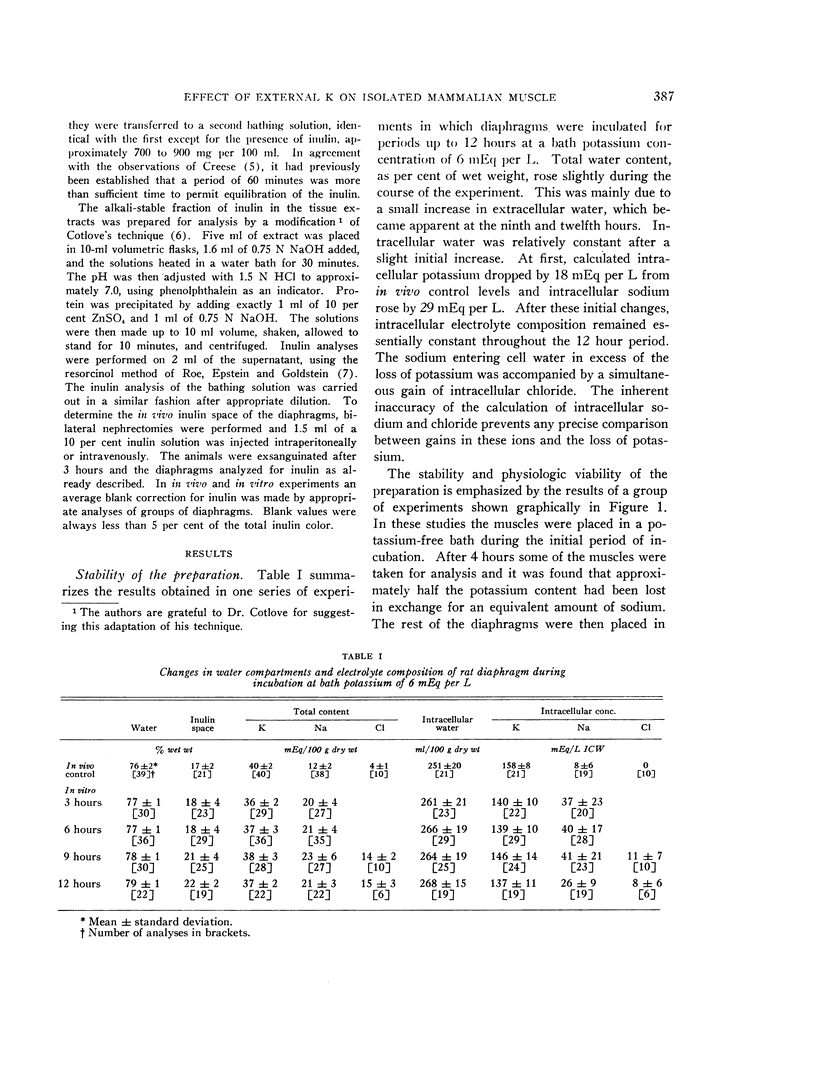
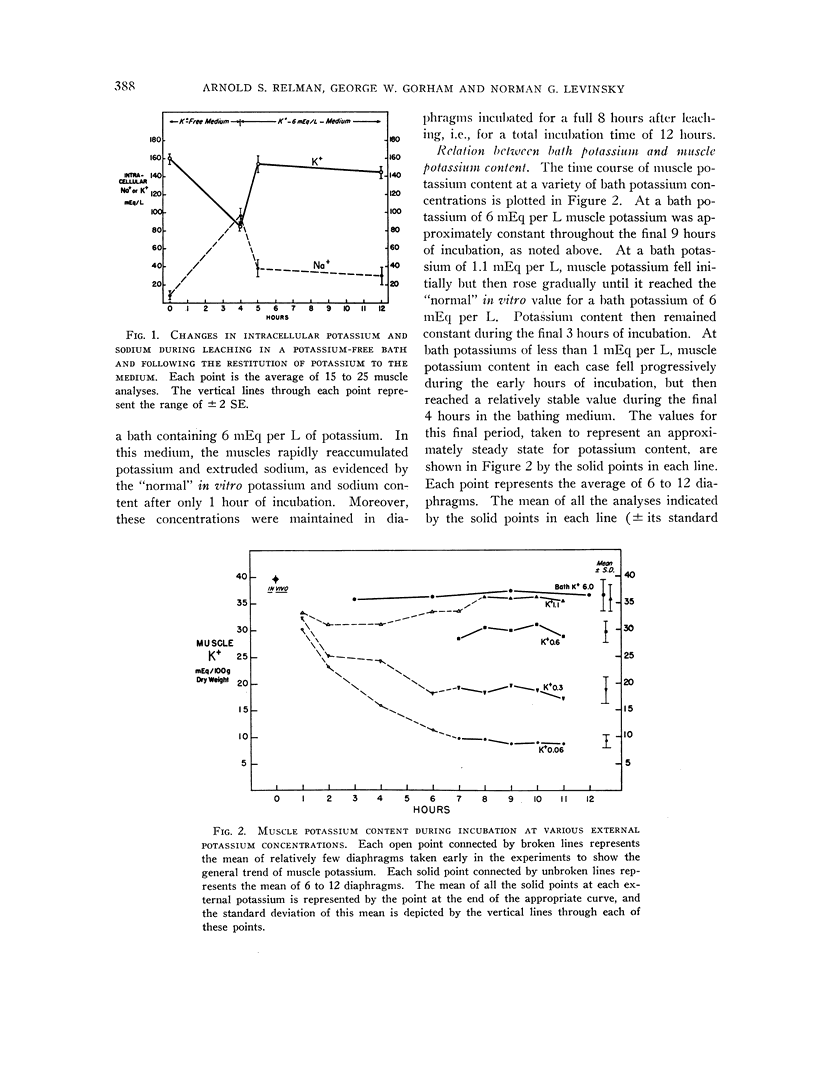
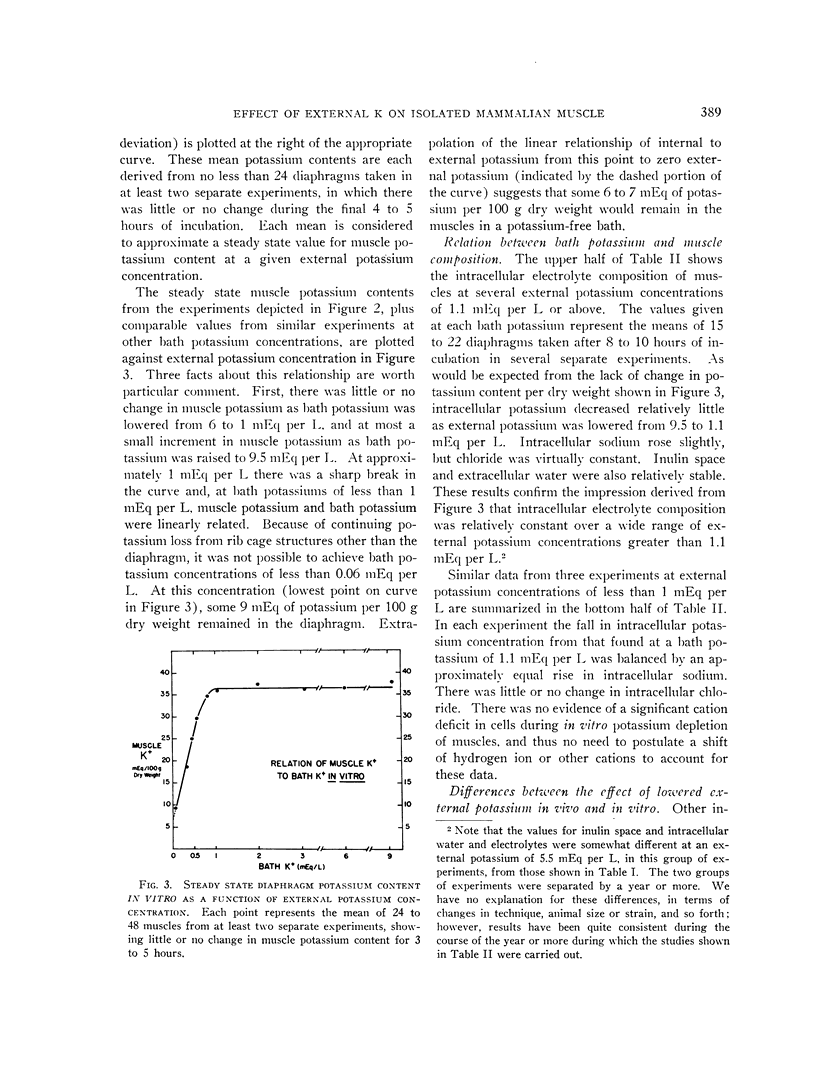
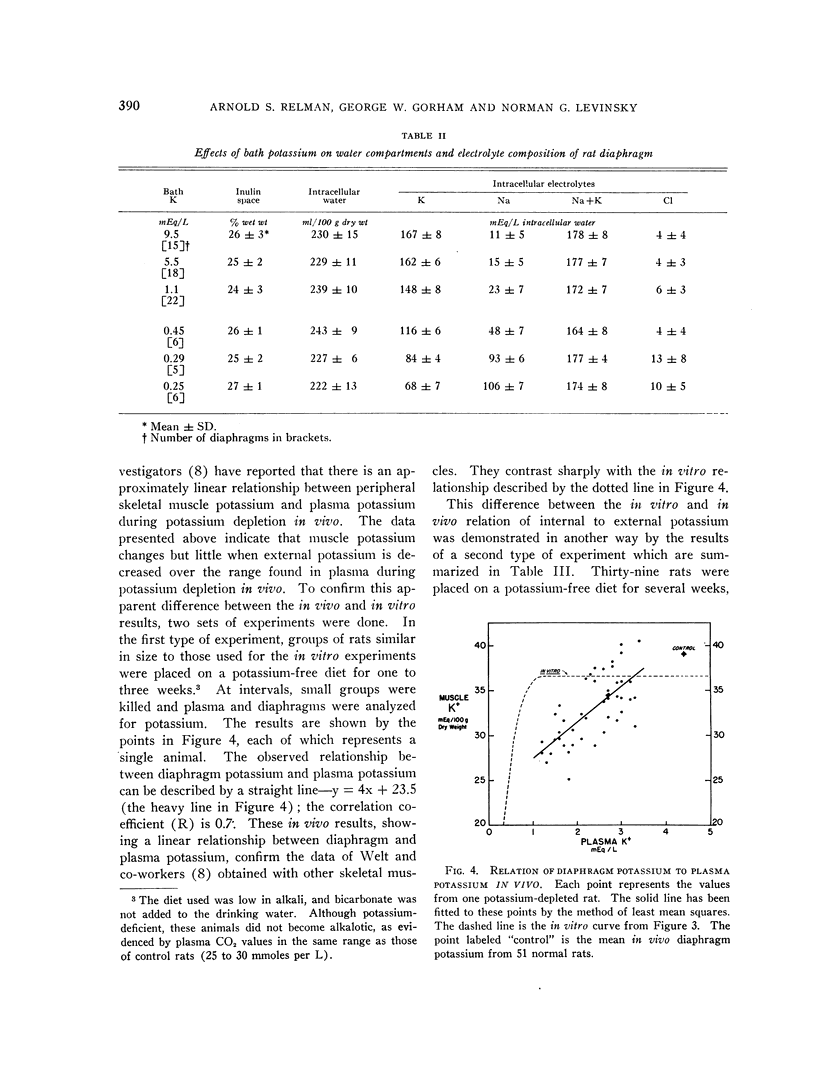
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CALKINS E., TAYLOR I. M., HASTINGS A. B. Potassium exchange in the isolated diaphragm; effect of anoxia and cold. Am J Physiol. 1954 May;177(2):211–218. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.177.2.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONWAY E. J. Nature and significance of concentration relations of potassium and sodium ions in skeletal muscle. Physiol Rev. 1957 Jan;37(1):84–132. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1957.37.1.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOKE R. E., SEGAR W. E., CHEEK D. B., COVILLE F. E., DARROW D. C. The extrarenal correction of alkalosis associated with potassium deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1952 Aug;31(8):798–805. doi: 10.1172/JCI102665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COTLOVE E., HOLLIDAY M. A., SCHWARTZ R., WALLACE W. M. Effects of electrolyte depletion and acid-base disturbance on muscle cations. Am J Physiol. 1951 Dec;167(3):665–675. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.167.3.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COTLOVE E. Mechanism and extent of distribution of inulin and sucrose in chloride space of tissues. Am J Physiol. 