Abstract
BALB/c mice develop autoimmune myocarditis after immunization with mouse cardiac myosin, whereas C57B/6 mice do not. To define the immunogenicity and pathogenicity of cardiac myosin in BALB/c mice, we immunized mice with different forms of cardiac myosin. These studies demonstrate the discordance of immunogenicity and pathogenicity of myosin heavy chains. The cardiac alpha-myosin heavy chains of BALB/c and C57B/6 mice differ by two residues that are near the junction of the head and rod in the S2 fragment of myosin. Myosin preparations from both strains are immunogenic in susceptible BALB/c as well as in nonsusceptible C57B/6 mice; however, BALB/c myosin induces a greater incidence of disease. To further delineate epitopes of myosin heavy chain responsible for immunogenicity and disease, mice were immunized with fragments of genetically engineered rat alpha cardiac myosin. Epitopes in the region of difference between BALB/c and C57B/6 (residues 735-1032) induce disease in both susceptible and nonsusceptible mice. The data presented here demonstrate that pathogenic epitopes of both mouse and rat myosin residue in the polymorphic region of the S2 subunit. In addition, these studies suggest that polymorphisms in the autoantigen may be part of the genetic basis for autoimmune myocarditis.
Full text
PDF

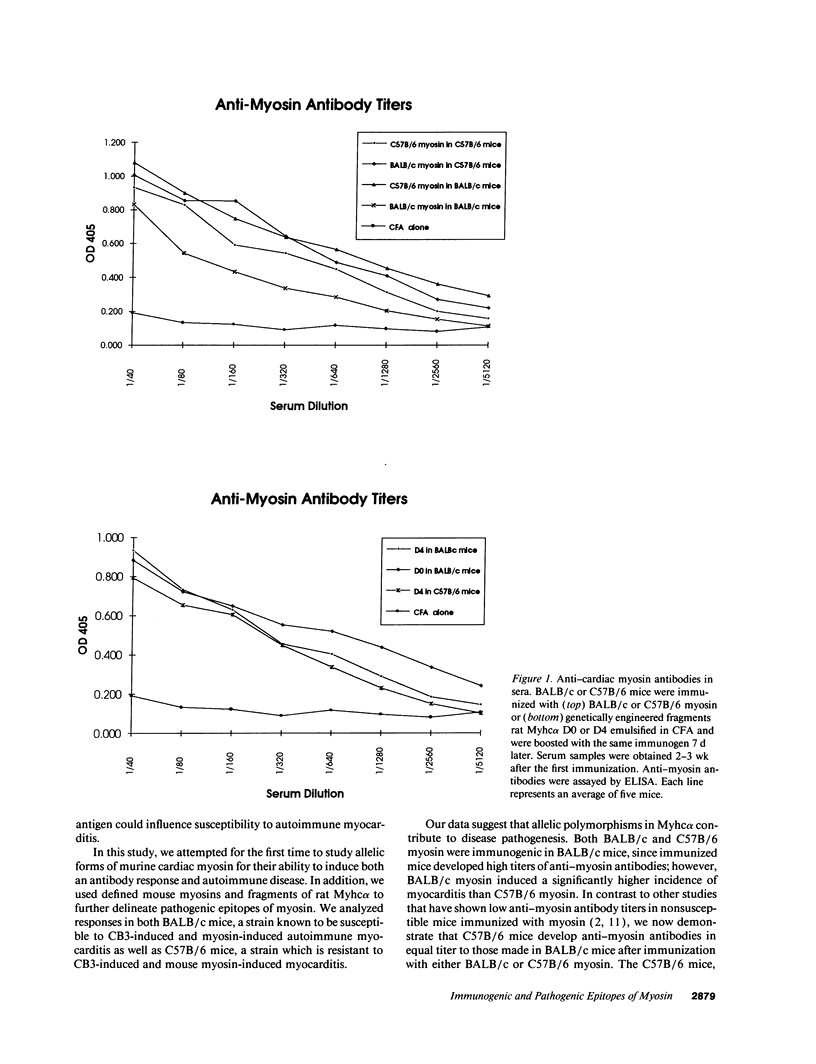
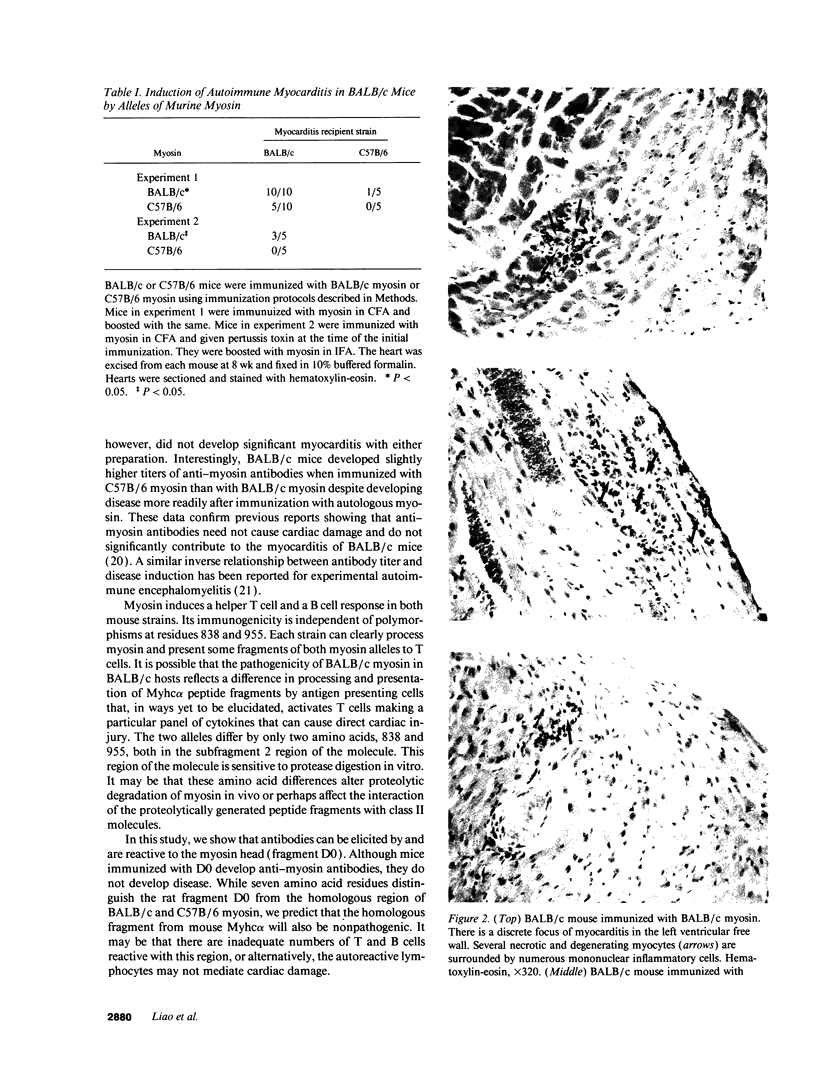
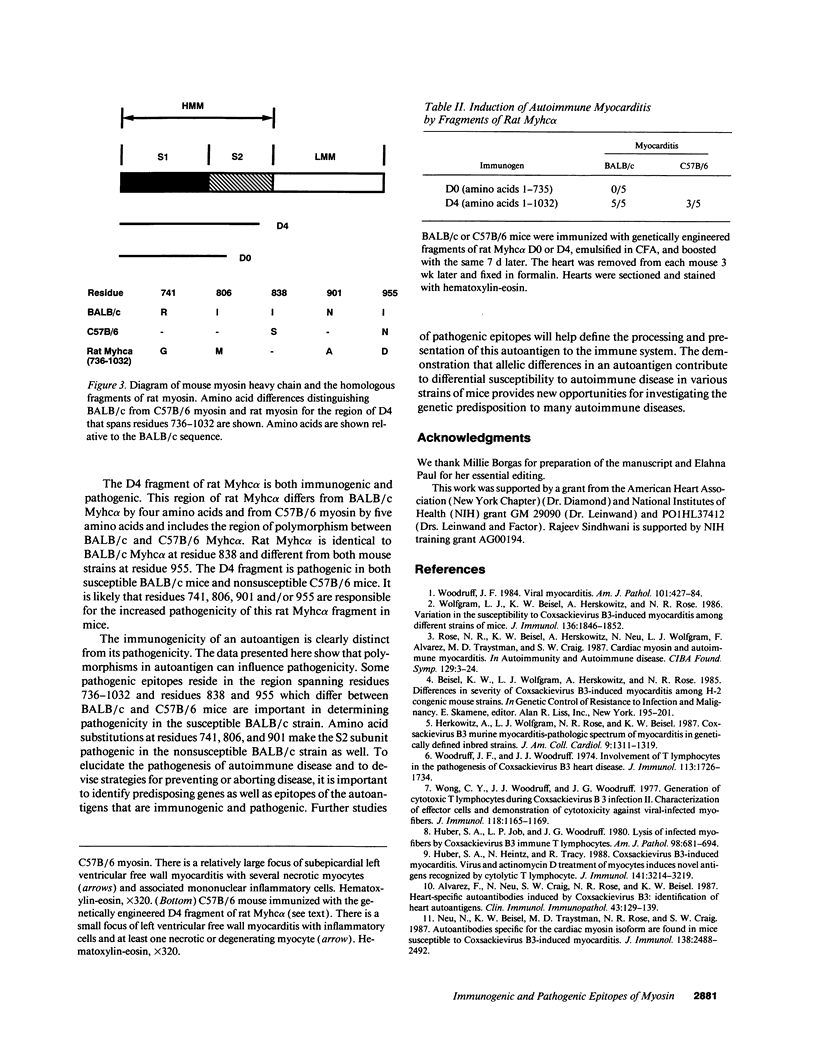

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvarez F. L., Neu N., Rose N. R., Craig S. W., Beisel K. W. Heart-specific autoantibodies induced by Coxsackievirus B3: identification of heart autoantigens. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Apr;43(1):129–139. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(87)90164-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aretz H. T., Billingham M. E., Edwards W. D., Factor S. M., Fallon J. T., Fenoglio J. J., Jr, Olsen E. G., Schoen F. J. Myocarditis. A histopathologic definition and classification. Am J Cardiovasc Pathol. 1987 Jan;1(1):3–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz A., Wolfgram L. J., Rose N. R., Beisel K. W. Coxsackievirus B3 murine myocarditis: a pathologic spectrum of myocarditis in genetically defined inbred strains. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1987 Jun;9(6):1311–1319. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(87)80471-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber S. A., Heintz N., Tracy R. Coxsackievirus B-3-induced myocarditis. Virus and actinomycin D treatment of myocytes induces novel antigens recognized by cytolytic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 1;141(9):3214–3219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber S. A., Job L. P., Woodruff J. F. Lysis of infected myofibers by coxsackievirus B-3-immune T lymphocytes. Am J Pathol. 1980 Mar;98(3):681–694. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber S. A., Lodge P. A. Coxsackievirus B-3 myocarditis. Identification of different pathogenic mechanisms in DBA/2 and Balb/c mice. Am J Pathol. 1986 Feb;122(2):284–291. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisak R. P., Heinze R. G., Kies M. W., Alvord E. C., Jr Antibodies to encephalitogenic basic protein in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Mar;130(3):814–818. doi: 10.3181/00379727-130-33662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNally E. M., Bravo-Zehnder M. M., Leinwand L. A. Identification of sequences necessary for the association of cardiac myosin subunits. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(3):585–590. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.3.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu N., Beisel K. W., Traystman M. D., Rose N. R., Craig S. W. Autoantibodies specific for the cardiac myosin isoform are found in mice susceptible to Coxsackievirus B3-induced myocarditis. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 15;138(8):2488–2492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu N., Rose N. R., Beisel K. W., Herskowitz A., Gurri-Glass G., Craig S. W. Cardiac myosin induces myocarditis in genetically predisposed mice. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 1;139(11):3630–3636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn-Laquer B. K., Kennedy J. E., Wei S. J., Beisel K. W. Characterization of the allelic differences in the mouse cardiac alpha-myosin heavy chain coding sequence. Genomics. 