Abstract
The transcription factor interferon regulatory factor-3 (IRF3) regulates expression of type I interferon-β and plays an important role in antiviral immunity. Despite the biological importance of IRF3, its in vivo phosphorylation pattern has not been reported. In this study, we have identified residues in IRF3 that are phosphorylated in vivo after infection with Sendai virus. We found that Sendai virus induced phosphorylation of the C-terminal residues Thr390 and Ser396, in addition to either Ser385 or Ser386. Moreover, Ser173 and Ser175 were constitutively phosphorylated. Ser396 has previously been suggested to be the major target of the IRF3-activating kinase TBK1 (TANK-binding kinase-1), whereas Thr390 has not previously been implicated in IRF3 regulation. Mutagenesis studies indicated that phosphorylation of Thr390 promotes Ser396 phosphorylation and binding to the coactivator cAMP-response element-binding protein. Taken together, our results show that IRF3 is subject to multiple interdependent phosphorylations, and we identify Thr390 as a novel in vivo phosphorylation site that modulates the phosphorylation status of TBK1-targeted Ser396.
Keywords: Innate Immunity, Interferon, Toll-like Receptors, Transcription Factors, Virus, Mass Spectrometry, Proteomics
Introduction
Innate immune responses upon viral infections include production of antiviral cytokines and type I interferons (IFNs).2 The transcription factor interferon regulatory factor-3 (IRF3) is critical for IFN production and directs expression of several diverse genes that are implicated in the antiviral immune response (1). IRF3 is constitutively expressed in multiple tissues and shuttles between the cytoplasm and nucleus in resting cells. Activation of IRF3 involves its virus-induced phosphorylation at several sites in the C-terminal IRF3 dimerization and translocation to the nucleus. In the nucleus, IRF3 associates with cAMP-response element-binding protein-binding protein (CBP) or the closely related p300, promoting binding to promoters containing interferon-stimulated response elements to initiate transcription of target genes (2).
Activation of IRF3 is initiated after recognition of viral nucleic acids by Toll-like receptors or by the cytoplasmic RNA helicases RIG-I and MDA5 (3, 4). These receptors recruit distinct adapter proteins to initiate signaling, which induce ubiquitination of the cytoplasmic adapter protein TRAF3, leading to activation of the IκB kinase-related kinase TANK-binding kinase-1 (TBK1) and phosphorylation of IRF3 (5, 6). The activation mechanism of TBK1 is still poorly understood, but it involves phosphorylation of Ser172 in the mitogen-activated protein kinase activation loop of TBK1 (7, 8).
From studies based on IRF3 mutagenesis, functional in vitro assays, and in vitro phosphorylations of IRF3 with TBK1 (9, 10), it has been proposed that IRF3 is regulated by phosphorylation of multiple residues that are clustered in its C terminus. The IRF3 residues that are phosphorylated in vivo upon viral infection have not been determined directly, but based on an antibody recognizing phosphorylated Ser396, this residue was suggested to be the main target of the IRF3-activating kinase TBK1 (11). It has been advocated that sequential phosphorylation of residues in site 1 (Ser385 and Ser386) and site 2 (Ser396, Ser398, Ser402, Thr404, and Ser405) directs unfolding of an autoinhibitory state and promotes IRF3 dimerization (12–16). However, the sequential order of site 1 and site 2 phosphorylations has been debated. In a recent study, Panne et al. (9) examined IRF3 phosphorylated in vitro with TBK1 and proposed that phosphorylation of residues in site 2 alleviates autoinhibition and promotes site 1 phosphorylation and resultant IRF3 dimerization. However, proof for such a mechanism is still lacking, because the phosphorylation pattern of IRF3 in vivo after viral infection remains elusive. In recent years, mass spectrometry (MS)-based analysis has emerged as a major tool to identify specific post-translational protein modifications, including phosphorylation. In this study, we have utilized MS analysis to identify phosphorylated residues in IRF3 after Sendai virus (SV) infection and to demonstrate several phosphorylated sites in the C-terminal regulatory domain of IRF3. In addition to the previously proposed phosphorylation sites Ser385, Ser386, and Ser396, we found that Thr390 was phosphorylated in response to SV infection. Moreover, Ser173 and Ser175 were found to be constitutively phosphorylated. Functional analysis after in vitro mutagenesis showed that Thr390, in addition to Ser396, contributes to IRF3 activation. This is the first study to identify in vivo phosphorylation sites in IRF3. Our findings show that several phosphorylation sites contribute to regulation of IRF3 activity in vivo. We propose that sequential phosphorylation of distinct sites (Ser385/Ser386 → Ser396 → Thr390 → Ser396, in a feedback mechanism) in the IRF3 C-terminal domain is instrumental for IRF3 activation.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Cell Culture and Reagents
HEK293 cells were obtained from ATCC. Cells were grown in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum, 5 mm l-glutamine, gentamicin, and G418 for selection of stable transfectants. Sendai virus, Cantell strain, was from Charles River Laboratories (Wilmington, MA).
Plasmids and Transfection Assays
The Gal4-IRF3 system has been described (12). The expression construct encoding IRF3FLAG was kindly provided by K. Fitzgerald (University of Massachusetts). Mutants were made using the QuikChange kit (Stratagene), and mutagenesis primers were found by employing the QuikChange primer design program. DNA sequencing was performed using the BigDye 1.1 and 3.1 kit (Applied Biosystems), DyeEx columns (Qiagen), and the ABI3130 capillary electrophoresis station (Applied Biosystems). Transfection was performed with GeneJuice (Novagen), using a reagent/DNA ratio of 4:1. For transfection in a 96-well format, 15,000 cells were seeded per well and allowed to attach before transfection. Cells were stimulated 24 h post-transfection. For 6-well assays, 300,000 cells were seeded per well, whereas 4.8 million cells were seeded per 15-cm plate for immunoprecipitation and subsequent MS analysis of IRF3FLAG.
Immunoprecipitation
After transfection and stimulation, cells were harvested in lysis buffer (50 mm Tris, pH 7.5, 150 mm NaCl, 10% glycerol, 0.5% Triton X-100, 2 mm EDTA, 40 mm β-glycerophosphate, 100 mm NaF, 200 μm Na3VO4, 10 μg/ml leupeptin, 1 μm pepstatin, and 1 mm phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride) and homogenized through a 23-gauge needle, and cell debris was removed by centrifugation. Anti-FLAG M2 Affinity Gel (Sigma) was added to the clarified extracts and left on rotation overnight. The pelleted (8200 × g) affinity gels were washed twice with lysis buffer, and bound proteins eluted with 4× lithium dodecyl sulfate (Invitrogen) or 3× FLAG peptide (Sigma). Representative results from two to four separate experiments are shown.
