Abstract
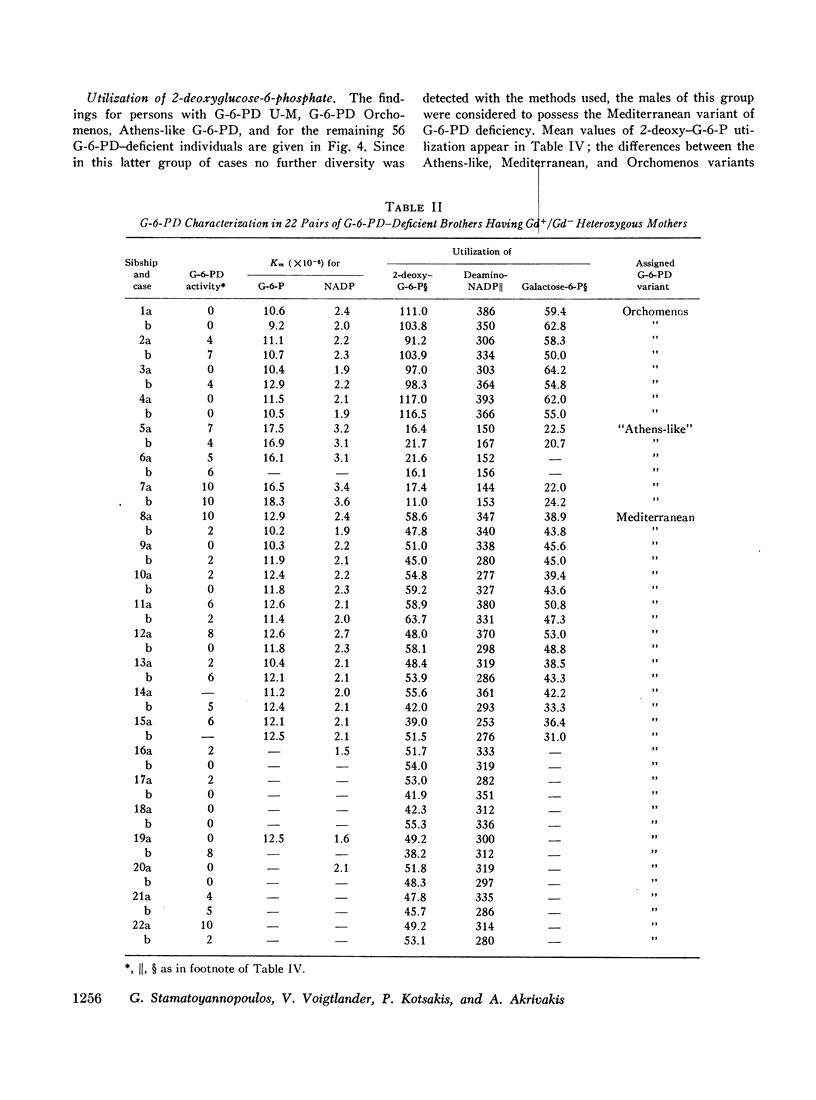
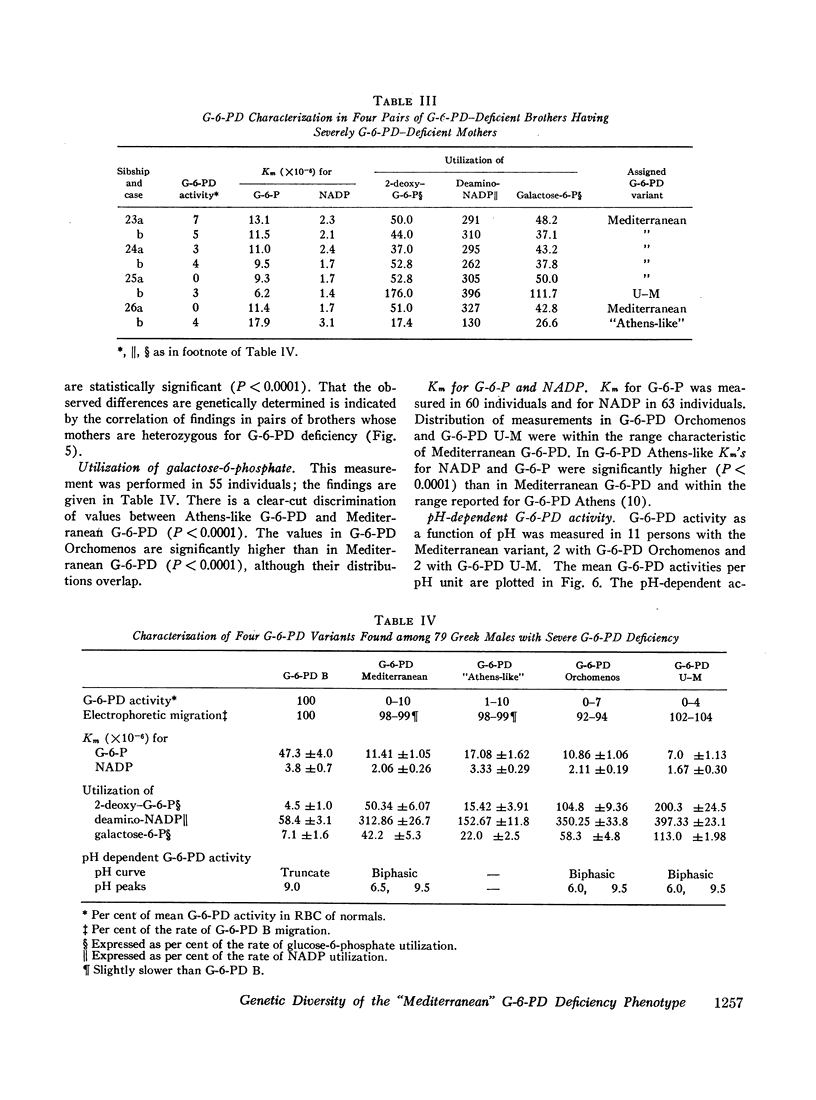
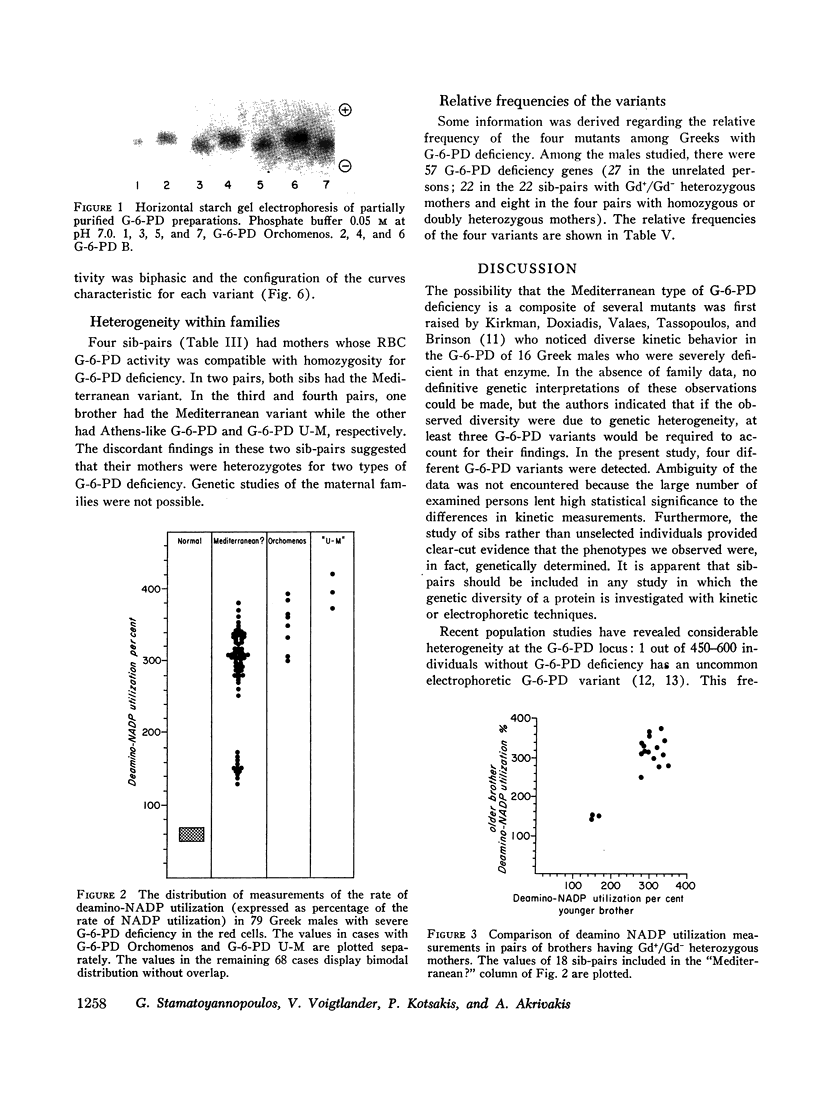
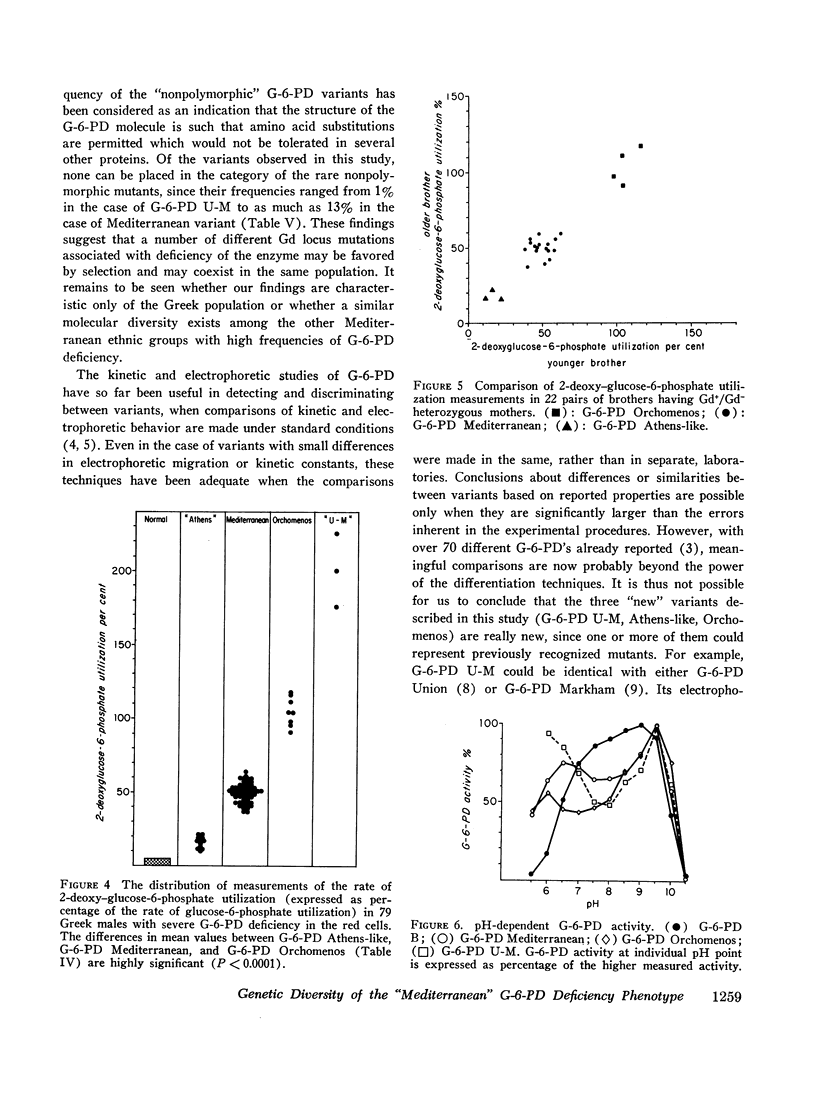
Genetic diversity of the “Mediterranean” phenotype of G-6-PD (glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase) deficiency was revealed when detailed studies were performed on blood specimens from 79 Greek males with G-6-PD levels 0-10% of normal. Four different mutants were found to be responsible for the severely deficient phenotypes: two mutants. G-6-PD U-M (Union-Markham) and G-6-PD Orchomenos, were distinguishable by electrophoresis, while the other two. G-6-PD Athens-like and G-6-PD Mediterranean, were distinguishable on the basis of their kinetic characteristics. Of the kinetic tests applied, the most useful for differentiating the variants were those measuring utilization rates of the analogue substrates deamino-NADP, 2-deoxyglucose-6-phosphate, and galactose-6-phosphate. Among unrelated males with severe G-6-PD deficiency, the relative frequencies of the four variants were: G-6-PD U-M. 5%; G-6-PD Orchomenos, 7%; G-6-PD Athens-like, 16%; G-6-PD Mediterranean, 72%. Genetic, biochemical, and clinical implications of the findings are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen P., Rosemeyer