Abstract
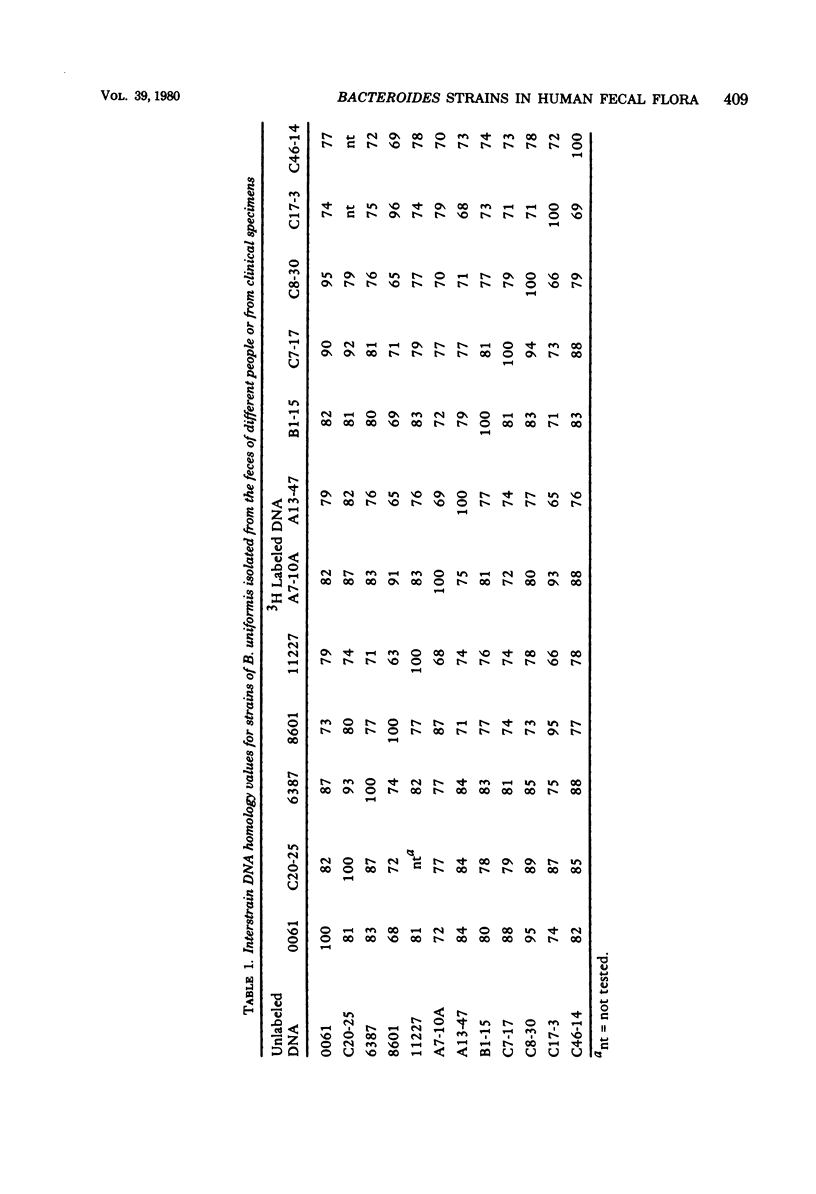
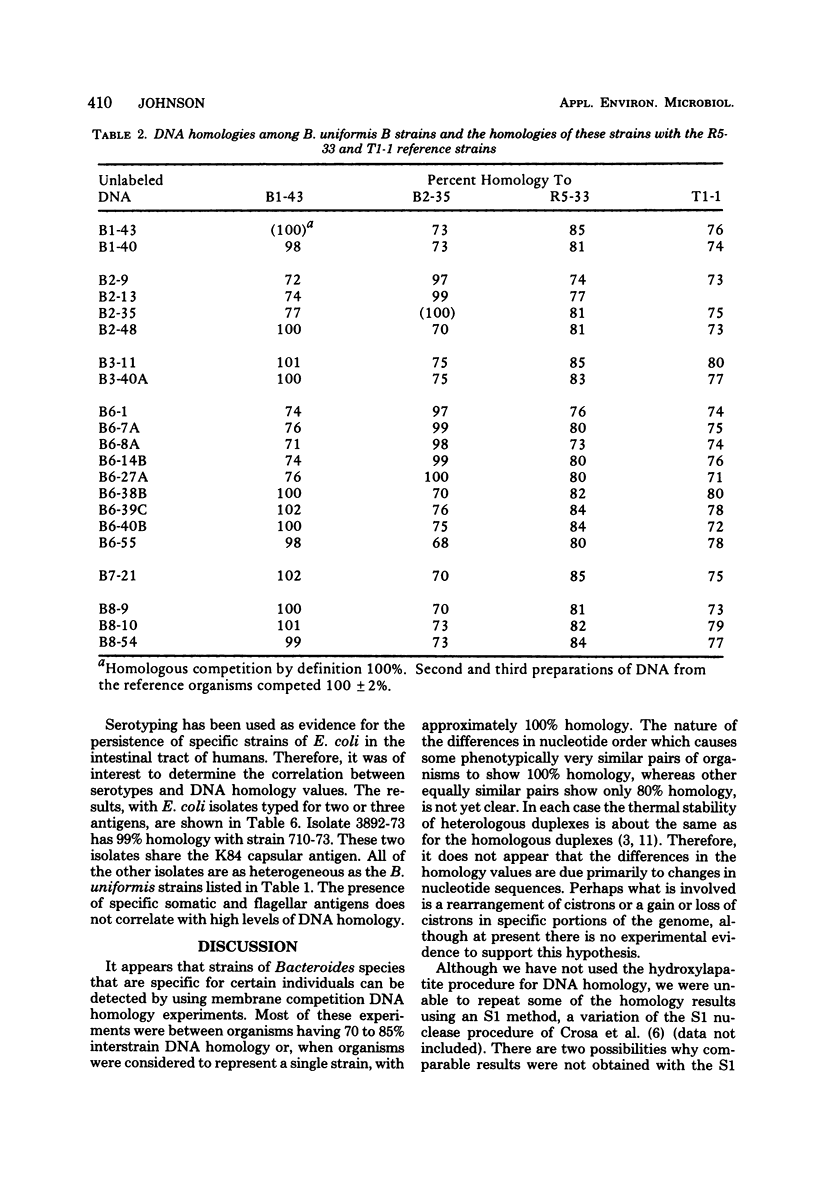
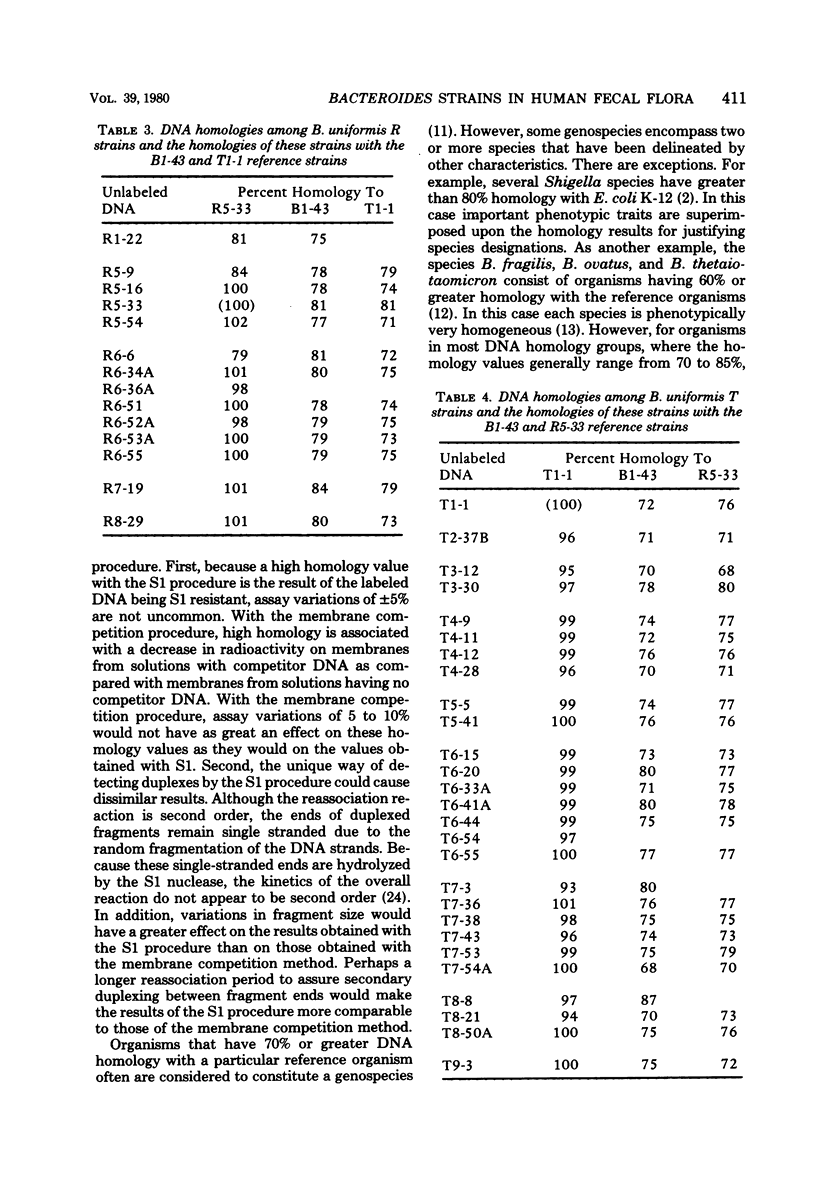
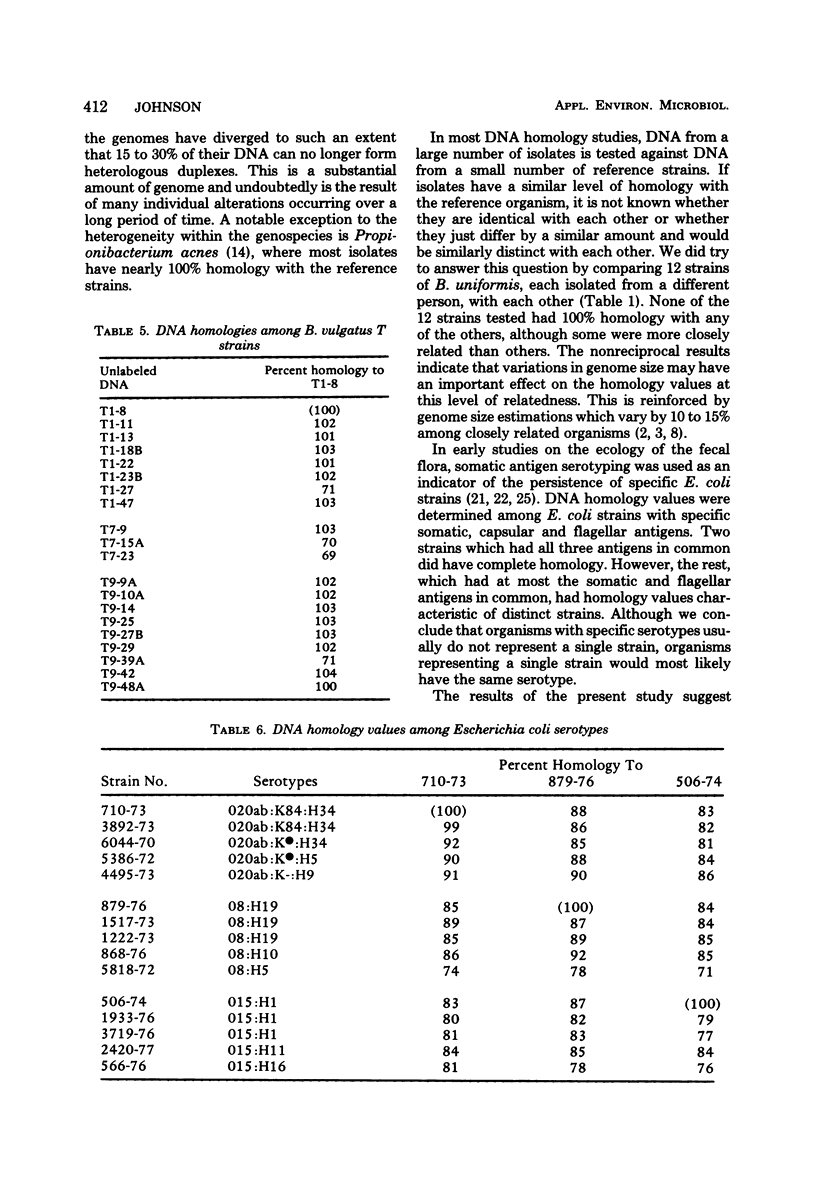
Membrane competition homology experiments were used to compare Bacteroides uniformis and Bacteroides vulgatus isolates obtained from fecal samples from different individuals and isolates obtained from fecal samples of single individuals. Isolates of B. uniformis, when isolated from different individuals, had interstrain deoxyribonucleic acid homology values that ranged from 63 to 95%, with most of the values being in the 70 to 85% range. When isolates obtained from a single individual were compared, each species was represented by one or two groups of very closely related organisms, with each group having essentially 100% interstrain homology. When strains from two groups were compared with each other, the homology values were in the same range as when organisms were isolated from different individuals. Isolates which have nearly 100% homology with each other persisted in fecal samples collected over a 5- to 6-month period. It appears that the colon of each person may be populated by bacterial strains that are specific for that individual. Somatic antigen serotyping has been used as an indicator for specific Escherichia coli strains in fecal samples. Two isolates having the same O, K, and H antigens had 99% homology, but when only O and H antigens were in common, the homology values were in the 70 to 85% range. It seems that isolates of a given serotype, when isolated from a single individual, may represent a unique strain, but isolates of a given serotype, when isolated from different individuals, probably do not.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. D., Gillespie W. A., Richmond M. H. Chemotherapy and antibiotic-resistance transfer between Enterobacteria in the human gastro-intestinal tract. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Nov;6(4):461–473. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-4-461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., Fanning G. R., Skerman F. J., Falkow S. Polynucleotide sequence divergence among strains of Escherichia coli and closely related organisms. J Bacteriol. 1972 Mar;109(3):953–965. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.3.953-965.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., Fanning G. R., Steigerwalt A. G., Orskov I., Orskov F. Polynucleotide sequence relatedness among three groups of pathogenic Escherichia coli strains. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):308–315. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.308-315.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke E. M., Hettiaratchy I. G., Buck A. C. Fate of ingested Escherichia coli in normal persons. J Med Microbiol. 1972 Aug;5(3):361–369. doi: 10.1099/00222615-5-3-361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke E. M., Kumar P. J., Shooter R. A., Rousseau S. A., Foulkes A. L. Hospital food as a possible source of Escherichia coli in patients. Lancet. 1970 Feb 28;1(7644):436–437. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90830-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H., Brenner D. J., Falkow S. Use of a single-strand specific nuclease for analysis of bacterial and plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid homo- and heteroduplexes. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):904–911. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.904-911.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggerth A. H., Gagnon B. H. The Bacteroides of Human Feces. J Bacteriol. 1933 Apr;25(4):389–413. doi: 10.1128/jb.25.4.389-413.1933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis M., De Ley J., De Cleene M. The determination of molecular weight of bacterial genome DNA from renaturation rates. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Jan;12(1):143–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00831.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdeman L. V., Good I. J., Moore W. E. Human fecal flora: variation in bacterial composition within individuals and a possible effect of emotional stress. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Mar;31(3):359–375. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.3.359-375.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarolmen H., Kemp G. R factor transmission in vivo. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):487–490. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.487-490.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. L., Cummins C. S. Cell wall composition and deoxyribonucleic acid similarities among the anaerobic coryneforms, classical propionibacteria, and strains of Arachnia propionica. J Bacteriol. 1972 Mar;109(3):1047–1066. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.3.1047-1066.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis K. H., Rettger L. F. Non-Sporulating Anaerobic Bacteria of the Intestinal Tract : I. Occurrence and Taxonomic Relationships. J Bacteriol. 1940 Aug;40(2):287–307. doi: 10.1128/jb.40.2.287-307.1940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Cato E. P., Holdeman L. V. Some current concepts in intestinal bacteriology. Am J Clin Nutr. 1978 Oct;31(10 Suppl):S33–S42. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/31.10.S33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V. Human fecal flora: the normal flora of 20 Japanese-Hawaiians. Appl Microbiol. 1974 May;27(5):961–979. doi: 10.1128/am.27.5.961-979.