Gel Electrophoresis and Immunoblotting
Protein samples were electrophoresed using the NuPAGE or blue native NuPAGE system (Invitrogen) and blotted onto Hybond-P nitrocellulose or polyvinylidene difluoride membranes (GE Healthcare) according to the manufacturer's descriptions. Prior to MS analysis, gels were stained with SimplyBlue SafeStain (Invitrogen) according to the maximum sensitivity protocol. Antibodies used in immunoblot analysis were anti-FLAG M2 (Sigma), anti-CBP A-22 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology), anti-IRF3 4962, anti-β-actin 4967, and anti-IRF3 S396-P 4947 (all from Cell Signaling Technology).
Reporter Assays
Luciferase assays were performed in a 96-well format using the luciferase assay system (Promega). After transfection and stimulation, medium was removed, and cells were lysed in 25 μl of diluted luciferase cell culture lysis 5× reagent (Promega). After freezing and thawing, luciferase activity was measured on a Victor luminescence plate reader (PerkinElmer Life Sciences) according to the manufacturer's instruction.
Production of Recombinant Full-length IRF3
Full-length GST-IRF3 in pGEX 6P1 was kindly provided by S. Sankar (Celgene). GST-IRF3 was produced in Escherichia coli BL21 DE3 RIPL (Stratagene), purified on GSTrap HP 1-ml columns (GE Healthcare), and eluted with PreScission protease (GE Healthcare). Aliquots were snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C. Products were verified by MS/MS.
In Vitro Kinase Assay
2 μg of purified IRF3 and 0.5 μg of TBK1 (Upstate Biotechnology, Inc.) was incubated with 1 μm of unlabeled ATP in 40 mm MOPS, pH 7.0, 1 mm EDTA, 5 mm dithiothreitol, 100 mm β-glycerophosphate, 5 mm Na3VO4, 50 mm MgCl2 at 30 °C for 30 min. The reaction was then subjected to immediate proteolysis or snap-frozen and stored at −80 °C.
Proteolytic Digestion and MS Analysis
Immunoprecipitated or recombinant in vitro phosphorylated IRF3 was subjected to proteolysis. Protein bands after gel electrophoresis were digested with trypsin as described previously (17). Peptides were desalted using in-house made C18 reversed phase columns (18), eluted on a stainless steel MALDI plate, and mixed with matrix (7 g/liter α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid). Peptide mass fingerprinting and MS/MS analysis were performed on a Ultraflex III MALDI TOF/TOF (Bruker Daltonics). For MS/MS analysis of phosphorylated peptides, the phosphopeptide fraction was enriched on titanium dioxide (TiO2) columns and eluted at pH >10.5 as described previously (19).
RESULTS
Mass Spectrometry Analysis of in Vivo IRF3 Phosphoforms
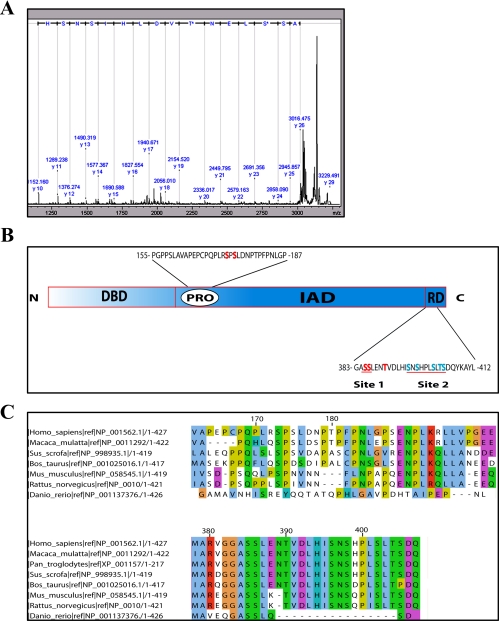
To determine the in vivo phosphorylation pattern of IRF3, HEK293 cells were transfected with FLAG-tagged IRF3 prior to infection with SV and immunoprecipitation using anti-FLAG antibody. Proteins were subjected to blue native (BN)-PAGE to separate proteins in a native state. Several bands were observed in the immunoprecipitates from both untreated and SV-treated cells, including two major bands corresponding to the molecular weights of monomeric and dimeric forms of IRF3 (supplemental Fig. 1A). Parallel immunoblot analysis of BN gels using anti-IRF3 demonstrated that the putative dimer-containing band in the native gel indeed contained IRF3 and that dimerization was induced subsequent to SV infection (supplemental Fig. 1B). To analyze potential phosphorylations in IRF3, bands representing IRF3-containing complexes with molecular weights corresponding to IRF3 monomer and higher oligomers (as indicated in supplemental Fig. 1A) were excised and subjected to phosphopeptide analysis. A representative MS/MS spectrum of a double phosphorylated peptide encompassing residues 384–399 is shown in Fig. 1A. The MALDI-TOF/TOF analyses revealed a complex phosphorylation pattern in IRF3 (Table 1). First, phosphorylation of either Ser173 or Ser175 was observed in all forms of IRF3, indicating that a single phosphorylation at either of these two serines is a constitutive modification in the protein, at least in HEK cells. Constitutive phosphorylation of IRF3 is also corroborated by previous findings from Whathelet et al. (20), who detected partially phosphorylated IRF3 in HEC-1B cells in the absence of virus infection. Ser173 and Ser175 are located within the IRF3 proline-rich domain (schematically depicted in Fig. 1B), and Ser173 was recently proposed to be a target of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) (21). Sequence alignment of IRF3 from different species (Fig. 1C) demonstrated that Ser173 is highly conserved, whereas Ser175 is less well conserved. Second, in the C-terminal regulatory domain (comprising amino acids 380–427 in human IRF3), several phosphorylations were observed that were induced by SV infection. One of the two consecutive serines at position 385 or 386 was found to be phosphorylated in uninfected cells, although we could not unequivocally identify which was targeted. Finally, phosphorylation at Thr390 and Ser396 was only observed in the SV-infected cells. Of these, Ser396 phosphorylation has been described previously and was recently suggested to mediate exposure of Ser339 to phosphorylation and subsequently hyperphosphorylation, dimerization, and association with CBP (10). Notably, phosphorylation of Thr390 has not been described previously. In our analyses, we find this phosphorylation always to occur concomitantly with phosphorylation of either Ser386 or Ser396, and we also identified a triply phosphorylated peptide at Ser385/Ser386/Thr390.
FIGURE 1.
Mass spectrometric identification of in vivo phosphorylation sites in IRF3. A, MS/MS spectrum of the doubly phosphorylated peptide 384–399. HEK293 cells were transfected with IRF3FLAG. 24 h later cells were infected with SV for 12 h. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG-Sepharose and separated by BN-PAGE. Bands corresponding to IRF3 monomer or dimer were excised, and IRF3 was digested with trypsin prior to isolation of phosphopeptides using TiO2. The isolated peptides were analyzed by MALDI/TOF MS/MS. B, schematic overview of IRF3. The DNA-binding domain (DBD), proline-rich domain (PRO), IRF association domain (IAD), and regulatory domain (RD) are indicated. Residues in site 1 and site 2 are indicated (red line). C, alignment of IRF3 sequences from different species using JalView. The amino acids adjacent to Ser173 and Ser175 (upper panel) and amino acids in the C-terminal regulatory domain (lower panel) are shown.
