Abstract
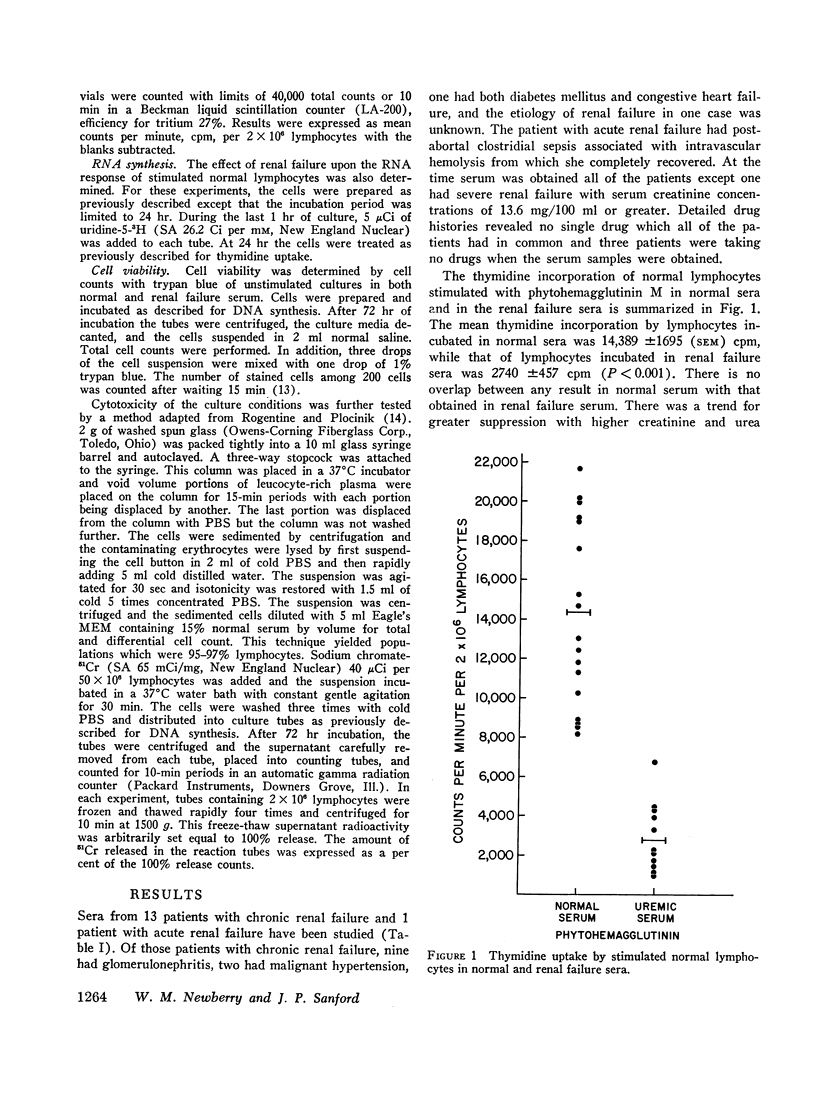
In defining host resistance factors in uremia, experiments were designed to assess the effect of renal failure serum upon the reactivity of normal human lymphocytes to phytohemagglutinin in vitro. Normal buffy coat cells were resuspended in sera obtained from normal subjects and from 14 patients with renal failure, then stimulated with phytohemagglutinin M and the cellular response measured by the increase in thymidine or uridine uptake. The mean thymidine uptake by stimulated cells in normal sera was 14,389 ±1695 (SEM) cpm per 2 × 106 lymphocytes. Uridine uptake under the same conditions was 12,540 ±1887 cpm. Compared to these are a mean thymidine uptake of 2740 ±457 cpm and uridine uptake of 3928 ±667 cpm in renal failure sera. Both differences are significant at P<0.01 level.
For controls representing “chronic illnesses,” sera from patients with pneumococcal meningitis, cirrhosis of the liver without jaundice, rheumatoid arthritis, and paraplegia with urinary tract infection did not cause suppression. No single drug had been taken by all the renal failure patients; three patients were taking no drugs.
