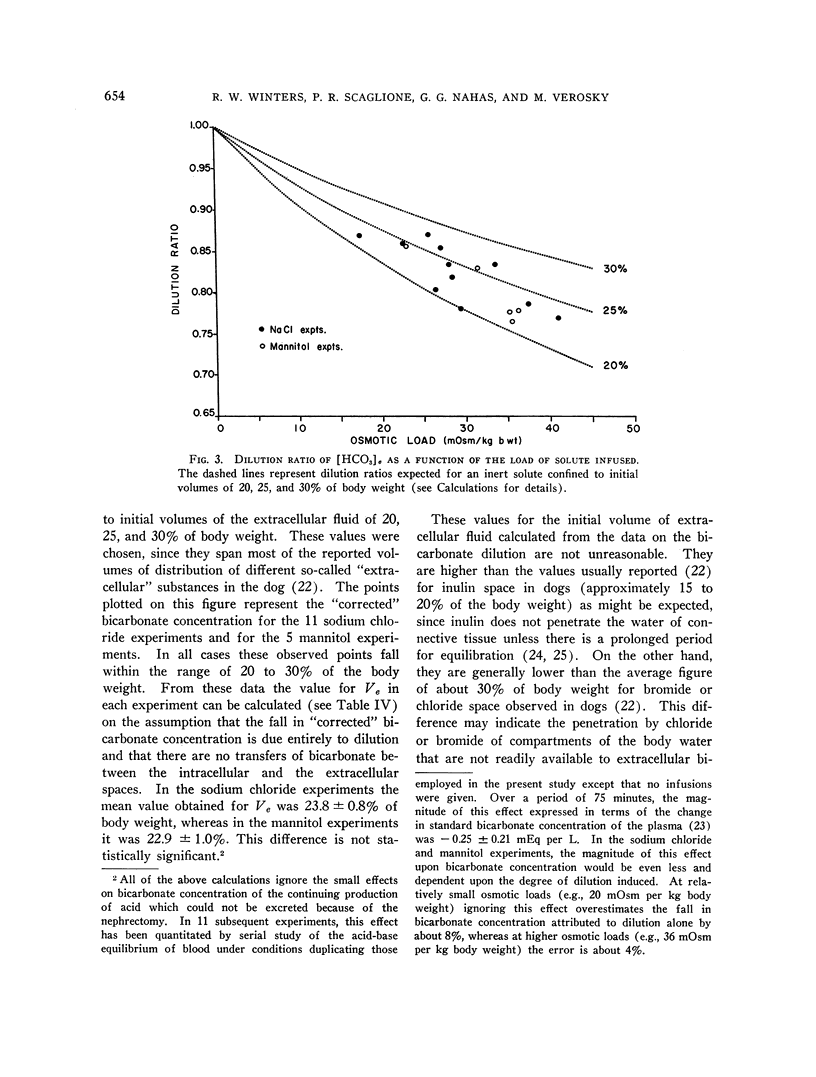
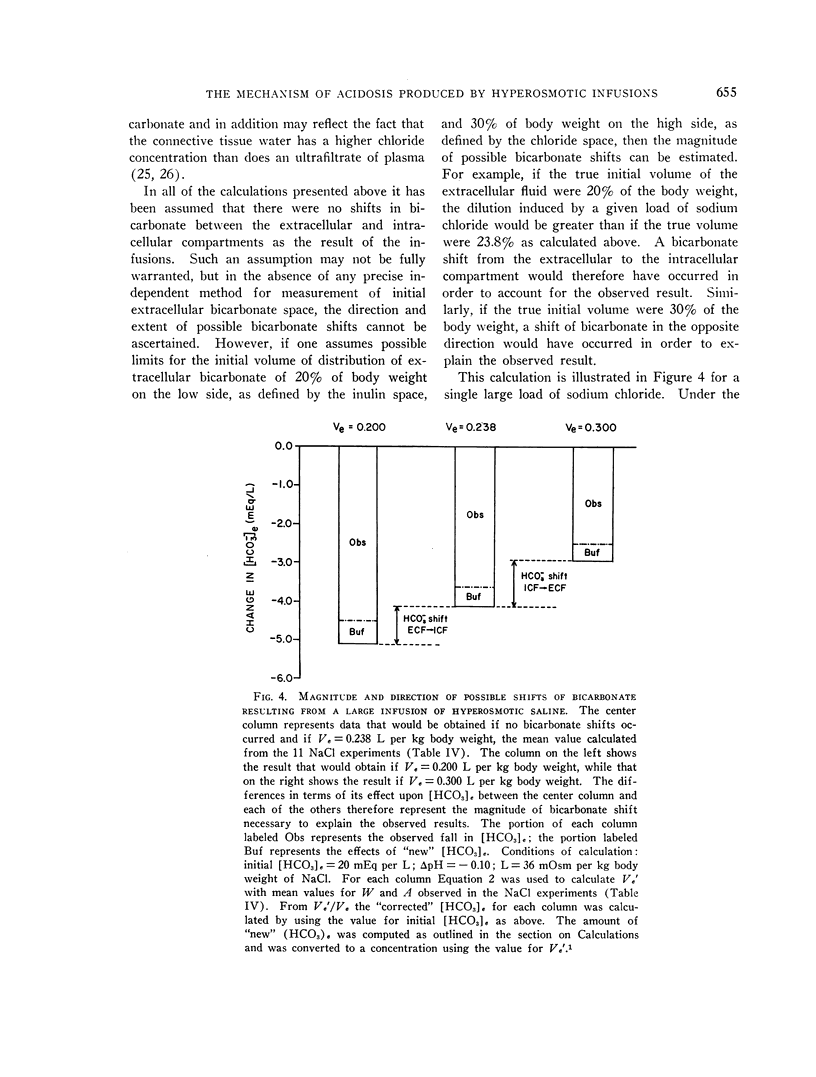
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALEXANDER S. C., GELFAND R., LAMBERTSEN C. J. The pK' of carbonic acid in cerebrospinal fluid. J Biol Chem. 1961 Feb;236:592–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY A. F., SEVERINGHAUS J. W., STUPFEL M. Accuracy of blood pH and PCO2 determinations. J Appl Physiol. 1956 Sep;9(2):189–196. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1956.9.2.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY A. F., SEVERINGHAUS J. W., STUPFEL M. Variations of serum carbonic acid pK with pH and temperature. J Appl Physiol. 1956 Sep;9(2):197–200. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1956.9.2.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COTLOVE E. Mechanism and extent of distribution of inulin and sucrose in chloride space of tissues. Am J Physiol. 1954 Mar;176(3):396–410. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.176.3.396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FENN W. O. Carbon dioxide and intracellular homeostasis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1961 Jun 17;92:547–558. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1961.tb45005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JORGENSEN K., ASTRUP P. Standard bicarbonate, its clinical significance, and a new method for its determination. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1957;9(2):122–132. doi: 10.3109/00365515709101210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDOWELL M. E., WOLF A. V., STEER A. Osmotic volumes of distribution; idiogenic changes in osmotic pressure associated with administration of hypertonic solutions. Am J Physiol. 1955 Mar;180(3):545–558. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1955.180.3.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEELY W. A. Apparent sodium space of the dog. Am J Physiol. 