Abstract
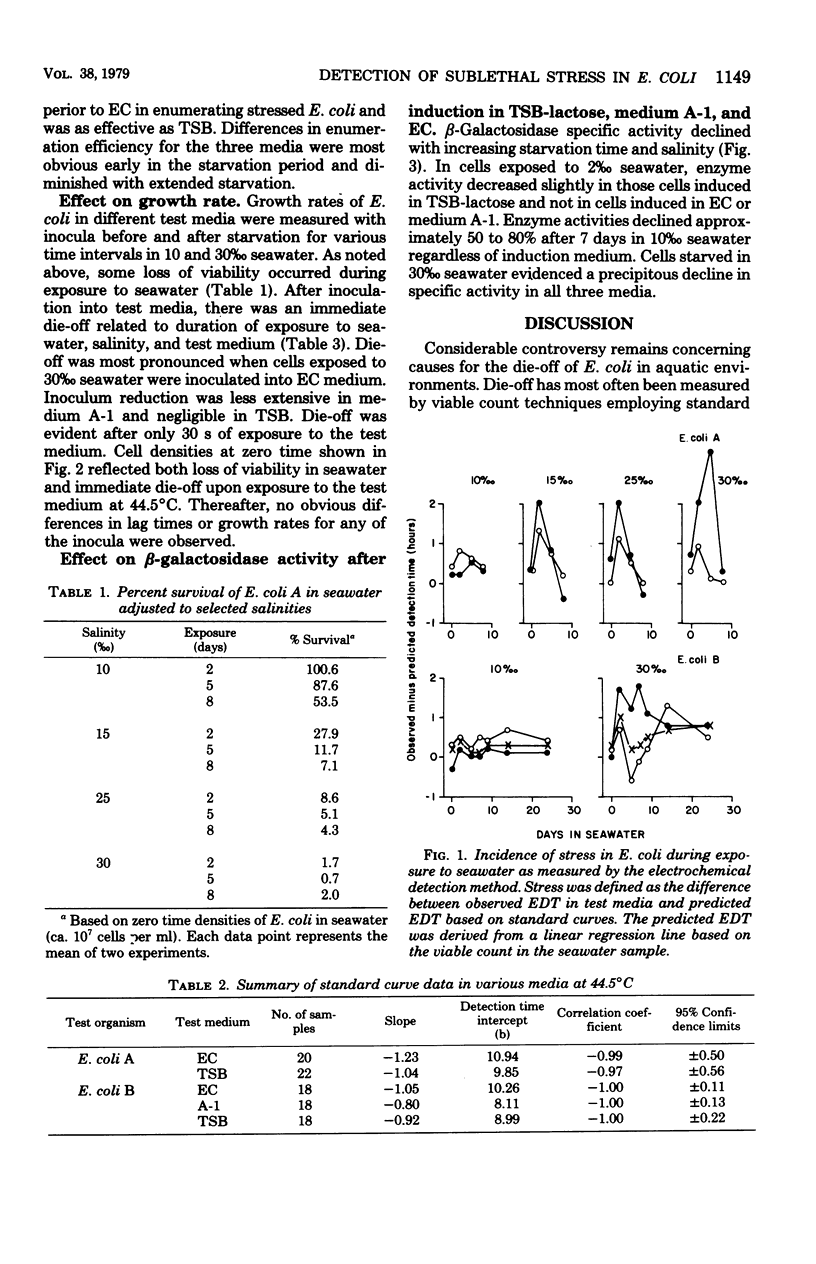
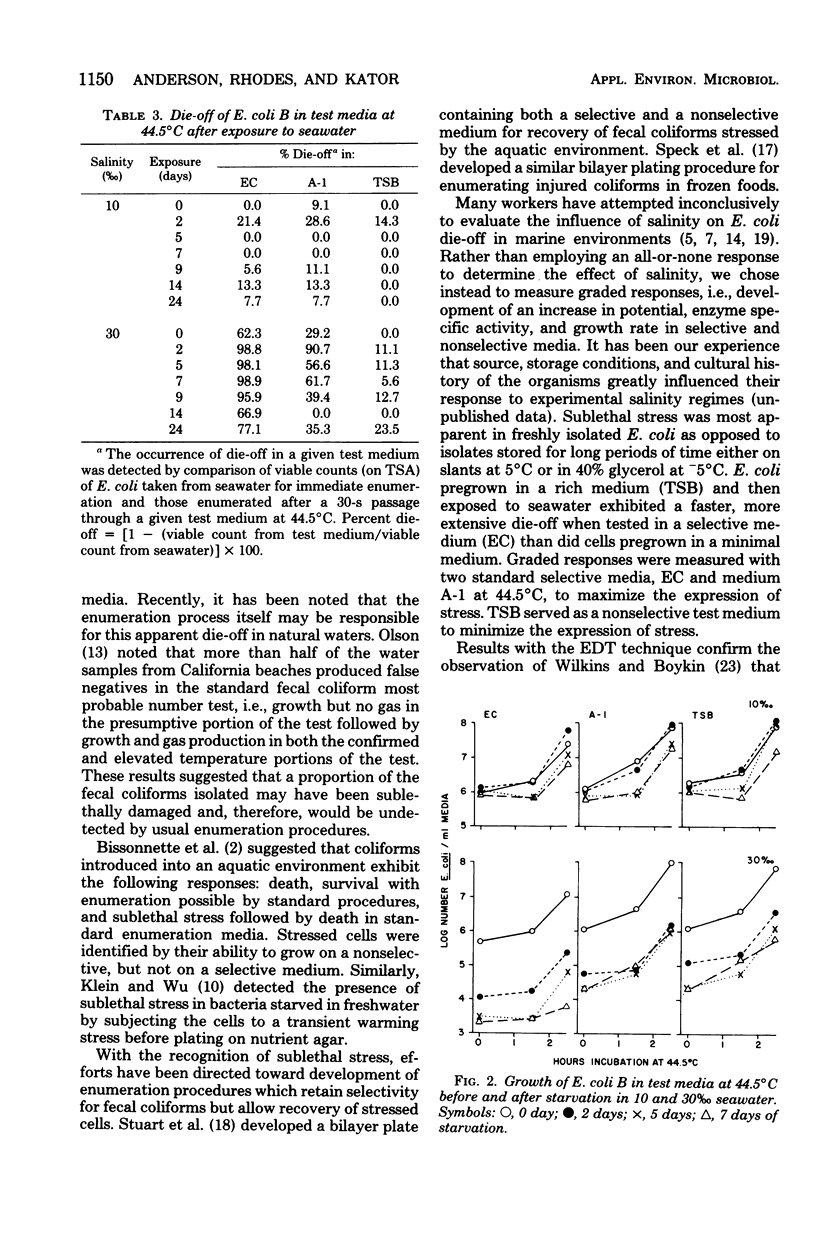
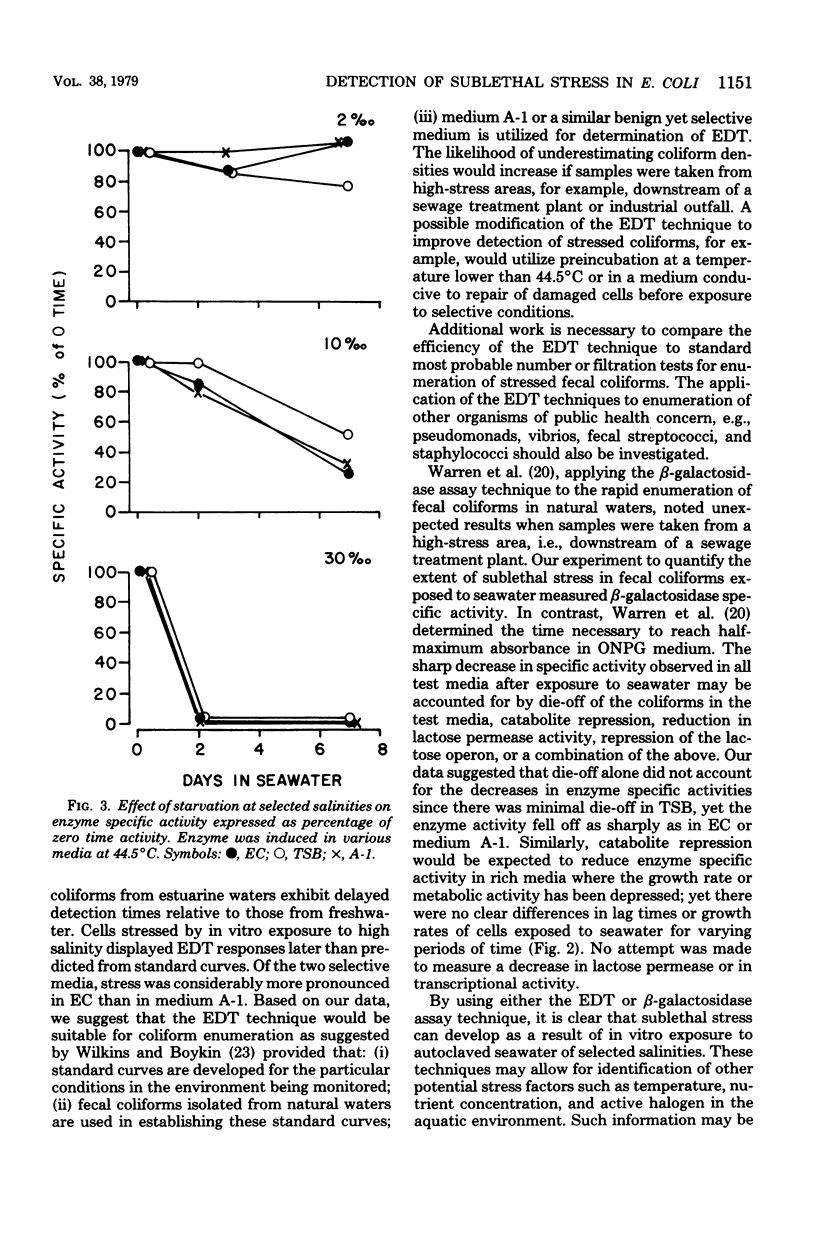
Sublethal stress in Escherichia coli was detected in various test media after exposure (in vitro) to seawater of various salinites. Stress was measured with an electrochemical detection technique and a beta-galactosidase assay. Test media included EC medium, medium A-1, and tryptic soy broth modified to contain lactose for beta-galactosidase assay experiments. Stress was defined as the difference between a predicted electrochemical response time calculated for unstarved cells from a standard curve and the observed electrochemical response time for cells starved in seawater. The higher the salinity, the greater the stress for all test media examined. Stress was most pronounced in EC and was attributed primarily to initial die-off of starved cells exposed to the test medium at the elevated temperature of 44.5 degrees C. Lag time and growth rates in test media were not significantly affected by salinity. beta-Galactosidase specific activity, assayed in starved cells after transfer to an induction medium at 44.5 degrees C for 150 min, was inversely related to the salinity of the starved cell suspension. The consequences of these observations with respect to coliform enumeration methods are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews W. H., Presnell M. W. Rapid recovery of Escherichia coli from estuarine water. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Mar;23(3):521–523. doi: 10.1128/am.23.3.521-523.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissonnette G. K., Jezeski J. J., McFeters G. A., Stuart D. G. Influence of environmental stress on enumeration of indicator bacteria from natural waters. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Feb;29(2):186–194. doi: 10.1128/am.29.2.186-194.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busta F. F. Introduction to injury and repair of microbial cells. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1978;23:195–201. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70069-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARLUCCI A. F., PRAMER D. An evaluation of factors affecting the survival of Escherichia coli in sea water. II. Salinity, pH, and nutrients. Appl Microbiol. 1960 Jul;8:247–250. doi: 10.1128/am.8.4.247-250.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARLUCCI A. F., PRAMER D. Factors affecting the survival of bacteria in sea water. Appl Microbiol. 1959 Nov;7:388–392. doi: 10.1128/am.7.6.388-392.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawe L. L., Penrose W. R. "Bactericidal" property of seawater: death or debilitation? Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 May;35(5):829–833. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.5.829-833.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust M. A., Aotaky A. E., Hargadon M. T. Effect of physical parameters on the in situ survival of Escherichia coli MC-6 in an estuarine environment. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Nov;30(5):800–806. doi: 10.1128/am.30.5.800-806.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENBERG A. E. Survival of enteric organisms in sea water. Public Health Rep. 1956 Jan;71(1):77–86. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoadley A. W., Cheng C. M. The recovery of indicator bacteria on selective media. J Appl Bacteriol. 1974 Mar;37(1):45–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1974.tb00413.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein D. A., Wu S. Stress: a factor to be considered in heterotrophic microorganism enumeration from aquatic environments. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Feb;27(2):429–431. doi: 10.1128/am.27.2.429-431.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKADA D., MAGASANIK B. THE ROLES OF INDUCER AND CATABOLITE REPRESSOR IN THE SYNTHESIS OF BETA-GALACTOSIDASE BY ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Mol Biol. 1964 Jan;8:105–127. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80153-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson B. H. Enchanced accuracy of coliform testing in seawater by a modification of the most-probable-number method. