Abstract
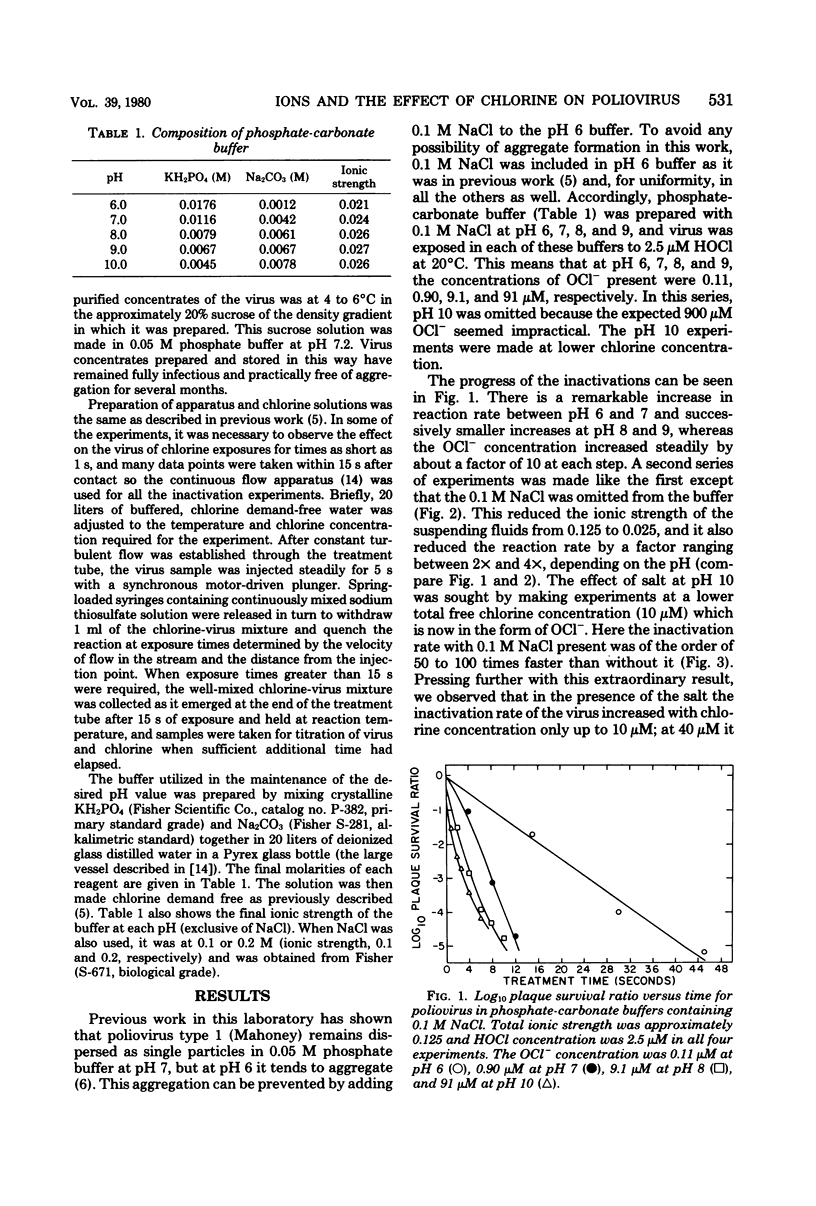
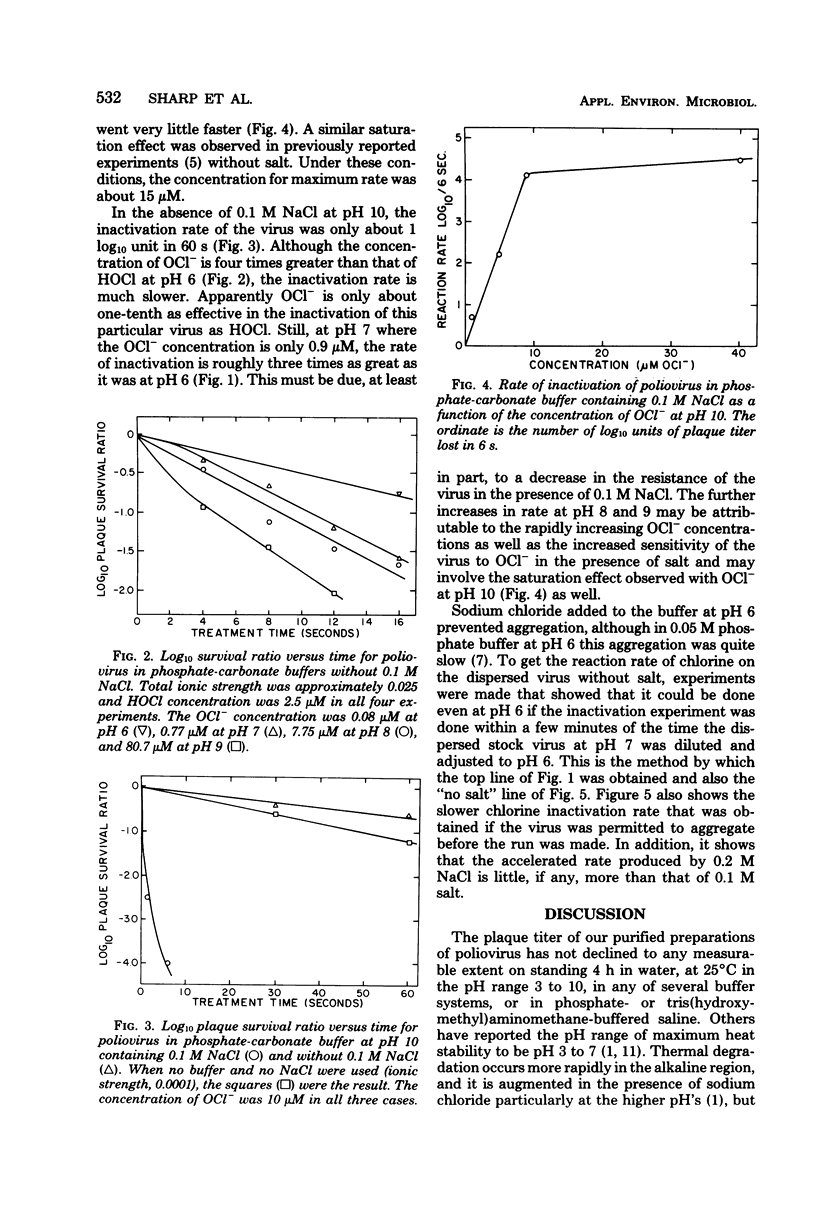
The rate of inactivation of poliovirus in water by chlorine is strongly influenced by the pH, which in turn influences the relative amounts of HOCl and OCl- that are present and acting on the virus in the region of pH 6 to 10. The distribution of HOCl and OCl- is influenced to a lesser extent by the addition of NaCl. The major part of the sharp increase in disinfection rate seen with this salt is thought to be due to its effect on the virus itself resulting in an increased chlorine sensitivity, especially at high pH.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boeyé A., Van Elsen A. Alkaline disruption of poliovirus: kinetics and purification of RNA-free particles. Virology. 1967 Oct;33(2):335–343. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd R., Johnson J. D., Sharp D. G. Inactivation by bromine of single poliovirus particles in water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Feb;31(2):298–303. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.2.298-303.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd R., Sharp D. G. Aggregation of poliovirus and reovirus by dilution in water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Jan;33(1):159–167. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.1.159-167.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd R., Sharp D. G. Viral aggregation: effects of salts on the aggregation of poliovirus and reovirus at low pH. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jun;35(6):1084–1094. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.6.1084-1094.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd R., Sharp D. G. Viral aggregation: quantitation and kinetics of the aggregation of poliovirus and reovirus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jun;35(6):1079–1083. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.6.1079-1083.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salo R. J., Cliver D. O. Effect of acid pH, salts, and temperature on the infectivity and physical integrity of enteroviruses. Arch Virol. 1976;52(4):269–282. doi: 10.1007/BF01315616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp D. G., Floyd R., Johnson J. D. Initial fast reaction of bromine on reovirus in turbulent flowing water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Feb;31(2):173–181. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.2.173-181.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDENKOPF S. J. Inactivation of type 1, poliomyelitis virus with chlorine. Virology. 1958 Feb;5(1):56–67. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(58)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


