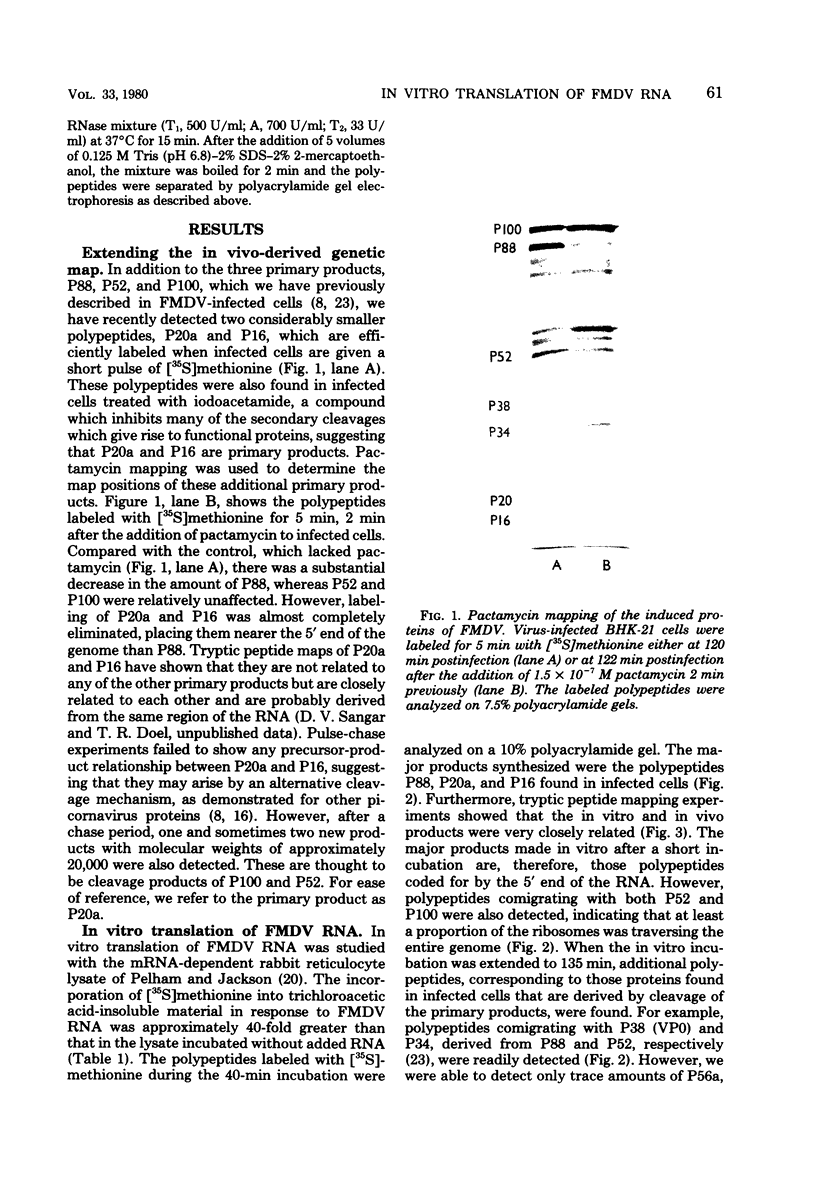
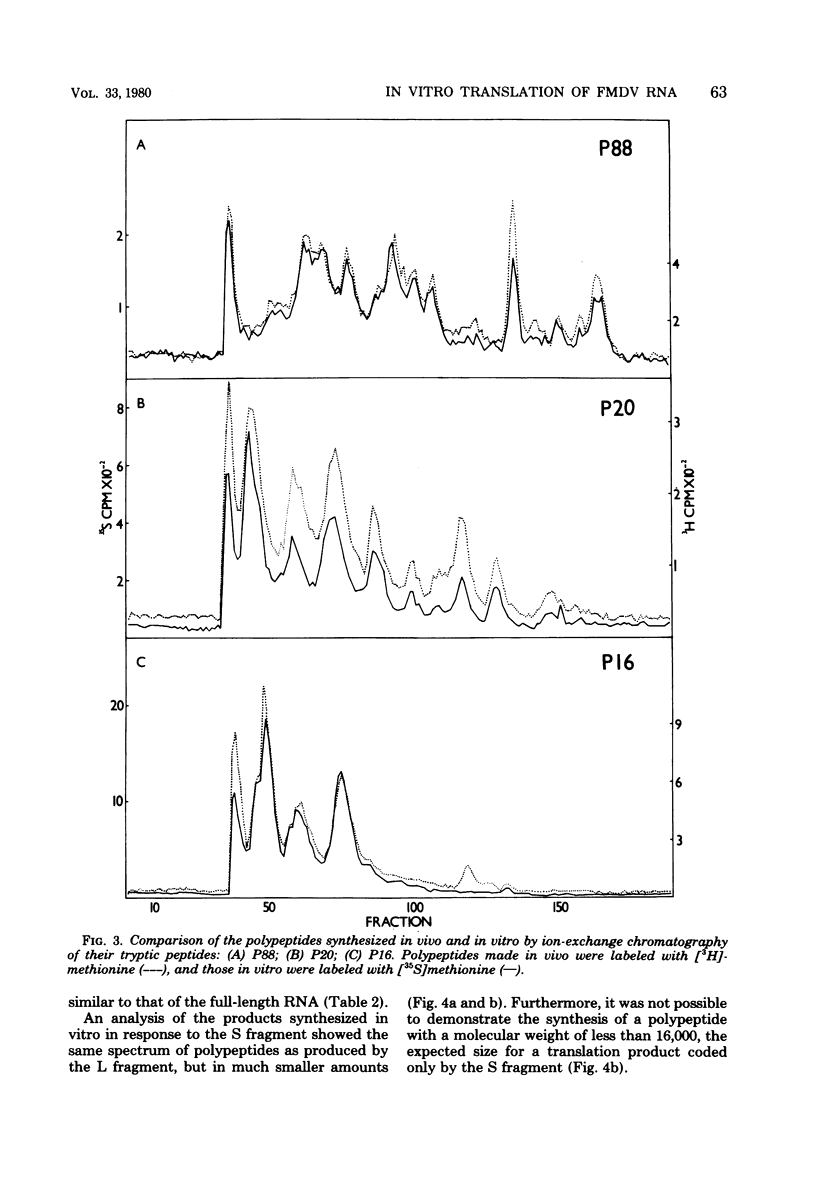
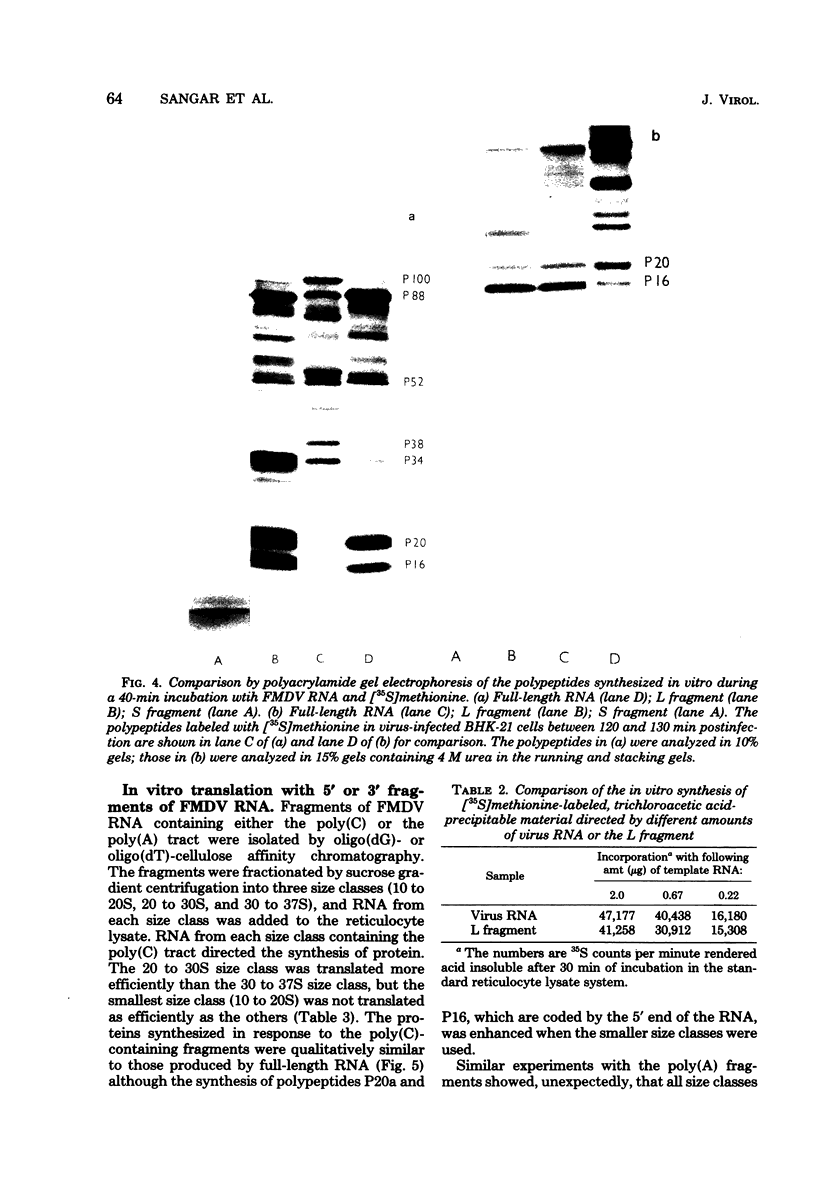
Abstract
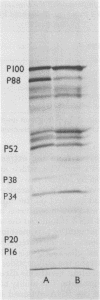
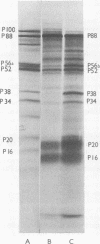
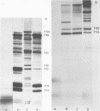
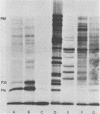
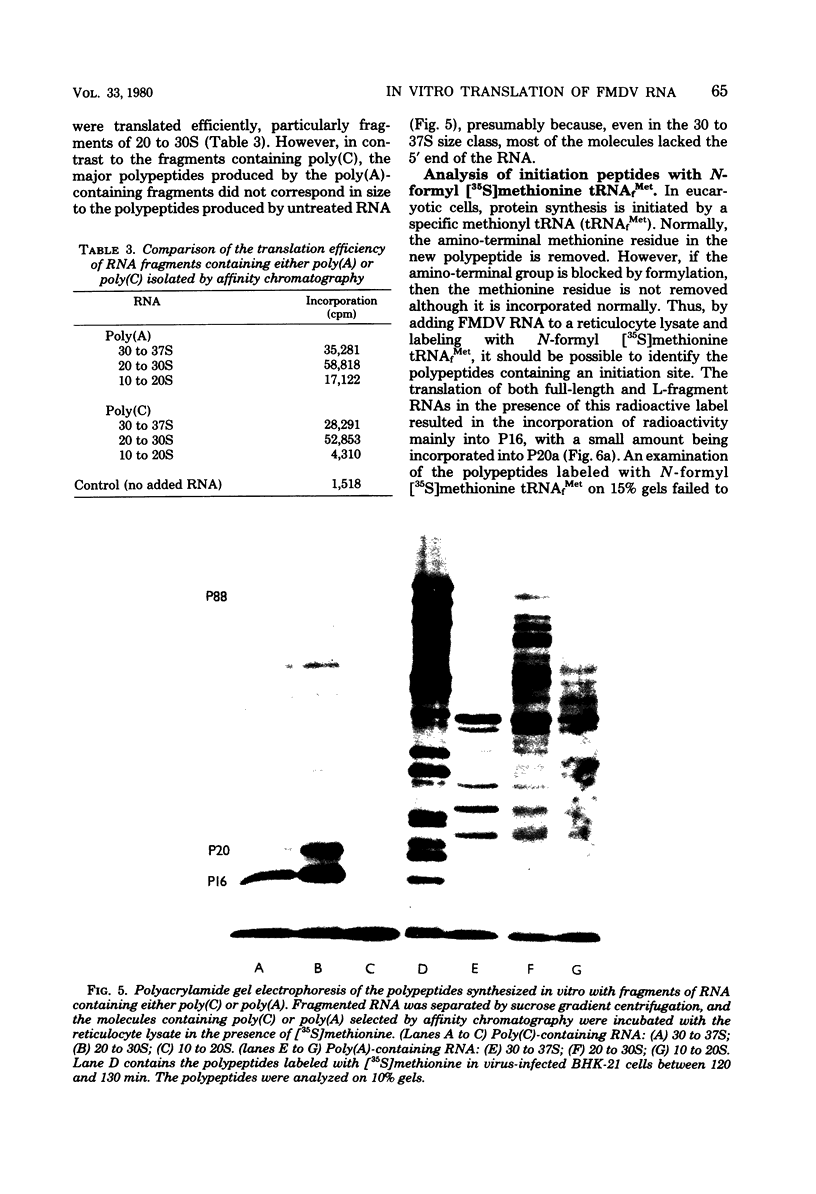
An mRNA-dependent reticulocyte lysate has been used to translate foot-and-mouth disease virus RNA in vitro. Polypeptides P16, P20a, and P88, which have been shown to be derived from the 5' end of the RNA by pactamycin mapping experiments with infected cells, were preferentially synthesized in vitro. Removal of VPg, the small protein covalently linked to the 5' end of the genome RNA, had no effect on the translation of the RNA. The two RNA fragments (L and S) produced by specific digestion of the polycytidylic acid [poly(C)] tract with RNase H were also translated in vitro. The L fragment, consisting of RNA to the 3' side of the poly(C) tract and including the polyadenylic acid [poly(A)] tract, directed the synthesis of the same products as those made by full-length RNA. However, no small defined products were produced when the S fragment, which contains the 5' end of the RNA, was translated. These results show that the major initiation site for protein synthesis on foot-and-mouth disease virus RNA is to the 3' side of the poly(C) tract. Furthermore, the use of N-formyl [35S]methionine tRNAfMet as a label for the initiation peptides showed that the major polypeptide labeled in lysates primed with both full-length RNA and the L fragment was P16, i.e., the protein nearest the initiation site for translation as deduced from pactamycin mapping experiments. Fragments of RNA were also translated in vitro. Those containing the poly(C) tract gave products similar to those produced when full-length RNA was translated. The polypeptides synthesized when fragments containing the poly(A) tract were used, however, did not resemble those made from full-length RNA.