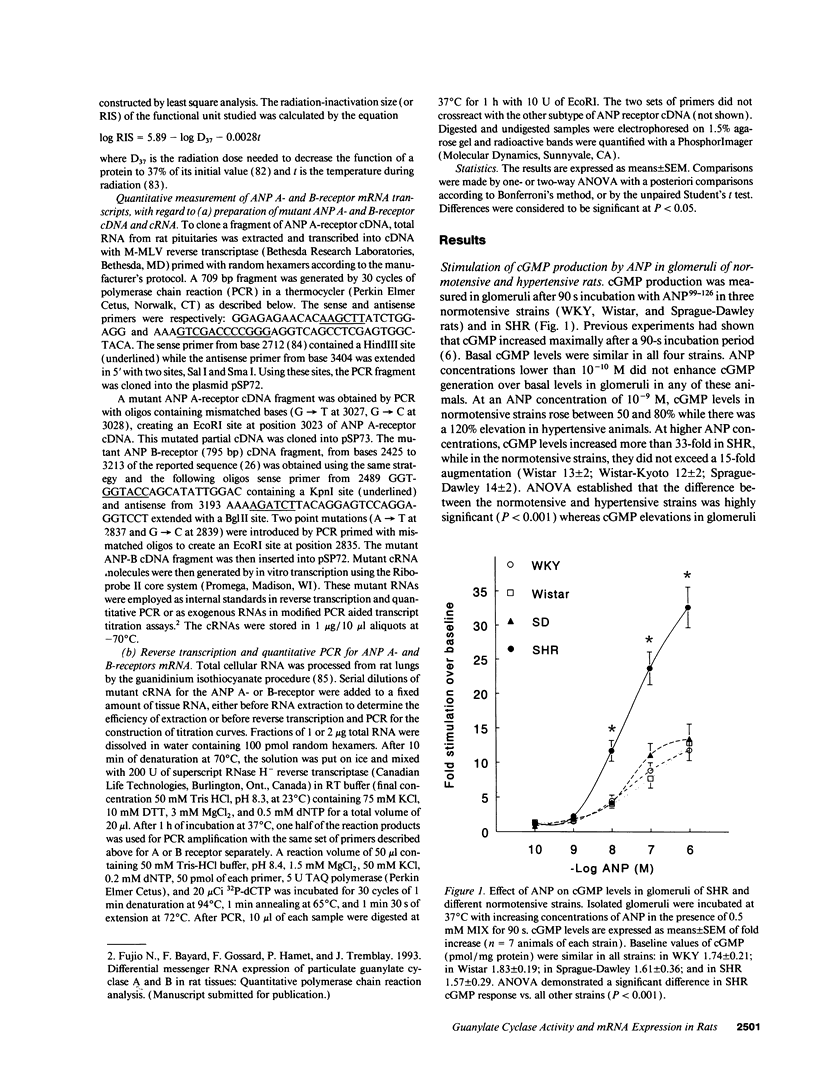
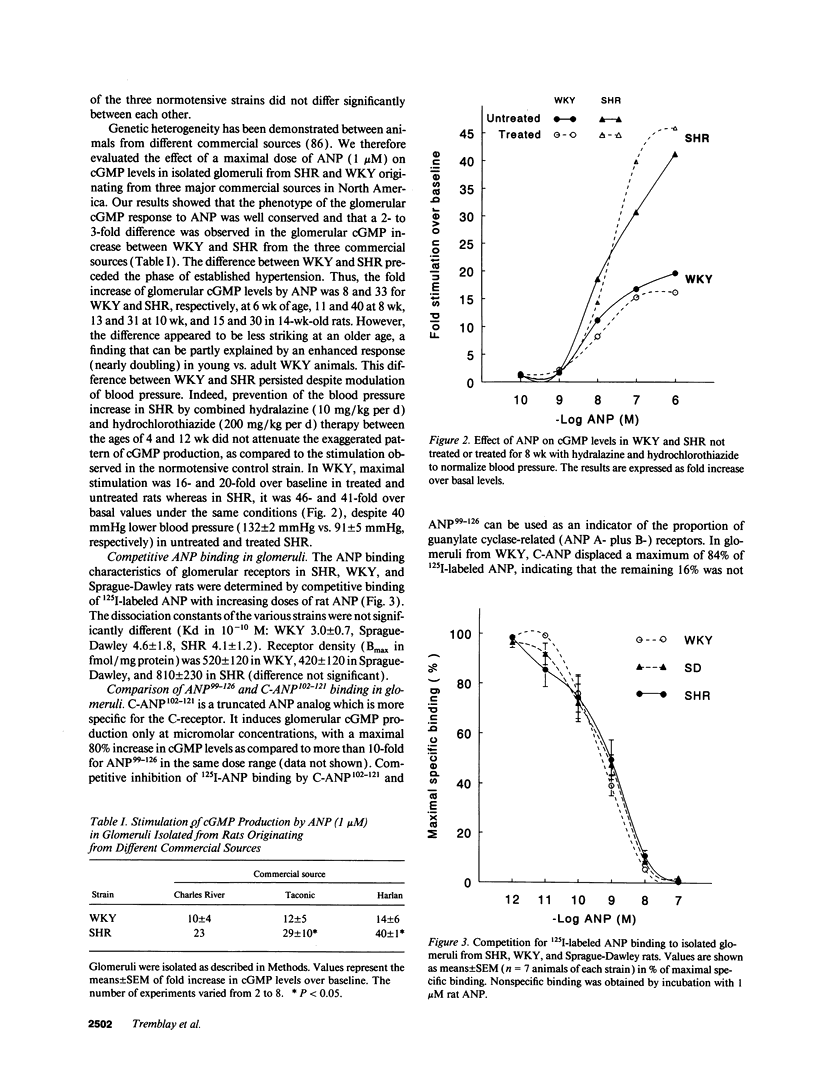
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) specifically stimulates particulate guanylate cyclase, and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) has been recognized as its second messenger. Spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) have elevated plasma ANP levels, but manifest an exaggerated natriuretic and diuretic response to exogenous ANP when compared to normotensive strains. In isolated glomeruli, the maximal cGMP response to ANP corresponds to a 12- to 14-fold increase over basal levels in normotensive strains (Wistar 13 +/- 2; Wistar-Kyoto 12 +/- 2; Sprague-Dawley 14 +/- 2) while a maximal 33 +/- 3-fold elevation occurs in SHR (P < 0.001). This hyperresponsiveness of cGMP is reproducible in intact glomeruli from SHR from various commercial sources. Furthermore, this abnormality develops early in life, even before hypertension is clearly established, and persists despite pharmacological modulation of blood pressure, indicating that it is a primary event in hypertension. In vitro studies have revealed a higher particulate guanylate cyclase activity in membranes from glomeruli and other tissues from SHR. This increase is not accounted for by different patterns of ANP binding to its receptor subtypes between normotensive and hypertensive strains, as assessed by competitive displacement with C-ANP102-121, an analog which selectively binds to one ANP receptor subtype. The hyperactivity of particulate guanylate cyclase in SHR and its behavior under basal, ligand (ANP), and detergent-enhanced conditions could be attributed either to increased expression or augmented sensitivity of the enzyme. Radiation-inactivation analysis does not evoke a disturbance in the size of regulatory elements normally repressing enzymatic activity, while the expression of particulate guanylate cyclase gene using mutated standard of A- and B-receptors partial cDNAs, quantified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) transcript titration assay, manifests a selective increase of one guanylate cyclase subtype. Our data suggest that in hypertension, genetic overexpression of the ANP A-receptor subtype is related to the exaggerated biological response to ANP in this disease.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ardaillou N., Nivez M. P., Ardaillou R. Stimulation of guanylate cyclase by atrial natriuretic factor in isolated human glomeruli. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 9;189(1):8–12. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80831-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atlas S. A., Laragh J. H. Atrial natriuretic peptide: a new factor in hormonal control of blood pressure and electrolyte homeostasis. Annu Rev Med. 1986;37:397–414. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.37.020186.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballermann B. J., Hoover R. L., Karnovsky M. J., Brenner B. M. Physiologic regulation of atrial natriuretic peptide receptors in rat renal glomeruli. J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;76(6):2049–2056. doi: 10.1172/JCI112207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauregard G., Giroux S., Potier M. Target size analysis by radiation inactivation: a large capacity tube rack for irradiation in a Gammacell 220. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 15;132(2):362–364. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauregard G., Potier M. Radiation inactivation of membrane proteins: molecular weight estimates in situ and after Triton X-100 solubilization. Anal Biochem. 1984 Aug 1;140(2):403–408. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90185-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker-André M., Hahlbrock K. Absolute mRNA quantification using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). A novel approach by a PCR aided transcript titration assay (PATTY). Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9437–9446. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill P. A., Redmond E. M., Keenan A. K. Vascular atrial natriuretic factor receptor subtypes are not independently regulated by atrial peptides. