Abstract
Five gibbon ape leukemia virus substrains (two from gibbons with lymphocytic leukemia and three from gibbons with myelogenous leukemia) were examined for unique genomic sequences specific for each form of leukemia. By using sequential adsorption procedures, the genome from each gibbon ape leukemia virus was fractionated into four sets of distinct nucleotide sequences. Based on their hybridization specificities toward DNAs of leukemic tissues, these sequences were designated as follows: (i) “COM,” (ii) “LYM” or “MYE,” (iii) “UNI,” and (iv) “UND.” The COM fraction represented sequences common to all of the viral genomes. The LYM fraction, which was isolated only from gibbon ape leukemia viruses associated with lymphocytic leukemia, represented genomic sequences associated with lymphocytic leukemia since the RNA hybridized at a 4- to 15-fold-higher rate to infected tissue DNA from lymphocytic leukemic gibbons than to infected tissue DNA from myelogenous leukemic gibbons. The MYE fraction, which was isolated only from gibbon ape leukemia viruses associated with myelogenous leukemia, represented genomic sequences associated with myelogenous leukemia since the RNA hybridized at a 5- to 15-fold-higher rate to infected tissue DNA from myelogenous leukemic gibbons than to infected tissue DNA from lymphocytic leukemic gibbons. The UNI fraction contained sequences unique to one virus substrain. The UND fraction contained sequences which varied depending upon the substrains involved in the adsorption procedures. These findings suggest that each gibbon ape leukemia virus examined in this study contains subgenomic sequences that are specifically identifiable only with the form of leukemia from which the virus was isolated.
Full text
PDF


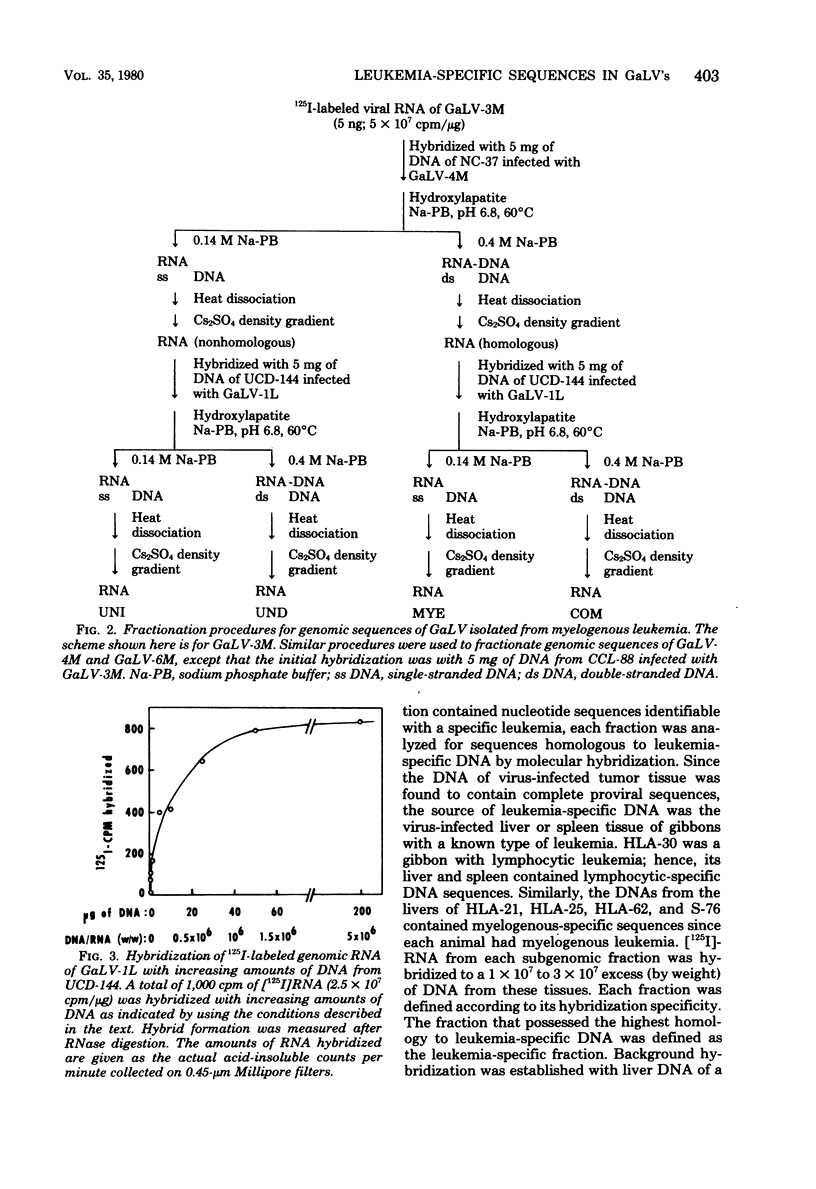
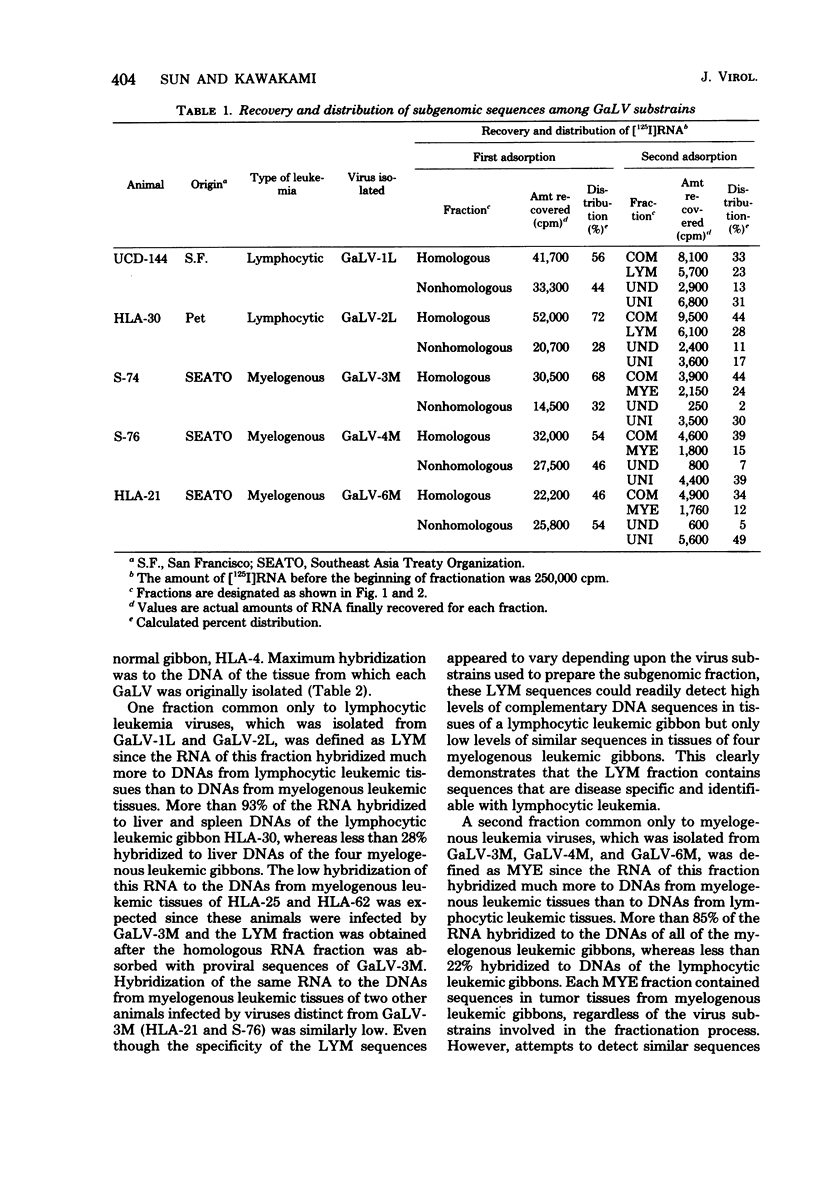
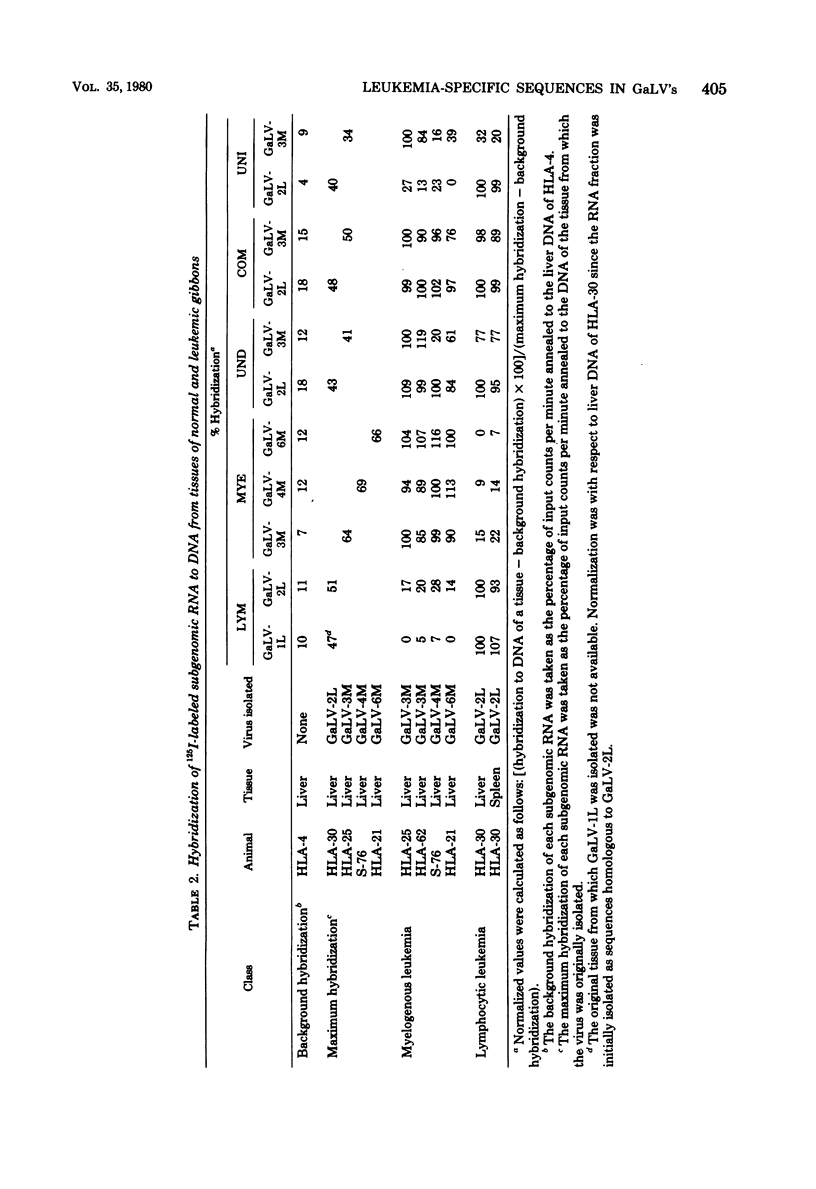



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aulakh G. S., Gallo R. C. Rauscher-leukemia-virus-related sequences in human DNA: presence in some tissues of some patients with hemotopoietic neoplasias and absence in DNA from other tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):353–357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEARD J. W. AVIAN VIRUS GROWTHS AND THEIR ETIOLOGIC AGENTS. Adv Cancer Res. 1963;7:1–127. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60982-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Tumor viruses: 1974. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):1187–1200. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R. E., Todaro G. J. Homology between type-C viruses of various species as determined by molecular hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3316–3320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boiron M. Current status of virological research in human leukemias and sarcomas. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1973 Jan;21(1):77–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charman H. P., Rahman R., White M. H., Kim N., Gilden R. V. Radioimmunoassay for the major structural protein of Mason-Pfizer monkey virus: Attempts to detect the presence of antigen or antibody in humans. Int J Cancer. 1977 Apr 15;19(4):498–504. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Commerford S. L. Iodination of nucleic acids in vitro. Biochemistry. 1971 May 25;10(11):1993–2000. doi: 10.1021/bi00787a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. E., Neubauer R. L., Fischinger P. J. Fractionation of DNA nucleotide transcripts from Moloney sarcoma virus and isolation of sarcoma virus-specific complementary DNA. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):481–490. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.481-490.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS L. "Spontaneous" leukemia developing in C3H mice following inoculation in infancy, with AK-leukemic extracts, or AK-embrvos. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 Jan;76(1):27–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabelman N., Waxman S., Smith W., Douglas S. D. Appearance of C-type virus-like particles after co-cultivation of a human tumor-cell line with rat (XC) cells. Int J Cancer. 1975 Sep 15;16(3):355–369. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910160302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher R. E., Gallo R. C. Type C RNA tumor virus isolated from cultured human acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Science. 1975 Jan 31;187(4174):350–353. doi: 10.1126/science.46123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C., Gallagher R. E., Miller N. R., Mondal H., Saxinger W. C., Mayer R. J., Smith R. G., Gillespie D. H. Relationships between components in primate RNA tumor viruses and in the cytoplasm of human leukemic cells: implications to leukemogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):933–961. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C., Gallagher R. E., Wong-Staal F., Aoki T., Markham P. D., Schetters H., Ruscetti F., Valerio M., Walling M. J., O'Keeffe R. T. Isolation and tissue distribution of type-C virus and viral components from a gibbon ape (Hylobates lar) with lymphocytic leukemia. Virology. 1978 Feb;84(2):359–373. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90255-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenisch R. Germ line integration of moloney leukemia virus: effect of homozygosity at the m-mulV locus. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):691–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90269-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan H. S., Goodenow R. S., Epstein A. L., Gartner S., Declève A., Rosenthal P. N. Isolation of a type C RNA virus from an established human histiocytic lymphoma cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2564–2568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami T. G., Buckley P. M. Antigenic studies on gibbon type-C viruses. Transplant Proc. 1974 Jun;6(2):193–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami T. G., Huff S. D., Buckley P. M., Dungworth D. L., Synder S. P., Gilden R. V. C-type virus associated with gibbon lymphosarcoma. Nat New Biol. 1972 Feb 9;235(58):170–171. doi: 10.1038/newbio235170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami T. G., Sun L., McDowell T. S. Infectious primate type-C virus shed by healthy gibbons. Nature. 1977 Aug 4;268(5619):448–450. doi: 10.1038/268448a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami T. G., Theilen G. H., Dungworth D. L., Munn R. J., Beall S. G. "C"-type viral particles in plasma of cats with feline leukemia. Science. 1967 Nov;158(3804):1049–1050. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3804.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister R. M., Melnyk J., Finkelstein J. Z., Adams E. C., Jr, Gardner M. B. Cultivation in vitro of cells derived from a human rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer. 1969 Sep;24(3):520–526. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196909)24:3<520::aid-cncr2820240313>3.0.co;2-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moloney J. B. A virus-induced rhabdomyosarcoma of mice. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1966 Sep;22:139–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nooter K., Aarssen A. M., Bentvelzen P., De Groot F. G., Van Pelt F. G. Isolation of infectious C-type oncornavirus from human leukaemic bone marrow cells. Nature. 1975 Aug 14;256(5518):595–597. doi: 10.1038/256595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panem S., Prochownik E. V., Reale F. R., Kirsten W. H. Isolation of type C virions from a normal human fibroblast strain. Science. 1975 Jul 25;189(4199):297–299. doi: 10.1126/science.49927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks W. P., Scolnick E. M., Noon M. C., Watson C. J., Kawakami T. G. Radioimmunoassay of mammalian type-C polypeptides. IV. Characterization of woolly monkey and gibbon viral antigens. Int J Cancer. 1973 Jul 15;12(1):129–137. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910120114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prensky W. The radioiodination of RNA and DNA to high specific activities. Methods Cell Biol. 1976;13:121–152. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61800-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochownik E. V., Kirsten W. H. Nucleic acid sequences of primate type C viruses in normal and neoplastic human tissues. Nature. 1977 May 12;267(5607):175–177. doi: 10.1038/267175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitz M. S., Jr, Luczak J. C., Gallo R. C. Mapping of related and nonrelated sequences of RNA from wooly monkey virus and gibbon ape leukemia virus. Virology. 