TABLE 1.
In vivo phosphorylation targets IRF3 from SV- and mock-infected cells
FLAG-tagged IRF3 was isolated from either SV- or mock-infected cells and subjected to in-gel digestion and MS analysis as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The 2nd column (PO4) indicates the number of phosphates present on each peptide. The “Sample” column indicates different molecular weights of IRF3-containing complexes that were isolated after BN-PAGE. NS1 and SV1 correspond to monomeric IRF3. NS2–4 and SV2–4 represent IRF3-containing complexes of higher molecular weights.
| IRF3 peptide | No. of PO4 | Amino acid | Sample |
|---|---|---|---|
| BN-PAGE | |||
| 173–193 | 1 | Mix 173 and 175a | NS1 |
| 173–193 | 1 | Mix 173 and 175a | NS2 |
| 173–193 | 1 | Mix 173 and 175a | NS3 |
| 381–409 | 1 | Ser385 or Ser386 | |
| 173–193 | 1 | Mix 173 and 175a | NS4 |
| 381–409 | 1 | Ser385 or Ser386 | |
| 173–193 | 1 | Mix 173 and 175a | SV1 |
| 381–409 | 1 | Ser386 | |
| 381–409 | 2 | ||
| 173–193 | 1 | Mix 173 and 175a | SV2 |
| 381–409 | 1 | Ser386 | |
| 381–409 | 1 | Ser386 and Thr390 | |
| 173–193 | 1 | Mix 173 and 175a | SV3 |
| 381–409 | 1 | Ser386 | |
| 381–409 | 2 | Ser386 and Thr390 | |
| 173–193 | 1 | Mix 173 and 175a | SV4 |
| 381–409 | 1 | Ser386 | |
| 381–409 | 2 | Ser386 and Thr390 | |
| SDS-PAGE | |||
| 173–193 | 1 | Mix 173 and 175a | NS |
| 381–409 | 1 | Ser385, Ser386, or (Thr390) | |
| 173–193 | 1 | Mix 173 and 175a | SV |
| 381–409 | 1 | Ser385 or Ser386 | |
| 381–409 | 2 | (Ser386 and Thr390), (Thr390 and Ser396), (Ser385 and Ser386) | |
a Either of the two phosphorylations (Ser173 or Ser175) is present, but the position could not be unequivocally determined.
Mass Spectrometric Analysis of IRF3 Phosphorylated in Vitro with TBK1
It has been reported that the IRF3-activating kinase TBK1 phosphorylates the C-terminal cluster of Ser and Thr residues (5, 9, 10). As we found that either Ser173 or Ser175 was phosphorylated in all identified phosphoforms of IRF3 (Table 1), we next examined if these residues could be phosphorylated by TBK1. Hence, full-length human GST-IRF3 was expressed in E. coli, and the glutathione S-transferase tag was proteolytically removed during purification. The IRF3 preparation was relatively pure, as assessed by SDS-PAGE and staining with Coomassie Blue (Fig. 2A). Purified IRF3 protein was coincubated with purified TBK1 for in vitro phosphorylation prior to protease digestion, enrichment of phosphopeptides by TiO2, and MS analysis. We found that Ser173 and Ser175 were phosphorylated one by one. Notably, Ser173 and Ser175 were not phosphorylated in bacterially expressed IRF3 that had been incubated in the absence of TBK1. This indicates that TBK1 may directly target Ser173 and Ser175, at least in vitro. Regarding the kinase that phosphorylates Thr390, following in vitro phosphorylation with recombinant purified IRF3 and TBK1, we found up to five simultaneous phosphorylations in the tryptic peptide encompassing amino acids 381–409 in human IRF3 (VGGASSLENTVDLHISNSHPLSLTSDQYK). Heavily phosphorylated peptides ionize poorly thus rendering these peptides more difficult to study by MS. Moreover, because of the complexity and close proximity of these five phosphorylations, we were unable to precisely determine which amino acids were phosphorylated, but most likely one of these is Thr390. However, further studies are needed to strictly determine whether TBK1 phosphorylates Thr390 in vitro and in vivo upon virus infection. Immunoblotting confirmed that incubation of IRF3 with TBK1 induced phosphorylation of Ser386 and Ser396 and IRF3 dimerization (Fig. 2B).
FIGURE 2.
Identification of phosphorylated peptides in IRF3 phosphorylated in vitro with TBK1. A, full-length GST-IRF3 was produced in E. coli and purified on GSTrap HP before elution and removal of the glutathione S-transferase tag with PreScission protease. The purity was examined by SDS-PAGE and staining with Coomassie Blue. B, IRF3 purified from E. coli was phosphorylated in vitro with TBK1 and separated by BN-PAGE prior to immunoblotting (IB) with antibodies recognizing IRF3 phosphorylated on Ser396, Ser386, or total IRF3.
Transcriptional Activity of IRF3 Phosphoinhibiting Mutants
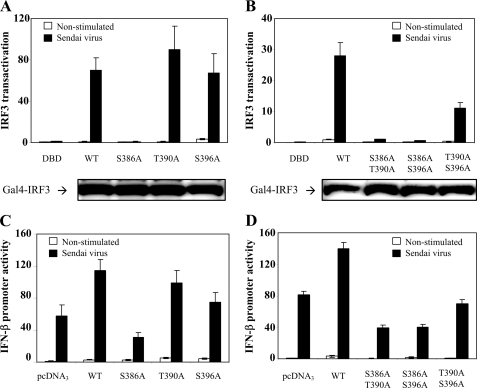
Given the putative critical roles of Ser386 and Ser396 phosphorylation in IRF activation, we wanted to investigate the potential role of the newly identified Thr390 phosphorylation in this context. We generated several phosphoinhibiting IRF3 mutants by replacing Ser or Thr with Ala residues and examined their transactivation capacities using a Gal4 reporter system. This is an in vivo assay for IRF3 activation in which wild type IRF3 or IRF3 mutants lacking the DNA-binding domain are fused to the Gal4-DNA-binding domain. The Gal4-IRF3 constructs are cotransfected with a Gal4-driven luciferase reporter to measure IRF3 activation (20). We introduced T390A mutations alone or in combination with S386A (site 1) or S396A (site 2) mutations. HEK293 cells were transfected with the indicated constructs and infected or not with SV. We found that the transactivation capacity of S386A was abrogated (Fig. 3A), in agreement with previous results (22). Transactivation by the T390A and S396A mutants was comparable with that of wild type IRF3 (Fig. 3A). Introducing double Ala mutants containing S386A also abrogated IRF3 transactivation, although mutating both Thr390 and Ser396 to Ala residues led to markedly decreased IRF3 activation (Fig. 3B). Immunoblot analysis showed that all of the mutants were expressed to similar levels (Fig. 3, A and B, lower panels).
FIGURE 3.
