Abstract
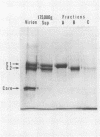
Glass wool column chromatography was used for separation of the two glycoproteins of western equine encephalitis virus. Cross-contamination of each protein separated was confirmed to be negligible by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell J. R., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Purification and amino acid compositions of the structural proteins of sindbis virus. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):287–294. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90340-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. J., Keegstra K. Purification and composition of the proteins from Sindbis virus grown in chick and BHK cells. J Virol. 1976 Dec;20(3):676–686. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.3.676-686.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalrymple J. M., Schlesinger S., Russell P. K. Antigenic characterization of two sindbis envelope glycoproteins separated by isoelectric focusing. Virology. 1976 Jan;69(1):93–103. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90197-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H., Simons K. Location of the spike glycoproteins in the Semliki Forest virus membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):3988–3992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.3988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H., Simons K., Renkonen O. Isolation and characterization of the membrane proteins of Semliki Forest virus. Virology. 1974 Oct;61(2):493–504. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90285-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H., Söderlund H. The amphiphilic membrane glycoproteins of Semliki Forest virus are attached to the lipid bilayer by their COOH-terminal ends. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 25;124(3):535–549. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90186-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto K., Simizu B. Isolation of the structural proteins of western equine encephalitis virus by isoelectric focusing. Arch Virol. 1979;60(3-4):299–309. doi: 10.1007/BF01317501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto K., Suzuki K., Simizu B. Morphological and physical properties of a multiploid-forming mutant of Western equine encephalitis virus. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1454–1466. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1454-1466.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Söderlund H. Stepwise dissociation of the Semliki Forest Virus membrane with trition X-100. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 11;307(2):287–300. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simizu B., Yamazaki S., Suzuki K., Terasima T. Gamma ray-induced small plaque mutants of western equine encephalitis virus. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1568–1578. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1568-1578.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symington J., McCann A. K., Schlesinger M. J. Infectious virus-antibody complexes of sindbis virus. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):720–725. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.720-725.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]