Abstract
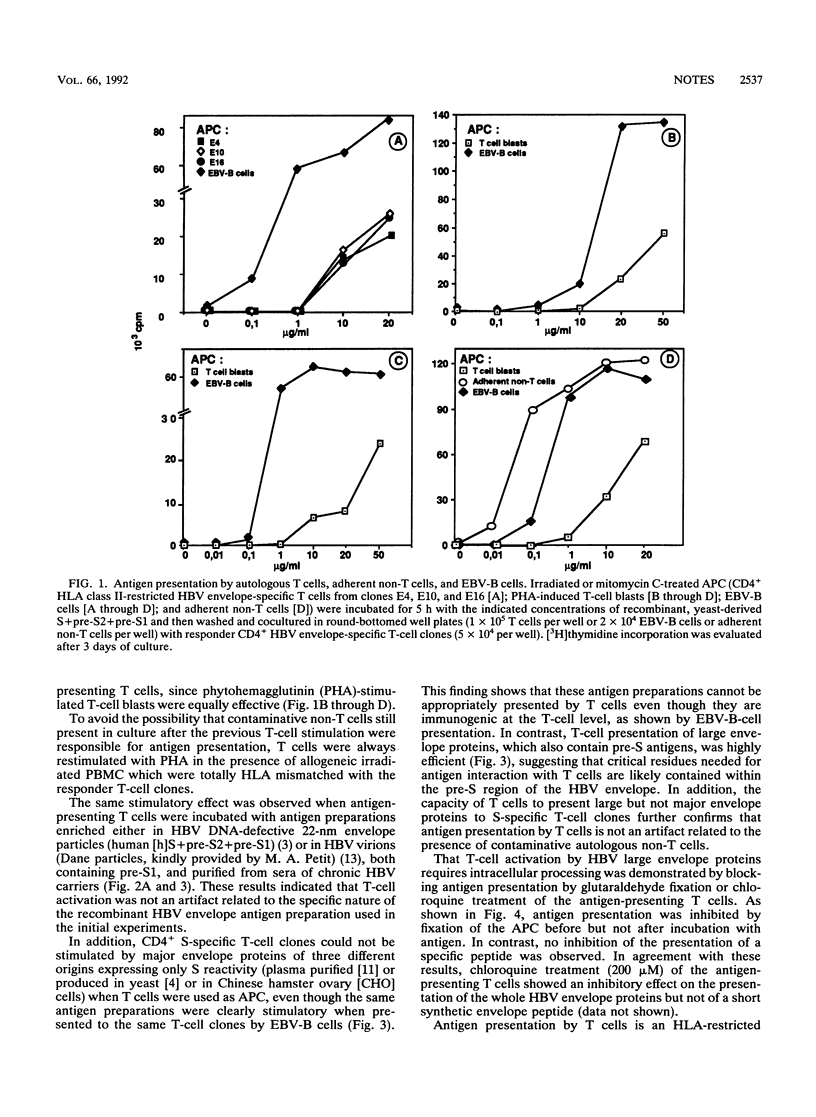
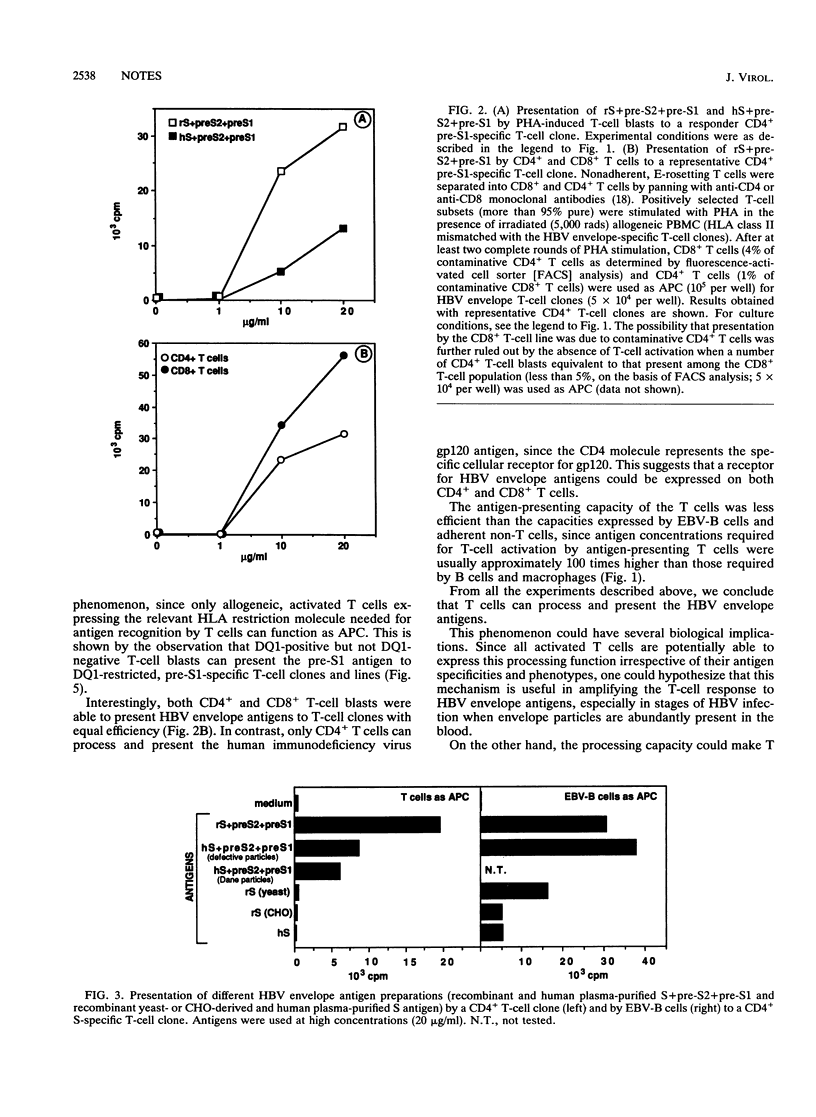
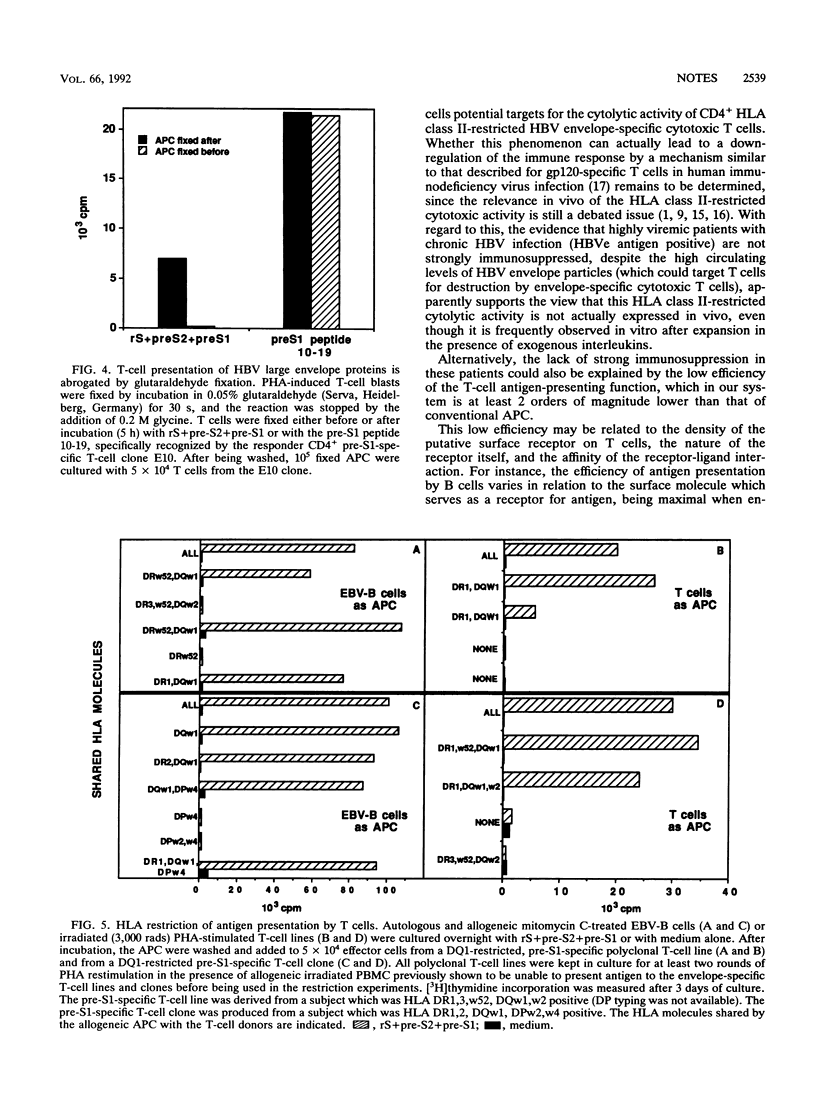
Processing and presentation by T cells appear to be limited to antigens that can directly interact with the T-cell surface, thereby overcoming the T-cell inefficiency in antigen capture and internalization. Our study provides evidence that the hepatitis B virus (HBV) envelope proteins can also be efficiently processed and presented by CD4+ and CD8+ T cells to other T cells in a human leukocyte antigen class II-restricted fashion. This phenomenon suggests a receptor-mediated interaction between T cells and the HBV envelope and defines a system that can, we hope, be exploited for the identification of the receptor binding site within the HBV envelope and for the characterization of the putative cellular HBV receptor.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Del Prete G. F., De Carli M., Ricci M., Romagnani S. Helper activity for immunoglobulin synthesis of T helper type 1 (Th1) and Th2 human T cell clones: the help of Th1 clones is limited by their cytolytic capacity. J Exp Med. 1991 Oct 1;174(4):809–813. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.4.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari C., Penna A., Bertoletti A., Cavalli A., Valli A., Schianchi C., Fiaccadori F. The preS1 antigen of hepatitis B virus is highly immunogenic at the T cell level in man. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1314–1319. doi: 10.1172/JCI114299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari C., Penna A., Sansoni P., Giuberti T., Neri T. M., Chisari F. V., Fiaccadori F. Selective sensitization of peripheral blood T lymphocytes to hepatitis B core antigen in patients with chronic active hepatitis type B. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Dec;66(3):497–506. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heermann K. H., Goldmann U., Schwartz W., Seyffarth T., Baumgarten H., Gerlich W. H. Large surface proteins of hepatitis B virus containing the pre-s sequence. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):396–402. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.396-402.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kniskern P. J., Hagopian A., Burke P., Dunn N., Emini E. A., Miller W. J., Yamazaki S., Ellis R. W. A candidate vaccine for hepatitis B containing the complete viral surface protein. Hepatology. 1988 Jan-Feb;8(1):82–87. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korba B. E., Wells F., Tennant B. C., Yoakum G. H., Purcell R. H., Gerin J. L. Hepadnavirus infection of peripheral blood lymphocytes in vivo: woodchuck and chimpanzee models of viral hepatitis. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.1-8.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzavecchia A. Antigen uptake and accumulation in antigen-specific B cells. Immunol Rev. 1987 Oct;99:39–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb01171.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzavecchia A. Is suppression a function of class II--restricted cytotoxic T cells? Immunol Today. 1989 May;10(5):157–159. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90172-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzavecchia A., Roosnek E., Gregory T., Berman P., Abrignani S. T cells can present antigens such as HIV gp120 targeted to their own surface molecules. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):530–532. doi: 10.1038/334530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milich D. R., Peterson D. L., Leroux-Roels G. G., Lerner R. A., Chisari F. V. Genetic regulation of the immune response to hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg). VI. T cell fine specificity. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):4203–4211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Kent S. B., Strick N., Parker K. Identification and chemical synthesis of a host cell receptor binding site on hepatitis B virus. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90663-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit M. A., Capel F., Pillot J. Demonstration of a firm association between hepatitis B surface antigen proteins bearing polymerized human albumin binding sites and core-specific determinants in serum hepatitis B viral particles. Mol Immunol. 1985 Nov;22(11):1279–1287. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(85)90047-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontisso P., Petit M. A., Bankowski M. J., Peeples M. E. Human liver plasma membranes contain receptors for the hepatitis B virus pre-S1 region and, via polymerized human serum albumin, for the pre-S2 region. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):1981–1988. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.1981-1988.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romagnani S. Human TH1 and TH2 subsets: doubt no more. Immunol Today. 1991 Aug;12(8):256–257. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90120-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott P., Kaufmann S. H. The role of T-cell subsets and cytokines in the regulation of infection. Immunol Today. 1991 Oct;12(10):346–348. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90063-Y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siliciano R. F., Lawton T., Knall C., Karr R. W., Berman P., Gregory T., Reinherz E. L. Analysis of host-virus interactions in AIDS with anti-gp120 T cell clones: effect of HIV sequence variation and a mechanism for CD4+ cell depletion. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):561–575. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki L. J., Sato V. L. "Panning" for lymphocytes: a method for cell selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2844–2848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


