Abstract
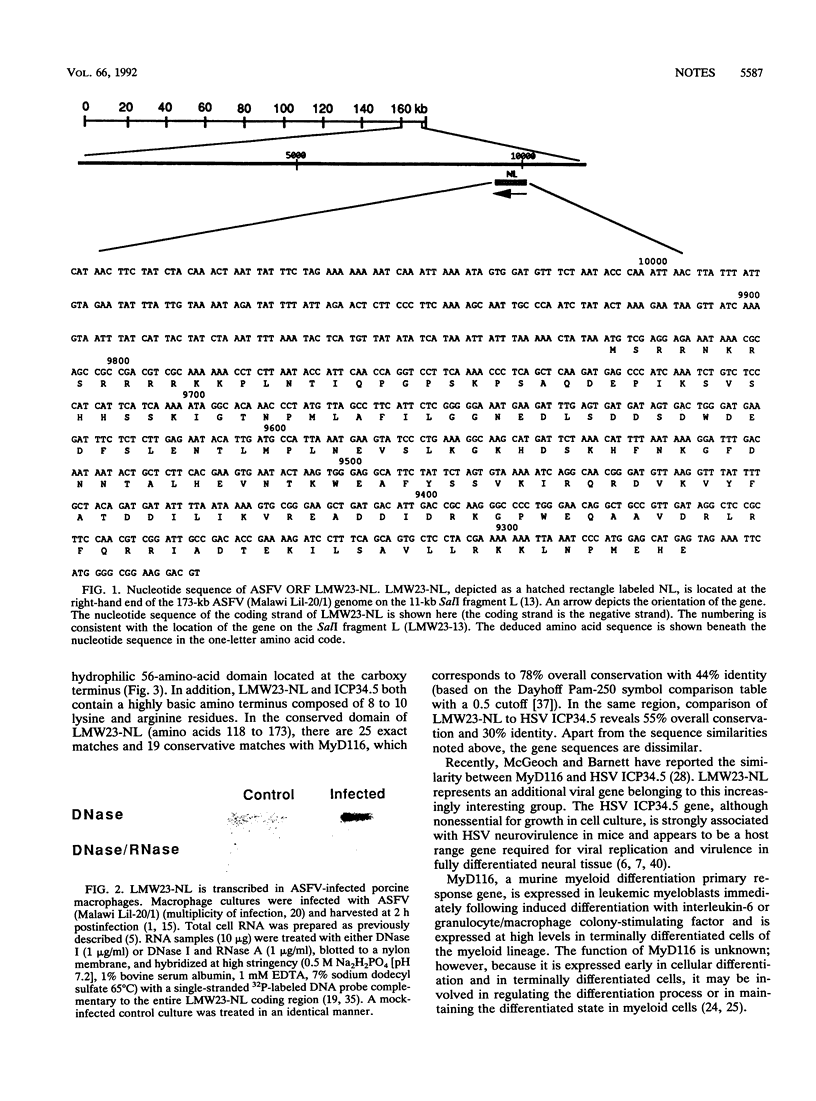
Here we describe an open reading frame (LMW23-NL) in the African swine fever virus genome that possesses striking similarity to a murine myeloid differentiation primary response gene (MyD116) and the neurovirulence-associated gene (ICP34.5) of herpes simplex virus. In all three proteins, a centrally located acidic region precedes a highly conserved, hydrophilic 56-amino-acid domain located at the carboxy terminus. LMW23-NL predicts a highly basic protein of 184 amino acids with an estimated molecular mass of 21.3 kDa. The similarity of LMW23-NL to genes involved in myeloid cell differentiation and viral host range suggests a role for it in African swine fever virus host range.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bankier A. T., Weston K. M., Barrell B. G. Random cloning and sequencing by the M13/dideoxynucleotide chain termination method. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:51–93. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasco R., López-Otín C., Muñz M., Bockamp E. O., Simón-Mateo C., Viñuela E. Sequence and evolutionary relationships of African swine fever virus thymidine kinase. Virology. 1990 Sep;178(1):301–304. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90409-K. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J., Kern E. R., Whitley R. J., Roizman B. Mapping of herpes simplex virus-1 neurovirulence to gamma 134.5, a gene nonessential for growth in culture. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1262–1266. doi: 10.1126/science.2173860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J., Roizman B. The herpes simplex virus 1 gene for ICP34.5, which maps in inverted repeats, is conserved in several limited-passage isolates but not in strain 17syn+. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1014–1020. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1014-1020.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Esch F. S., Taylor S. S., Hunter T. Phosphorylation sites in enolase and lactate dehydrogenase utilized by tyrosine protein kinases in vivo and in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7835–7841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Moss B. Structure of vaccinia virus late promoters. J Mol Biol. 1989 Dec 20;210(4):771–784. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90108-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon L. K. Molecular cloning and restriction enzyme mapping of an African swine fever virus isolate from Malawi. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1683–1694. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enjuanes L., Cubero I., Viñuela E. Sensitivity of macrophages from different species to African swine fever (ASF) virus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Mar;34(3):455–463. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-34-3-455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genovesi E. V., Villinger F., Gerstner D. J., Whyard T. C., Knudsen R. C. Effect of macrophage-specific colony-stimulating factor (CSF-1) on swine monocyte/macrophage susceptibility to in vitro infection by African swine fever virus. Vet Microbiol. 1990 Nov;25(2-3):153–176. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(90)90074-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González A., Calvo V., Almazán F., Almendral J. M., Ramírez J. C., de la Vega I., Blasco R., Viñuela E. Multigene families in African swine fever virus: family 360. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2073–2081. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2073-2081.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond J. M., Dixon L. K. Vaccinia virus-mediated expression of African swine fever virus genes. Virology. 1991 Apr;181(2):778–782. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90917-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess W. R. African swine fever virus. Virol Monogr. 1971;9:1–33. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-3987-5_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konno S., Taylor W. D., Dardiri A. H. Acute African swine fever. Proliferative phase in lymphoreticular tissue and the reticuloendothelial system. Cornell Vet. 1971 Jan;61(1):71–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord K. A., Hoffman-Liebermann B., Liebermann D. A. Complexity of the immediate early response of myeloid cells to terminal differentiation and growth arrest includes ICAM-1, Jun-B and histone variants. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):387–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord K. A., Hoffman-Liebermann B., Liebermann D. A. Sequence of MyD116 cDNA: a novel myeloid differentiation primary response gene induced by IL6. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 11;18(9):2823–2823. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.9.2823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Otín C., Freije J. M., Parra F., Méndez E., Viñuela E. Mapping and sequence of the gene coding for protein p72, the major capsid protein of African swine fever virus. Virology. 1990 Apr;175(2):477–484. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90432-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Otín C., Simón C., Méndez E., Viñuela E. Mapping and sequence of the gene encoding protein p37, a major structural protein of African swine fever virus. Virus Genes. 1988 Jun;1(3):291–303. doi: 10.1007/BF00572708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALMQUIST W. A., HAY D. Hemadsorption and cytopathic effect produced by African Swine Fever virus in swine bone marrow and buffy coat cultures. Am J Vet Res. 1960 Jan;21:104–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. D. Glycoproteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41:673–702. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.003325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Barnett B. C. Neurovirulence factor. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):609–609. doi: 10.1038/353609b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mebus C. A. African swine fever. Adv Virus Res. 1988;35:251–269. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60714-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B. Regulation of vaccinia virus transcription. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:661–688. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.003305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulton J., Coggins L. Comparison of lesions in acute and chronic African swine fever. Cornell Vet. 1968 Jul;58(3):364–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive sequence comparison with FASTP and FASTA. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:63–98. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83007-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinna L. A. Casein kinase 2: an 'eminence grise' in cellular regulation? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Sep 24;1054(3):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. An interactive graphics program for comparing and aligning nucleic acid and amino acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2951–2961. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R., McLachlan A. D. Codon preference and its use in identifying protein coding regions in long DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):141–156. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taha M. Y., Clements G. B., Brown S. M. The herpes simplex virus type 2 (HG52) variant JH2604 has a 1488 bp deletion which eliminates neurovirulence in mice. J Gen Virol. 1989 Nov;70(Pt 11):3073–3078. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-11-3073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viñuela E. African swine fever virus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;116:151–170. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70280-8_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodgett J. R., Gould K. L., Hunter T. Substrate specificity of protein kinase C. Use of synthetic peptides corresponding to physiological sites as probes for substrate recognition requirements. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 17;161(1):177–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