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed N. D., Sieckmann D. G., Georgi C. E. Transfer of infectious drug resistance in microbially defined mice. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):22–26. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.22-26.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEARS H. J., BROWNLEE I. Further observations on the persistence of individual strains of Escherichia coli in the intestinal tract of man. J Bacteriol. 1952 Jan;63(1):47–57. doi: 10.1128/jb.63.1.47-57.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEARS H. J., BROWNLEE I., UCHIYAMA J. K. Persistence of individual strains of Escherichia coli in the intestinal tract of man. J Bacteriol. 1950 Feb;59(2):293–301. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.2.293-301.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W. Transfer of antibiotic resistance from animal and human strains of Escherichia coli to resident E. coli in the alimentary tract of man. Lancet. 1969 Jun 14;1(7607):1174–1176. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)92164-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. J., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Studies on nucleic acid reassociation kinetics: reactivity of single-stranded tails in DNA-DNA renaturation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4805–4809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallick H., Stuart C. A. Antigenic Relationships of Escherichia coli Isolated from One Individual. J Bacteriol. 1943 Feb;45(2):121–126. doi: 10.1128/jb.45.2.121-126.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubrzycki L., Spaulding E. H. STUDIES ON THE STABILITY OF THE NORMAL HUMAN FECAL FLORA. J Bacteriol. 1962 May;83(5):968–974. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.5.968-974.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