M. A. Subunit interactions of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from human erythrocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Mar;8(1):8–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00488.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FESSAS P., DOXIADIS S. A., VALAES T. Neonatal jaundice in glucose-6-phosphate-dehydrogenase-deficient infants. Br Med J. 1962 Nov 24;2(5316):1359–1362. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5316.1359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRKMAN H. N., DOXIADIS S. A., VALAES T., TASSOPOULOS N., BRINSON A. G. DIVERSE CHARACTERISTICS OF GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE FROM GREEK CHILDREN. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Feb;65:212–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kattamis C. A., Chaidas A., Chaidas S. G6PD deficiency and favism in the island of Rhodes (Greece). J Med Genet. 1969 Sep;6(3):286–291. doi: 10.1136/jmg.6.3.286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reys L., Manso C., Stamatoyannopoulos G. Genetic studies on southeastern Bantu of Mozambique. I. Variants of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Am J Hum Genet. 1970 Mar;22(2):203–215. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamatoyannopoulos G., Fraser G. R., Motulsky A. C., Fessas P., Akrivakis A., Papayannopoulou T. On the familial predisposition to favism. Am J Hum Genet. 1966 May;18(3):253–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamatoyannopoulos G., Kotsakis P., Voigtlander V., Akrivakis A., Moutulsky A. G. Electrophoretic diversity of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase among Greeks. Am J Hum Genet. 1970 Sep;22(5):587–596. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamatoyannopoulos G., Yoshida A., Bacopoulos C., Motulksy A. G. Athens variant of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Science. 1967 Aug 18;157(3790):831–833. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3790.831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida A., Baur E. W., Moutlsky A. G. A Philippino glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase variant (G6PD Union) with enzyme deficiency and altered substrate specificity. Blood. 1970 Apr;35(4):506–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida A. Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase of human erythrocytes. I. Purification and characterization of normal (B+) enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1966 Nov 10;241(21):4966–4976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]