Abstract
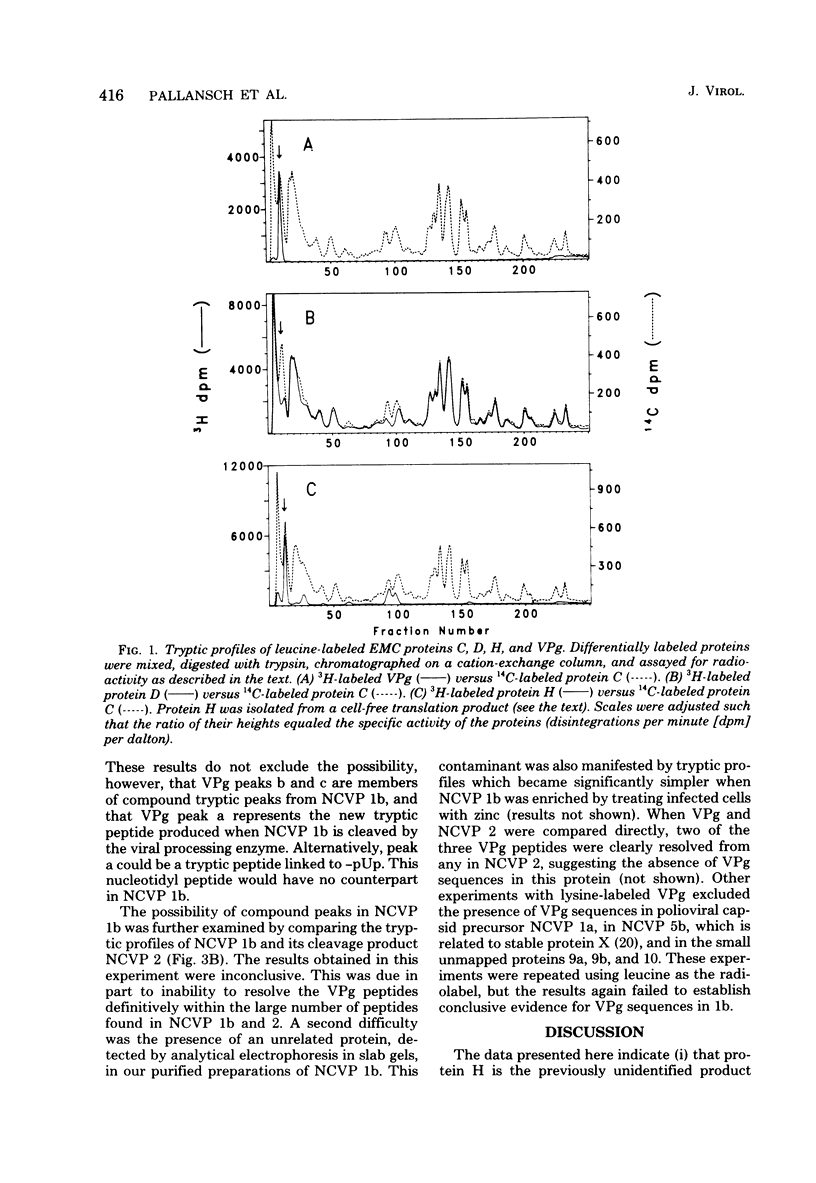
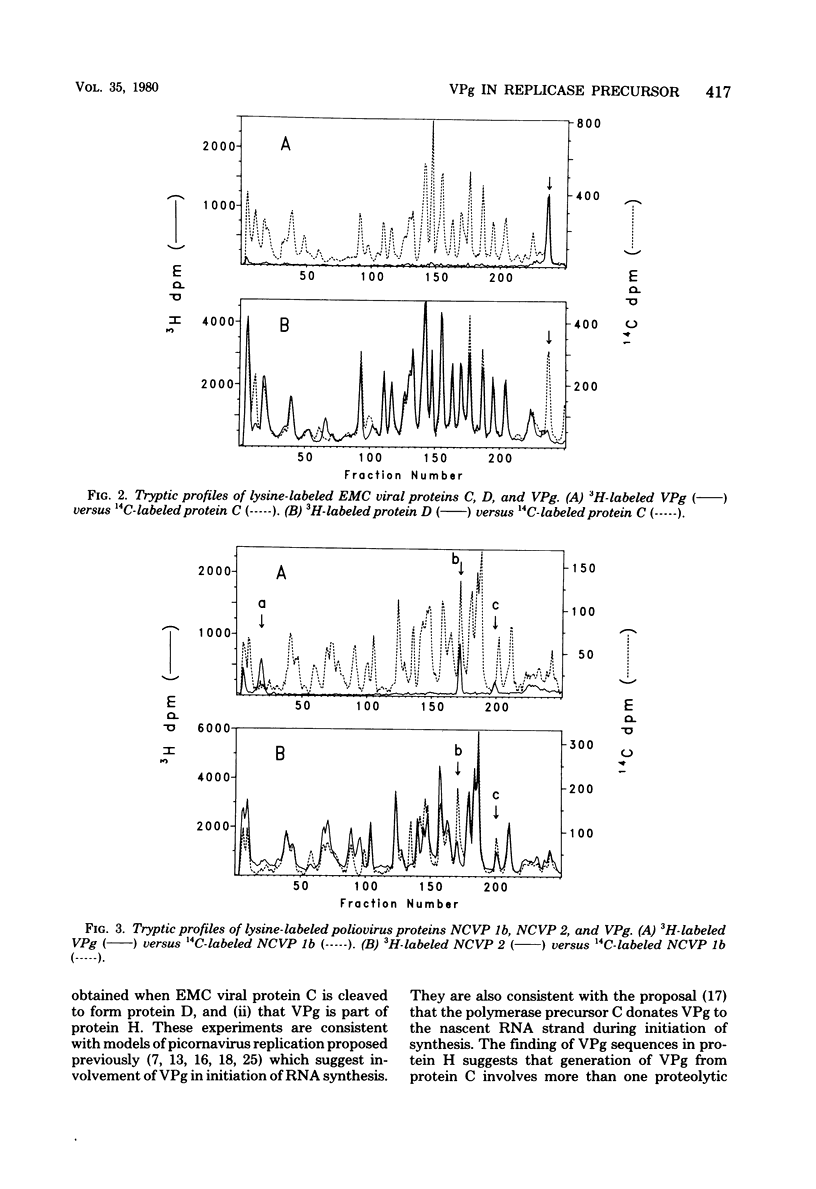
It has previously been shown that the RNA replicase of encephalomyocarditis virus contains two virus-coded proteins, D and E, which are produced in two successive proteolytic steps: (i) C leads to D + ?; and (ii) D leads to p22 + E. It is here shown (i) that virus protein H (molecular weight, 12,000) is the previously unidentified product of the first step and (ii) that VPg, a protein linked covalently to the virion RNA, yields two tryptic peptides found in protein C but not in protein D. The results suggest that VPg is derived by cleavage of protein C and that protein H may be intermediate. Preliminary experiments with VPg sequences in polioviral noncapsid protein 1b, the counterpart of encephalomyocarditis viral protein C, were inconclusive.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Butterworth B. E. A comparison of the virus-specific polypeptides of encephalomyocarditis virus, human rhinovirus-1A, and poliovirus. Virology. 1973 Dec;56(2):439–453. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth B. E., Hall L., Stoltzfus C. M., Rueckert R. R. Virus-specific proteins synthesized in encephalomyocarditis virus-infected HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3083–3087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth B. E., Korant B. D. Characterization of the large picornaviral polypeptides produced in the presence of zinc ion. J Virol. 1974 Aug;14(2):282–291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.2.282-291.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth B. E., Rueckert R. R. Gene order of encephalomyocarditis virus as determined by studies with pactamycin. J Virol. 1972 May;9(5):823–828. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.5.823-828.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P. D., Steiner-Pryor A., Wright P. J. A proposed regulator for poliovirus: the equestron. Intervirology. 1973;1(1):1–10. doi: 10.1159/000148826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta A., Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Poliovirus replicase: a soluble enzyme able to initiate copying of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2679–2683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Petterson R. F., Ambros V., Hewlett N. J., Baltimore D. Covalent linkage of a protein to a defined nucleotide sequence at the 5'-terminus of virion and replicative intermediate RNAs of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):961–965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golini F., Nomoto A., Wimmer E. The genome-linked protein of picornaviruses. IV. Difference in the VPg's of encephalomyocarditis virus and poliovirus as evidence that the genome-linked proteins are virus-coded. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):112–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90045-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall L., Rueckert R. R. Infection of mouse fibroblasts by cardioviruses: premature uncoating and its prevention by elevated pH and magnesium chloride. Virology. 1971 Jan;43(1):152–165. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby D. E., Roberts W. K. Encephalomyocarditis virus RNA. III. Presence of a genome-associated protein. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):413–415. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.413-415.