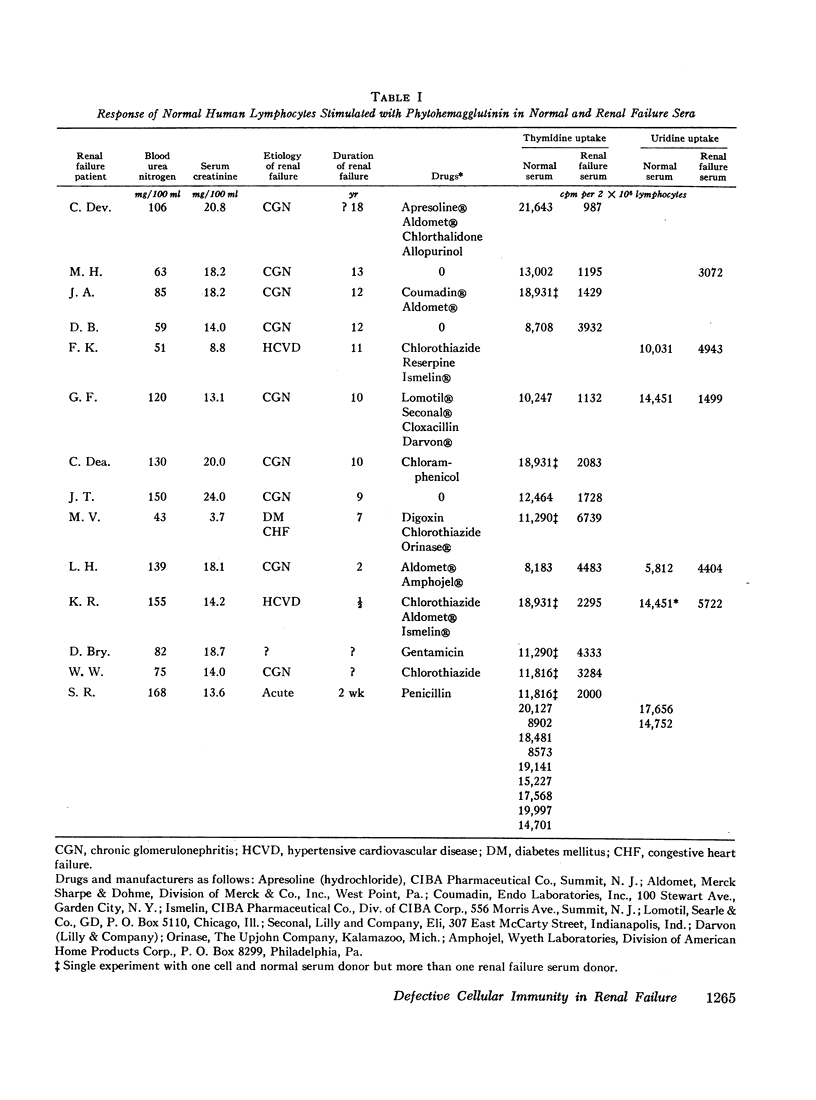
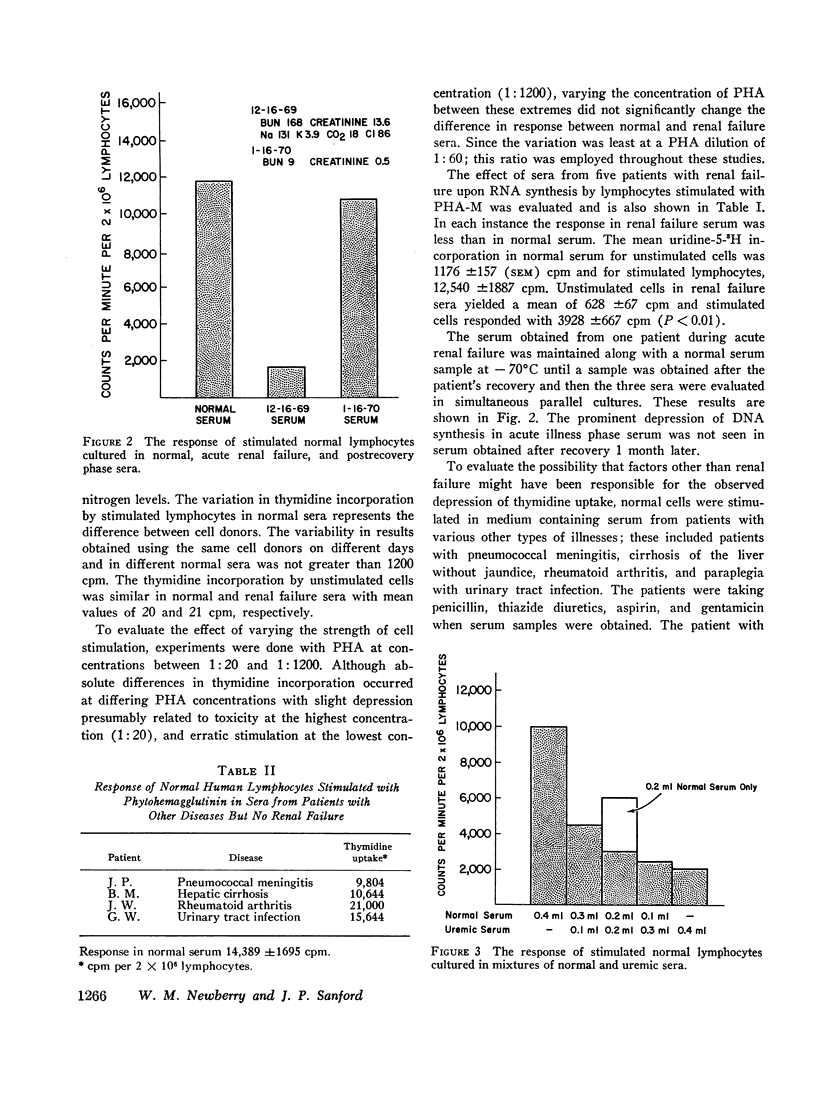
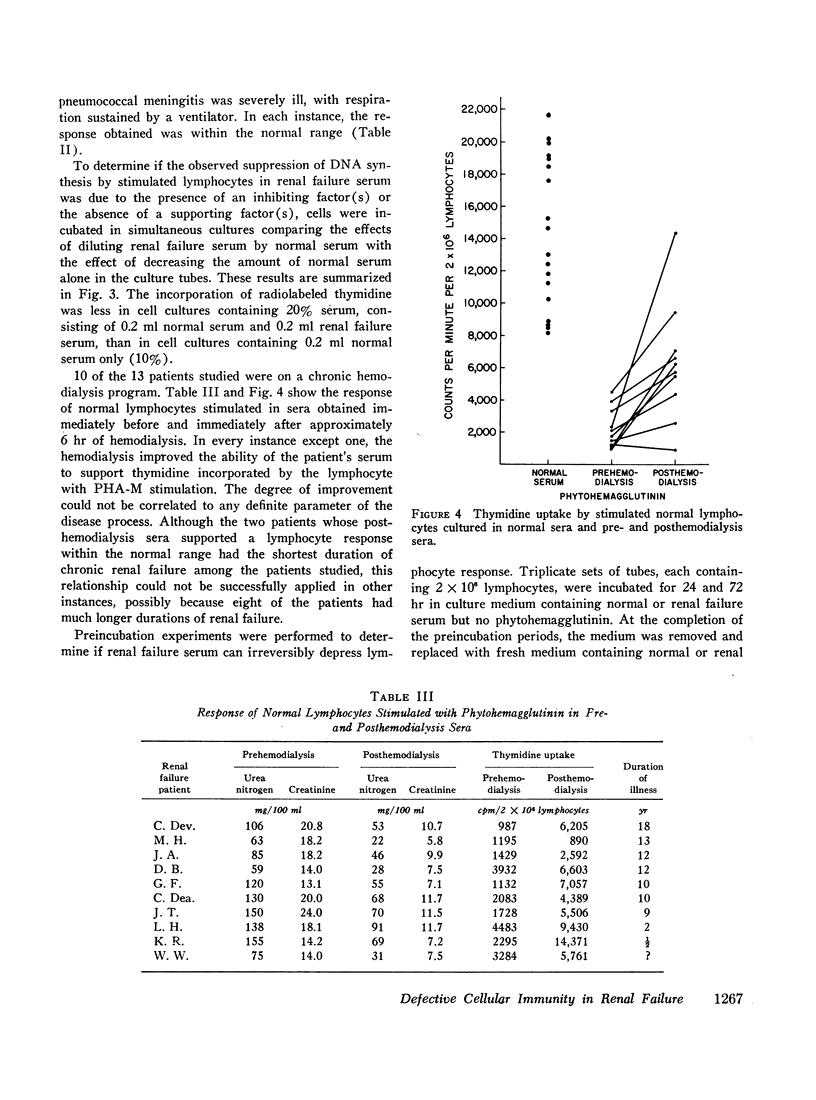
The serum from one patient with acute renal failure suppressed thymidine uptake while her serum obtained after recovery from her illness supported a normal lymphocyte response. Improvement of lymphocyte response was also noted in 9 of 10 sera obtained from patients immediately after hemodialysis. These observations plus the inhibition of stimulated cells by normal serum mixed with renal failure serum indicate the presence of a dialyzable inhibitory factor rather than the absence of a supporting factor in the renal failure sera.
