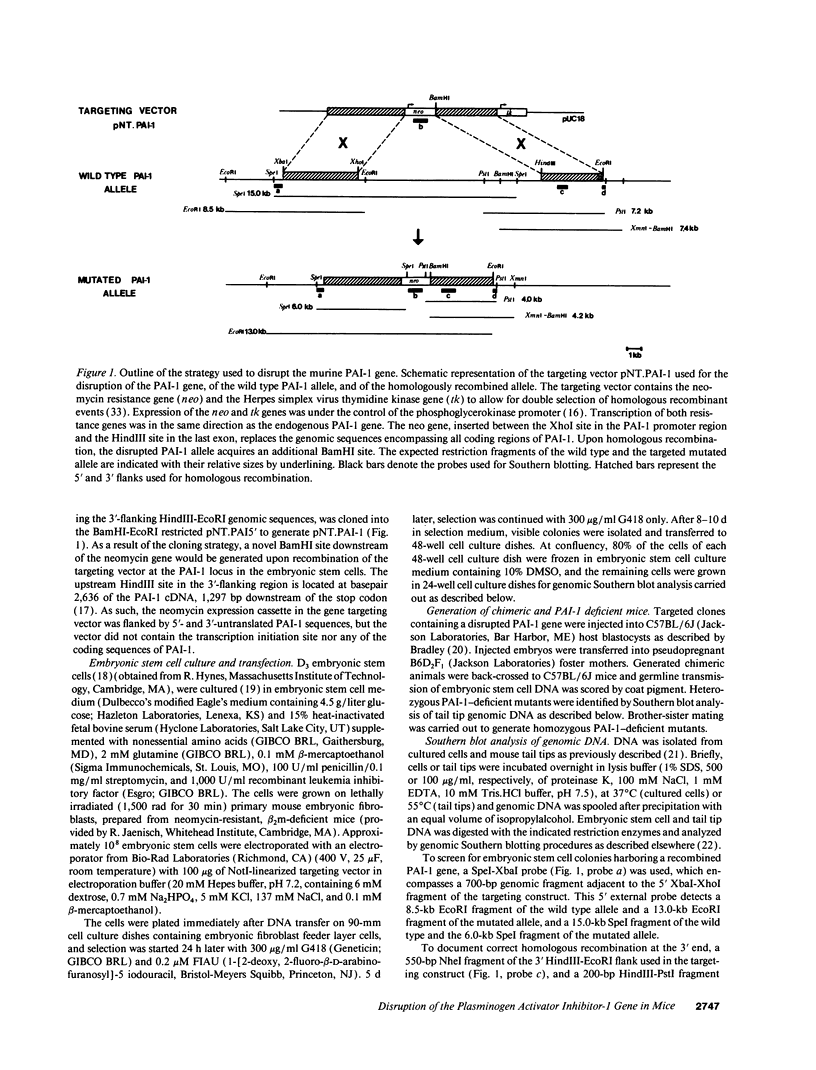
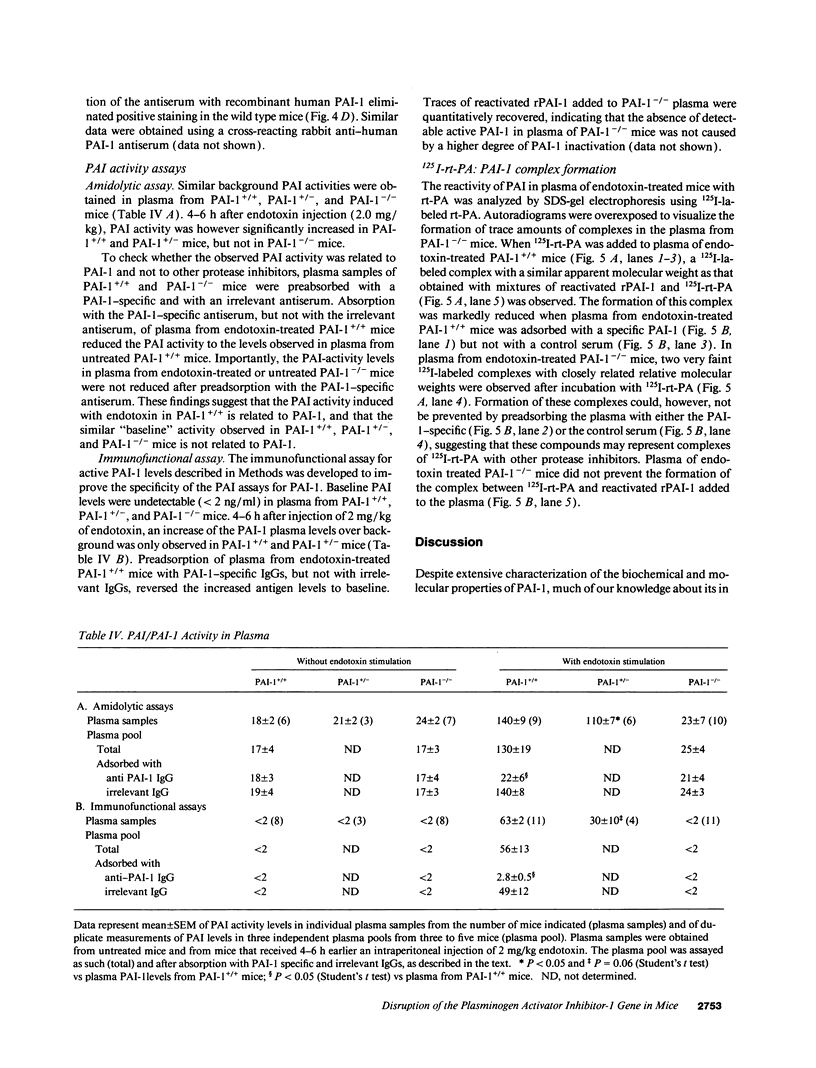
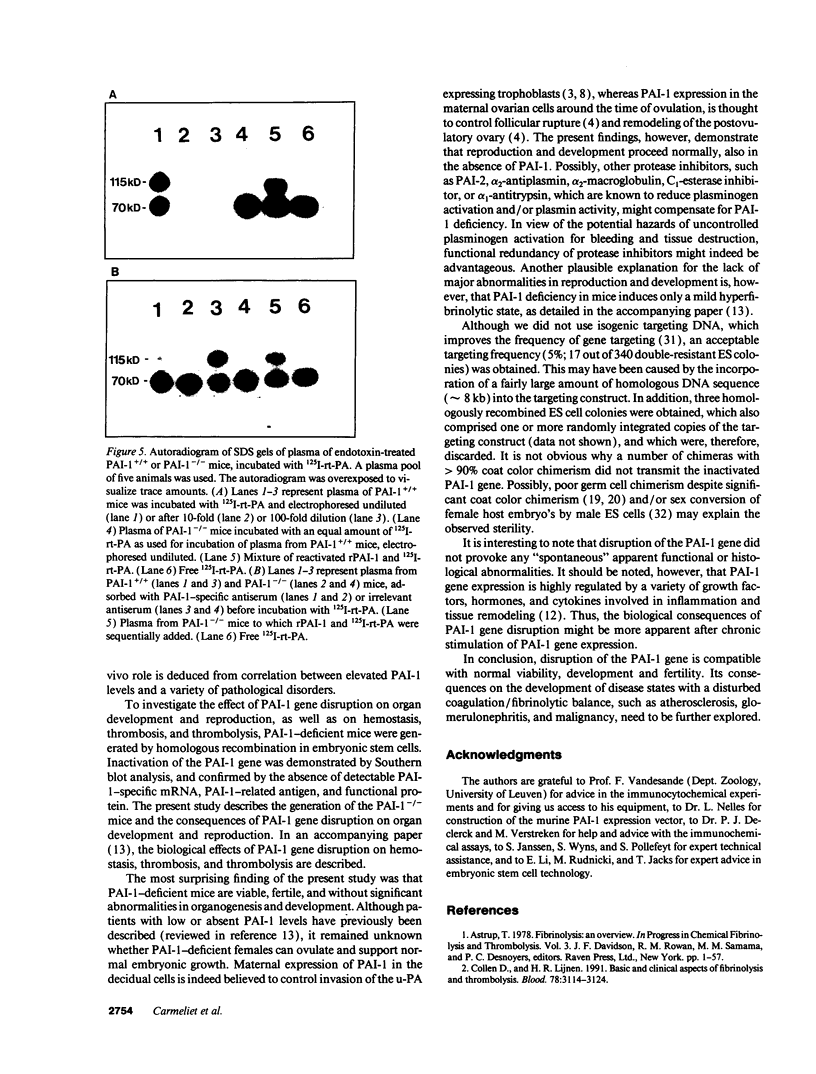
Abstract
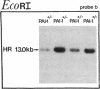
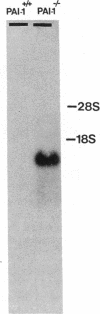
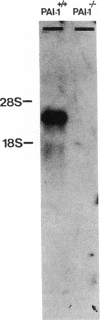
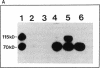
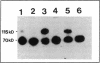
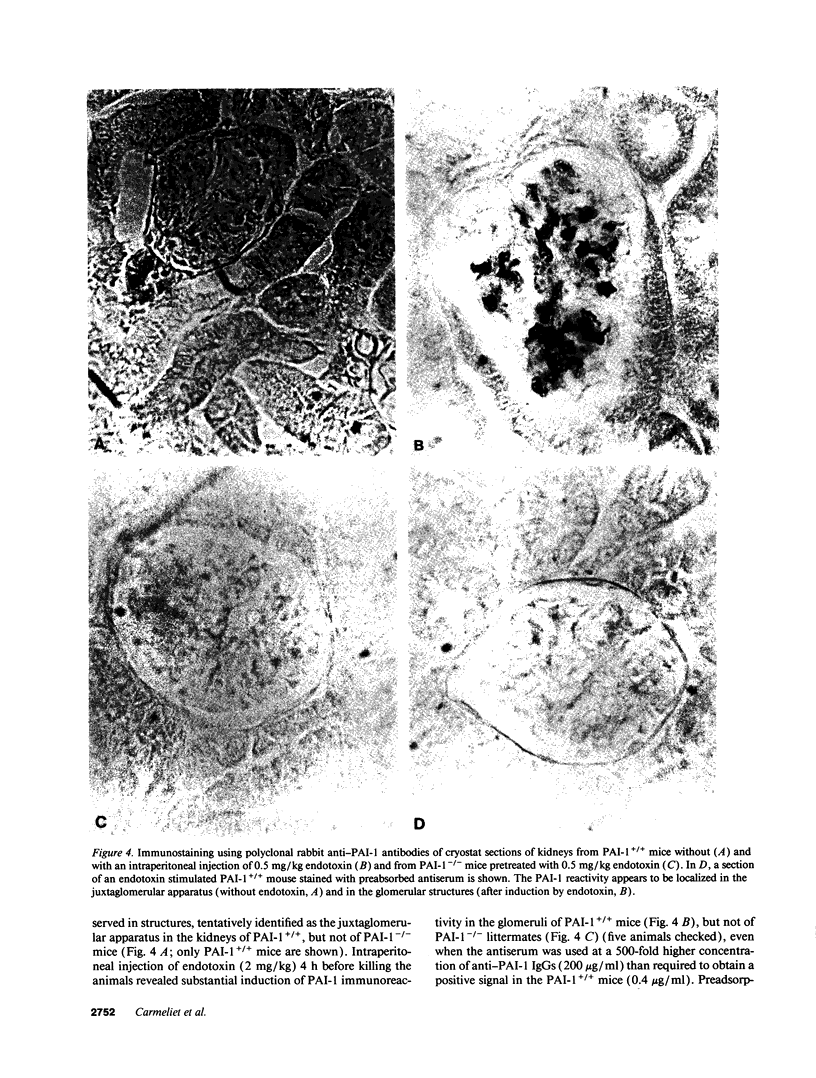
Homozygous plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1)-deficient (PAI-1-/-) mice were generated by homologous recombination in D3 embryonic stem cells. Deletion of the genomic sequences encompassing the transcription initiation site and the entire coding regions of murine PAI-1 was demonstrated by Southern blot analysis. A 3.0-kb PAI-1-specific mRNA was identified by Northern blot analysis in liver from PAI-1 wild type (PAI-1+/+) but not from PAI-1-/- mice. Plasma PAI-1 levels, measured 2-4 h after endotoxin (2.0 mg/kg) injection were 63 +/- 2 ng/ml, 30 +/- 10 ng/ml, and undetectable (< 2 ng/ml) in PAI-1+/+, heterozygous (PAI-1+/-) and PAI-1-/- mice, respectively (mean +/- SEM, n = 4-11). PAI-1-specific immunoreactivity was demonstrable in kidneys of PAI-1+/+ but not of PAI-1-/- mice. SDS-gel electrophoresis of plasma incubated with 125I-labeled recombinant human tissue-type plasminogen activator revealed an approximately 115,000-M(r) component with plasma from endotoxin-stimulated (0.5 mg/kg) PAI-1+/+ but not from PAI-1-/- mice, which could be precipitated with a polyclonal anti-PAI-1 antiserum. PAI-1-/- mice were viable, produced similar sizes of litters as PAI-1+/+ mice, and showed no apparent macroscopic or microscopic histological abnormalities.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blasi F., Verde P. Urokinase-dependent cell surface proteolysis and cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 1990 Apr;1(2):117–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmeliet P., Stassen J. M., Schoonjans L., Ream B., van den Oord J. J., De Mol M., Mulligan R. C., Collen D. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene-deficient mice. II. Effects on hemostasis, thrombosis, and thrombolysis. J Clin Invest. 