Abstract
The mechanical properties of the lungs were studied in two groups of coal miners. The first group consisted of miners with either simple or no pneumoconiosis and was divided into two subgroups (1A and 1B). The former (1A) consisted of 62 miners most of whom had simple pneumoconiosis but a few of whom had clear films. Although their spirometry was normal, all claimed to have respiratory symptoms. The other subgroup (1B) consisted of 25 working miners with definite radiographic evidence of simple pneumoconiosis but normal spirometric findings. The second major group consisted of 25 men with complicated pneumoconiosis.
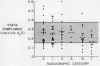
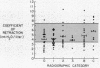
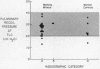
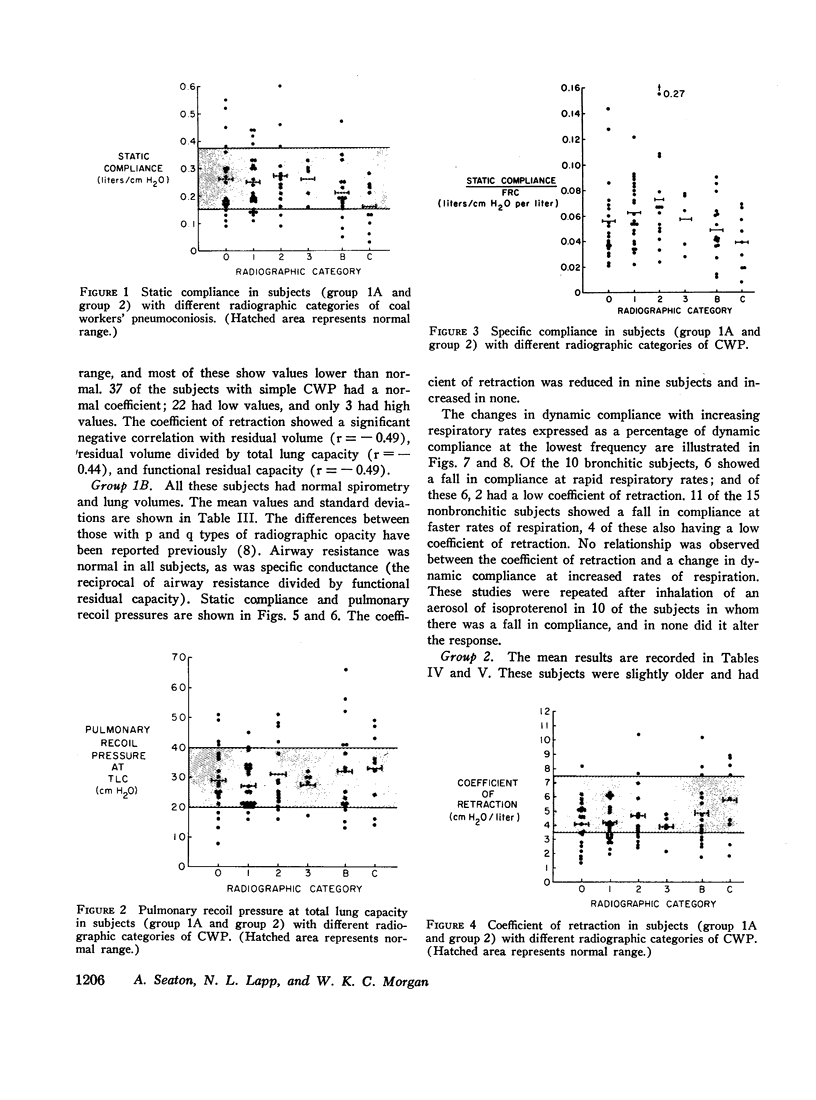
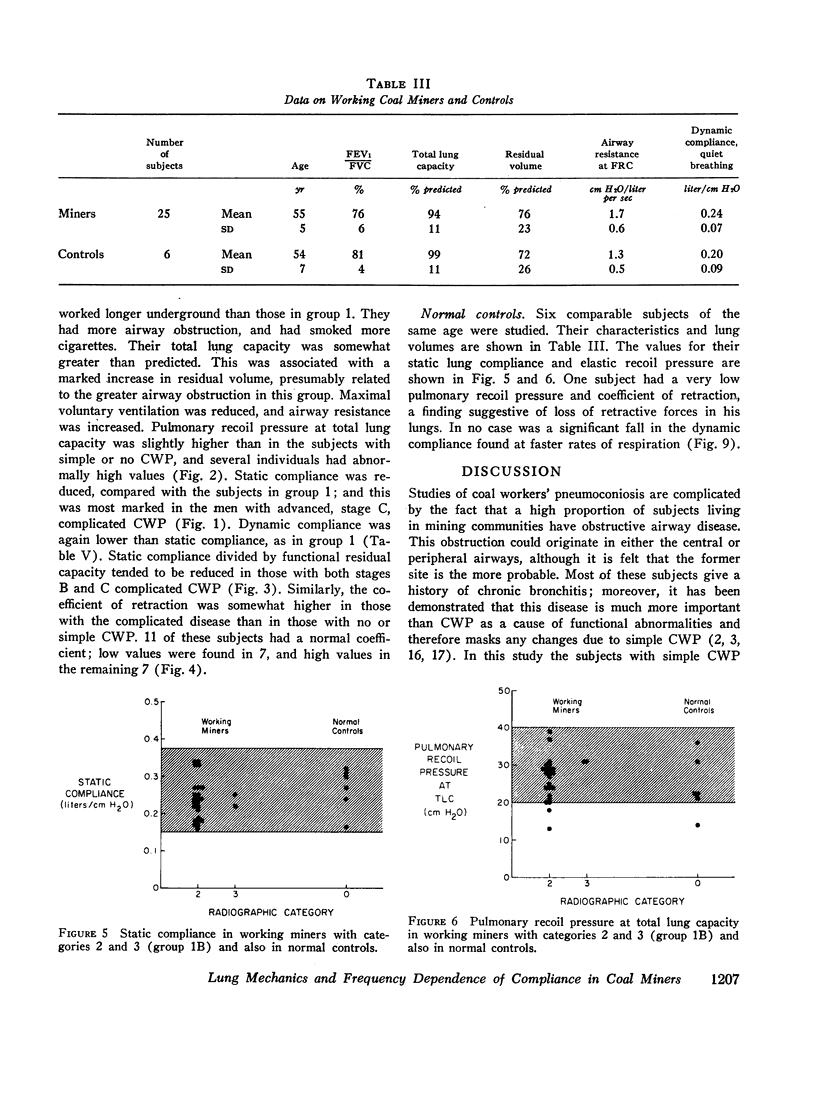
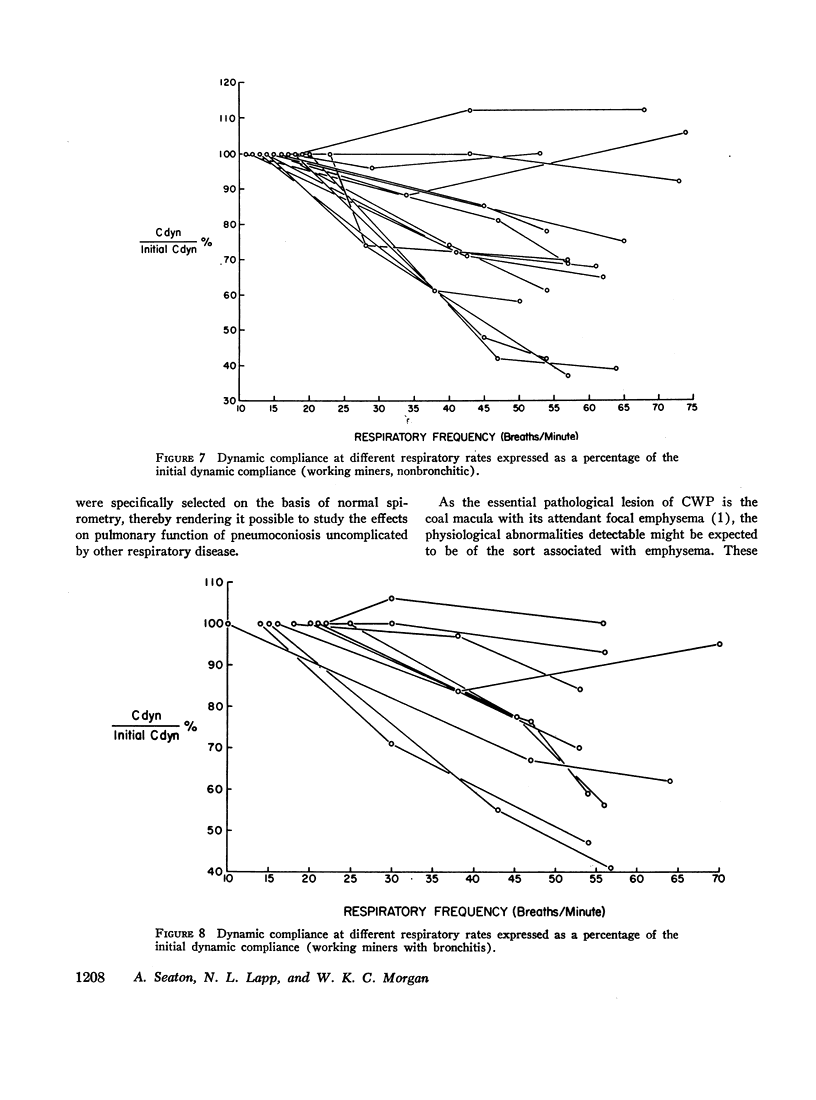
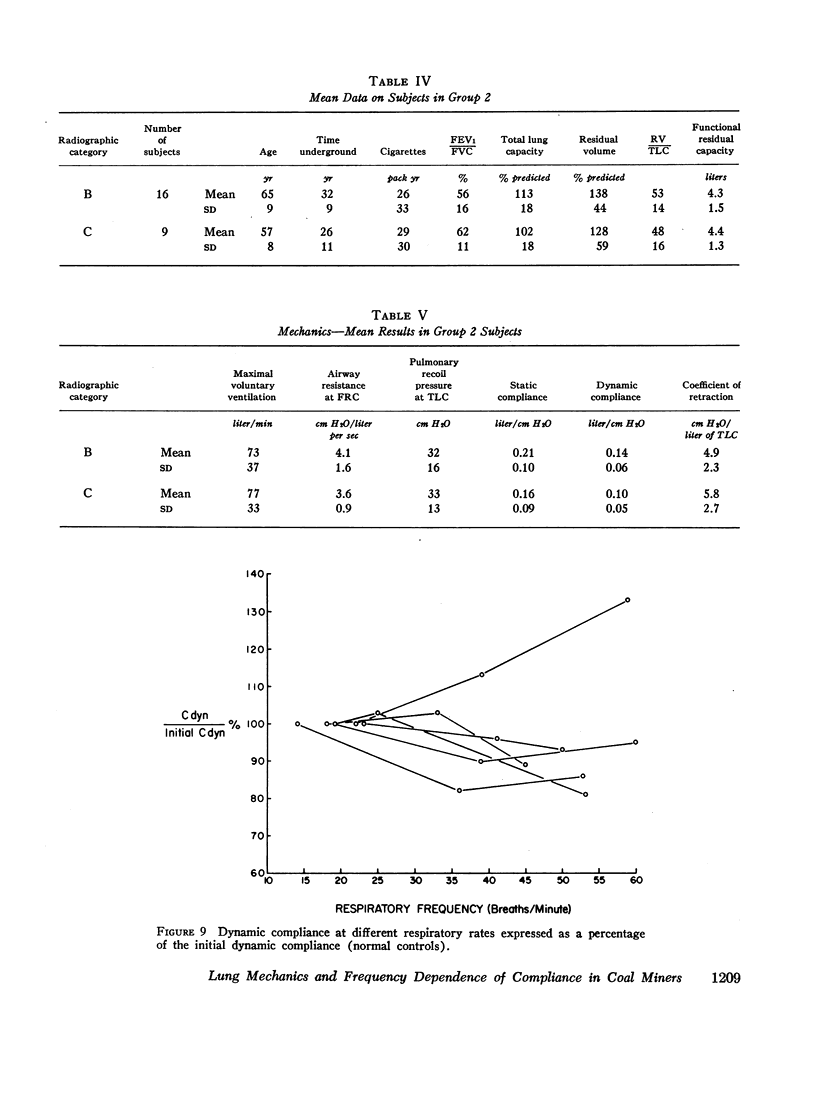
In subjects with simple pneumoconiosis, static compliance was mostly in the normal range, whereas it was often reduced in subjects with the complicated disease. The coefficient of retraction was normal or reduced in most subjects except those with advanced complicated disease, in several of whom it was elevated. So far as simple pneumoconiosis was concerned, abnormalities, when present, reflected “emphysema” rather than fibrosis. In severe complicated pneumoconiosis, changes suggesting fibrosis tended to predominate. In the 25 working miners (subgroup 1B) dynamic compliance was measured at different respiratory rates. 17 of the subjects in this subgroup demonstrated frequency dependence of their compliance, a finding unrelated to bronchitis and suggestive of increased resistance to flow in the smallest airways.