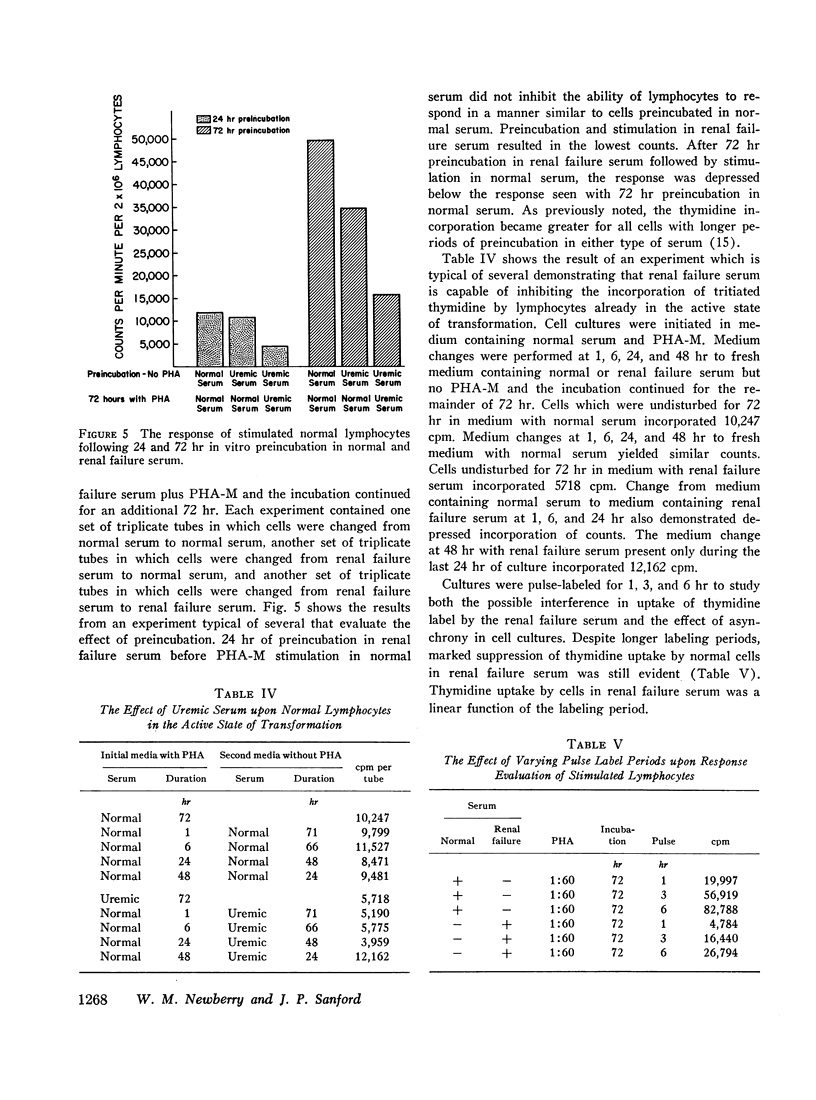
Lymphocytes preincubated for 24 hr in renal failure serum responded normally when transferred to normal serum and stimulated. Cells stimulated in normal serum and transferred to renal failure serum within the initial 24 hr of incubation demonstrated depressed thymidine uptake. Also, cell survival for 72 hr incubation as judged by trypan blue exclusion and chromium-51 release was similar in normal and renal failure sera. Thus, the suppressive effect of renal failure serum does not depend upon the initial phytohemagglutinin-cell interaction nor upon a significant cytotoxic effect.