Transcriptional activation and IFN-β production of phosphoinhibiting IRF3 mutants. A and B, HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with Gal4-based IRF3 luciferase reporter constructs containing wild type (WT) IRF3 or the indicated IRF3 mutants. 24 h post-transfection, cells were infected or not with SV for 12 h and lysed, and the luciferase reporter gene activity was measured. The transcriptional activity is shown as fold induction over nonstimulated wild type IRF3. The expression level of IRF3 mutants was assessed by immunoblotting of whole cell lysates (lower panels). DBD, DNA-binding domain. C and D, HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with an IFN-β luciferase reporter and wild type IRF3 or the indicated IRF3 mutants. 24 h post-transfection, cells were infected or not with SV for 12 h and lysed, and luciferase reporter gene activity was measured. The transcriptional activity is shown as fold induction over cells transfected with empty vector.
We also examined the transcriptional activation of wild type IRF3 and IRF3 mutants using a luciferase reporter construct monitoring the IRF3-sensitive IFN-β promoter. Virus-induced IFN-β transcription is directed by the transcription factors IRF3, NF-κB, and ATF2 (2). HEK293 cells were cotransfected with an IFN-β reporter, full-length wild type IRF3, or IRF3 mutants prior to infection with SV. IFN-β promoter activation in the presence of IRF3 mutants largely reflected the results obtained by Gal4-based transactivation (Fig. 3, C and D). However, the effect of mutating both Thr390 and Ser396 was less pronounced in this assay compared with the Gal4-based assay. This possibly reflects that additional transcription factors are necessary for IFN-β transcription. Taken together, these results show that mutation of Thr390 or Ser396 alone is not sufficient to significantly decrease IRF3 activation. Hence, our results corroborate the notion that the phosphorylatable residues clustered in the IRF3 C terminus act together as also proposed from previous studies (9).
Transcriptional Activity of IRF3 Phosphomimicking Mutants
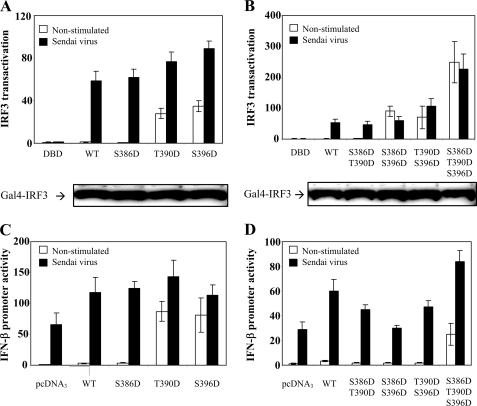
To further examine the functional roles of the IRF3 phosphorylation sites identified from our MS analysis, various IRF3 phosphoforms were mimicked by introducing Ser and Thr to Asp mutations. IRF3S396D has previously been reported to be a strong transactivator of interferon-stimulated response element-containing promoters (11). Wild type IRF3 and IRF3 mutants were transiently transfected into HEK293 cells, and their transactivation capacity was assessed using the Gal4 reporter system. We found that IRF3T390D induced transactivation to similar levels as IRF3S396D in unstimulated cells, whereas SV-stimulated IRF3 activation was higher for IRF3S396D than for IRF3T390D (Fig. 4A). Introducing several Asp residues for Ser or Thr residues enhanced transactivation capacity under basal conditions, whereas SV-stimulated activation was moderately altered. The double mutant IRF3S386D/T390D did not stimulate transactivation in unstimulated cells, whereas IRF3S386D/S396D and IRF3T390D/S396D reproducibly increased IRF3 activation in uninfected cells (Fig. 4B). This may suggest that Ser396 is particularly important for IRF3 transactivation capacity. Notably, the triple mutant IRF3S386D/T390D/S396D very potently induced IRF3 transactivation in the absence of SV infection (Fig. 4B), possibly reflecting the importance of multiple negative charges for optimal IRF3 activation. IRF3S386D/S396D, IRF3T390D/S396D, and IRF3S386D/T390D/S396D could not be further activated by SV infection. The various IRF3 phosphomimicking mutants were expressed to similar levels as wild type IRF3 (Fig. 4, A and B, lower panels), thus precluding differential expression as a cause of altered activity.
FIGURE 4.
Transcriptional activation and IFN-β production of phosphomimicking IRF3 mutants. A and B, HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with Gal4-based IRF3 luciferase reporter constructs containing wild type (WT) IRF3 or the indicated IRF3 mutants. 24 h post-transfection, cells were infected or not with SV for 12 h and lysed, and luciferase reporter gene activity was measured. The transcriptional activity is shown as fold induction over nonstimulated wild type IRF3. The expression level of IRF3 mutants was assessed by immunoblotting of whole cell lysates (lower panels). DBD, DNA-binding domain. C and D, HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with an IFN-β luciferase reporter and wild type IRF3 or the indicated IRF3 mutants. 24 h post-transfection, cells were infected or not with SV for 12 h and lysed, and luciferase reporter gene activity was measured. The transcriptional activity is shown as fold induction over cells transfected with empty vector.
We next examined if the effect of Asp mutations on SV elicited IFN-β transcription (Fig. 4, C and D). Indeed, IRF3T390D and IRF3S396D stimulated IFN-β transcription in uninfected cells, thus corroborating Gal4 reporter-based results. Surprisingly, however, IFN-β transcription after transfection of double Asp mutants differed from data from Gal4-based IRF3 activation for these mutants. As mentioned previously, this might reflect the involvement of several transcription factors in IFN-β promoter activation as compared with the Gal4-based IRF3 activation assay. Thus specific phosphomimicking mutations may mediate both increased and decreased association to such transcription factors in the IFN-β system. Nevertheless, taken together, our results show that Thr390 contributes to IRF3 transcriptional activation. However, the precise mechanism likely depends on the availability and status of other transcription modulators as well as the post-translational modification status at other sites in IRF3 itself.