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21896–21906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M. S., Lowe D. G., Lewis M., Hellmiss R., Chen E., Goeddel D. V. Differential activation by atrial and brain natriuretic peptides of two different receptor guanylate cyclases. Nature. 1989 Sep 7;341(6237):68–72. doi: 10.1038/341068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinkers M., Garbers D. L., Chang M. S., Lowe D. G., Chin H. M., Goeddel D. V., Schulz S. A membrane form of guanylate cyclase is an atrial natriuretic peptide receptor. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):78–83. doi: 10.1038/338078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinkers M., Garbers D. L. The protein kinase domain of the ANP receptor is required for signaling. Science. 1989 Sep 22;245(4924):1392–1394. doi: 10.1126/science.2571188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cusson J. R., Thibault G., Kuchel O., Hamet P., Cantin M., Larochelle P. Cardiovascular, renal and endocrine responses to low doses of atrial natriuretic factor in mild essential hypertension. J Hum Hypertens. 1989 Apr;3(2):89–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Léan A., Vinay P., Cantin M. Distribution of atrial natriuretic factor receptors in dog kidney fractions. FEBS Lett. 1985 Dec 2;193(2):239–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80160-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller F., Porter J. G., Arfsten A. E., Miller J., Schilling J. W., Scarborough R. M., Lewicki J. A., Schenk D. B. Atrial natriuretic peptide clearance receptor. Complete sequence and functional expression of cDNA clones. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9395–9401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia R., Cantin M., Gutkowska J., Thibault G. Atrial natriuretic factor during development and reversal of one-kidney, one clip hypertension. Hypertension. 1987 Feb;9(2):144–149. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.9.2.144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia R., Gauquelin G., Cantin M., Schiffrin E. L. Renal glomerular atrial natriuretic factor receptors in one-kidney, one clip rats. Hypertension. 1988 Feb;11(2):185–190. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.11.2.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia R., Thibault G., Gutkowska J., Horký K., Hamet P., Cantin M., Genest J. Chronic infusion of low doses of atrial natriuretic factor (ANF Arg 101-Tyr 126) reduces blood pressure in conscious SHR without apparent changes in sodium excretion. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1985 Jul;179(3):396–401. doi: 10.3181/00379727-179-rc1aa. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia R., Thibault G., Hamet P., Gutkowska J., Cantin M., Genest J. Effect of atrial natriuretic factor [ANF (Arg 101--Tyr 126)] on kallikrein and cyclic GMP in the renovascular hypertensive rat. Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1985;7(11):1597–1618. doi: 10.3109/10641968509073612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauquelin G., Schiffrin E. L., Cantin M., Garcia R. Atrial natriuretic factor: specific binding to renal glomeruli during the development of two-kidney, one clip hypertension in the rat. J Hypertens. 1988 Jul;6(7):587–592. doi: 10.1097/00004872-198807000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauquelin G., Schiffrin E. L., Cantin M., Garcia R. Specific binding of atrial natriuretic factor to renal glomeruli in Doca- and Doca-salt-treated rats correlation with atrial and plasma levels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 May 29;145(1):522–531. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91352-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genest J., Cantin M. Atrial natriuretic factor. Circulation. 1987 Jan;75(1 Pt 2):I118–I124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutkowska J., Genest J., Thibault G., Garcia R., Larochelle P., Cusson J. R., Kichel O., Hamet P., De Léan A., Cantin M. Circulating forms and radioimmunoassay of atrial natriuretic factor. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 1987 Mar;16(1):183–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haass M., Zamir N., Zukowska-Grojec Z. Plasma levels of atrial natriuretic peptides in conscious adult spontaneously hypertensive rats. Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1986;8(2):277–287. doi: 10.3109/10641968609074776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamet P., Pang S. C., Tremblay J. Atrial natriuretic factor-induced egression of cyclic guanosine 3':5'-monophosphate in cultured vascular smooth muscle and endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12364–12369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamet P., Testaert E., Palmour R., Larochelle P., Cantin M., Gutkowska J., Langlois Y., Ervin F., Tremblay J. Effect of prolonged infusion of ANF in normotensive and hypertensive monkeys. Am J Hypertens. 1989 Sep;2(9):690–695. doi: 10.1093/ajh/2.9.690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy D. P., Fanestil D. D. Localization of atrial natriuretic peptide binding sites within the rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1986 Mar;250(3 Pt 2):F573–F578. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.3.F573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata Y., Hirose S., Takata S., Takagi Y., Matsubara H. Down-regulation of atrial natriuretic peptide receptor and cyclic GMP response in cultured rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Mar 31;135(3):439–442. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90697-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. J., Struthers R. S., Fong A. M., Insel P. A. Regulation of the atrial natriuretic peptide receptor on a smooth muscle cell. Am J Physiol. 1987 Dec;253(6 Pt 1):C809–C816. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.6.C809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huot C., Tremblay J., Hamet P. Cell biology of atrial natriuretic peptide. Blood Vessels. 1991;28(1-3):84–92. doi: 10.1159/000158847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imada T., Takayanagi R., Inagami T. Changes in the content of atrial natriuretic factor with the progression of hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Dec 17;133(2):759–765. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90969-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen W. M., de Zeeuw D., van der Hem G. K., de Jong P. E. Antihypertensive effect of a 5-day infusion of atrial natriuretic factor in humans. Hypertension. 1989 Jun;13(6 Pt 1):640–646. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.13.6.640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempner E. S., Haigler H. T. The influence of low temperature on the radiation sensitivity of enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13297–13299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempner E. S., Schlegel W. Size determination of enzymes by radiation inactivation. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jan 1;92(1):2–10. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90617-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalil F., Fine B., Kuriyama S., Hatori N., Nakamura A., Nakamura M., Aviv A. Increased atrial natriuretic factor receptor density in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells of the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1987;9(4):741–752. doi: 10.3109/10641968709161447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller K. J., Lowe D. G., Bennett G. L., Minamino N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Goeddel D. V. Selective activation of the B natriuretic peptide receptor by C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP). Science. 1991 Apr 5;252(5002):120–123. doi: 10.1126/science.1672777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo K., Kida O., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Tanaka K. Enhanced diuretic response to alpha-human atrial natriuretic polypeptide (alpha-hANP) in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 1985 Sep;27(9):1313–1315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno T., Andresen J. W., Kamisaki Y., Waldman S. A., Chang L. Y., Saheki S., Leitman D. C., Nakane M., Murad F. Co-purification of an atrial natriuretic factor receptor and particulate guanylate cyclase from rat lung. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5817–5823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurihara M., Gutkind J. S., Saavedra J. M. Alteration of atrial natriuretic peptide binding sites in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Hypertens. 