Abstract
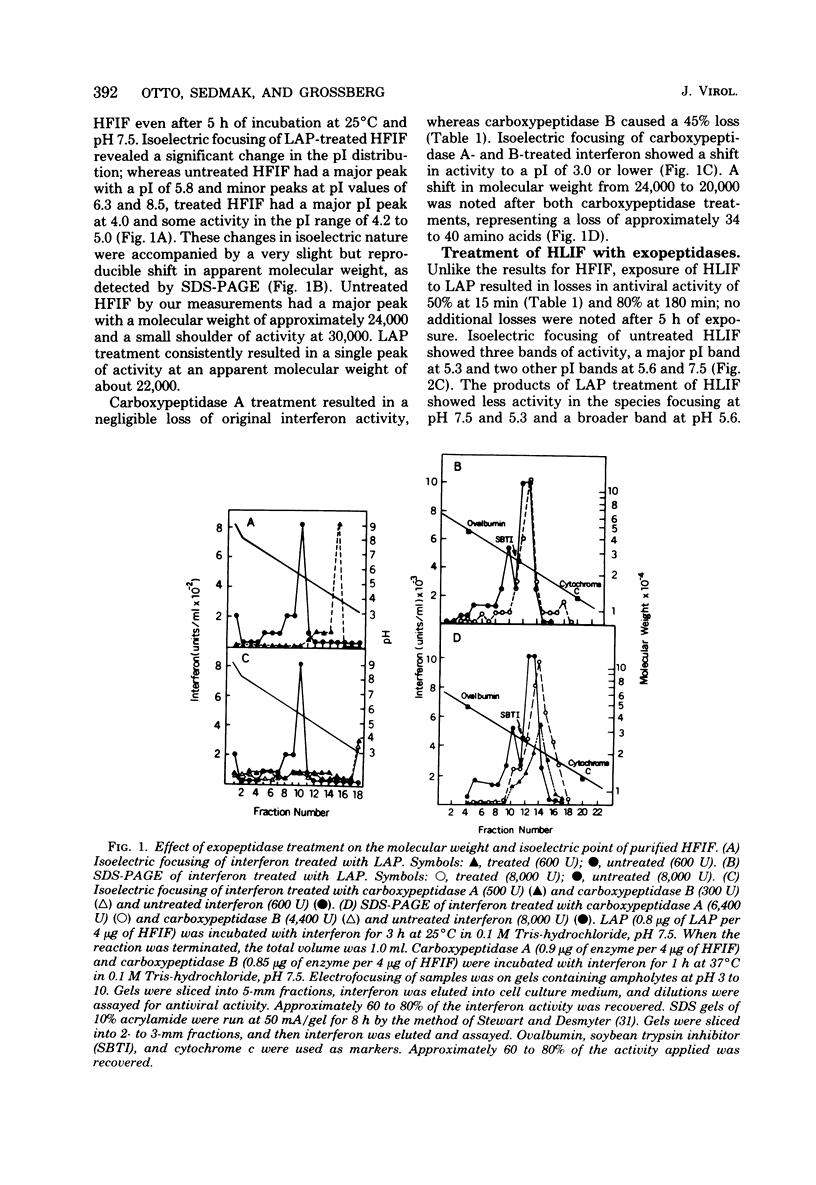
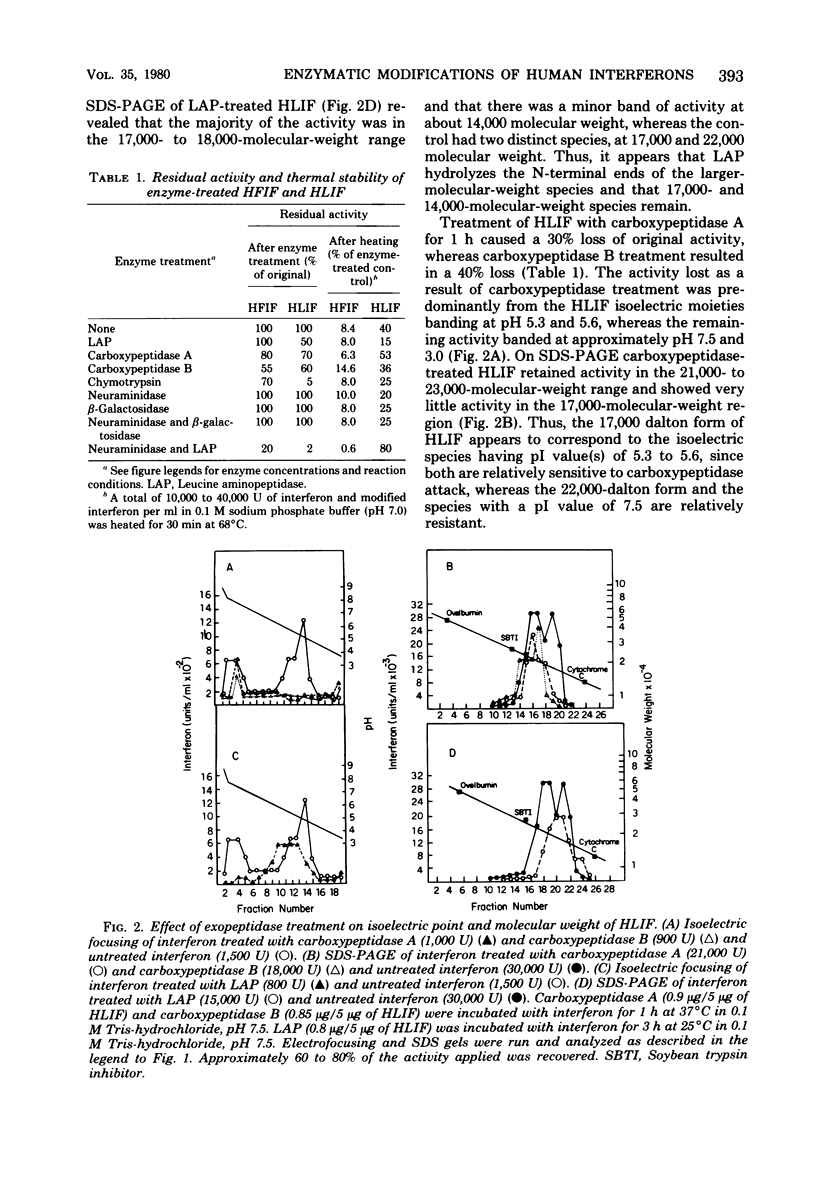
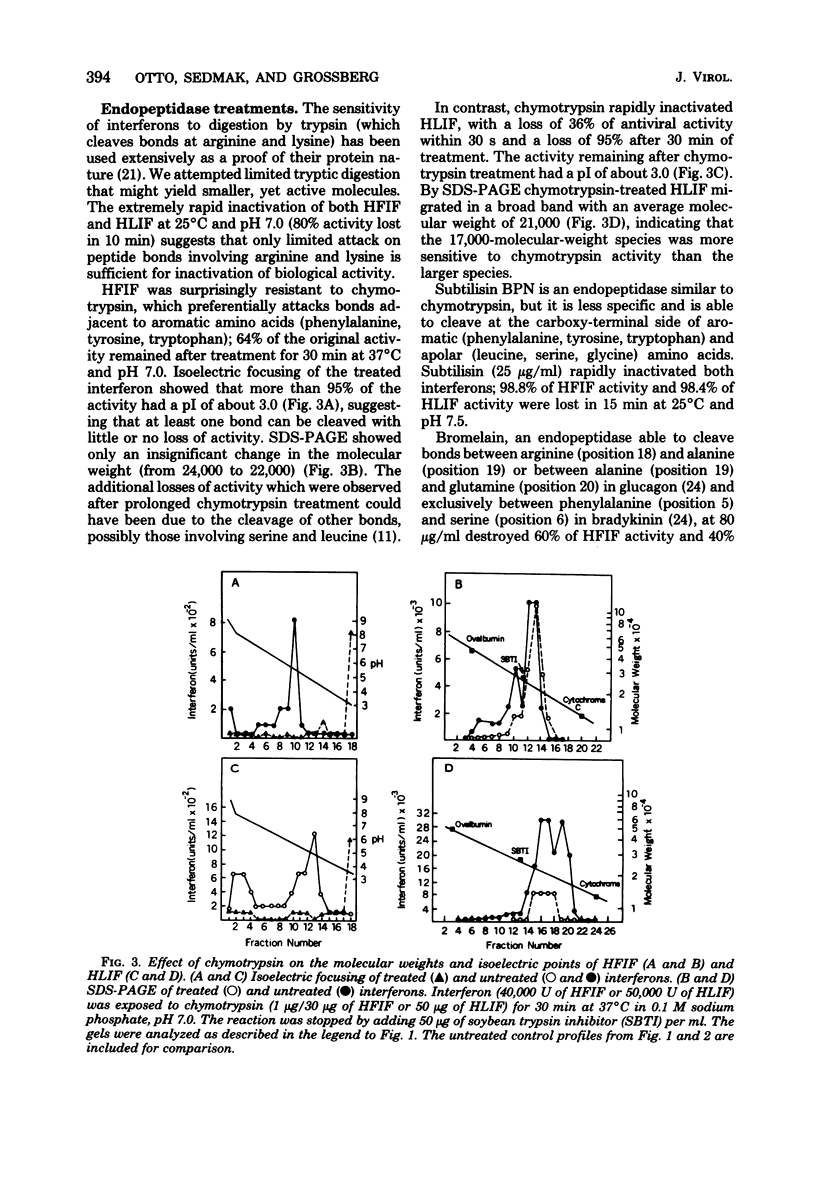
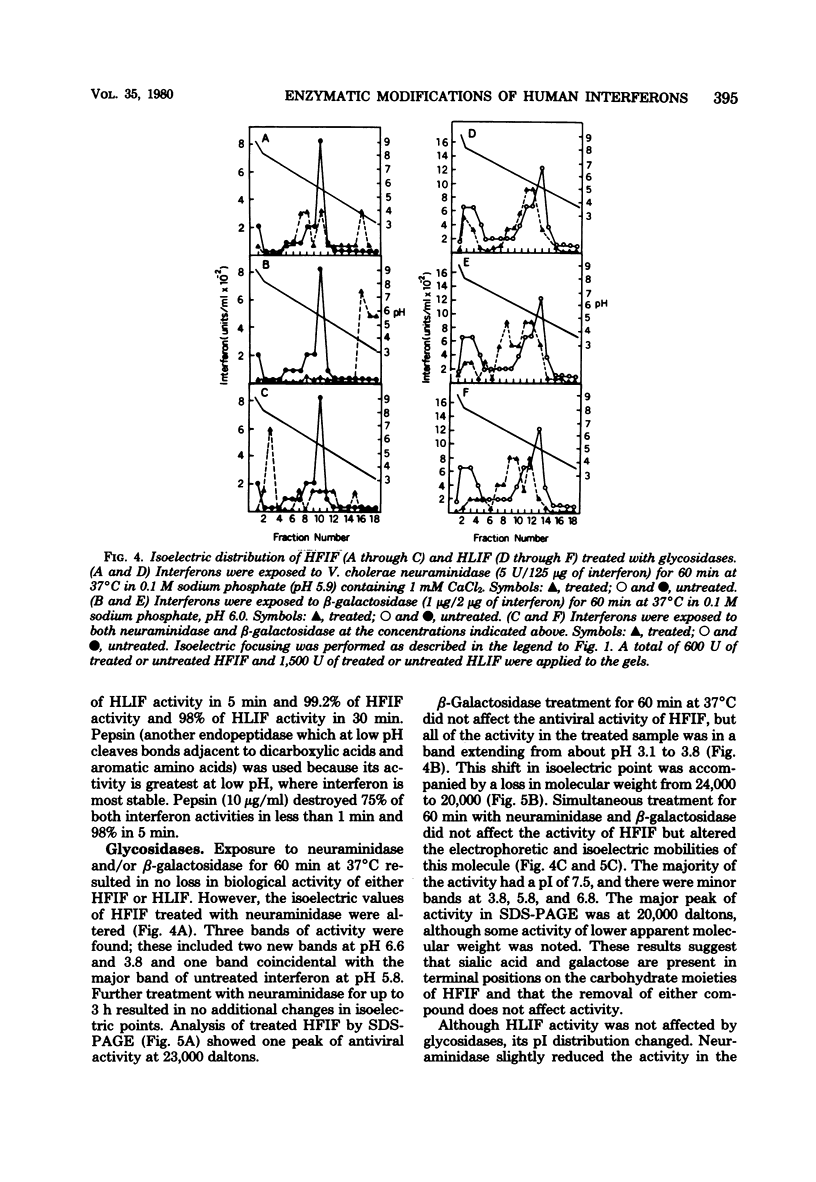
The sensitivity of highly purified human fibroblast interferon and partially purified human leukocyte interferon to several proteolytic and glycolytic enzymes was determined with respect to antiviral activity, isoelectric point, molecular weight, and thermal stability. Leucine aminopeptidase altered the distribution of isoelectric points for both interferons but produced little change in molecular weights; this enzyme somewhat reduced the activity of only leukocyte interferon. Treatment of fibroblast interferon with carboxypeptidases A and B did not greatly decrease antiviral activity, but it did slightly reduce the molecular weight of the interferon and substantially altered the distribution of isoelectric point values; similar treatment of leukocyte interferon caused some loss in activity, especially of the 17,000-molecular-weight species. Both interferons were inactivated rapidly by treatment with the endoproteases trypsin, pepsin, bromelain, and subtilisin. Chymotrypsin shifted the isoelectric points of both interferons, but only leukocyte interferon was significantly inactivated. Treatment with neuraminidase and beta-galactosidase changed the isoelectric point distribution but did not affect the activity or thermal stability of either interferon; such a treatment reduced the molecular weight of fibroblast interferon and the size heterogeneity of leukocyte interferon. Treatment with neuraminidase and then leucine aminopeptidase greatly reduced the activity of both interferons, especially leukocyte interferon. The data indicate that biologically active forms of fibroblast and leukocyte interferons can be distinguished by their relative sensitivity to certain proteases.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berthold W., Tan C., Tan Y. H. Chemical modifications of tyrosyl residue(s) and action of human-fibroblast interferon. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(2):367–370. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12385.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bose S., Gurari-Rotman D., Ruegg U. T., Corley L., Anfinsen C. B. Apparent dispensability of the carbohydrate moiety of human interferon for antiviral activity. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 25;251(6):1659–1662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braude I. A., Lin L. S., Stewart W. E., 2nd Differential inactivation and separation of homologous and heterologous antiviral activity of human leukocyte interferon by a proteolytic enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jul 27;89(2):612–619. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90674-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridgen P. J., Anfinsen C. B., Corley L., Bose S., Zoon K. C., Rüegg U. T., Buckler C. E. Human lymphoblastoid interferon. Large scale production and partial purification. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 10;252(19):6585–6587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright T., Senussi O., Grady D. Reagents which inhibit disulphide bond formation stabilize human fibroblast interferon. J Gen Virol. 1977 Aug;36(2):323–327. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-2-323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cesario T. C., Schryer P. J., Tilles J. G. Relationship between the physicochemical nature of human interferon, the cell induced, and the inducing agent. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Feb;11(2):291–298. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.2.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadha K. C., Sclair M., Sulkowski E., Carter W. A. Molecular size heterogeneity of human leukocyte interferon. Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 10;17(1):196–200. doi: 10.1021/bi00594a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENENKEL A. G., SMILLIE L. B. SPECIFICITY OF CHYMOTRYPSIN B TOWARD GLUCAGON. Biochemistry. 1963 Nov-Dec;2:1449–1454. doi: 10.1021/bi00906a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung K. P., Ng M. H. Purification of human diploid fibroblast interferon by immobilized neuraminidase. Arch Virol. 1978;56(1-2):1–6. doi: 10.1007/BF01317278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A., Vilcek J. Production of high-titered interferon in cultures of human diploid cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Dec;2(6):476–484. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.6.476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A., Yamazaki S., Vilcek J. Altered molecular species of human interferon produced in the presence of inhibitors of glycosylation. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4425–4427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson P., Dixon M. A., Grossberg S. E. A sensitive interferon assay for many species of cells: encephalomyocarditis virus hemagglutinin yield reduction. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Jun;155(2):173–178. doi: 10.3181/00379727-155-39768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowski W. J., Davey M. W., O'Malley J. A., Sulkowski E., Carter W. A. Molecular structure of human fibroblast and leukocyte interferons: probe by lectin and hydrophobic chromatography. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1124–1130. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1124-1130.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowski W. J., von Muenchhausen W., Sulkowski E., Carter W. A. Binding of human interferons to immobolized Cibacron Blue F3GA: The nature of molecular interaction. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 16;15(23):5182–5187. doi: 10.1021/bi00668a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E., Jr, Hunkapiller M. W., Korant B. D., Hardy R. W., Hood L. E. Human fibroblast interferon: amino acid analysis and amino terminal amino acid sequence. Science. 1980 Feb 1;207(4430):525–526. doi: 10.1126/science.7352259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E., Jr Interferon: purification and initial characterization from human diploid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):520–523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. S., Wiranowska-Stewart M., Chudzio T., Stewart W. E., 2nd Characterization of the heterogeneous molecules of human interferons: differences in the cross-species antiviral activities of various molecular populations in human leukocyte interferons. J Gen Virol. 1978 Apr;39(1):125–130. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-39-1-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURACHI T., NEURATH H. Fractionation and specificity studies on stem bromelain. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jan;235:99–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen K. E., Cantell K. Human leukocyte interferon: a role for disulphide bonds. J Gen Virol. 