Effect of Mutations in the IRF3 C-terminal Domain on Interaction between IRF3 and CBP
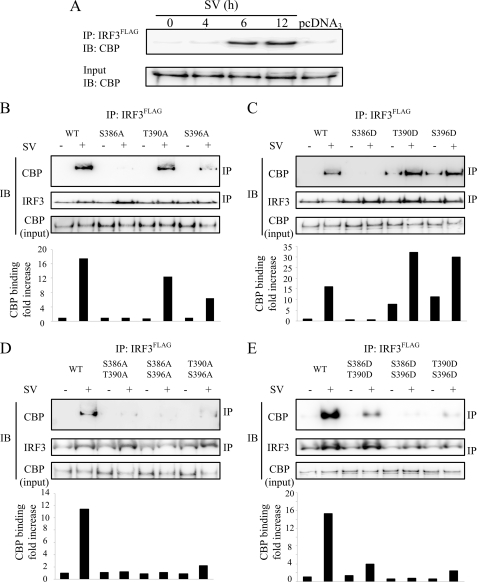
The coactivator CBP and the closely related p300 associate with IRF3 causing increased IRF3-mediated transcription (12). CBP acts to recruit RNA polymerase II and chromatin remodeling proteins. Ser396 has previously been implicated in binding to CBP (11, 15). Servant et al. (11) found that replacement of Ser396 with Ala abrogated binding of IRF3 to CBP, whereas replacement of this residue with Asp leads to CBP binding in the absence of IRF3-triggering stimulus. We examined the role of IRF3 C-terminal phosphorylations for interaction with CBP by coimmunoprecipitation assays using an anti-FLAG antibody for immunoprecipitation of FLAG-tagged IRF3 and detecting coprecipitated endogenous CBP. First, we investigated the kinetics of IRF3 and CBP association after SV infection. We found that CBP and IRF3 interacted after 6 and 12 h of SV infection (Fig. 5A). Mutating Thr390 to Ala reduced CBP-IRF3 interaction to 70% that of wild type IRF3, whereas mutating Ser396 to Ala decreased the association of IRF3 with CBP to 40% of wild type IRF3 (Fig. 5B). Interestingly, both IRF3T390D and IRF3S396D were able to bind CBP in uninfected cells, exhibiting CBP binding of 50 and 72% that of SV-stimulated wild type IRF3 (Fig. 5C). Moreover, SV-stimulated CBP binding of IRF3T390D and IRF3S396D was markedly increased to 199 and 186% that of wild type IRF3 (Fig. 5C). This indicates that Thr390 and Ser396 contribute to IRF3-mediated CBP binding. Mutating Ser386 to either Ala or Asp completely abolished CBP binding, thus corroborating previous results in which Ser385 and Ser386 were replaced with Ala (13). Very weak binding was observed between the double mutants IRF3S386A/T390A, IRF3S386A/S396A, or IRF3T390A/S396A and CBP in resting or SV-infected cells (Fig. 5D). Collectively, these results suggest that both Thr390 and Ser396 mediate binding of IRF3 to the cofactor CBP. Introducing two Asp residues for Ser or Thr residues leads to decreased SV-stimulated CBP binding of IRF3S386D/T390D, IRF3S386D/S396D, and IRF3T390D/S396D relative to wild type IRF3 (giving reductions to 24, 5, and 16% of wild type CBP binding, respectively; Fig. 5E). Immunoblotting showed that the double Asp mutants were expressed at levels comparable with that of wtIRF3 (Fig. 6D). Notably, IRF3T390D/S396D exhibited considerably reduced CBP binding. Hence, although Asp residues introduced separately at either Thr390 or Ser396 promote CBP binding, double Asp substitution at these sites results in abrogated CBP binding. This result was rather surprising. However, substitution of Ser/Thr by Asp (or Glu) can only substitute partially for phosphates at these positions, and conceivably, a double phosphomimicking mutant may introduce structural perturbations that affect binding to CBP. Moreover, an aspartate only introduces one negative charge in contrast to the two negative charges introduced by one phosphate. Consequently, the IRF3T390D/S396D double mutant carries a total of two negative charges at these sites, whereas either of the single mutants actually has the potential of carrying three negative charges if phosphorylated at the nonmutated residue. This may possibly lead to reduced capability of binding to CBP by the double phosphomimicking mutant as compared with the single mutants.
FIGURE 5.
Association of IRF3 mutants with the transcriptional coactivator CBP. A, HEK293 cells were transfected with wild type IRF3FLAG for 24 h and infected with SV for 2, 6, or 12 h. Cells transfected with pcDNA3 were stimulated with SV for 12 h. Lysates were prepared, and IRF3 was immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-FLAG-Sepharose followed by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-CBP. Input lysates were probed with anti-CBP to show endogenous levels of CBP. B–E, HEK293 cells were transfected with the indicated FLAG-tagged IRF3 wild type (WT) or mutants and infected with SV for 12 h. Lysates were prepared, and IRF3 variants were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG-Sepharose followed by immunoblotting with anti-CBP to detect endogenous CBP. Membranes were reprobed with anti-IRF3 to detect immunoprecipitated IRF3. Expression of CBP in input lysates was monitored by immunoblotting. Band intensities were quantified using the Kodak image analysis software. Intensities of CBP were normalized to intensities of immunoprecipitated IRF3 or IRF3 mutants and expressed as fold increase relative to medium-treated cells transfected with wtIRF3 (lower panel).
FIGURE 6.
SV-elicited phosphorylation of Ser396 and Ser386. A–D, HEK293 cells were transfected with the indicated IRF3 wild type (WT) or mutants and infected or not with SV for 12 h. Lysates were prepared, and phosphorylation of Ser396 was examined by immunoblotting with an antibody recognizing phosphorylated Ser396. Membranes were reprobed with anti-FLAG. Band intensities were quantified using the Kodak image analysis software. Intensities of phosphorylated Ser396 were normalized to intensities of FLAG-tagged IRF3 or IRF3 mutants and expressed as fold increase relative to medium-treated cells transfected with wtIRF3 (lower panels; A and B). E, lysates were prepared from SV-infected HEK293 cells and separated by native PAGE or SDS-PAGE prior to immunoblotting (IB) with anti-Ser(P)386, anti-Ser(P)396, or total IRF3.
Sequential Phosphorylations in the IRF3 C-terminal Domain
Given the suggested role of Ser396 phosphorylation in IRF3 activation and CBP binding (11), we then examined the effect of mutations at Ser386 or Thr390 on SV-stimulated phosphorylation of Ser396. Lysates from HEK293 cells transfected with wild type or mutant IRF3 were immunoblotted with anti-Ser(P)396. Mutation of Ser386 to either Ala or Asp abolished SV-elicited phosphorylation of Ser396 (Fig. 6, A and B). Note that endogenous IRF3 comigrates with transfected IRF3 mutants. Interestingly, mutation of the Ser386 residue consistently appeared to affect the phosphorylation of Ser396 negatively, regardless of being mutated to Ala or Asp. Conversely, mutation of Thr390 to Asp apparently has the opposite effect. This was especially evident in the IRF3T390D mutant, which was significantly more phosphorylated at Ser396 than the wild type after SV infection, showing a 200% increase relative to SV-stimulated wild type IRF3 (Fig. 6B). Phosphorylation of Ser396 was also evident in IRF3T390D in the absence of SV infection, resulting in 35% phosphorylation compared with SV-infected wild type IRF3. Replacement of Thr390 with Ala reduced SV-elicited Ser396 phosphorylation to 64% that of wild type IRF3 (Fig. 6A). The double mutant IRF3S386D/T390D exhibited significantly reduced Ser396 phosphorylation (Fig. 6D), reflecting that Ser386 mutations negatively affect phosphorylation of Ser396, similarly to the effect of Ser386 mutations on CBP binding. Importantly, these results suggest that phosphorylation of Thr390 modulates virus-induced phosphorylation of Ser396. This may indicate that the phosphorylation status at these two residues (Ser386 and Thr390) constitutes a structural “switch” in the protein, indirectly modulating the accessibility for phosphorylation of Ser396.