1954 Mar;176(3):396–410. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.176.3.396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREESE R. Measurement of cation fluxes in rat diaphragm. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1954 Sep 27;142(909):497–513. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1954.0039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECKEL R. E., NORRIS J. E., POPE C. E., 2nd Basic amino acids as intracellular cations in K deficiency. Am J Physiol. 1958 Jun;193(3):644–652. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.193.3.644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLYNN I. M. Sodium and potassium movements in nerve, muscle, and red cells. Int Rev Cytol. 1959;8:449–480. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62737-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASHISH S. E. The effects of low temperatures and heparin on potassium exchangeability in rat diaphragm. Acta Physiol Scand. 1958 Oct 8;43(3-4):189–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1958.tb01587.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIPNIS D. M., CORI C. F. Studies of tissue permeability. III. The effect of insulin on pentose uptake by the diaphragm. J Biol Chem. 1957 Feb;224(2):681–693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIBMAN J., EDELMAN I. S. Interrelations of plasma potassium concentration, plasma sodium concentration, arterial pH and total exchangeable potassium. J Clin Invest. 1959 Dec;38:2176–2188. doi: 10.1172/JCI103997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LING G. Muscle electrolytes. Am J Phys Med. 1955 Feb;34(1):89–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCLENNAN H. Physical and chemical factors affecting potassium movements in mammalian muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Oct;22(1):30–37. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90219-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLENNAN H. The transfer of potassium between mammalian muscle and the surrounding medium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Jan;16(1):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90186-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menozzi P., Norman D., Polleri A., Lester G., Hechter O. SPECIFIC INTRACELLULAR BINDING OF RUBIDIUM BY RAT DIAPHRAGM MUSCLE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 Jan;45(1):80–88. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.1.80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RELMAN A. S., LAMBIE A. T., BURROWS B. A., ROY A. M. Cation accumulation by muscle tissue: the displacement of potassium by rubidium and cesium in the living animal. J Clin Invest. 1957 Aug;36(8):1249–1256. doi: 10.1172/JCI103522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIXON R. H., STEVENSON J. A. Movements of sodium, potassium and water in rat diaphragm in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1958 Aug;194(2):363–368. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.194.2.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ W. B., RELMAN A. S. Metabolic and renal studies in chronic potassium depletion resulting from overuse of laxatives. J Clin Invest. 1953 Mar;32(3):258–271. doi: 10.1172/JCI102735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHANES A. M. Electrochemical aspects of physiological and pharmacological action in excitable cells. I. The resting cell and its alteration by extrinsic factors. Pharmacol Rev. 1958 Mar;10(1):59–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAW F. H., SIMON S. E. The nature of the sodium and potassium balance in nerve and muscle cells. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1955 Apr;33(2):153–177. doi: 10.1038/icb.1955.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMON S. E. Ionic partition and fine structure in muscle. Nature. 1959 Dec 26;184:1978–1982. doi: 10.1038/1841978a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELT L. G., CAP M. P., GEHAN E. A., WINTERS R. W., DEWALT J. L., DIAMOND E. L. The prediction of muscle potassium from blood electrolytes in potassium depleted rats. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1958;71:250–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


