Abstract
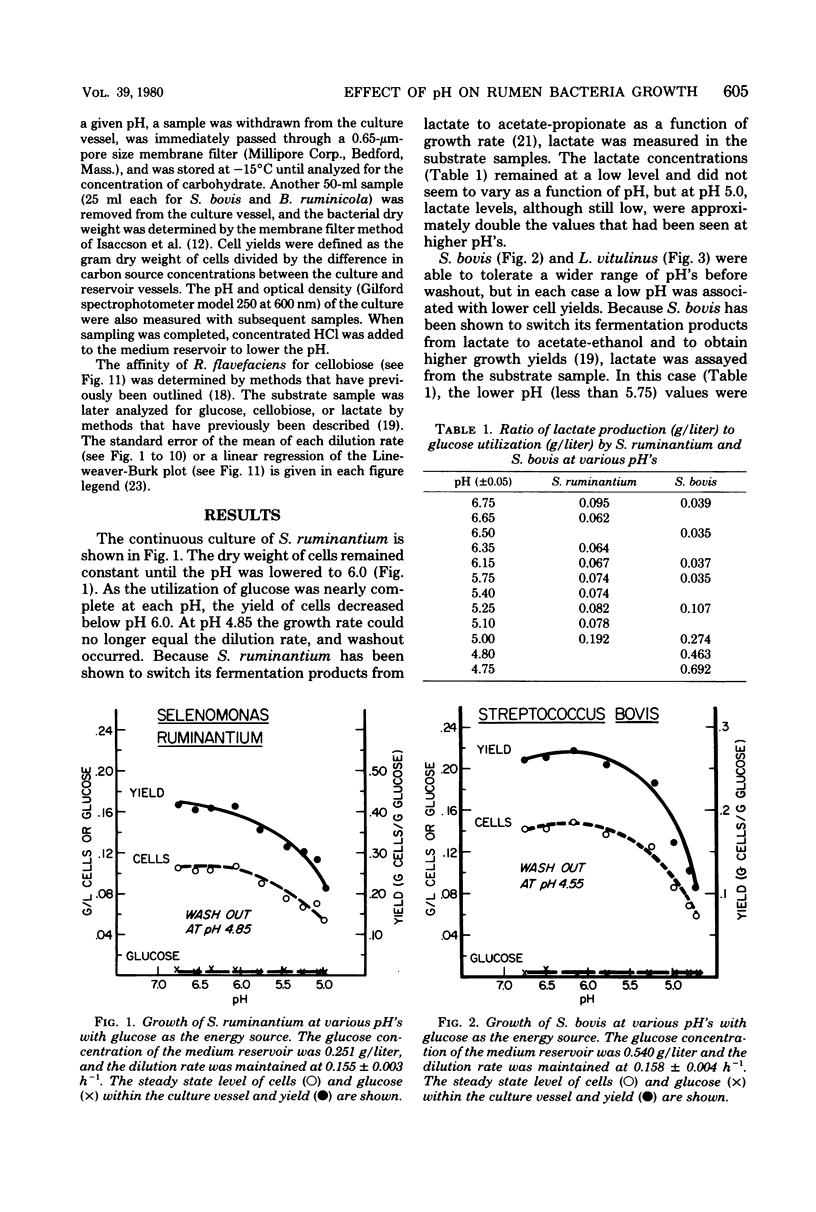
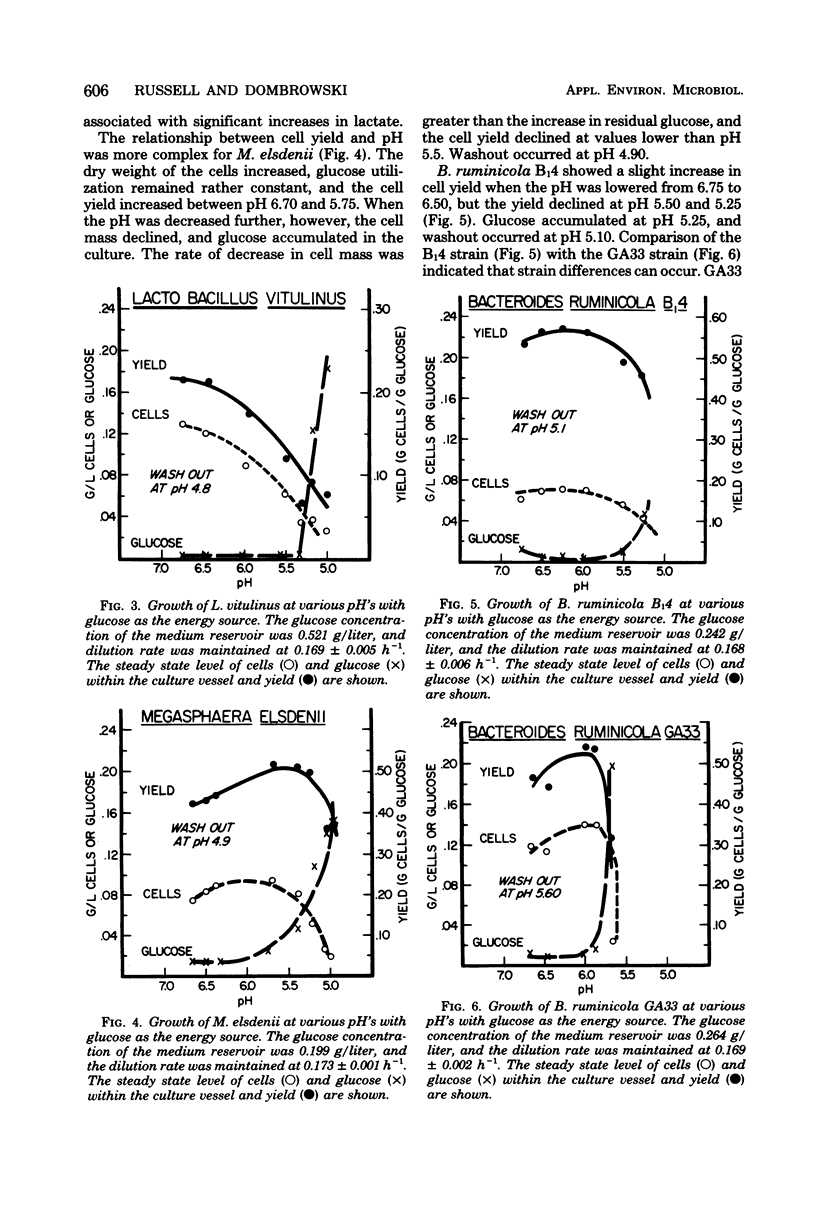
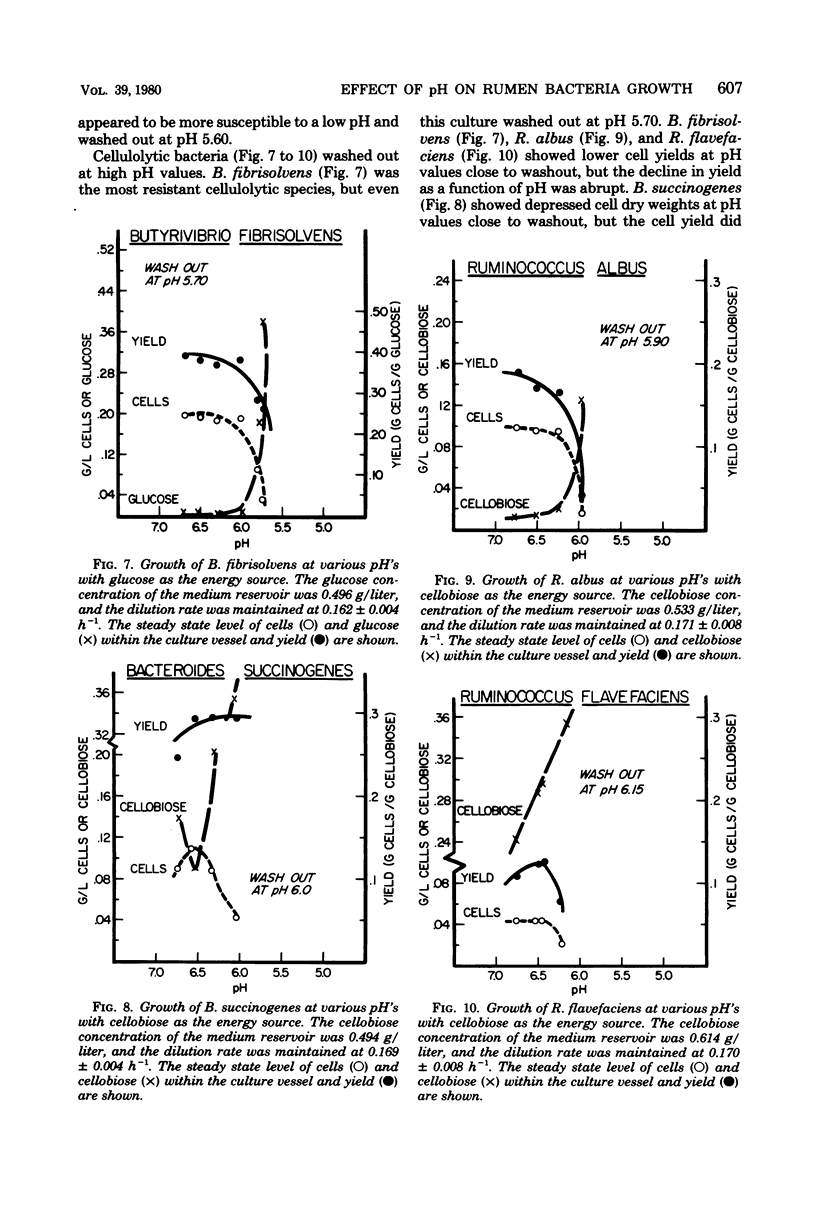
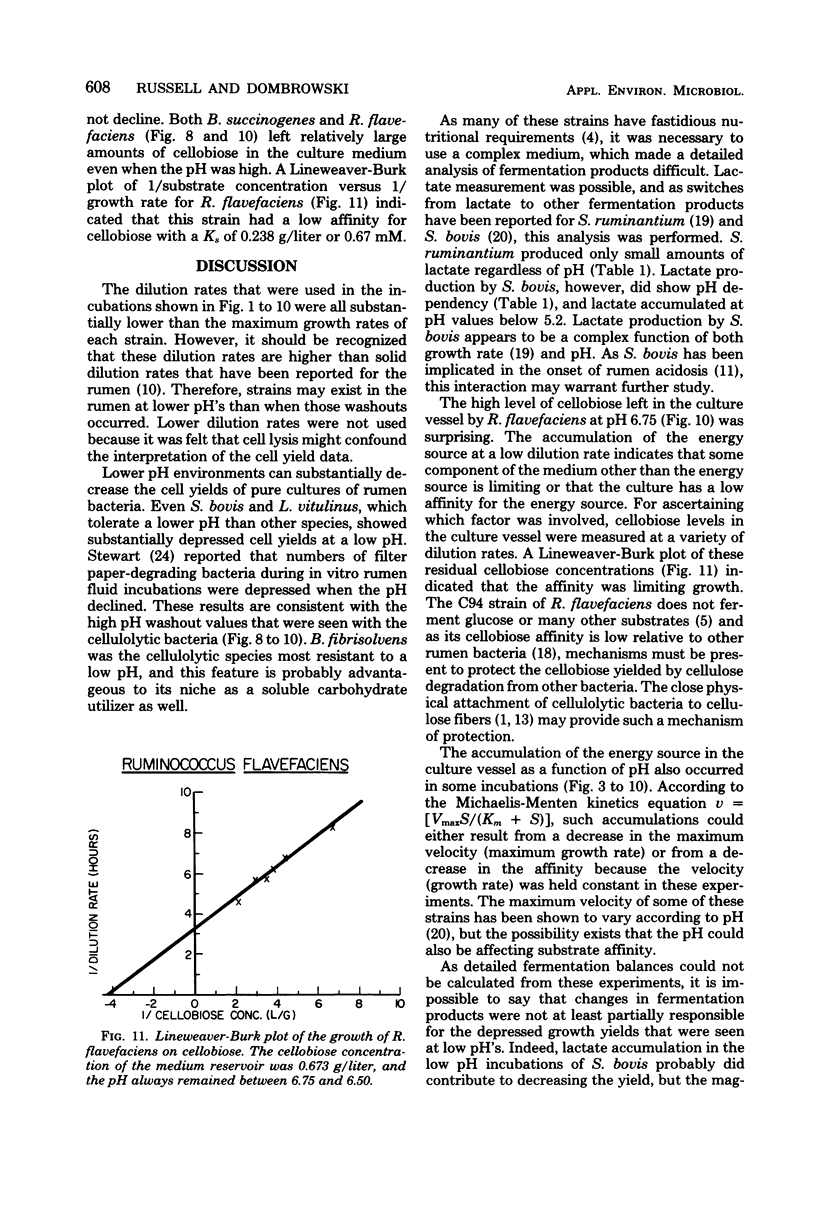
A total of 10 strains of rumen bacteria, Selenomonas ruminantium HD4, Megasphaera elsdenii B159, Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens A38, Streptococcus bovis JB1, Lactobacillus vitulinus GA1, Bacteroides ruminicola B14, B. ruminicola GA33, Ruminococcus albus 7, Ruminococcus flavefaciens C94, and Bacteroides succinogenes S85, were grown in energy-limiteH of the medium reservoir was lowered approximately 0.3 pH units, and the energy source concentration remaining in the culture vessel, optical density, cell mass, and pH were determined. A low pH appeared to have a detrimental effect on cell yields. Large variations were seen among strains in both the magnitude of yield depressions at lower pH values and in the pH at which the culture washed out. Lactate analysis indicated ta are discussed in relation to the effect of pH on the efficiency of protein synthesis in the rumen and rumen microbial ecology.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRYANT M. P., ROBINSON I. M. Some nutritional characteristics of predominant culturable ruminal bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1962 Oct;84:605–614. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.4.605-614.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYANT M. P., SMALL N., BOUMA C., ROBINSON I. M. Characteristics of ruminal anaerobic celluloytic cocci and Cillobacterium cellulosolvens n. sp. J Bacteriol. 1958 Nov;76(5):529–537. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.5.529-537.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOBSON P. N. CONTINUOUS CULTURE OF SOME ANEROBIC AND FACULTATIVELY ANAEROBIC RUMEN BACTERIA. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Feb;38:167–180. doi: 10.1099/00221287-38-2-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNGATE R. E., DOUGHERTY R. W., BRYANT M. P., CELLO R. M. Microbiological and physiological changes associated with acute indigestion in sheep. Cornell Vet. 1952 Oct;42(4):423–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobson P. N., Stewart C. S. Growth of two rumen bacteria in mixed culture. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Nov;63(3):xi–xi. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson H. R., Hinds F. C., Bryant M. P., Owens F. N. Efficiency of energy utilization by mixed rumen bacteria in continuous culture. J Dairy Sci. 1975 Nov;58(11):1645–1659. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(75)84763-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leatherwood J. M. Cellulose degradation by Ruminococcus. Fed Proc. 1973 Jul;32(7):1814–1818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P. Coupling of phosphorylation to electron and hydrogen transfer by a chemi-osmotic type of mechanism. Nature. 1961 Jul 8;191:144–148. doi: 10.1038/191144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relationship of lactate dehydrogenase specificity and growth rate to lactate metabolism by Selenomonas ruminantium. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Dec;30(6):916–921. doi: 10.1128/am.30.6.916-921.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riebeling V., Thauer R. K., Jungermann K. The internal-alkaline pH gradient, sensitive to uncoupler and ATPase inhibitor, in growing Clostridium pasteurianum. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jul 1;55(2):445–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02181.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Baldwin R. L. Comparison of maintenance energy expenditures and growth yields among several rumen bacteria grown on continuous culture. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):537–543. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.537-543.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Baldwin R. L. Comparison of substrate affinities among several rumen bacteria: a possible determinant of rumen bacterial competition. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):531–536. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.531-536.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Baldwin R. L. Substrate preferences in rumen bacteria: evidence of catabolite regulatory mechanisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Aug;36(2):319–329. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.2.319-329.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Sharp W. M., Baldwin R. L. The effect of pH on maximum bacterial growth rate and its possible role as a determinant of bacterial competition in the rumen. J Anim Sci. 1979 Feb;48(2):251–255. doi: 10.2527/jas1979.482251x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slyter L. L., Oltjen R. R., Kern D. L., Blank F. C. Influence of type and level of grain and diethylstilbestrol on the rumen microbial populations of steers fed all-concentrate diets. J Anim Sci. 1970 Nov;31(5):996–1002. doi: 10.2527/jas1970.315996x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. S. Factors affecting the cellulolytic activity of rumen contents. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Mar;33(3):497–502. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.3.497-502.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


