Abstract
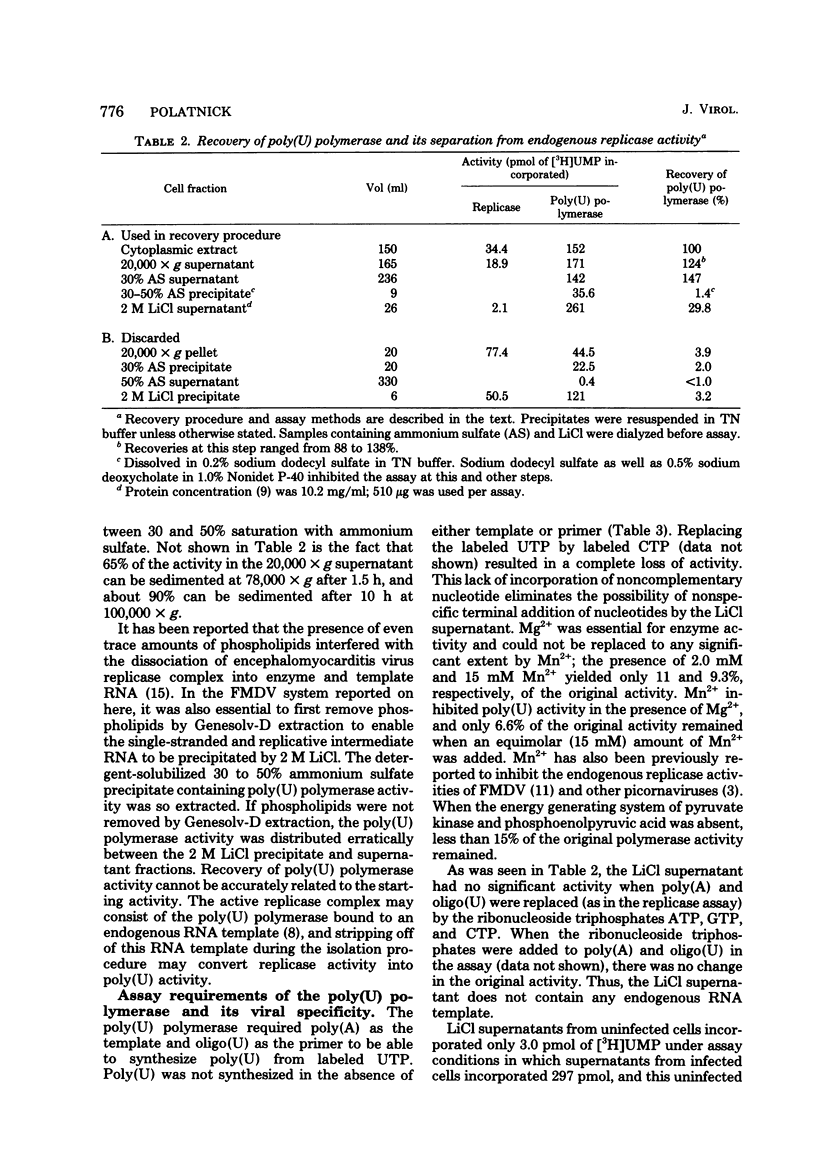
A template-dependent polyuridylic acid [poly(U)] polymerase has been isolated from BHK cells infected with foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV). Enzyme activity in a 20,000 x g supernatant of a cytoplasmic extract was concentrated by precipitation with 30 to 50% saturated ammonium sulfate. The poly(U) polymerase was freed of membranes by sodium dodecyl sulfate and 1,1,2-trichlorotrifluoroethane extraction, and RNA was removed by precipitation with 2 M LiCl. The solubilized poly(U) polymerase required polyadenylic acid as template complexed to an oligouridylic acid primer and Mg2+ for activity, but was inhibited by Mn2+. Antisera from animals infected with FMDV had previously been shown to inhibit the activity of FMDV RNA replicase complexed to the endogenous RNA template. The same antisera also inhibited the activity of poly(U) polymerase. Antisera depleted of antibody by absorption with the virus infection-associated antigen of FMDV no longer inhibited replicase and polymerase activities. The evidence suggests that FMDV RNA replicase, poly(U) polymerase, and the virus infection-associated antigen share a common protein.