1959 Jun;196(6):1333–1335. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.196.6.1333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICHOLS G., Jr, NICHOLS N., WEIL W. B., WALLACE W. M. The direct measurement of the extracellular phase of tissues. J Clin Invest. 1953 Dec;32(12):1299–1308. doi: 10.1172/JCI102858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBIN E. D., WILSON R. J., BROMBERG P. A. Intracellular acidbase relations and intracellular buffers. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1961 Jun 17;92:539–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1961.tb45004.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGER R. B., CLARK J. K., BARKER E. S., CROSLEY A. P., Jr, ELKINTON J. R. The acute effects in man of rapid intravenous infusion of hypertonic sodium bicarbonate solution. I. Changes in acid-base balance and distribution of the excess buffer base. Medicine (Baltimore) 1955 Feb;34(1):51–95. doi: 10.1097/00005792-195502000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOTOS J. F., DODGE P. R., TALBOT N. B. Studies in experimental hypertonicity. II. Hypertonicity of body fluids as a cause of acidosis. Pediatrics. 1962 Aug;30:180–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. D., Rourke G. M. THE EFFECTS OF LARGE INTRAVENOUS INFUSIONS ON BODY FLUID. J Clin Invest. 1942 Mar;21(2):197–205. doi: 10.1172/JCI101291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLF A. V., McDOWELL M. E. Apparent and osmotic volumes of distribution of sodium, chloride, sulfate and urea. Am J Physiol. 1954 Feb;176(2):207–212. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.176.2.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler A. W., Elkinton J. R., Hopper J., Hoff H. E. EXPERIMENTAL HYPERTONICITY: ALTERATIONS IN THE DISTRIBUTION OF BODY WATER, AND THE CAUSE OF DEATH. J Clin Invest. 1944 Jan;23(1):103–109. doi: 10.1172/JCI101464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