It is uncertain whether Ser386 is phosphorylated prior to Ser396 phosphorylation or vice versa. To examine the sequential order of Ser386 and Ser396 phosphorylations, lysates from cells infected with SV were separated by native PAGE and immunoblotted with antibodies recognizing phosphorylated Ser386 or Ser396. We found that phosphorylation of Ser386 and Ser396 appeared to have similar kinetics. However, Ser386 was phosphorylated in both monomeric and dimeric IRF3, whereas Ser396 was only phosphorylated in IRF3 dimers (Fig. 6E). These results strongly indicate that phosphorylation of Ser386 occurs first, inducing IRF3 dimerization and Ser396 phosphorylation. We have previously reported the kinetics of IFN-β transcription (23), and phosphorylation of Ser386 and Ser396 coincided with IFN-β induction in these cells.
DISCUSSION
Despite the important role of IRF3 in antiviral signaling, its in vivo phosphorylation pattern has not been reported. The role of phosphorylation in IRF3 activation has to date been studied by indirect methods using in vitro mutagenesis and deletion mapping, phosphospecific antibodies, or in vitro phosphorylation studies with IRF3 (purified from bacteria or insect cells) and recombinant TBK1 (9–11, 14, 22). In this study we immunoprecipitated FLAG-tagged IRF3 from SV-infected cells and by MS analysis directly identified sites that are phosphorylated in IRF3. Our results show that Ser386, Thr390, and Ser396, which are located in the C-terminal regulatory domain of IRF3 (amino acids 380–427), are phosphorylated after SV infection. Moreover, our mutagenesis studies indicate that Thr390, which has not previously been implicated in IRF3 activation, contributes to IRF3-mediated transcription through positively affecting SV-induced phosphorylation of Ser396, binding of the cofactor CBP and IRF3 transcriptional activation. We found that substitutions of either Thr390 or Ser396 with Ala did not ablate binding to CBP and did not significantly affect IRF3 transactivation. However, in a double IRF3 mutant in which both Thr390 and Ser396 were mutated to Ala, CBP binding was abrogated, and IRF3 transactivation was significantly impaired. This likely reflects that IRF3 regulation is an intricate process controlled by multisite hierarchical phosphorylations that are mutually dependent to achieve optimal IRF3 activation.
The residue corresponding to Thr390 is evolutionarily strictly conserved in mammals, whereas the eight residues upstream and downstream of Thr390 are highly conserved. One previous study has suggested a role for threonine phosphorylation in IRF3 regulation in vivo. Weaver et al. (24) isolated 32P-labeled IRF3 from Newcastle disease virus-infected cells prior to phosphoamino acid analysis of IRF3. The authors found that IRF3 was phosphorylated mainly on serine residues but also in part on threonine residues (24), suggesting a role for threonine phosphorylation in IRF3 responses in vivo. In this study we used SV, which is a single-stranded RNA virus that is recognized by the cytoplasmic RNA helicase RIG-I (25). It is possible that IRF3 phosphorylation may be subject to quantitative and qualitative changes depending on the nature of the virus and host recognition mechanisms. Indeed, Noyce et al. (26) reported that human cytomegalovirus (double-stranded DNA virus) and Newcastle disease virus (single-stranded RNA virus) produced different migration patterns after two-dimensional PAGE separation of IRF3. This indicates that distinct IRF3 post-translational modifications may prevail after infection with specific viruses. From MS analysis, we observed that Ser173 and Ser175 were phosphorylated both in uninfected and in SV-infected cells, but the results do not disclose the stoichiometry of phosphorylation at these sites, i.e. if phosphorylation is positively or negatively affected by viral exposure. The sequence around Ser173 resembles SP-phosphodegron motifs, and IRF3 protein levels have been reported to be sensitive to proteasome inhibitors. Hence, phosphorylation of Ser173 and Ser175 may be implicated in ubiquitin-mediated IRF3 degradation. These aspects are currently under investigation in our laboratory.
In this study, we transfected IRF3 and examined its phosphorylation pattern in medium- and SV-treated cells. We also attempted to map the phosphorylation sites of endogenous IRF3. However, endogenous levels of IRF3 are low and consist of multiple, distinct phosphoforms. The inherent problem of lower detection limit for phosphorylated peptides compared with nonphosphorylated peptides necessitates significant amounts of IRF3 for identification of phosphopeptides by MS. We did not succeed to efficiently affinity purify IRF3 for this purpose. Difficulties with effective affinity enrichment of endogenous IRF3 might rely on intrinsic biological mechanisms such as shielding of the most immunogenic epitopes of the protein within IRF3 dimers/multimers or even within larger multiprotein complexes. Nevertheless, we examined activation properties of transfected IRF3 and found that it does not bind CBP or induce IFN-β production in the absence of viral infection, whereas transfection of IRF3 leads to enhanced SV-induced IFN-β production (Figs. 3–5). Moreover, transfected IRF3 is not spontaneously phosphorylated at Ser396, but its Ser396 phosphorylation is induced by SV and follows comparable kinetics as endogenous IRF3. Also, SV-induced Ser396 phosphorylation is increased for transfected IRF3 (compared with endogenous IRF3; supplemental Fig. 2). Taken together, this suggests that overexpressed IRF3 is not activated aberrantly but follows the similar virus-induced regulatory switches that apply to endogenous IRF3. Thus, our findings on phosphorylation sites in (transfected) IRF3 should be valuable and contribute to understanding of IRF3 activity regulation.
There have been numerous reports on IRF3 phosphorylation, but these are based on mutation of presumed phosphorylation sites, in vitro phosphorylations (using partially purified IRF3 and TBK1), or phosphorylation state-specific antibodies toward Ser386 or Ser396 (9–11). This is the first study to directly determine sites that are simultaneously phosphorylated in IRF3 after a viral infection (Table 1). Our findings implicate Thr390 (which has not previously been identified as an IRF3 phosphorylation site) in IRF3 activation and IFN-β transcription. Our results show that the phosphorylation site considered to be of highest importance for IRF3 antiviral activity, Ser396, is regulated by the phosphorylation status of Thr390. Additionally, by making use of a phosphoproteomic approach, we were able to identify multisite phosphorylated peptides, thus providing information on multisite, hierarchical phosphorylations. We found that phosphorylation of Thr390 always occurred concomitantly with phosphorylation of either Ser386 or Ser396, and we also identified a triply phosphorylated peptide with Ser385/Ser386 and Thr390(Table 1). Although the implication of this is presently not clear, it has been shown in other settings that specific combinations of phosphorylations and their timely occurrence within a biological pathway are crucial for modulation of activity. We have recently demonstrated this for another protein, the uracil-DNA glycosylase UNG2 (27).