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DUBOIS A. B., BOTELHO S. Y., BEDELL G. N., MARSHALL R., COMROE J. H., Jr A rapid plethysmographic method for measuring thoracic gas volume: a comparison with a nitrogen washout method for measuring functional residual capacity in normal subjects. J Clin Invest. 1956 Mar;35(3):322–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI103281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOIS A. B., BOTELHO S. Y., COMROE J. H., Jr A new method for measuring airway resistance in man using a body plethysmograph: values in normal subjects and in patients with respiratory disease. J Clin Invest. 1956 Mar;35(3):327–335. doi: 10.1172/JCI103282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERRIS B. G., Jr, FRANK N. R. Pulmonary function in coal miners. J Occup Med. 1962 May;4:274–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEPPLESTON A. G. The pathological anatomy of simple pneumokoniosis in coal workers. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1953 Jul;66(1):235–246. doi: 10.1002/path.1700660127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HYATT R. E., KISTIN A. D., MAHAN T. K. RESPIRATORY DISEASE IN SOUTHERN WEST VIRGINIA COAL MINERS. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1964 Mar;89:387–401. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1964.89.3.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins I. T., Higgins M. W., Lockshin M. D., Canale N. Chronic respiratory disease in mining communities in Marion County, West Virginia. Br J Ind Med. 1968 Jul;25(3):165–175. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEATHART G. L. The mechanical properties of the lung in pneumoconiosis of coal-miners. Br J Ind Med. 1959 Apr;16(2):153–165. doi: 10.1136/oem.16.2.