Abstract
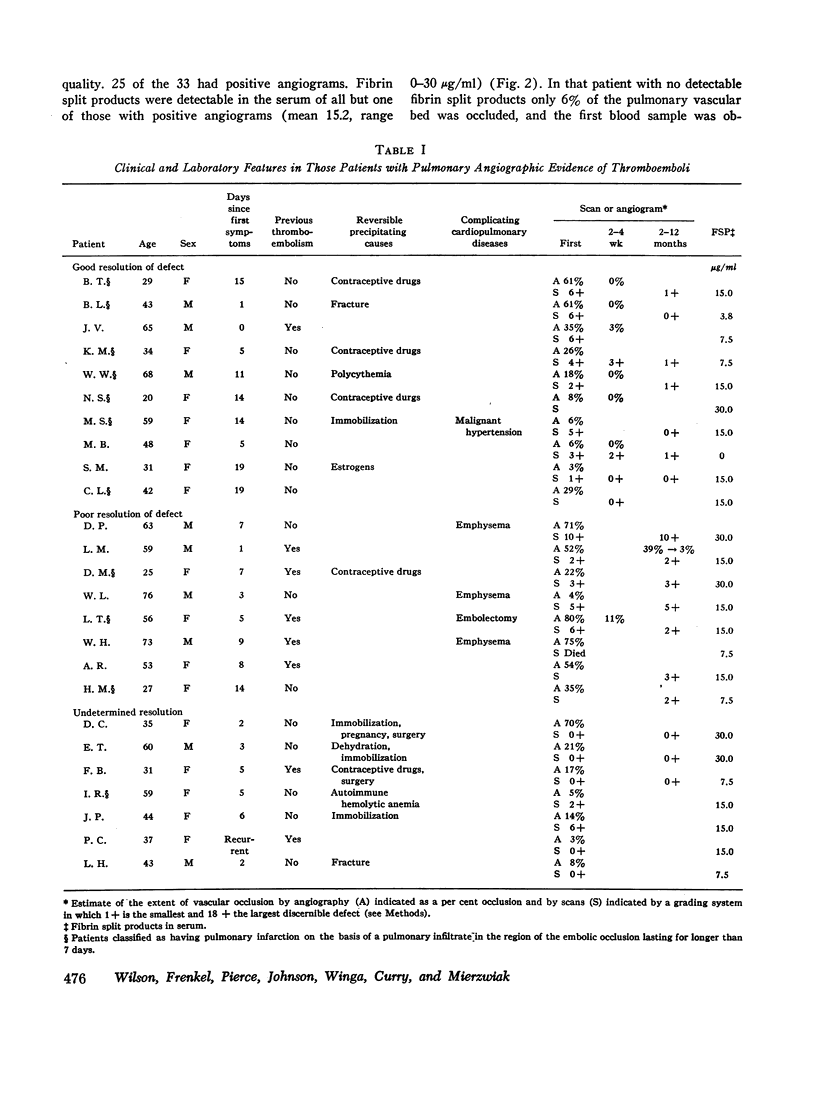
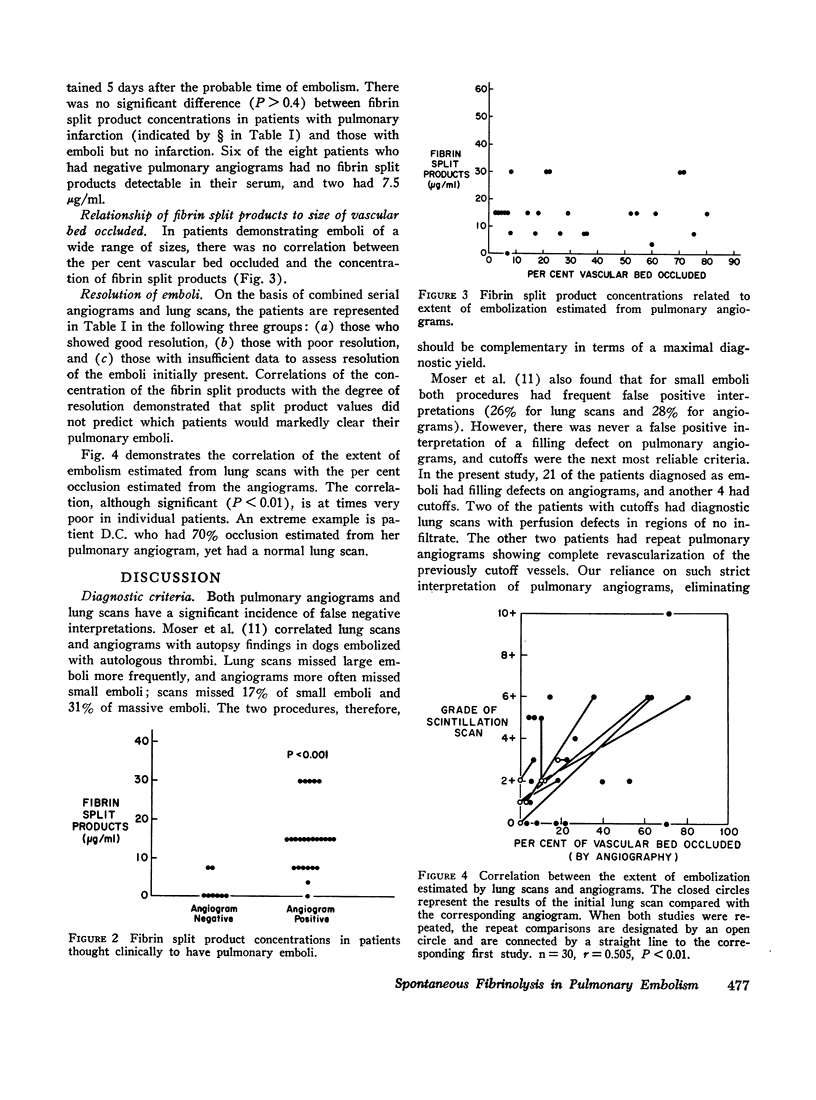
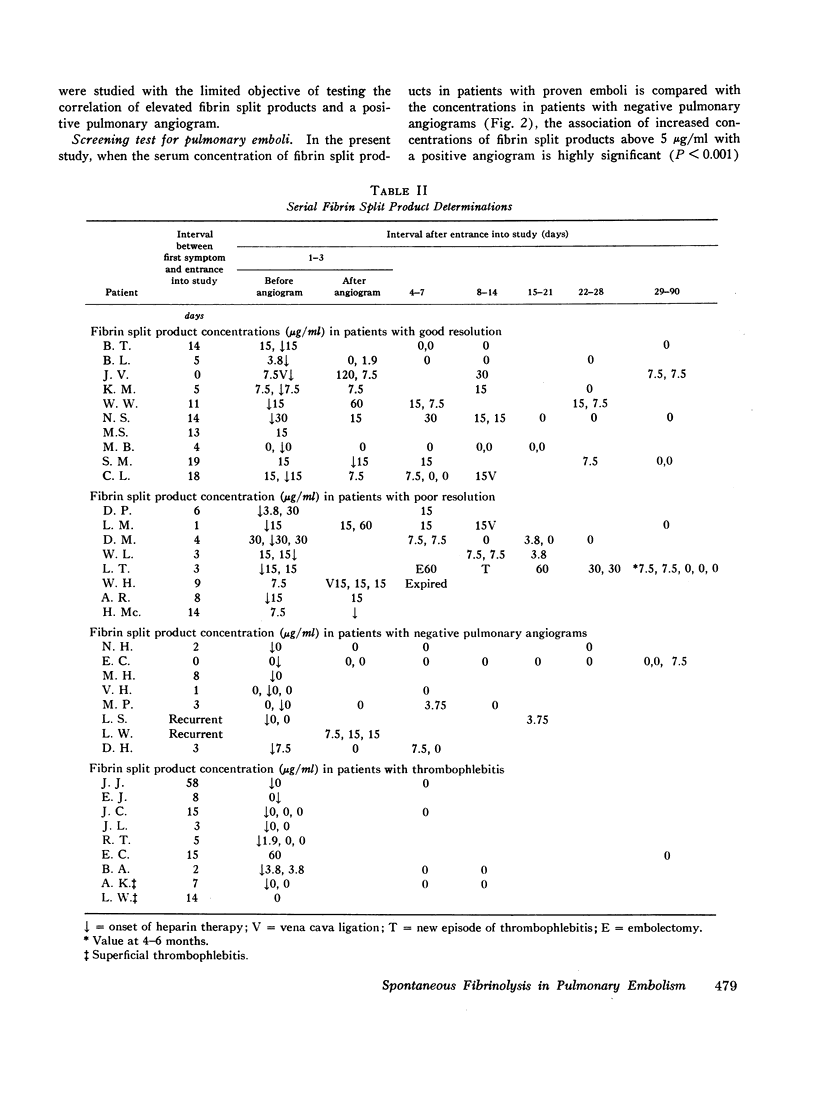
This study correlated levels of activated fibrinolysis with the presence, extent, and rate of resolution of angiographically documented pulmonary emboli. Pulmonary emboli demonstrable by angiography were associated with detectable fibrin split products in the serum of 24 of 25 patients. In the absence of increased fibrin split products, pulmonary emboli large enough to be demonstrated by angiography were found in only 2 of 25 positive pulmonary angiograms. Spontaneous resolution of pulmonary emboli could not be correlated with the the concentration or persistence of fibrin split products but did correlate well with the presence of a reversible precipitating cause.