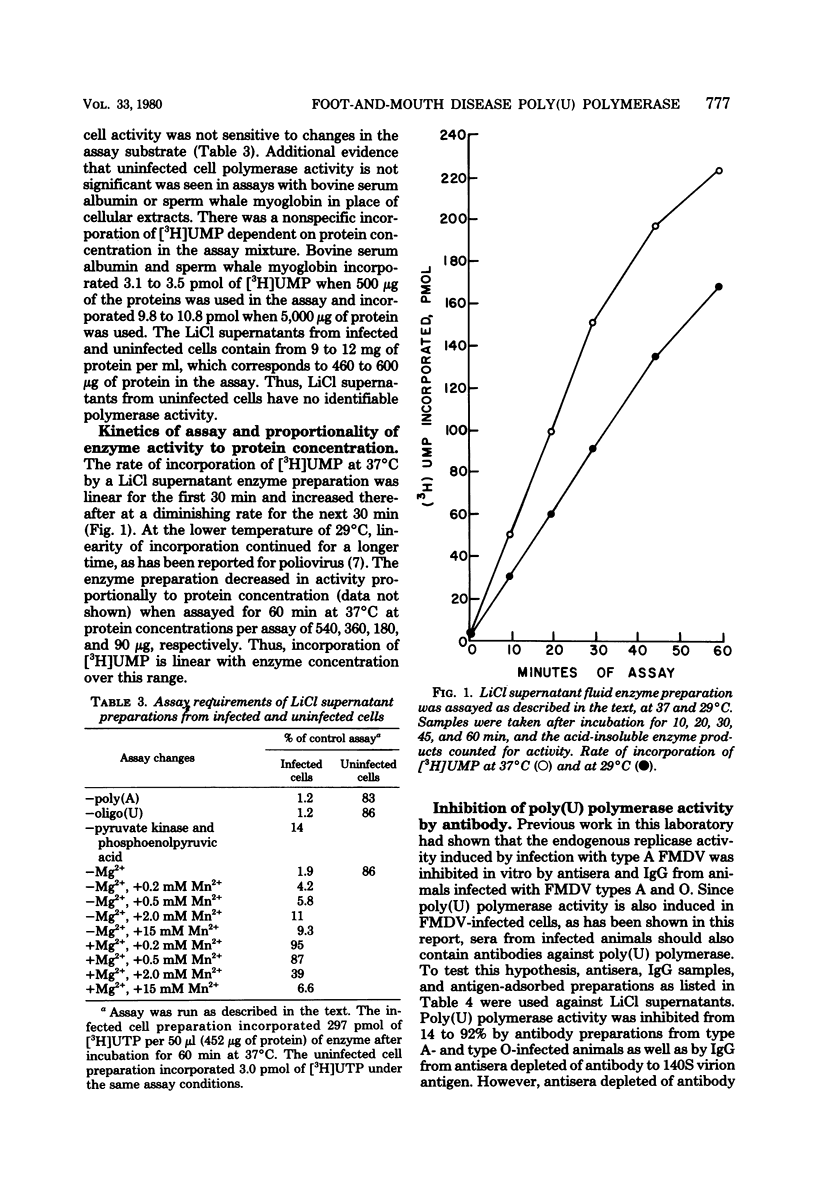
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arlinghaus R. B., Bachrach H. L., Polatnick J. Site of foot-and-mouth disease virus-ribonucleic acid synthesis and some properties of its double-stranded ribonucleic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jun 18;161(1):170–179. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90306-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arlinghaus R. B., Polatnick J. The isolation of two enzyme-ribonucleic acid complexes involved in the synthesis of foot-and-mouth disease virus ribonucleic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Mar;62(3):821–828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.3.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee N. K., Bachrach H. L., Polatnick J. Foot-and-mouth disease virus RNA. Presence of 3'-terminal polyriboadenylic acid and absence of amino acid binding ability. Virology. 1976 Feb;69(2):369–377. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90469-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee N. K., Polatnick J., Bachrach H. L. Cell-free translation of foot-and-mouth disease virus RNA into identifiable non-capsid and capsid proteins. J Gen Virol. 1976 Sep;32(3):383–394. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-32-3-383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan K. M., Graves J. H. A third antigenic component associated with foot-and-mouth disease infection. Virology. 1966 Nov;30(3):528–540. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90128-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Baltimore D. Poliovirus polyuridylic acid polymerase and RNA replicase have the same viral polypeptide. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):352–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.352-360.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Baltimore D. Poliovirus-specific primer-dependent RNA polymerase able to copy poly(A). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3677–3680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundquist R. E., Maizel J. V., Jr In vivo regulation of the poliovirus RNA polymerase. Virology. 1978 Sep;89(2):484–493. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90190-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman J. F., Cartwright B., Doel T. R., Brown F. Purification and identification of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1979 Nov;45(2):497–507. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-45-2-497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLATNICK J., BACHRACH H. L. PRODUCTION AND PURIFICATION OF MILLIGRAM AMOUNTS OF FOOT-AND-MOUTH DISEASE VIRUS FROM BABY HAMSTER KIDNEY CELL CULTURES. Appl Microbiol. 1964 Jul;12:368–373. doi: 10.1128/am.12.4.368-373.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polatnick J., Arlinghaus R. B. Foot-and-mouth disease virus-induced ribonucleic acid polymerase in baby hamster kidney cells. Virology. 1967 Apr;31(4):601–608. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90188-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polatnick J., Arlinghaus R. B., Graves J. H., Cowan K. M. Inhibition of cell-free foot-and-mouth disease virus-ribonucleic acid synthesis by antibody. Virology. 1967 Apr;31(4):609–615. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90189-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Baltimore D. Polyadenylic acid on poliovirus RNA IV. Poly(U) in replicative intermediate and double-stranded RNA. Virology. 1975 Oct;67(2):498–505. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90450-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub A., Duskin B., Rosenberg H., Kalmar E. Isolation and properties of the replicase of encephalomyocarditis virus. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):375–382. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.375-382.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


