Abstract
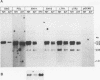
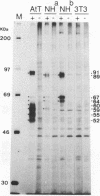
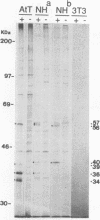
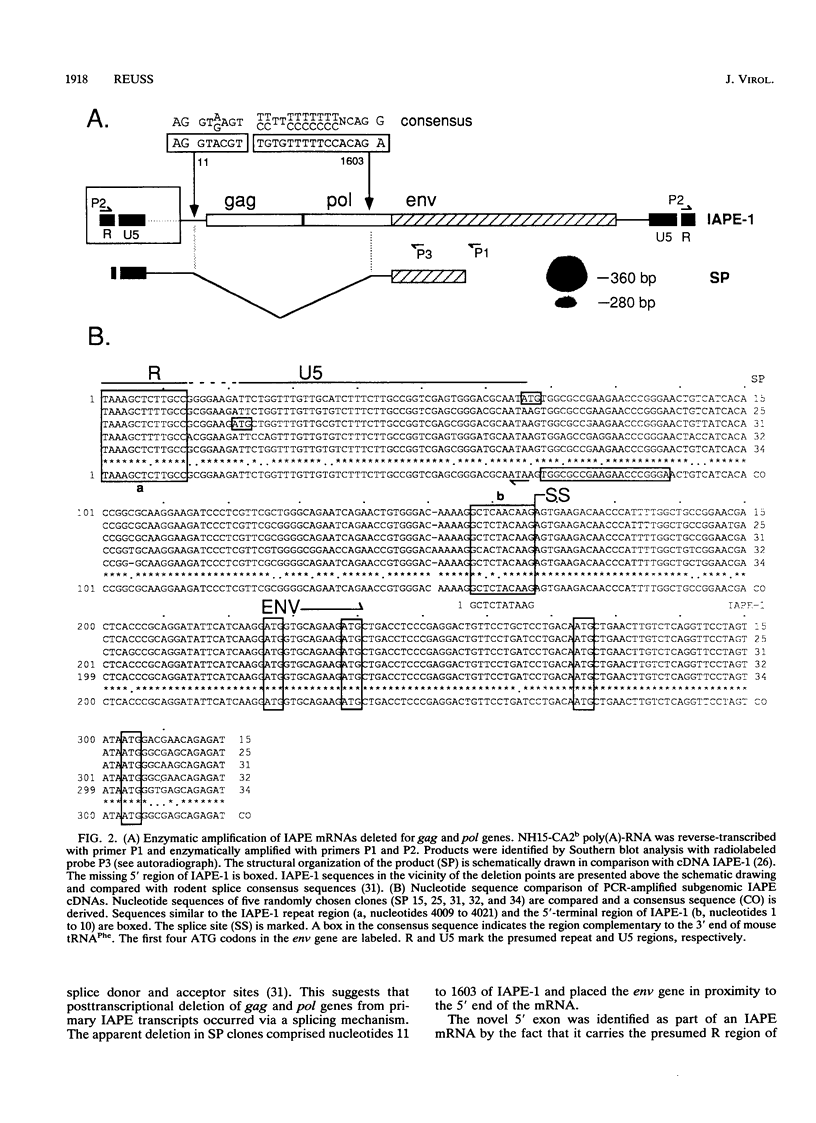
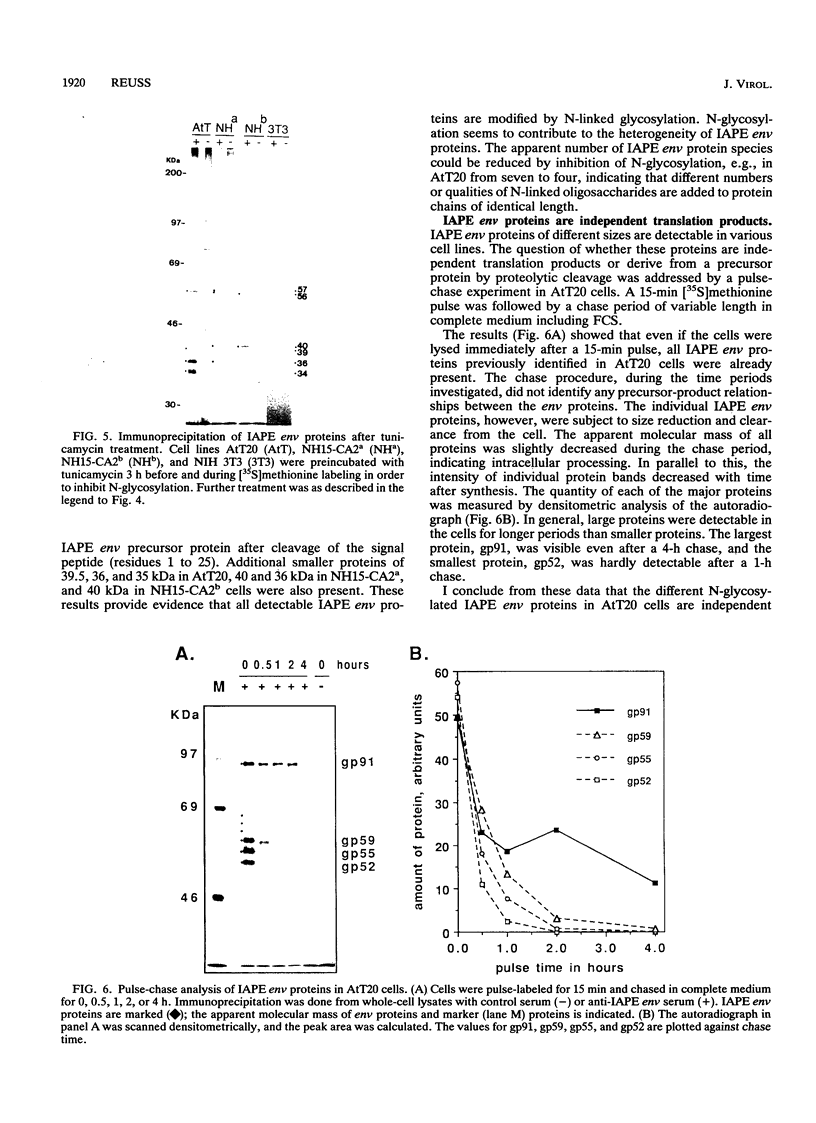
Intracisternal A-particle (IAP) retrotransposons of rodents express gag and pol proteins for assembly of intracellular viruslike particles but lack an env gene. The recently described IAP-related family of retroviral elements contains a reading frame with close resemblance to retroviral env genes (IAPEs) (F. U. Reuss and H. C. Schaller, J. Virol. 65:5702-5709, 1991). I now report the analysis of cellular IAPE mRNAs and detection of IAPE env proteins. IAPE elements are transcribed in cell lines NH15-CA2 and AtT20. Four major transcripts of 4.2, 3.9, 2.8, and 1.3 kb are detected and characterized by probes specific for defined regions of the cloned IAPE-1 cDNA. The 2.8-kb mRNA is shown to lack gag and pol genes but comprises an env gene and U3 region, as expected for a subgenomic env mRNA. Polymerase chain reaction amplification and cloning of such mRNAs confirmed the absence of gag and pol genes 5' from the env gene and implicates env mRNA generation by a splicing event. A polyclonal anti-IAPE env antiserum, raised against a bacterial IAPE-env fusion protein, specifically detects N-glycosylated env proteins of 91 kDa or less in cell lines positive for IAPE mRNA. IAPE env proteins of different sizes represent independent translation products. After inhibition of N-glycosylation, env proteins in the size predicted from the env gene sequence or smaller are present. These results provide evidence that putative IAPE env proteins are synthesized in vivo. Envelope protein expression by an IAP-related retroviral element identifies IAPEs as a possible missing link between IAP retrotransposons and retroviruses.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernard H. U., Remaut E., Hershfield M. V., Das H. K., Helinski D. R., Yanofsky C., Franklin N. Construction of plasmid cloning vehicles that promote gene expression from the bacteriophage lambda pL promoter. Gene. 1979 Jan;5(1):59–76. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Corces V. G. Transcription and reverse transcription of retrotransposons. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1989;43:403–434. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.43.100189.002155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN A. I., FURTH J., BUFFETT R. F. Histologic and physiologic characteristics of hormone-secreting transplantable adrenal tumors in mice and rats. Am J Pathol. 1957 Jul-Aug;33(4):631–651. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson C., Atterwill M. Structure and processing of the mouse mammary tumor virus glycoprotein precursor pr73env. J Virol. 1980 Aug;35(2):349–361. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.2.349-361.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson C., Puma J. P., Nandi S. Identification of a precursor protein to the major glycoproteins of mouse mammary tumor virus. J Virol. 1975 Jan;17(1):275–282. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.1.275-282.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison J. R., Holland J. J. Carbohydrate composition of the membrane glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus grown in four mammalian cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4011–4014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felleisen R., Klinkert M. Q., Beck E. Schistosoma mansoni: localisation of antigenic regions on the 31 kilodalton diagnostic protein. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Jul;30(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90128-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ficht T. A., Chang L. J., Stoltzfus C. M. Avian sarcoma virus gag and env gene structural protein precursors contain a common amino-terminal sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):362–366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauss D. H., Sprinzl M. Compilation of tRNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 11;11(1):r1–53. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heumann R., Ocalan M., Kachel V., Hamprecht B. Clonal hybrid cell lines expressing cholinergic and adrenergic properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4674–4677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter E., Swanstrom R. Retrovirus envelope glycoproteins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;157:187–253. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75218-6_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz R. A., Skalka A. M. Control of retroviral RNA splicing through maintenance of suboptimal processing signals. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):696–704. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuff E. L., Fewell J. W. Intracisternal A-particle gene expression in normal mouse thymus tissue: gene products and strain-related variability. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):474–483. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuff E. L., Lueders K. K. The intracisternal A-particle gene family: structure and functional aspects. Adv Cancer Res. 1988;51:183–276. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60223-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majors J. E., Varmus H. E. Nucleotide sequencing of an apparent proviral copy of env mRNA defines determinants of expression of the mouse mammary tumor virus env gene. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):495–504. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.495-504.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBurney M. W., Rogers B. J. Isolation of male embryonal carcinoma cells and their chromosome replication patterns. Dev Biol. 1982 Feb;89(2):503–508. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90338-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal J. S., Kennedy M. S., Sligh J. M., Cort S. P., Mawle A., Nicholson J. K. Binding of HTLV-III/LAV to T4+ T cells by a complex of the 110K viral protein and the T4 molecule. Science. 1986 Jan 24;231(4736):382–385. doi: 10.1126/science.3001934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mietz J. A., Grossman Z., Lueders K. K., Kuff E. L. Nucleotide sequence of a complete mouse intracisternal A-particle genome: relationship to known aspects of particle assembly and function. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3020–3029. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3020-3029.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R., Dixon M., Smith R., Peters G., Dickson C. Complete nucleotide sequence of a milk-transmitted mouse mammary tumor virus: two frameshift suppression events are required for translation of gag and pol. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):480–490. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.480-490.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K., Compans R. W. Host cell- and virus strain-dependent differences in oligosaccharides of hemagglutinin glycoproteins of influenza A viruses. Virology. 1979 May;95(1):8–23. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90397-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono M., Toh H., Miyata T., Awaya T. Nucleotide sequence of the Syrian hamster intracisternal A-particle gene: close evolutionary relationship of type A particle gene to types B and D oncovirus genes. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):387–394. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.387-394.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Harvey R., Smith A. E. The size of Rous sarcoma virus mRNAs active in cell-free translation. Nature. 1977 Aug 4;268(5619):416–420. doi: 10.1038/268416a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuss F. U., Schaller H. C. cDNA sequence and genomic characterization of intracisternal A-particle-related retroviral elements containing an envelope gene. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5702–5709. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5702-5709.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmons B., Knedlitschek G., Kennedy N., Groner B., Ponta H. The endogenous mouse mammary tumour virus locus Mtv-8 contains a defective envelope gene. Virus Res. 1986 Jun;4(4):377–389. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(86)90084-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schloss P., Hermans-Borgmeyer I., Betz H., Gundelfinger E. D. Neuronal acetylcholine receptors in Drosophila: the ARD protein is a component of a high-affinity alpha-bungarotoxin binding complex. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2889–2894. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03146.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M. B., Senapathy P. RNA splice junctions of different classes of eukaryotes: sequence statistics and functional implications in gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7155–7174. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K., Luzio J. P. Construction of a new family of high efficiency bacterial expression vectors: identification of cDNA clones coding for human liver proteins. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1429–1434. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B. S., Engleman E. G. Intracellular processing of the gp160 HIV-1 envelope precursor. Endoproteolytic cleavage occurs in a cis or medial compartment of the Golgi complex. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2640–2649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B. S., Gowda S. D., Lifson J. D., Penhallow R. C., Bensch K. G., Engleman E. G. pH-independent HIV entry into CD4-positive T cells via virus envelope fusion to the plasma membrane. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):659–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90542-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltzfus C. M. Synthesis and processing of avian sarcoma retrovirus RNA. Adv Virus Res. 1988;35:1–38. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60707-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tooze J., Tooze S., Haisma H., Hilgers J. AtT20 pituitary tumour cells contain mouse mammary tumour virus and intracisternal A-type particles in addition to murine leukemia virus. Eur J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;39(1):224–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willey R. L., Bonifacino J. S., Potts B. J., Martin M. A., Klausner R. D. Biosynthesis, cleavage, and degradation of the human immunodeficiency virus 1 envelope glycoprotein gp160. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9580–9584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ooyen A. J., Michalides R. J., Nusse R. Structural analysis of a 1.7-kilobase mouse mammary tumor virus-specific RNA. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):362–370. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.362-370.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]