Abstract
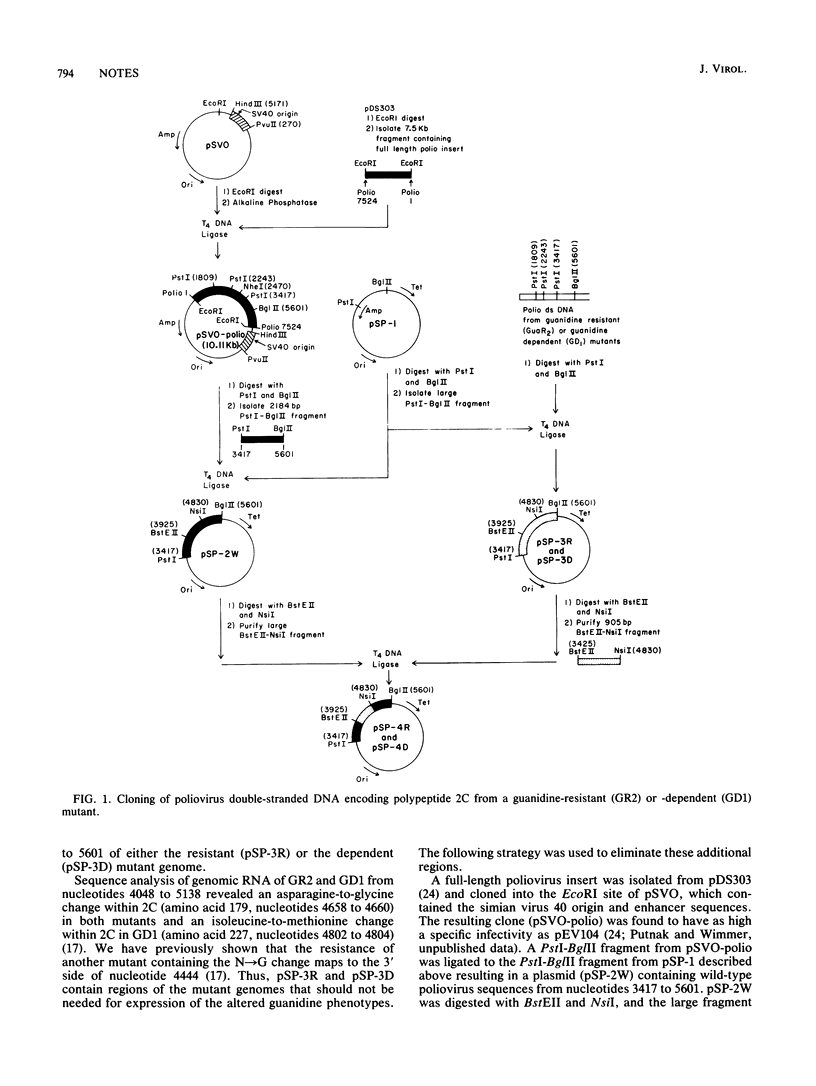
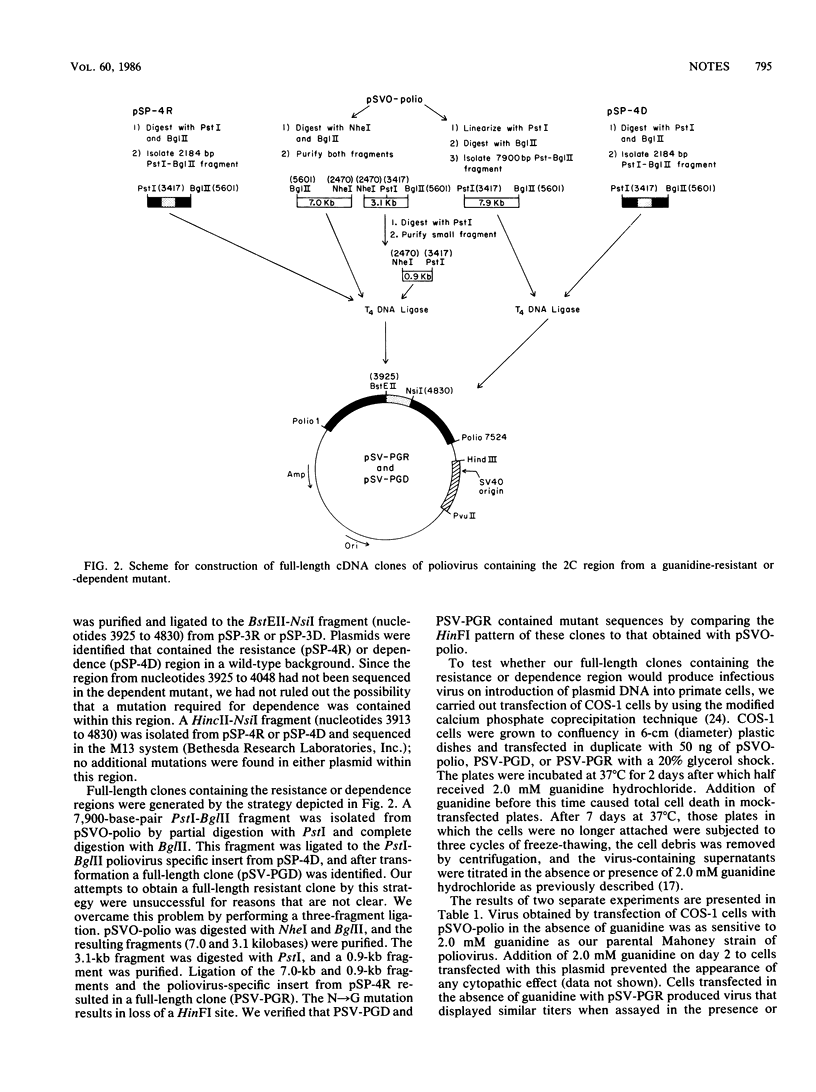
cDNA fragments representing the region in polypeptide 2C containing mutations in a guanidine-resistant or -dependent mutant were cloned into the wild-type background of an infectious clone. Transfection of COS-1 cells with these plasmids yielded viruses that were either completely resistant to 2.0 mM guanidine hydrochloride or dependent on this concentration of drug for growth.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson-Sillman K., Bartal S., Tershak D. R. Guanidine-resistant poliovirus mutants produce modified 37-kilodalton proteins. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):922–928. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.922-928.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Sonenberg N., Baltimore D. Poliovirus mutant that does not selectively inhibit host cell protein synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2913–2923. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROWTHER D., MELNICK J. L. Studies of the inhibitory action of guanidine on poliovirus multiplication in cell cultures. Virology. 1961 Sep;15:65–74. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., Tamm I. Action of guanidine on the replication of poliovirus RNA. Virology. 1968 Jul;35(3):408–417. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90219-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., Tamm I. The role of cytoplasmic membranes in poliovirus biosynthesis. Virology. 1970 Sep;42(1):100–111. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90242-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Leibowitz J., Diamond D. C., Bonin J., Wimmer E. Recombinants of Mahoney and Sabin strain poliovirus type 1: analysis of in vitro phenotypic markers and evidence that resistance to guanidine maps in the nonstructural proteins. Virology. 1984 Aug;137(1):74–85. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Balitmore D. Initiation of polyribosome formation in poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 14;47(3):275–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90302-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Adler C., Wimmer E. Structure and expression of the picornavirus genome. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;354:183–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb27967.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Semler B. L., Rothberg P. G., Larsen G. R., Adler C. J., Dorner A. J., Emini E. A., Hanecak R., Lee J. J., van der Werf S. Primary structure, gene organization and polypeptide expression of poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):547–553. doi: 10.1038/291547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara M., Omata T., Kameda A., Semler B. L., Itoh H., Wimmer E., Nomoto A. In vitro phenotypic markers of a poliovirus recombinant constructed from infectious cDNA clones of the neurovirulent Mahoney strain and the attenuated Sabin 1 strain. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):786–792. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.786-792.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LODDO B., FERRARI W., BROTZU G., SPANEDDA A. In vitro inhibition of infectivity of polio viruses by guanidine. Nature. 1962 Jan 6;193:97–98. doi: 10.1038/193097a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble J., Levintow L. Dynamics of poliovirus-specific RNA synthesis and the effects of inhibitors of virus replication. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):634–642. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90208-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Toyoda H., Imura N., Noguchi S., Sekiya T. Restriction map of double-stranded DNA copy synthesized from poliovirus Sabin 1 RNA. J Biochem. 1982 May;91(5):1593–1600. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. E., Diamond D. C., Emini E. A., Wimmer E. Guanidine-selected mutants of poliovirus: mapping of point mutations to polypeptide 2C. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):638–646. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.638-646.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnak J. R., Phillips B. A. Picornaviral structure and assembly. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Jun;45(2):287–315. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.2.287-315.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIGHTSEL W. A., DICE J. R., McALPINE R. J., TIMM E. A., McLEAN I. W., Jr, DIXON G. J., SCHABEL F. M., Jr Antiviral effect of guanidine. Science. 1961 Aug 25;134(3478):558–559. doi: 10.1126/science.134.3478.558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Baltimore D. Cloned poliovirus complementary DNA is infectious in mammalian cells. Science. 1981 Nov 20;214(4523):916–919. doi: 10.1126/science.6272391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rueckert R. R., Wimmer E. Systematic nomenclature of picornavirus proteins. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):957–959. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.957-959.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P., Bernstein H. D., Baltimore D. A poliovirus temperature-sensitive RNA synthesis mutant located in a noncoding region of the genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):571–575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders K., King A. M. Guanidine-resistant mutants of aphthovirus induce the synthesis of an altered nonstructural polypeptide, P34. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):389–394. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.389-394.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semler B. L., Dorner A. J., Wimmer E. Production of infectious poliovirus from cloned cDNA is dramatically increased by SV40 transcription and replication signals. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 25;12(12):5123–5141. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.12.5123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semler B. L., Johnson V. H., Tracy S. A chimeric plasmid from cDNA clones of poliovirus and coxsackievirus produces a recombinant virus that is temperature-sensitive. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1777–1781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanway G., Hughes P. J., Westrop G. D., Evans D. M., Dunn G., Minor P. D., Schild G. C., Almond J. W. Construction of poliovirus intertypic recombinants by use of cDNA. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1187–1190. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1187-1190.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tershak D. R. Inhibition of poliovirus polymerase by guanidine in vitro. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):313–318. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.313-318.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