1974 Jan;22(1):95–103. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-22-1-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morser J., Kabayo J. P., Hutchinson D. W. Differences in sialic acid content of human interferons. J Gen Virol. 1978 Oct;41(1):175–178. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-41-1-175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., McInnes J., Weiss D., Havell E. A., Vilcek J. De novo cell-free synthesis of human interferon. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1977 Mar 4;284:697–702. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1977.tb22005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisner A. H., Nemes P., Bucholtz C. The use of Coomassie Brilliant Blue G250 perchloric acid solution for staining in electrophoresis and isoelectric focusing on polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1975 Apr;64(2):509–516. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90461-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein M., Rubinstein S., Familletti P. C., Miller R. S., Waldman A. A., Pestka S. Human leukocyte interferon: production, purification to homogeneity, and initial characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):640–644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salit M. G., Ogburn C. A. Human leukocyte interferon: separation of biologically different species by modification of carbohydrate moieties. Arch Virol. 1980;63(2):133–142. doi: 10.1007/BF01320770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedmak J. J., Grossberg S. E. A rapid, sensitive, and versatile assay for protein using Coomassie brilliant blue G250. Anal Biochem. 1977 May 1;79(1-2):544–552. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90428-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedmak J. J., Grossberg S. E. Comparative enzyme kinetics of influenza neuraminidases with the synthetic substrate methoxyphenylneuraminic acid. Virology. 1973 Dec;56(2):658–661. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart II W. E., De Somer P., Edy V. G., Paucker K., Berg K., Ogburn C. A. Distinct molecular species of human interferons: requirements for stabilzation and reactivation of human leukocyte and fibroblast interferons. J Gen Virol. 1975 Mar;26(3):327–331. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-26-3-327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. E., 2nd, Desmyter J. Molecular heterogeneity of human leukocyte interferon: two populations differing in molecular weights, requirements for renaturation, and cross-species antiviral activity. Virology. 1975 Sep;67(1):68–73. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90403-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. E., 2nd, Lin L. S., Wiranowska-Stewart M., Cantell K. Elimination of size and charge heterogeneities of human leukocyte interferons by chemical cleavage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4200–4204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. E., 2nd, Wiranowska-Stewart M., Koistinen V., Cantell K. Effect of glycosylation inhibitors on the production and properties of human leukocyte interferon. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):473–476. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90359-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulkowski E., Davey M. W., Carter W. A. Interaction of human interferons with immobilized hydrophobic amino acids and dipeptides. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 10;251(17):5381–5385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Törmä E. T., Paucker K. Purification and characterization of human leukocyte interferon components. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 25;251(16):4810–4816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilcek J., Havell E. A., Yamazaki S. Antigenic, physicochemical, and biologic characterization of human interferons. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1977 Mar 4;284:703–710. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1977.tb22006.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G., Pereira H. G. A common surface antigen in influenza viruses from human and avian sources. J Gen Virol. 1968 Sep;3(2):201–208. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-3-2-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoon K. C., Smith M. E., Bridgen P. J., Anfinsen C. B., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E. Amino terminal sequence of the major component of human lymphoblastoid interferon. Science. 1980 Feb 1;207(4430):527–528. doi: 10.1126/science.7352260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