1988 Jul;1(3 Pt 3):12S–14S. doi: 10.1093/ajh/1.3.12s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurihara M., Katamine S., Saavedra J. M. Atrial natriuretic peptide, ANP(99-126), receptors in rat thymocytes and spleen cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jun 15;145(2):789–796. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz T. W., Montano M., Chan L., Kabra P. Molecular evidence of genetic heterogeneity in Wistar-Kyoto rats: implications for research with the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Hypertension. 1989 Feb;13(2):188–192. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.13.2.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larochelle P., Cusson J. R., Gutkowska J., Schiffrin E. L., Hamet P., Kuchel O., Genest J., Cantin M. Plasma atrial natriuretic factor concentrations in essential and renovascular hypertension. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 May 16;294(6582):1249–1252. doi: 10.1136/bmj.294.6582.1249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitman D. C., Andresen J. W., Kuno T., Kamisaki Y., Chang J. K., Murad F. Identification of multiple binding sites for atrial natriuretic factor by affinity cross-linking in cultured endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11650–11655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe D. G., Chang M. S., Hellmiss R., Chen E., Singh S., Garbers D. L., Goeddel D. V. Human atrial natriuretic peptide receptor defines a new paradigm for second messenger signal transduction. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1377–1384. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03518.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maack T., Suzuki M., Almeida F. A., Nussenzveig D., Scarborough R. M., McEnroe G. A., Lewicki J. A. Physiological role of silent receptors of atrial natriuretic factor. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):675–678. doi: 10.1126/science.2823385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meloche S., McNicoll N., Liu B., Ong H., De Léan A. Atrial natriuretic factor R1 receptor from bovine adrenal zona glomerulosa: purification, characterization, and modulation by amiloride. Biochemistry. 1988 Oct 18;27(21):8151–8158. doi: 10.1021/bi00421a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morii N., Nakao K., Kihara M., Sugawara A., Sakamoto M., Yamori Y., Imura H. Decreased content in left atrium and increased plasma concentration of atrial natriuretic polypeptide in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) and SHR stroke-prone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Feb 26;135(1):74–81. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90944-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Napier M. A., Vandlen R. L., Albers-Schönberg G., Nutt R. F., Brady S., Lyle T., Winquist R., Faison E. P., Heinel L. A., Blaine E. H. Specific membrane receptors for atrial natriuretic factor in renal and vascular tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5946–5950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman P., Greenwald J. E. Atriopeptin: a cardiac hormone intimately involved in fluid, electrolyte, and blood-pressure homeostasis. N Engl J Med. 1986 Mar 27;314(13):828–834. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198603273141306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuser D., Bellemann P. Receptor binding, cGMP stimulation and receptor desensitization by atrial natriuretic peptides in cultured A10 vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 15;209(2):347–351. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81140-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussenzveig D. R., Lewicki J. A., Maack T. Cellular mechanisms of the clearance function of type C receptors of atrial natriuretic factor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):20952–20958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey K. N., Pavlou S. N., Inagami T. Identification and characterization of three distinct atrial natriuretic factor receptors. Evidence for tissue-specific heterogeneity of receptor subtypes in vascular smooth muscle, kidney tubular epithelium, and Leydig tumor cells by ligand binding, photoaffinity labeling, and tryptic proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13406–13413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang S. C., Hoang M. C., Tremblay J., Cantin M., Garcia R., Genest J., Hamet P. Effect of natural and synthetic atrial natriuretic factor on arterial blood pressure, natriuresis and cyclic GMP excretion in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985 Dec;69(6):721–726. doi: 10.1042/cs0690721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul A. K., Marala R. B., Jaiswal R. K., Sharma R. K. Coexistence of guanylate cyclase and atrial natriuretic factor receptor in a 180-kD protein. Science. 