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapp N. L., Seaton A., Kaplan K. C., Hunsaker M. R., Morgan W. K. Pulmonary hemodynamics in symptomatic coal miners. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 Sep;104(3):418–426. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.104.3.418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILIC-EMILI J., MEAD J., TURNER J. M. TOPOGRAPHY OF ESOPHAGEAL PRESSURE AS A FUNCTION OF POSTURE IN MAN. J Appl Physiol. 1964 Mar;19:212–216. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1964.19.2.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macklem P. T., Mead J. Resistance of central and peripheral airways measured by a retrograde catheter. J Appl Physiol. 1967 Mar;22(3):395–401. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.22.3.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead J. The lung's "quiet zone". N Engl J Med. 1970 Jun 4;282(23):1318–1319. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197006042822311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. K., Burgess D. B., Lapp N. L., Seaton A. Hyperinflation of the lungs in coal miners. Thorax. 1971 Sep;26(5):585–590. doi: 10.1136/thx.26.5.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEEDHAM C. D., ROGAN M. C., McDONALD I. Normal standards for lung volumes, intrapulmonary gas-mixing, and maximum breathing capacity. Thorax. 1954 Dec;9(4):313–325. doi: 10.1136/thx.9.4.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEMBERTON J. Chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and bronchial spasm in bituminous coal workers; an epidemiologic study. AMA Arch Ind Health. 1956 Jun;13(6):529–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen D. L., Nelson C. W. Respiratory function in southern Appalachian coal miners. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 Feb;103(2):240–248. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.103.2.240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlueter D. P., Immekus J., Stead W. W. Relationship between maximal inspiratory pressure and total lung capacity (coefficient of retraction) in normal subjects and in patients with emphysema, asthma, and diffuse pulmonary infiltration. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1967 Oct;96(4):656–665. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1967.96.4.656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seaton A., Lapp N. L., Chang C. H. Lung perfusion scanning in coal workers pneumoconiosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 Mar;103(3):338–349. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.103.3.338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seaton A., Lapp N. L., Morgan W. K. Relationship of pulmonary impairment in simple coal workers' pneumoconiosis to type of radiographic opacity. Br J Ind Med. 1972;29(1):50–55. doi: 10.1136/oem.29.1.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner J. M., Mead J., Wohl M. E. Elasticity of human lungs in relation to age. J Appl Physiol. 1968 Dec;25(6):664–671. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1968.25.6.664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolcock A. J., Vincent N. J., Macklem P. T. Frequency dependence of compliance as a test for obstruction in the small airways. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jun;48(6):1097–1106. doi: 10.1172/JCI106066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]