A functional role for phosphorylation of the IRF3 C terminus has been proposed from the cocrystal structure of IRF3 with the IRF3-binding domain of CBP. Based on this structure, it has been suggested that IRF3 in unstimulated cells exists in a latent form that is autoinhibited by interactions within the IRF association domain of each monomer (15). This autoinhibited state of IRF3 masks a hydrophobic surface, which upon unfolding of IRF3 mediates IRF3-CBP binding as illustrated in Fig. 7A. Thus, it has been suggested that phosphorylation of the IRF3 C terminus leads to unfolding of the regulatory domain because of repulsions between negative charges and the hydrophobic region. Hence, initial phosphorylation(s) in the C-terminal regulatory domain may trigger conformational changes (e.g. partial relief of the autoinhibitory folding of IRF3) that facilitate phosphorylation at other sites in IRF3.
FIGURE 7.
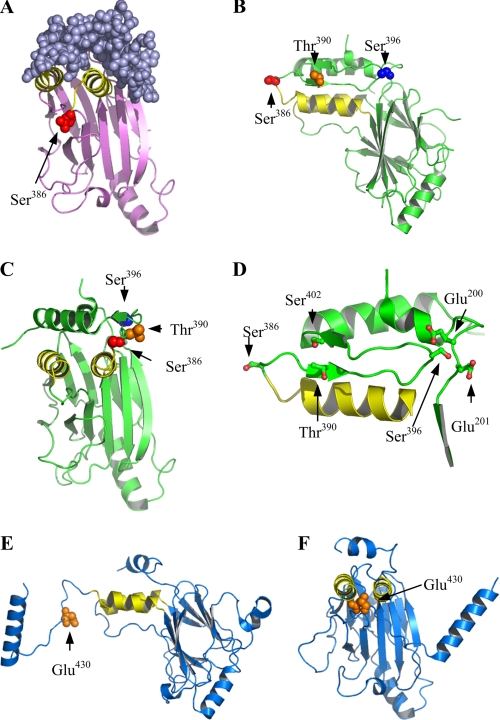
Structural views of IRF3 residues implicated in phosphorylation. A, IRF3 lacking the C-terminal regulatory domain cocrystallized with the IRF3-binding domain of CBP (15). The two IRF3-CBP units found in the crystal structure are shown. IRF3 is displayed in ribbon representation (pink), and CBP is space-filled (purple). The two α-helices in IRF3 interacting with CBP are shown in yellow. B and C, backbone of IRF3 (28) is shown in ribbon representation (green). The phosphorylatable residues Ser386, Thr390, and Ser396 are space-filled and colored (Ser386, red; Thr390, orange; Ser396, blue). D, close up and reduced view of views in A and B illustrating residues in proximity to Ser386, Thr390, and Ser396 (shown in ball-and-stick format). E and F, structure of IRF5S430D (29). The backbone of IRF5 is shown in ribbon presentation (blue), and the Asp residue at position 430 (replacement for Ser430 which corresponds to Thr390 in IRF3) is shown in orange. The two α-helices corresponding to the CBP-binding helices in D are shown in yellow. A, Protein Data Bank accession code 1ZOQ (15); B and C, Protein Data Bank accession code 1J2F (28); E and F, Protein Data Bank accession code 3DSH (29). Structural figures were generated using the PyMOL program (DeLano Scientific LCC).
In an attempt to rationalize our results obtained with IRF3 phosphorylation site mutants in terms of structural insight, we examined the published crystal structures of IRF3 and the closely related IRF5 (15, 16, 28, 29). In two tertiary structures of IRF3 (16, 28), the phosphorylation targets in the C-terminal regulatory domain are partially surface-exposed. This is especially evident for Ser386 that is located in a solvent-accessible turn and should thus be readily available for phosphorylation. This is illustrated in two different structural views of IRF3 (Fig. 7, B and C). Previous results and our findings presented herein suggest that phosphorylation of Ser396 is of particular importance for IRF3 activation. The structure of IRF3 shows that Ser396 is located in the proximity of the negatively charged residues Glu200 and Glu201 (Fig. 7D). Hence, as suggested by Qin et al. (16), phosphorylation of Ser396 would introduce a negative charge that could cause conformational changes because of electrostatic repulsion. This provides a structural basis for the importance of Ser396 phosphorylation in IRF3 activation.
Based on results obtained with various Ala and Asp mutations, it has been discussed whether Ser386 (site 1) or Ser396 (site 2) is the critical/initial virus-induced phosphorylation residue (11, 14, 22). Panne et al. (9) suggested that phosphorylation of site 2 residues alleviated IRF3 autoinhibition, allowing for CBP binding and facilitating phosphorylation at site 1 (Ser385/Ser386). Mori et al. (22) proposed that phosphorylation of site 1 was the initial event and was instrumental for IRF3 dimerization. In our study, MS analysis revealed that Ser385 or Ser386, in contrast to Ser396, was phosphorylated in noninfected cells. Also, we found that Ser386 was phosphorylated in monomeric and dimeric IRF3, whereas Ser396 was predominantly phosphorylated in IRF3 dimers (Fig. 6E). Hence, from our results we propose that Ser386 phosphorylation is the primary event. This also agrees with the higher solvent accessibility of Ser386 compared with Ser396. Phosphorylation of Ser386 might, however, promote partial unfolding of the autoinhibitory IRF3 structure and increase the accessibility of Ser396 to facilitate its phosphorylation, as suggested by Qin et al. (16).
Regarding the mechanistic role of Thr390 phosphorylation, our results show that Asp replacement of Thr390 facilitates phosphorylation of Ser396 and even induced CBP binding in the absence of viral infection (Figs. 5C and 6B). This suggest that phosphorylation of Thr390 may constitute an additional priming event for Ser396 phosphorylation. Thr390 is situated in a β-sheet that forms a “stem-loop” structure within the regulatory domain (β12) (16, 28), in which Ser396 is located at the turn (Fig. 7D). A recent crystal structure of an IRF5 mutant (IRF5S430D) might elucidate the role of Thr390 phosphorylation. The tertiary structure of IRF5S430D illustrates that IRF3 and IRF5 have extensive structural homology (29). Importantly, amino acid sequence alignment of IRF3 and IRF5 indicates that Ser430 in IRF5 corresponds to Thr390 in IRF3 (29). Based on thermodynamic measurements and tertiary structure, Chen et al. (29, 30) suggested that Ser430 phosphorylation is important for IRF5 dimerization and CBP binding. Interestingly, the tertiary structure of IRF5S430D revealed that the Asp replacement resulted in an extended structure in which the C-terminal regulatory domain is displaced, rendering the CBP binding region in IRF5 surface-accessible (Fig. 7, E and F). It is thus tempting to speculate that a similar mechanism applies to IRF3 and that phosphorylation of Thr390 in IRF3 could disrupt the β-sheet around Thr390 and unfold the stem-loop structure. Hence, phosphorylation of Thr390 might stabilize an open, uninhibited form of IRF3 that might promote IRF3-CBP binding in the absence of viral infection and also enhance accessibility of Ser396 for phosphorylation (as observed in this study for the IRF3T390D mutant, see Fig. 6B). Moreover, in analogy with IRF5S430D, it is possible that Thr390 phosphorylation in IRF3 promotes dimerization. Importantly, this could provide a structural basis for the role of Thr390 in IRF3 activation.