1987 Mar 6;235(4793):1224–1226. doi: 10.1126/science.2881352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potier M., Giroux S. Regulatory proteins (inhibitors or activators) affect estimates of Mr of enzymes and receptors by radiation inactivation. A theoretical model. Biochem J. 1985 Mar 15;226(3):797–801. doi: 10.1042/bj2260797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potier M., Huot C., Koch C., Hamet P., Tremblay J. Radiation-inactivation analysis of multidomain proteins: the case of particulate guanylyl cyclase. Methods Enzymol. 1991;195:423–435. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)95189-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman R. A., Kopf G. S., Hamet P., Johnson R. A. Preparation of cyclic nucleotide antisera with thyroglobulin-cyclic nucleotide conjugates. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1980;6(6):461–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roubert P., Lonchampt M. O., Chabrier P. E., Plas P., Goulin J., Braquet P. Down-regulation of atrial natriuretic factor receptors and correlation with cGMP stimulation in rat cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Oct 14;148(1):61–67. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91076-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagnella G. A., Markandu N. D., Buckley M. G., Shore A. C., Sugden A. L., Singer D. R., MacGregor G. A. Plasma atrial natriuretic peptide in essential hypertension. Comparison with normotensive subjects and effects of changes in dietary sodium intake. Am J Hypertens. 1988 Apr;1(2):112–118. doi: 10.1093/ajh/1.2.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagnella G. A., Markandu N. D., Shore A. C., MacGregor G. A. Raised circulating levels of atrial natriuretic peptides in essential hypertension. Lancet. 1986 Jan 25;1(8474):179–181. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90653-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Inui K., Matsukawa Y., Okano T., Maegawa H., Nakao K., Morii N., Imura H., Makino S., Hori R. Specific binding of atrial natriuretic polypeptide to renal basolateral membranes in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) and stroke-prone SHR. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jun 30;137(3):1079–1085. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90335-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto M., Tanaka I., Oki Y., Ikeda Y., Nanno M., Yoshimi T. Atrial natriuretic peptide and vasopressin in human plasma. Peptides. 1988 Jan-Feb;9(1):187–191. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(88)90026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarborough R. M., Schenk D. B., McEnroe G. A., Arfsten A., Kang L. L., Schwartz K., Lewicki J. A. Truncated atrial natriuretic peptide analogs. Comparison between receptor binding and stimulation of cyclic GMP accumulation in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):12960–12964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz S., Singh S., Bellet R. A., Singh G., Tubb D. J., Chin H., Garbers D. L. The primary structure of a plasma membrane guanylate cyclase demonstrates diversity within this new receptor family. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1155–1162. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90513-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh S., Lowe D. G., Thorpe D. S., Rodriguez H., Kuang W. J., Dangott L. J., Chinkers M., Goeddel D. V., Garbers D. L. Membrane guanylate cyclase is a cell-surface receptor with homology to protein kinases. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):708–712. doi: 10.1038/334708a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart R. E., Swithers S. E., McCarty R. Alterations in binding sites for atrial natriuretic factor in kidneys and adrenal glands of Dahl hypertension-sensitive rats. J Hypertens. 