1979 Feb;93(1):48–56. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90274-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitz M. S., Jr, wong-Staal F., Haseltine W. A., Kleid D. G., Trainor C. D., Gallagher R. E., Gallo R. C. Gibbon ape leukemia virus-Hall's Island: new strain of gibbon ape leukemia virus. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):395–400. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.395-400.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitz M. S., Miller N. R., Wong-Staal F., Gallagher R. E., Gallo R. C., Gillespie D. H. Primate type-C virus nucleic acid sequences (woolly monkey and baboon types) in tissues from a patient with acute myelogenous leukemia and in viruses isolated from cultured cells of the same patient. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):2113–2117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.2113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel M., Saule S., Lagrou C., Rommens C., Beug H., Graf T., Stehelin D. Three new types of viral oncogene of cellular origin specific for haematopoietic cell transformation. Nature. 1979 Oct 11;281(5731):452–455. doi: 10.1038/281452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STUDIER F. W. SEDIMENTATION STUDIES OF THE SIZE AND SHAPE OF DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Feb;11:373–390. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E. M., Howk R. S., Anisowicz A., Peebles P. T., Scher C. D., Parks W. P. Separation of sarcoma virus-specific and leukemia virus-specific genetic sequences of Moloney sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4650–4654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E. M., Parks W. P., Todaro G. J., Aaronson S. A. Immunological characterization of primate C-type virus reverse transcriptases. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jan 12;235(54):35–40. doi: 10.1038/newbio235035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E. M., Parks W. P., Todaro G. J. Reverse transcriptases of primate viruses as immunological markers. Science. 1972 Sep 22;177(4054):1119–1121. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4054.1119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E. M., Parks W., Kawakami T., Kohne D., Okabe H., Gilden R., Hatanaka M. Primate and murine type-C viral nucleic acid association kinetics: analysis of model systems and natural tissues. J Virol. 1974 Feb;13(2):363–369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.2.363-369.