Abstract
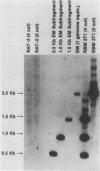
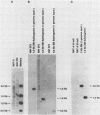
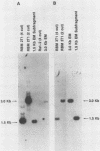
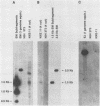
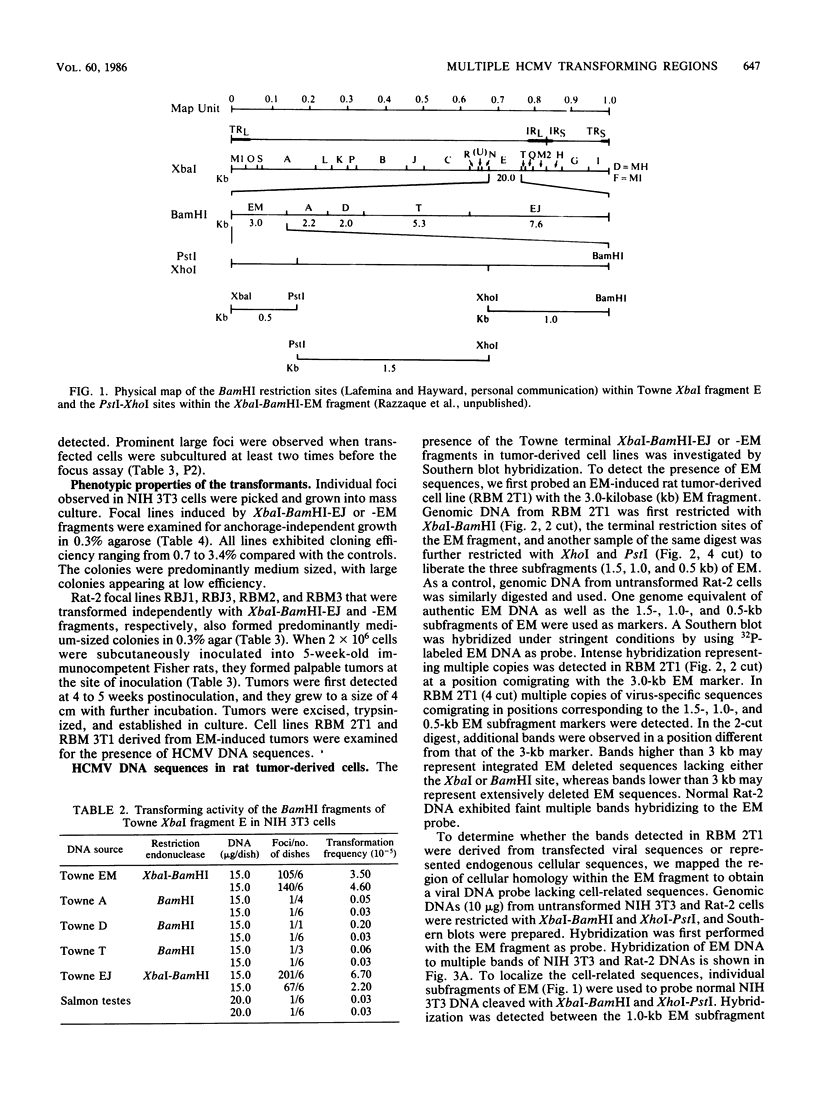
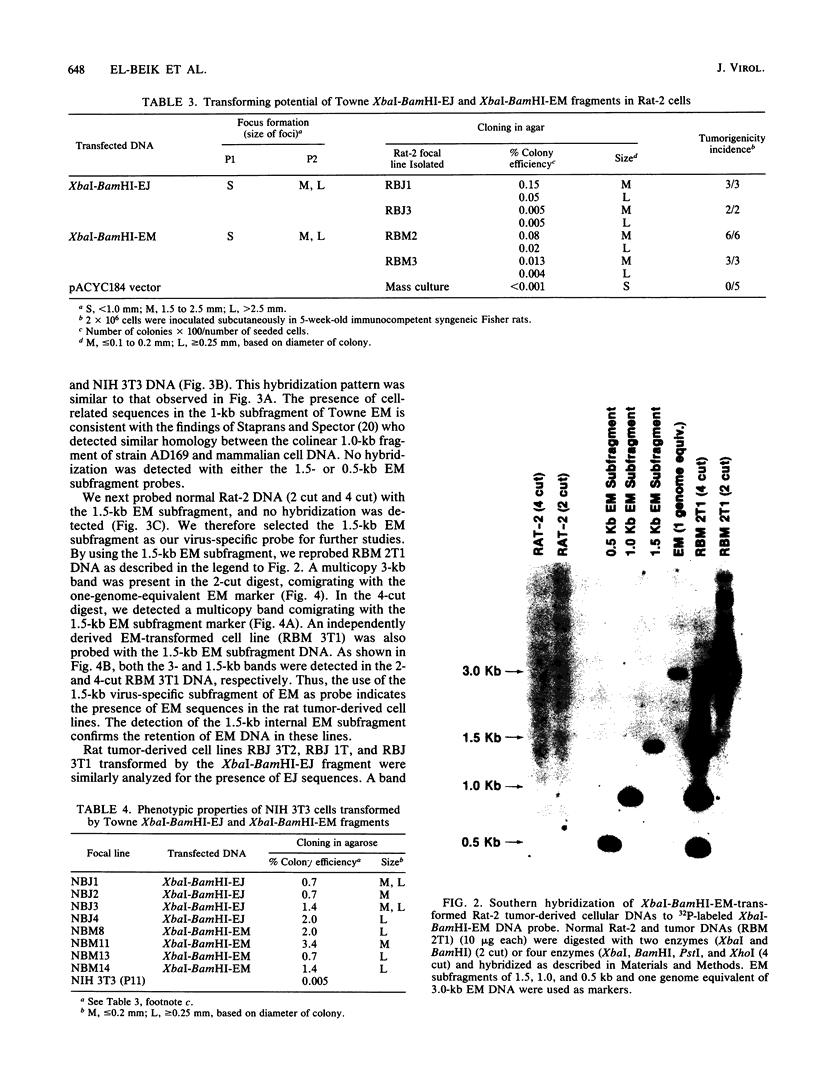
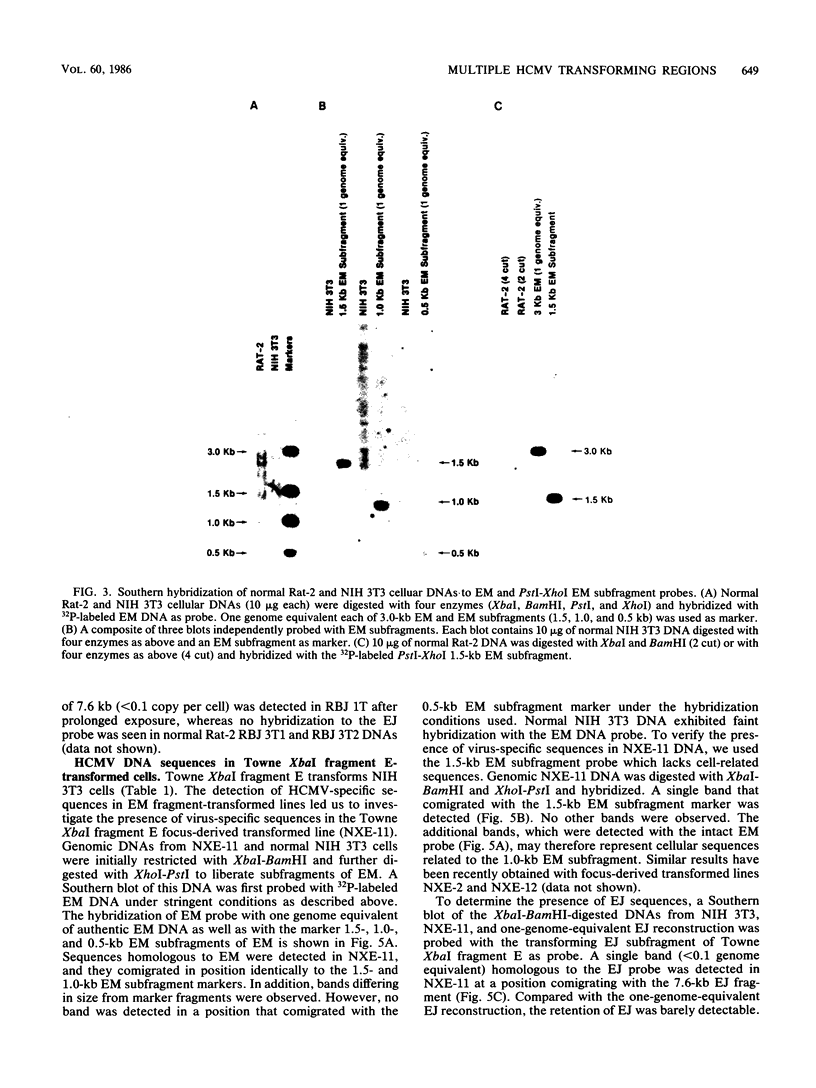
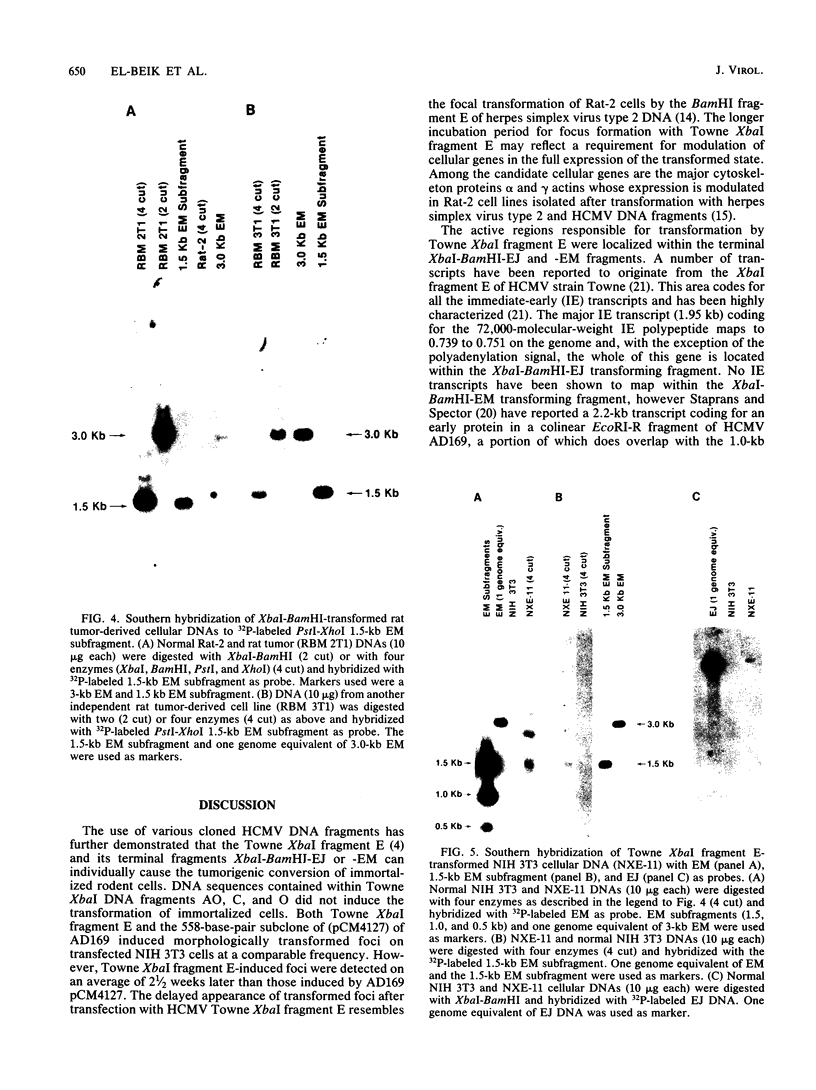
The transforming (focus forming) activity of defined cloned DNA fragments from human cytomegalovirus Towne and AD169 was carried out in immortalized rodent cells. The frequency of focus formation in NIH 3T3 cells by Towne XbaI fragment E was 80- to 100-fold higher than that observed with Towne XbaI fragments AO, O, C, or carrier DNA alone but was similar to that observed with pCM4127, a transforming fragment from HCMV AD169 (J. A. Nelson, B. Fleckenstein, D. A. Galloway, and J. K. McDougall, J. Virol. 43:83-91, 1982; J. A. Nelson, B. Fleckenstein, G. Jahn, D. A. Galloway, and J. K. McDougall, J. Virol. 49:109-115, 1984). Foci were first detected in Towne XbaI fragment E-transfected NIH 3T3 cells at 5 to 6 weeks posttransfection, whereas foci were detected at 2 to 3 weeks after transfection with AD169 pCM4127. Digestion of Towne XbaI fragment E with BamHI did not significantly reduce its focus-forming activity. When BamHI subclones of Towne XbaI fragment E were assayed individually for focus formation in NIH 3T3 and Rat-2 cells, transforming activity was localized within each terminal fragment (EJ and EM). Foci induced by EJ or EM DNA alone were smaller compared with those induced by Towne XbaI fragment E. Isolated focal lines exhibited growth in soft agar and were tumorigenic in immunocompetent syngeneic animals. High-molecular-weight DNAs from transformed and tumor-derived lines were analyzed by Southern blot hybridization with intact EM and a 1.5-kilobase subfragment