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Sep;36(3):438–444. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.3.438-444.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck M. L., Ray B., Read R. B., Jr Repair and enumeration of injured coliforms by a plating procedure. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Apr;29(4):549–550. doi: 10.1128/am.29.4.549-550.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart D. G., McFeters G. A., Schillinger J. E. Membrane filter technique for the quantification of stressed fecal coliforms in the aquatic environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Jul;34(1):42–46. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.1.42-46.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcelos G. J., Swartz R. G. Survival of bacteria in seawater using a diffusion chamber apparatus in situ. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jun;31(6):913–920. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.6.913-920.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren L. S., Benoit R. E., Jessee J. A. Rapid enumeration of Fecal Coliforms in water by a colorimetric beta-galactosidase assay. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jan;35(1):136–141. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.1.136-141.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warseck M., Ray B., Speck M. L. Repair and enumeration of injured coliforms in frozen foods. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Dec;26(6):919–924. doi: 10.1128/am.26.6.919-924.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins J. R., Stoner G. E., Boykin E. H. Microbial detection method based on sensing molecular hydrogen. Appl Microbiol. 1974 May;27(5):949–952. doi: 10.1128/am.27.5.949-952.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins J. R. Use of platinum electrodes for the electrochemical detection of bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Nov;36(5):683–687. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.5.683-687.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