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Black D. N., Stephenson P., Rowlands D. J., Brown F. Sequence and location of the poly C tract in aphtho- and cardiovirus RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jun 11;6(7):2381–2390. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.7.2381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown F., Newman J., Stott J., Porter A., Frisby D., Newton C., Carey N., Fellner P. Poly(C) in animal viral RNAs. Nature. 1974 Sep 27;251(5473):342–344. doi: 10.1038/251342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee N. K., Bachrach H. L., Polatnick J. Foot-and-mouth disease virus RNA. Presence of 3'-terminal polyriboadenylic acid and absence of amino acid binding ability. Virology. 1976 Feb;69(2):369–377. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90469-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee N. K., Polatnick J., Bachrach H. L. Cell-free translation of foot-and-mouth disease virus RNA into identifiable non-capsid and capsid proteins. J Gen Virol. 1976 Sep;32(3):383–394. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-32-3-383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denoya C. D., Scodeller E. A., Vasquez C., La Torre J. L. Ribonuclease activities associated with purified foot and mouth disease virus. Arch Virol. 1978;57(2):153–159. doi: 10.1007/BF01315676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doel T. R., Brown F. Tryptic peptide analysis of the structural proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1978 Feb;38(2):351–361. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-38-2-351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doel T. R., Sangar D. V., Rowlands D. J., Brown F. A re-appraisal of the biochemical map of foot-and-mouth disease virus RNA. J Gen Virol. 1978 Nov;41(2):395–404. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-41-2-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris T. J., Brown F. Biochemical analysis of a virulent and an avirulent strain of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jan;34(1):87–105. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-34-1-87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris T. J., Brown F. The location of the ploy(C) tract in the RNA of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1976 Dec;33(3):493–501. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-3-493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris T. J., Wildy P. The synthesis of polyadenylated messenger RNA in herpes simplex type I virus infected BHK cells. J Gen Virol. 1975 Sep;28(3):299–312. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-28-3-299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett M. J., Rose J. K., Baltimore D. 5'-terminal structure of poliovirus polyribosomal RNA is pUp. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):327–330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. F., Asso J., Baltimore D. Further evidence on the formation of poliovirus proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 May 14;49(3):657–669. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90289-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. F., Nomoto A., Detjen B. M., Wimmer E. A protein covalently linked to poliovirus genome RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):59–63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean C., Matthews T. J., Rueckert R. R. Evidence of ambiguous processing and selective degradation in the noncapsid proteins of rhinovirus 1A. J Virol. 1976 Sep;19(3):903–914. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.3.903-914.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman J. F., Cartwright B., Doel T. R., Brown F. Purification and identification of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1979 Nov;45(2):497–507. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-45-2-497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA in vitro yields an active proteolytic processing enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr 17;85(2):457–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Translation of fragmented viral RNA in vitro: initiation at multiple sites. FEBS Lett. 1979 Apr 1;100(1):195–199. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81162-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlands D. J., Harris T. J., Brown F. More precise location of the polycytidylic acid tract in foot and mouth disease virus RNA. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):335–343. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.335-343.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sangar D. V., Black D. N., Rowlands D. J., Brown F. Biochemical mapping of the foot-and-mouth disease virus genome. J Gen Virol. 1977 May;35(2):281–297. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-35-2-281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sangar D. V., Rowlands D. J., Harris T. J., Brown F. Protein covalently linked to foot-and-mouth disease virus RNA. Nature. 1977 Aug 18;268(5621):648–650. doi: 10.1038/268648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih D. S., Shih C. T., Kew O., Pallansch M., Rueckert R., Kaesberg P. Cell-free synthesis and processing of the proteins of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5807–5811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svitkin Y. V., Agol V. I. Complete translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA and faithful cleavage of virus-specific proteins in a cell-free system from Krebs-2 cells. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):7–11. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]