lacking cell-related sequences. Virus-specific EM sequences were detected at less than one copy per cell in Towne XbaI fragment E-transformed NIH 3T3 cells and at multiple copies in rat tumor-derived cell lines. In contrast, virus-specific EJ sequences were barely detected in EJ-transformed and tumor-derived lines with intact EJ as probe.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrecht T., Rapp F. Malignant transformation of hamster embryo fibroblasts following exposure to ultraviolet-irradiated human cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1973 Sep;55(1):53–61. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(73)81007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clanton D. J., Jariwalla R. J., Kress C., Rosenthal L. J. Neoplastic transformation by a cloned human cytomegalovirus DNA fragment uniquely homologous to one of the transforming regions of herpes simplex virus type 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3826–3830. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew W. L., Mintz L., Miner R. C., Sands M., Ketterer B. Prevalence of cytomegalovirus infection in homosexual men. J Infect Dis. 1981 Feb;143(2):188–192. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.2.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway D. A., Nelson J. A., McDougall J. K. Small fragments of herpesvirus DNA with transforming activity contain insertion sequence-like structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4736–4740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geder L., Sanford E. J., Rohner T. J., Rapp F. Cytomegalovirus and cancer of the prostate: in vitro transformation of human cells. Cancer Treat Rep. 1977 Mar-Apr;61(2):139–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giraldo G., Beth E., Henle W., Henle G., Mike V., Safai B., Huraux J. M., McHardy J., deThé G. Antibody patterns to herpesviruses in Kaposi's sarcoma. II. Serological association of American Kaposi's sarcoma with cytomegalovirus. Int J Cancer. 