Thrombophlebitis in the absence of clinical evidence of pulmonary embolism was not associated with increased concentrations of fibrin split products in eight of nine patients. The one patient with increased fibrin split product concentration had evidence on lung scan of silent pulmonary embolism.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALKJAERSIG N., FLETCHER A. P., SHERRY S. The mechanism of clot dissolution by plasmin. J Clin Invest. 1959 Jul;38(7):1086–1095. doi: 10.1172/JCI103885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AMBRUS C. M., MARKUS G. Plasmin-antiplasmin complex as a reservoir of fibrinolytic enzyme. Am J Physiol. 1960 Sep;199:491–494. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.199.3.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astrup T. Relation between formation and lysis of fibrin in the body. Thromb Diath Haemorrh Suppl. 1966;20:71–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astrup T. Tissue activators of plasminogen. Fed Proc. 1966 Jan-Feb;25(1):42–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COCCHERI S., ASTRUP T. Thromboplastic and fibrinolytic activities of large human vessels. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Nov;108:369–372. doi: 10.3181/00379727-108-26941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLP C. R., WILLIAMS M. H., Jr Pulmonary function following pulmonary embolization. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1962 Jun;85:799–807. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1962.85.6.799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalen J. E., Banas J. S., Jr, Brooks H. L., Evans G. L., Paraskos J. A., Dexter L. Resolution rate of acute pulmonary embolism in man. N Engl J Med. 1969 May 29;280(22):1194–1199. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196905292802202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison R. C., Brown J. Fibrinolysis in pulmonary vascular disease. Lancet. 1965 Apr 10;1(7389):786–788. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)92957-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel D. A., Sautter R. D., Wenzel F. J. Conservative treatment of massive pulmonary embolism. JAMA. 1966 Sep 12;197(11):924–926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fred H. L., Axelrad M. A., Lewis J. M., Alexander J. K. Rapid resolution of pulmonary thromboemboli in man. An angiographic study. JAMA. 1966 Jun 27;196(13):1137–1139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genton E., Wolf P. S. Experimental pulmonary embolism: effects of urokinase therapy on organizing thrombi. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Aug;70(2):311–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwaan H. C., Astrup T. Fibrinolytic activity in thrombosed veins. Circ Res. 1965 Dec;17(6):477–483. doi: 10.1161/01.res.17.6.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIEBERMAN J., KELLOGG F. Fibrinolytic activity of arterial tissues. Circ Res. 1961 May;9:515–521. doi: 10.1161/01.res.9.3.515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laursen B., Gormsen J. Spontaneous fibrinolysis demonstrated by immunological technique. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1967 Feb 28;17(1-2):42–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merskey C., Kleiner G. J., Johnson A. J. Quantitative estimation of split products of fibrinogen in human serum, relation to diagnosis and treatment. Blood. 1966 Jul;28(1):1–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser K. M., Harsanyi P., Rius-Garriga G., Guisan M., Landis G. A., Miale A., Jr Assessment of pulmonary photoscanning and angiography in experimental pulmonary embolism. Circulation. 1969 May;39(5):663–674. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.39.5.663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NILEHN J. E., NILSSON I. M. DEMONSTRATION OF FIBRINOLYTIC SPLIT PRODUCTS IN HUMAN SERUM BY AN IMMUNOLOGICAL METHOD IN SPONTANEOUS AND INDUCED FIBRINOLYTIC STATES. Scand J Haematol. 1964;1:313–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1964.tb00029.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NILSSON I. M., KROOK H., STERNBY N. H., SODERBERG E., SODERSTROM N. Severe thrombotic disease in a young man with bone marrow and skeletal changes and with a high content of an inhibitor in the fibrinolytic system. Acta Med Scand. 1961 Mar;169:323–337. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1961.tb07838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandolfi M., Nilsson I. M., Robertson B., Isacson S. Fibrinolytic activity of human veins. Lancet. 1967 Jul 15;2(7507):127–128. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)92964-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry S. Fibrinolysis. Annu Rev Med. 1968;19:247–268. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.19.020168.001335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODD A. S. The histological localisation of fibrinolysin activator. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1959 Jul;78:281–283. doi: 10.1002/path.1700780131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSITOURIS G., SANDBERG H., DELEON A. C., Jr, LECKS L., BELLET S. Studies of the plasmin-plasminogen system in thromboembolic diseases; its modifications by thrombolysin therapy. Am J Cardiol. 1960 May;5:680–687. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(60)90136-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tow D. E., Wagner H. N., Jr Recovery of pulmonary arterial blood flow in patients with pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med. 1967 May 11;276(19):1053–1059. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196705112761902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. E., 3rd, Pierce A. K., Johnson R. L., Jr, Winga E. R., Harrell W. R., Curry G. C., Mullins C. B. Hypoxemia in pulmonary embolism, a clinical study. J Clin Invest. 1971 Mar;50(3):481–491. doi: 10.1172/JCI106516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