These studies demonstrate that a dialyzable factor(s) in the serum of patients with renal failure can greatly suppress one parameter by which an immune function of circulating lymphocytes is assessed and provides at least, a partial explanation for delayed homograft rejections in renal failure as well as the susceptibility of such patients to various infections.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BALCH H. H., MERONEY W. H., SAKO Y. Observations on the surgical care of patients with posttraumatic renal insufficiency. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1955 Apr;100(4):439–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACK L., BERENBAUM M. C. FACTORS AFFECTING THE DYE EXCLUSION TEST FOR CELL VIABILITY. Exp Cell Res. 1964 Jun;35:9–13. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(64)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLUEMLE L. W., Jr, WEBSTER G. D., Jr, ELKINTON J. R. Acute tubular necrosis; analysis of one hundred cases with respect to mortality, complications, and treatment with and without dialysis. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1959 Aug;104(2):180–197. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1959.00270080006002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAMMIN G. J., COUCH N. P., MURRAY J. E. Prolonged survival of skin homografts in uremic patients. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1957 Mar 22;64(5):967–976. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1957.tb52488.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannetti S., Biagini M., Cioni L. Evidence that methylguanidine is retained in chronic renal failure. Experientia. 1968 Apr 15;24(4):341–343. doi: 10.1007/BF02140809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HICKS J. M., YOUNG D. S., WOOTTON I. D. THE EFFECT OF URAEMIC BLOOD CONSTITUENTS ON CERTAIN CEREBRAL ENZYMES. Clin Chim Acta. 1964 Mar;9:228–235. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(64)90099-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz H. I., Cohen B. D., Martinez P., Papayoanou M. F. Defective ADP-induced platelet factor 3 activation in uremia. Blood. 1967 Sep;30(3):331–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber H., Pastner D., Dittrich P., Braunsteiner H. In vitro reactivity of human lymphocytes in uraemia--a comparison with the impairment of delayed hypersensitivity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Jul;5(1):75–82. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENSSON O. Observations on the leucocyte blood picture in acute uraemia. Br J Haematol. 1958 Oct;4(4):422–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1958.tb06043.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick C. H., Ruth W. E. Chronic pulmonary disease and immunologic deficiency. Am J Med. 1966 Sep;41(3):427–439. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(66)90088-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang P. A., Ritzmann S. E., Merian F. L., Lawrence M. C., Levin W. C., Gregory R. Cellular evolution in induced inflammation in uremic patients. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1966 Spring;24(1):107–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann J. D., Smith J. W., Miller T. E., Barnett J. A., Sanford J. P. Local immune response in experimental pyelonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;47(11):2541–2550. doi: 10.1172/JCI105936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIIS P., STOUGAARD J. The peripheral blood leukocytes in chronic renal insufficiency. Dan Med Bull. 1959 May;6(3):85–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogentine G. N., Jr, Plocinik B. A. Application of the 51Cr cytotoxicity technique to the analysis of human lymphocyte isoantigens. Transplantation. 1967 Sep 5;5(5):1323–1333. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196709000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silk M. R. The effect of uremic plasma on lymphocyte transformation. Invest Urol. 1967 Sep;5(2):195–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein I. M., Cohen B. D., Kornhauser R. S. Guanidinosuccinic acid in renal failure, experimental azotemia and inborn errors of the urea cycle. N Engl J Med. 1969 Apr 24;280(17):926–930. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196904242801704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON W. E., KIRKPATRICK C. H., TALMAGE D. W. IMMUNOLOGIC STUDIES IN HUMAN ORGAN TRANSPLANTATION. 3. THE RELATIONSHIP OF DELAYED CUTANEOUS HYPERSENSITIVITY TO THE ONSET OF ATTEMPTED KIDNEY ALLOGRAFT REJECTION. J Clin Invest. 1964 Oct;43:1881–1891. doi: 10.1172/JCI105062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