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries S., Knauert F., Ehrenfeld E. Capsid protein precursor is one of two initiated products of translation of poliovirus RNA in vitro. J Virol. 1979 May;30(2):481–488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.2.481-488.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kew O. M., Pallansch M. A., Omilianowski D. R., Rueckert R. R. Changes in three of the four coat proteins of oral polio vaccine strain derived from type 1 poliovirus. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):256–263. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.256-263.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. F., Nomoto A., Detjen B. M., Wimmer E. A protein covalently linked to poliovirus genome RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):59–63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor S. Evidence for the existence of protomers in the assembly of encephalomyocarditis virus. J Virol. 1975 May;15(5):1107–1120. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.5.1107-1120.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medappa K. C., McLean C., Rueckert R. R. On the structure of rhinovirus 1A. Virology. 1971 May;44(2):259–270. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90258-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Detjen B., Pozzatti R., Wimmer E. The location of the polio genome protein in viral RNAs and its implication for RNA synthesis. Nature. 1977 Jul 21;268(5617):208–213. doi: 10.1038/268208a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmenberg A. C., Pallansch M. A., Rueckert R. R. Protease required for processing picornaviral coat protein resides in the viral replicase gene. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):770–778. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.770-778.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson R. F., Flanegan J. B., Rose J. K., Baltimore D. 5'-Terminal nucleotide sequences of polio virus polyribosomal RNA and virion RNA are identical. Nature. 1977 Jul 21;268(5617):270–272. doi: 10.1038/268270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberg P. G., Harris T. J., Nomoto A., Wimmer E. O4-(5'-uridylyl)tyrosine is the bond between the genome-linked protein and the RNA of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4868–4872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sangar D. V., Rowlands D. J., Harris T. J., Brown F. Protein covalently linked to foot-and-mouth disease virus RNA. Nature. 1977 Aug 18;268(5621):648–650. doi: 10.1038/268648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih D. S., Shih C. T., Kew O., Pallansch M., Rueckert R., Kaesberg P. Cell-free synthesis and processing of the proteins of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5807–5811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih D. S., Shih C. T., Zimmern D., Rueckert R. R., Kaesberg P. Translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA in reticulocyte lysates: kinetic analysis of the formation of virion proteins and a protein required for processing. J Virol. 1979 May;30(2):472–480. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.2.472-480.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers D. F., Maizel J. V., Jr, Darnell J. E., Jr Evidence for virus-specific noncapsid proteins in poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Aug;54(2):505–513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