1993 Dec;92(6):2756–2760. doi: 10.1172/JCI116893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D., Lijnen H. R. Basic and clinical aspects of fibrinolysis and thrombolysis. Blood. 1991 Dec 15;78(12):3114–3124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denker H. W. Implantation. The role of proteinases, and blockage of implantation by proteinase inhibitors. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 1977;53(5):3–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doetschman T. C., Eistetter H., Katz M., Schmidt W., Kemler R. The in vitro development of blastocyst-derived embryonic stem cell lines: formation of visceral yolk sac, blood islands and myocardium. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1985 Jun;87:27–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg R. F., Kao L. C., Haimowitz J. E., Queenan J. T., Jr, Wun T. C., Strauss J. F., 3rd, Kliman H. J. Plasminogen activator inhibitor types 1 and 2 in human trophoblasts. PAI-1 is an immunocytochemical marker of invading trophoblasts. Lab Invest. 1989 Jul;61(1):20–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hekman C. M., Loskutoff D. J. Endothelial cells produce a latent inhibitor of plasminogen activators that can be activated by denaturants. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11581–11587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird P. W., Zijderveld A., Linders K., Rudnicki M. A., Jaenisch R., Berns A. Simplified mammalian DNA isolation procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 11;19(15):4293–4293. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.15.4293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lala P. K., Graham C. H. Mechanisms of trophoblast invasiveness and their control: the role of proteases and protease inhibitors. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1990 Dec;9(4):369–379. doi: 10.1007/BF00049525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loskutoff D. J., Sawdey M., Mimuro J. Type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1989;9:87–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour S. L., Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Disruption of the proto-oncogene int-2 in mouse embryo-derived stem cells: a general strategy for targeting mutations to non-selectable genes. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):348–352. doi: 10.1038/336348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson M., Peng X. R., Liu Y. X., Jia X. C., Hsueh A. J., Ny T. Hormone regulation of tissue-type plasminogen activator gene expression and plasminogen activator-mediated proteolysis. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1991 Jul;17(3):286–290. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1002622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pannekoek H., Veerman H., Lambers H., Diergaarde P., Verweij C. L., van Zonneveld A. J., van Mourik J. A. Endothelial plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI): a new member of the Serpin gene family. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2539–2544. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04532.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Diamond L. E., Dahl D., Cole M. D. The c-myc-regulated gene mrl encodes plasminogen activator inhibitor 1. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1265–1269. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian Z., Gilbert M. E., Colicos M. A., Kandel E. R., Kuhl D. Tissue-plasminogen activator is induced as an immediate-early gene during seizure, kindling and long-term potentiation. Nature. 1993 Feb 4;361(6411):453–457. doi: 10.1038/361453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkin D. B., Moscatelli D., Bizik J., Quarto N., Blei F., Dennis P., Flaumenhaft R., Mignatti P. Growth factor control of extracellular proteolysis. Cell Differ Dev. 1990 Dec 2;32(3):313–318. doi: 10.1016/0922-3371(90)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seetharam R., Dwivedi A. M., Duke J. L., Hayman A. C., Walton H. L., Huckins N. R., Kamerkar S. M., Corman J. I., Woodeshick R. W., Wilk R. R. Purification and characterization of active and latent forms of recombinant plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 produced in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1992 Oct 20;31(41):9877–9882. doi: 10.1021/bi00156a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanssens P., Opsomer C., McKeown Y. M., Kramer W., Zabeau M., Fritz H. J. Efficient oligonucleotide-directed construction of mutations in expression vectors by the gapped duplex DNA method using alternating selectable markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4441–4454. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Reich E., Sherman M. I. Plasminogen activator in early embryogenesis: enzyme production by trophoblast and parietal endoderm. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):231–240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsafriri A., Bicsak T. A., Cajander S. B., Ny T., Hsueh A. J. Suppression of ovulation rate by antibodies to tissue-type plasminogen activator and alpha 2-antiplasmin. Endocrinology. 1989 Jan;124(1):415–421. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-1-415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tybulewicz V. L., Crawford C. E., Jackson P. K., Bronson R. T., Mulligan R. C. Neonatal lethality and lymphopenia in mice with a homozygous disruption of the c-abl proto-oncogene. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1153–1163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90011-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Sappino A. P., Belin D. The plasminogen activator/plasmin system. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1067–1072. doi: 10.1172/JCI115405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan D. E., Declerck P. J., Van Houtte E., De Mol M., Collen D. Reactivated recombinant plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (rPAI-1) effectively prevents thrombolysis in vivo. Thromb Haemost. 1992 Jul 6;68(1):60–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheijen J. H., Chang G. T., Kluft C. Evidence for the occurrence of a fast-acting inhibitor for tissue-type plasminogen activator in human plasma. Thromb Haemost. 1984 Jul 29;51(3):392–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- te Riele H., Maandag E. R., Berns A. Highly efficient gene targeting in embryonic stem cells through homologous recombination with isogenic DNA constructs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):5128–5132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.5128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]