1992 May;13(1):176–188. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90218-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose N. R., Beisel K. W., Herskowitz A., Neu N., Wolfgram L. J., Alvarez F. L., Traystman M. D., Craig S. W. Cardiac myosin and autoimmune myocarditis. Ciba Found Symp. 1987;129:3–24. doi: 10.1002/9780470513484.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traystman M. D., Chow L. H., McManus B. M., Herskowitz A., Nesbitt M. N., Beisel K. W. Susceptibility to Coxsackievirus B3-induced chronic myocarditis maps near the murine Tcr alpha and Myhc alpha loci on chromosome 14. Am J Pathol. 1991 Mar;138(3):721–726. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weydert A., Daubas P., Lazaridis I., Barton P., Garner I., Leader D. P., Bonhomme F., Catalan J., Simon D., Guénet J. L. Genes for skeletal muscle myosin heavy chains are clustered and are not located on the same mouse chromosome as a cardiac myosin heavy chain gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7183–7187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfgram L. J., Beisel K. W., Herskowitz A., Rose N. R. Variations in the susceptibility to Coxsackievirus B3-induced myocarditis among different strains of mice. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 1;136(5):1846–1852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfgram L. J., Beisel K. W., Rose N. R. Heart-specific autoantibodies following murine coxsackievirus B3 myocarditis. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):1112–1121. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.1112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C. Y., Woodruff J. J., Woodruff J. F. Generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes during coxsackievirus tb-3 infection. II. Characterization of effector cells and demonstration cytotoxicity against viral-infected myofibers1. J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1165–1169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff J. F., Woodruff J. J. Involvement of T lymphocytes in the pathogenesis of coxsackie virus B3 heart disease. J Immunol. 1974 Dec;113(6):1726–1734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