1987 Aug;5(4):481–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara A., Nakao K., Sakamoto M., Morii N., Yamada T., Itoh H., Shiono S., Imura H. Plasma concentration of atrial natriuretic polypeptide in essential hypertension. Lancet. 1985 Dec 21;2(8469-70):1426–1427. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92592-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swithers S. E., Stewart R. E., McCarty R. Binding sites for atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) in kidneys and adrenal glands of spontaneously hypertensive (SHR) rats. Life Sci. 1987 Apr 27;40(17):1673–1681. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayanagi R., Imada T., Grammer R. T., Misono K. S., Naruse M., Inagami T. Atrial natriuretic factor in spontaneously hypertensive rats: concentration changes with the progression of hypertension and elevated formation of cyclic GMP. J Hypertens Suppl. 1986 Oct;4(3):S303–S307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayanagi R., Snajdar R. M., Imada T., Tamura M., Pandey K. N., Misono K. S., Inagami T. Purification and characterization of two types of atrial natriuretic factor receptors from bovine adrenal cortex: guanylate cyclase-linked and cyclase-free receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 14;144(1):244–250. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80502-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda S., Kusano E., Murayama N., Asano Y., Hosoda S., Sokabe H., Kawashima H. Atrial natriuretic peptide elevates cGMP contents in glomeruli and in distal tubules of rat kidney. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 May 14;136(3):947–954. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90424-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe D. S., Garbers D. L. The membrane form of guanylate cyclase. Homology with a subunit of the cytoplasmic form of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6545–6549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay J., Gerzer R., Pang S. C., Cantin M., Genest J., Hamet P. ANF stimulation of detergent-dispersed particulate guanylate cyclase from bovine adrenal cortex. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 6;194(2):210–214. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80086-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay J., Gerzer R., Vinay P., Pang S. C., Béliveau R., Hamet P. The increase of cGMP by atrial natriuretic factor correlates with the distribution of particulate guanylate cyclase. FEBS Lett. 1985 Feb 11;181(1):17–22. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81105-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay J., Huot C., Koch C., Potier M. Characterization of the functional domains of the natriuretic peptide receptor/guanylate cyclase by radiation inactivation. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8171–8175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wambach G., Bönner G., Stimpel M., Kaufmann W. Relationship between plasma atrial natriuretic peptide and left atrial and left ventricular involvement in essential hypertension. J Hypertens. 1988 Jul;6(7):573–577. doi: 10.1097/00004872-198807000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. M., Doyle M. V., Mark D. F. Quantitation of mRNA by the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9717–9721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidmann P., Gnädinger M. P., Ziswiler H. R., Shaw S., Bachmann C., Rascher W., Uehlinger D. E., Hasler L., Reubi F. C. Cardiovascular, endocrine and renal effects of atrial natriuretic peptide in essential hypertension. J Hypertens Suppl. 1986 Jun;4(2):S71–S83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi M., Rutledge L. J., Garbers D. L. The primary structure of the rat guanylyl cyclase A/atrial natriuretic peptide receptor gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20414–20420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaji T., Ishibashi M., Sekihara H., Takaku F., Nakaoka H., Fujii J. Plasma levels of atrial natriuretic peptide in primary aldosteronism and essential hypertension. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Oct;63(4):815–818. doi: 10.1210/jcem-63-4-815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bold A. J. Atrial natriuretic factor: a hormone produced by the heart. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):767–770. doi: 10.1126/science.2932797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]