In contrast to Ser396, Thr390 is not within contact length to other charged residues in IRF3 (irrespective of phosphorylation status) but is within van der Waals contact length to Ser402 that is located opposite the β-strand (β13) of the stem-loop β-sheet (Fig. 7D). In theory, double phosphorylation of both Thr390 and Ser402 should thus promote additional disruption of this stem-loop structure. Although phosphorylation of Ser402 was not observed in our analyses, a previous study found Ser402 to be phosphorylated by TBK1 in vitro (10). The precise role of this phosphorylation in IRF3 activation thus warrants further investigation.
In conclusion, our novel results show that Ser386 (or Ser385), Thr390, and Ser396 that are located in the C-terminal regulatory domain of IRF3 are phosphorylated in vivo in response to SV infection. Moreover, our results suggest a sequential interplay between these phosphorylation sites, reflecting that mutually dependent phosphorylations regulate IRF3 activation in vivo.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Sissel Havåg and Veslemøy M. Landsem for excellent technical assistance.
This work was supported by the National Programme for Research in Functional Genomics (FUGE) in Norway (to M. W. A.), FUGE Mid-Norway (to M. W. A.), the Research Council of Norway (to M. W. A.), the Faculty of Medicine, Norwegian University of Science and Technology (to I. B. J. and M. W. A.), the Cancer Fund at St. Olavs Hospital (to M. W. A.), and the Norwegian Cancer Society.

The on-line version of this article (available at http://www.jbc.org) contains supplemental Figs. 1 and 2.
- IFN
- interferon
- TLR
- Toll-like receptors
- SV
- Sendai virus
- TRAF
- tumor necrosis receptor-associated factor
- IRF
- interferon regulatory factor
- CBP
- CREB-binding protein
- MS
- mass spectrometry
- BN
- blue native
- MOPS
- 4-morpholinepropanesulfonic acid
- MALDI-TOF'/TOF
- matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight/time-of-flight.
REFERENCES
- 1.Andersen J., VanScoy S., Cheng T. F., Gomez D., Reich N. C. (2008) Genes Immun. 9, 168–175 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Panne D., Maniatis T., Harrison S. C. (2007) Cell 129, 1111–1123 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Alexopoulou L., Holt A. C., Medzhitov R., Flavell R. A. (2001) Nature 413, 732–738 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kato H., Takeuchi O., Sato S., Yoneyama M., Yamamoto M., Matsui K., Uematsu S., Jung A., Kawai T., Ishii K. J., Yamaguchi O., Otsu K., Tsujimura T., Koh C. S., Reis e Sousa C., Matsuura Y., Fujita T., Akira S. (2006) Nature 441, 101–105 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Fitzgerald K. A., McWhirter S. M., Faia K. L., Rowe D. C., Latz E., Golenbock D. T., Coyle A. J., Liao S. M., Maniatis T. (2003) Nat. Immunol. 4, 491–496 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kayagaki N., Phung Q., Chan S., Chaudhari R., Quan C., O'Rourke K. M., Eby M., Pietras E., Cheng G., Bazan J. F., Zhang Z., Arnott D., Dixit V. M. (2007) Science 318, 1628–1632 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Clark K., Plater L., Peggie M., Cohen P. (2009) J. Biol. Chem. 284, 14136–14146 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kishore N., Huynh Q. K., Mathialagan S., Hall T., Rouw S., Creely D., Lange G., Caroll J., Reitz B., Donnelly A., Boddupalli H., Combs R. G., Kretzmer K., Tripp C. S. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277, 13840–13847 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Panne D., McWhirter S. M., Maniatis T., Harrison S. C. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282, 22816–22822 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Clément J. F., Bibeau-Poirier A., Gravel S. P., Grandvaux N., Bonneil E., Thibault P., Meloche S., Servant M. J. (2008) J. Virol. 82, 3984–3996 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Servant M. J., Grandvaux N., tenOever B. R., Duguay D., Lin R., Hiscott J. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278, 9441–9447 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Yoneyama M., Suhara W., Fukuhara Y., Fukuda M., Nishida E., Fujita T. (1998) EMBO J. 17, 1087–1095 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lin R., Mamane Y., Hiscott J. (1999) Mol. Cell. Biol. 19, 2465–2474 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lin R., Heylbroeck C., Pitha P. M., Hiscott J. (1998) Mol. Cell. Biol. 18, 2986–2996 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Qin B. Y., Liu C., Srinath H., Lam S. S., Correia J. J., Derynck R., Lin K. (2005) Structure 13, 1269–1277 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Qin B. Y., Liu C., Lam S. S., Srinath H., Delston R., Correia J. J., Derynck R., Lin K. (2003) Nat. Struct. Biol. 10, 913–921 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Shevchenko A., Wilm M., Vorm O., Mann M. (1996) Anal. Chem. 68, 850–858 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Rappsilber J., Ishihama Y., Mann M. (2003) Anal. Chem. 75, 663–670 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Thingholm T. E., Jørgensen T. J., Jensen O. N., Larsen M. R. (2006) Nat. Protoc. 1, 1929–1935 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wathelet M. G., Lin C. H., Parekh B. S., Ronco L. V., Howley P. M., Maniatis T. (1998) Mol. Cell 1, 507–518 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Zhang B., Li M., Chen L., Yang K., Shan Y., Zhu L., Sun S., Li L., Wang C. (2009) Cell Res. 19, 412–428 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mori M., Yoneyama M., Ito T., Takahashi K., Inagaki F., Fujita T. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279, 9698–9702 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Johnsen I. B., Nguyen T. T., Bergstroem B., Fitzgerald K. A., Anthonsen M. W. (2009) J. Biol. Chem. 284, 19122–19131 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Weaver B. K., Kumar K. P., Reich N. C. (1998) Mol. Cell. Biol. 18, 1359–1368 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Rothenfusser S., Goutagny N., DiPerna G., Gong M., Monks B. G., Schoenemeyer A., Yamamoto M., Akira S., Fitzgerald K. A. (2005) J. Immunol. 175, 5260–5268 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Noyce R. S., Collins S. E., Mossman K. L. (2009) J. Virol. 83, 4013–4022 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hagen L., Kavli B., Sousa M. M., Torseth K., Liabakk N. B., Sundheim O., Pena-Diaz J., Otterlei M., Hørning O., Jensen O. N., Krokan H. E., Slupphaug G. (2008) EMBO J. 27, 51–61 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Takahasi K., Suzuki N. N., Horiuchi M., Mori M., Suhara W., Okabe Y., Fukuhara Y., Terasawa H., Akira S., Fujita T., Inagaki F. (2003) Nat. Struct. Biol. 10, 922–927 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chen W., Lam S. S., Srinath H., Jiang Z., Correia J. J., Schiffer C. A., Fitzgerald K. A., Lin K., Royer W. E., Jr. (2008) Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 15, 1213–1220 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Chen W., Srinath H., Lam S. S., Schiffer C. A., Royer W. E., Jr., Lin K. (2008) J. Mol. Biol. 379, 251–260 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.