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stehelin D., Guntaka R. V., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Purification of DNA complementary to nucleotide sequences required for neoplastic transformation of fibroblasts by avian sarcoma viruses. J Mol Biol. 1976 Mar 5;101(3):349–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90152-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., Aaronson S. A. Search for antigens and antibodies crossreactive with type C viruses of the woolly monkeys and gibbon ape in animal models and in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1725–1729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun L., Kawakami T. G., Matoba S. I. Genomic stability of gibbon oncornavirus. J Virol. 1978 Dec;28(3):767–771. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.3.767-771.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tereba A., McCarthy B. J. Hybridization of 125I-labeled ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 6;12(23):4675–4679. doi: 10.1021/bi00747a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Huebner R. J. N.A.S. symposium: new evidence as the basis for increased efforts in cancer research. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Apr;69(4):1009–1015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.4.1009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Lieber M. M., Benveniste R. E., Sherr C. J. Infectious primate type C viruses: Three isolates belonging to a new subgroup from the brains of normal gibbons. Virology. 1975 Oct;67(2):335–343. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90435-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronick S. R., Stephenson J. R., Aaronson S. A., Kawakami T. G. Antigenic characterization of type C RNA virus isolates of gibbon apes. J Virol. 1975 Jan;15(1):115–120. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.1.115-120.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troxler D. H., Boyars J. K., Parks W. P., Scolnick E. M. Friend strain of spleen focus-forming virus: a recombinant between mouse type C ecotropic viral sequences and sequences related to xenotropic virus. J Virol. 1977 May;22(2):361–372. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.2.361-372.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALKER P. M., MCLAREN A. SPECIFIC DUPLEX FORMATION IN VITRO OF MAMMALIAN DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jun;12:394–409. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80263-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong-Staal F., Gillespie D., Gallo R. C. Proviral sequences of baboon endogenous type C RNA virus in DNA of human leukaemic tissues. Nature. 1976 Jul 15;262(5565):190–195. doi: 10.1038/262190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong-Staal F., Reitz M. S., Jr, Gallo R. C. Retrovirus sequences in a leukemic gibbon and its contact: evidence for partial provirus in the nonleukemic gibbon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):2032–2036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.2032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


