Abstract
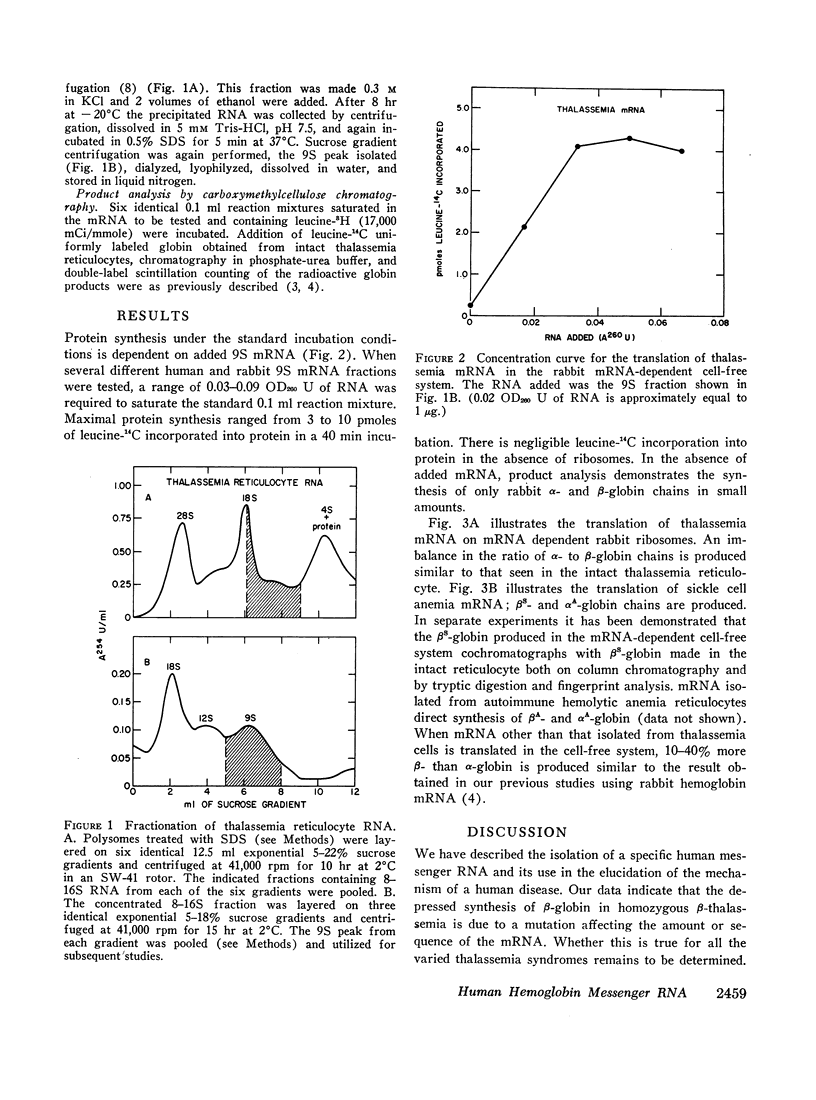
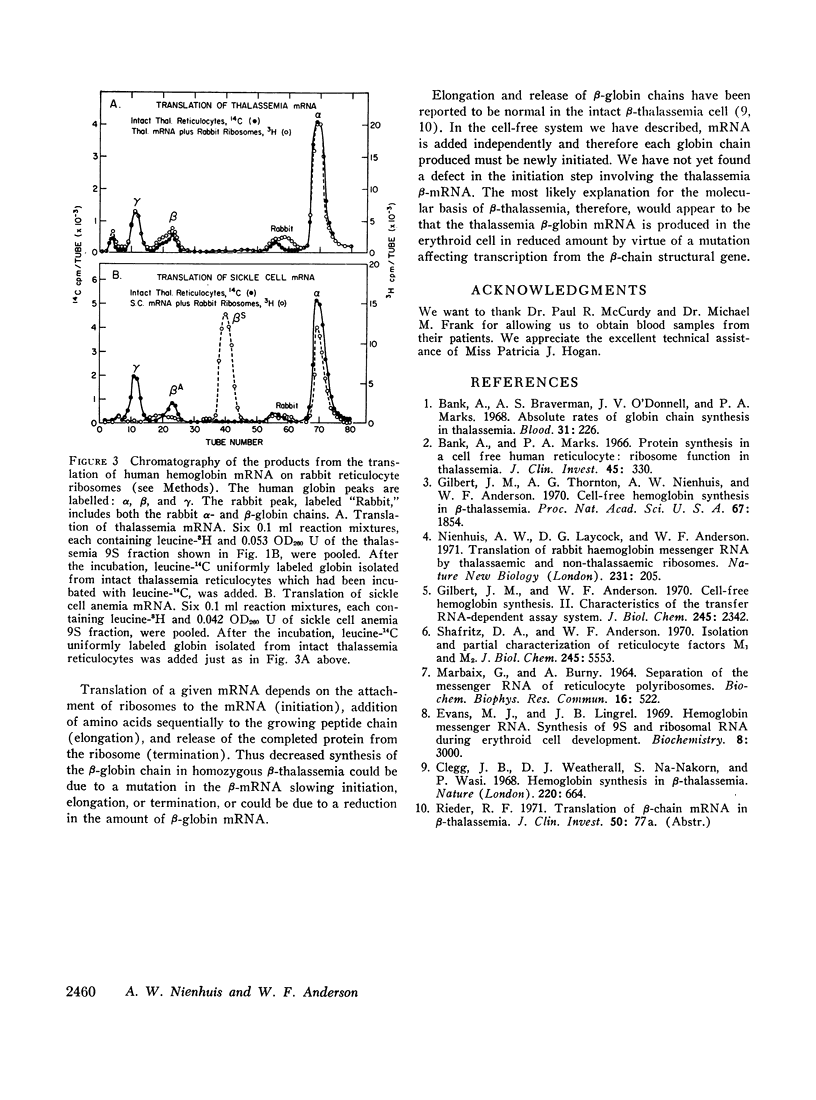
Human hemoglobin messenger RNA was isolated by sucrose gradient centrifugation from reticulocytes of patients having various hemolytic anemias. Using a messenger RNA-dependent cell-free system derived entirely from rabbit reticulocytes, the human hemoglobin messenger RNA has been translated and the products analyzed by carboxymethylcellulose column chromatography. Normal messenger RNA directs synthesis of normal human α- and β-globin chains in nearly equal amounts. Sickle cell anemia messenger RNA directs the synthesis of normal α- and sickle β-chains, β-thalassemia messenger RNA directs the synthesis of normal α- and β-chains, but the amount of β-globin synthesized is markedly reduced. Thus the inability of the thalassemia reticulocyte to produce β-globin is clearly attributable to the β-globin messenger RNA.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bank A., Braverman A. S., O'Donnell J. V., Marks P. A. Absolute rates of globin chain synthesis in thalassemia. Blood. 1968 Feb;31(2):226–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bank A., Marks P. A. Protein synthesis in a cell free human reticulocyte system: ribosome function in thalassemia. J Clin Invest. 1966 Mar;45(3):330–336. doi: 10.1172/JCI105347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J., Na-Nakorn S., Wasi P. Haemoglobin synthesis in beta-thalassaemia. Nature. 1968 Nov 16;220(5168):664–668. doi: 10.1038/220664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. J., Lingrel J. B. Hemoglobin messenger ribonucleic acid. Synthesis of 9S and ribosomal ribonucleic acid during erythroid cell development. Biochemistry. 1969 Jul;8(7):3000–3005. doi: 10.1021/bi00835a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert J. M., Anderson W. F. Cell-free hemoglobin synthesis. II. Characteristics of the transfer ribonucleic acid-dependent assay system. J Biol Chem. 1970 May 10;245(9):2342–2349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert J. M., Thornton A. G., Nienhuis A. W., Anderson W. F. Cell-free hemoglobin synthesis in beta-thalassemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Dec;67(4):1854–1861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.4.1854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marbaix G., Burny A. Separation of the messenger RNA of reticulocyte polyribosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964 Aug 11;16(6):522–527. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90186-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nienhuis A. W., Laycock D. G., Anderson W. F. Translation of rabbit haemoglobin messenger RNA by thalassaemic and non-thalassaemic ribosomes. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 16;231(24):205–208. doi: 10.1038/newbio231205a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafritz D. A., Anderson W. F. Isolation and partial characterization of reticulocyte factors M1 and M2. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5553–5559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