1978 Aug 15;22(2):126–131. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910220204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giraldo G., Beth E., Huang E. S. Kaposi's sarcoma and its relationship to cytomegalovirus (CMNV). III. CMV DNA and CMV early antigens in Kaposi's sarcoma. Int J Cancer. 1980 Jul 15;26(1):23–29. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910260105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. S., Roche J. K. Cytomegalovirus D.N.A. and adenocarcinoma of the colon: Evidence for latent viral infection. Lancet. 1978 May 6;1(8071):957–960. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90248-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jariwalla R. J., Aurelian L., Ts'o P. O. Immortalization and neoplastic transformation of normal diploid cells by defined cloned DNA fragments of herpes simplex virus type 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5902–5906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jariwalla R. J., Aurelian L., Ts'o P. O. Tumorigenic transformation induced by a specific fragment of DNA from herpes simplex virus type 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2279–2283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jariwalla R. J., Tanczos B., Jones C., Ortiz J., Salimi-Lopez S. DNA amplification and neoplastic transformation mediated by a herpes simplex DNA fragment containing cell-related sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1738–1742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavitt J., Gunning P., Kedes L., Jariwalla R. Smooth muscle alpha-action is a transformation-sensitive marker for mouse NIH 3T3 and Rat-2 cells. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):840–842. doi: 10.1038/316840a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. A., Fleckenstein B., Galloway D. A., McDougall J. K. Transformation of NIH 3T3 cells with cloned fragments of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):83–91. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.83-91.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. A., Fleckenstein B., Jahn G., Galloway D. A., McDougall J. K. Structure of the transforming region of human cytomegalovirus AD169. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):109–115. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.109-115.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacsa A. S., Kummerländer L., Pejtsik B., Pali K. Herpesvirus antibodies and antigens in patients with cervical anaplasia and in controls. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Oct;55(4):775–781. doi: 10.1093/jnci/55.4.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staprans S. I., Spector D. H. 2.2-kilobase class of early transcripts encoded by cell-related sequences in human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):591–602. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.591-602.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F., Thomsen D. R., Stenberg R. M., Goldstein L. C. Organization and expression of the immediate early genes of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):1–14. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.1-14.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen D. R., Stinski M. F. Cloning of the human cytomegalovirus genome as endonuclease XbaI fragments. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90077-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]