Abstract
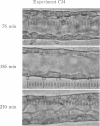
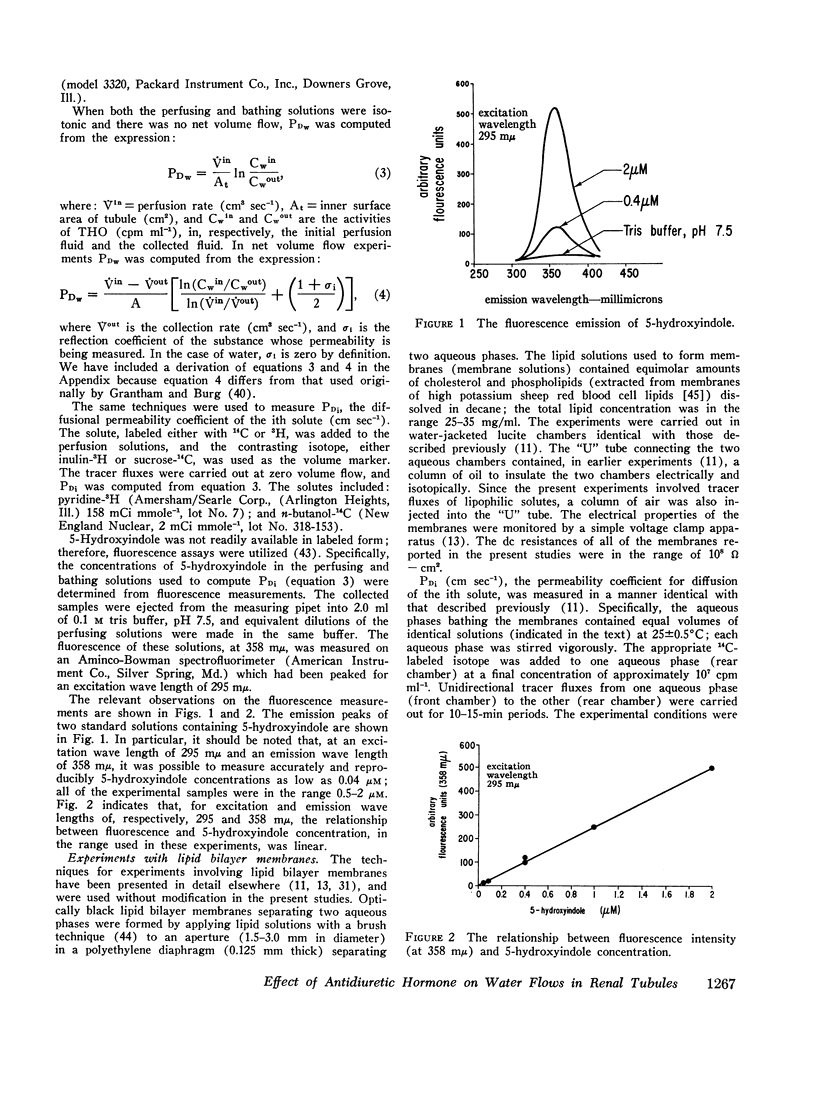
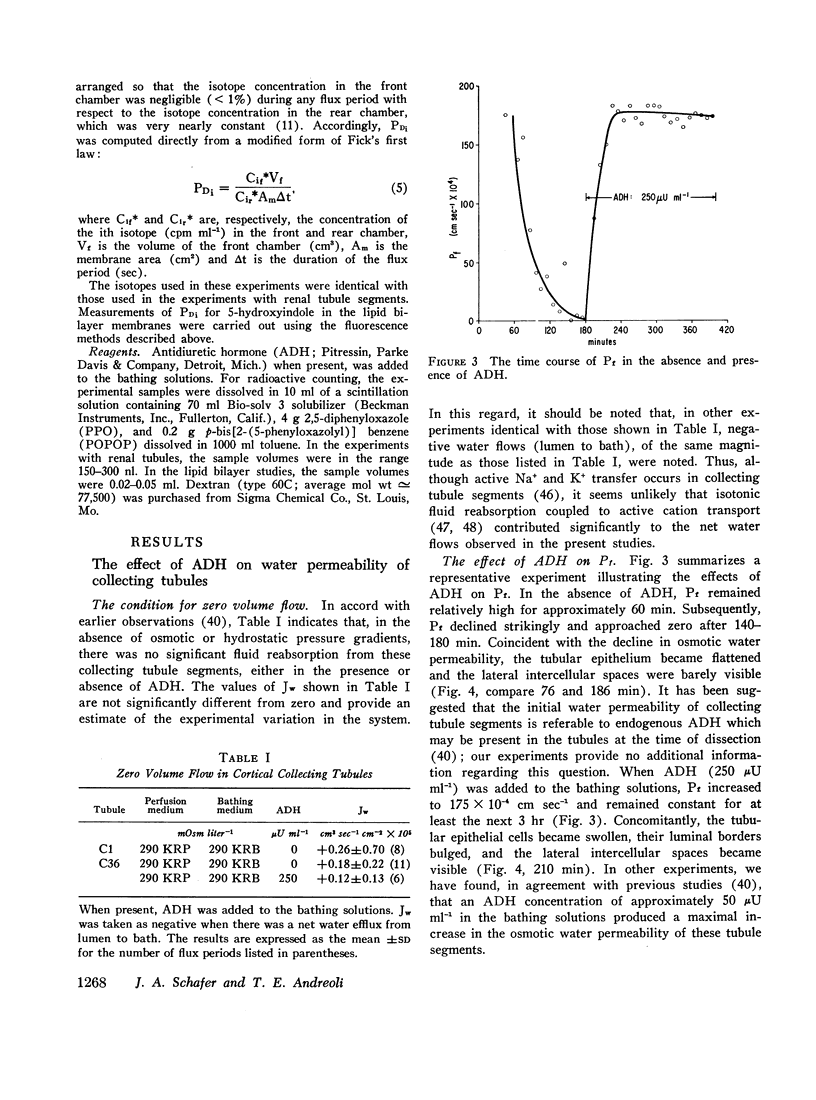
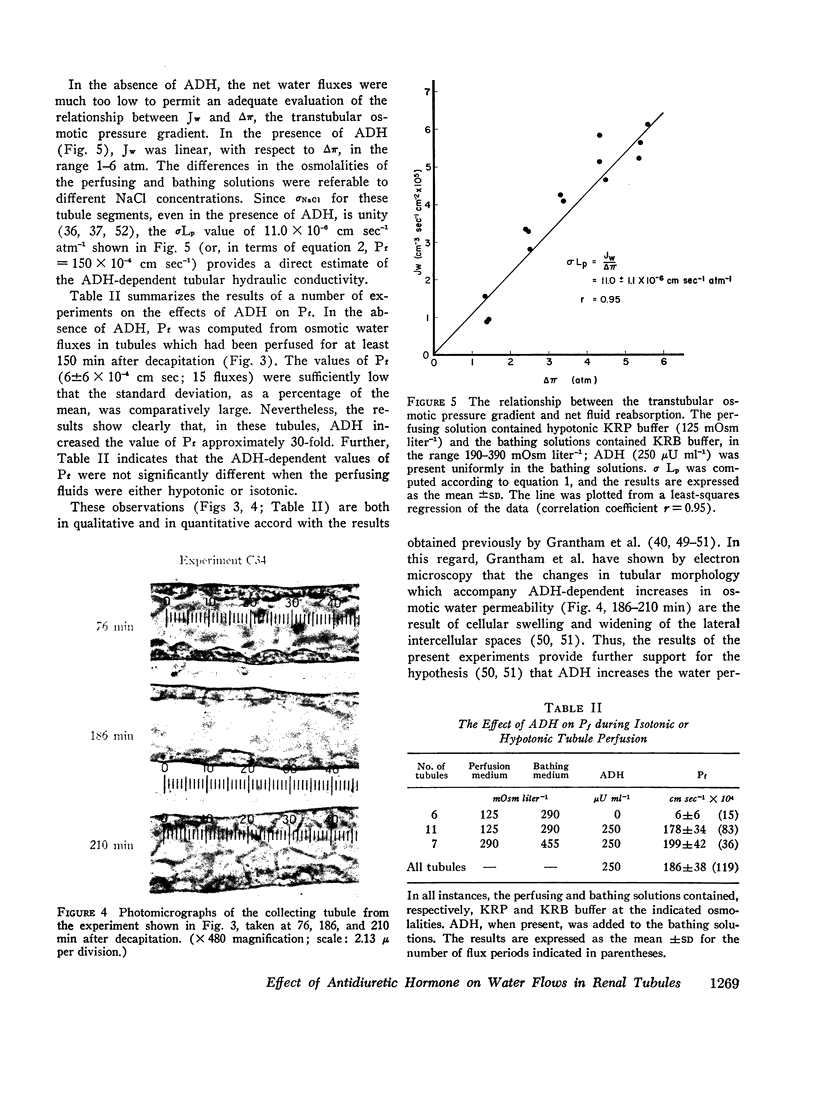
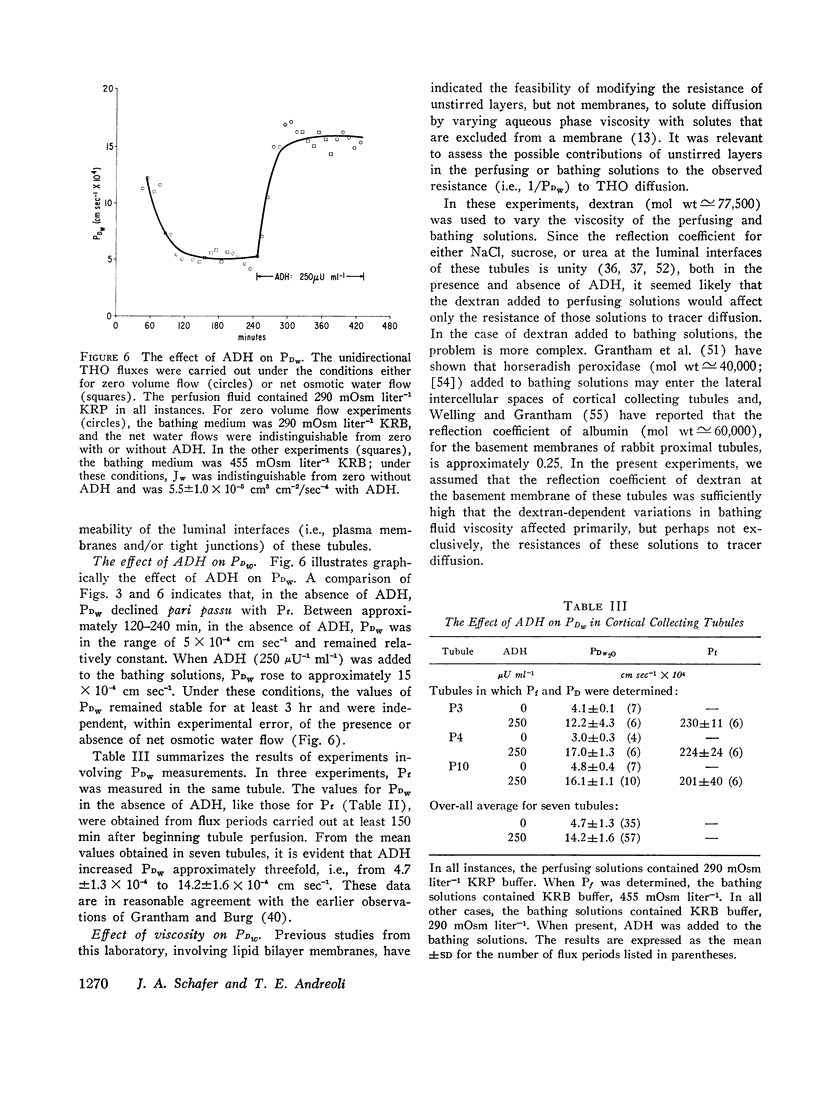
These experiments were intended to evaluate the effects of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) on dissipative water transport in cortical collecting tubules isolated from rabbit kidney. In the absence of ADH, the osmotic (Pf, cm sec-1) and diffusional (PDW cm sec-1) water permeability coefficients were, respectively, 6±6 and 4.7±1.3 (SD). When ADH was added to the bathing solutions, Pf and PDW rose to, respectively, 186±38 and 14.2±1.6 (SD). In the absence of ADH, the tubular cells were flat and the lateral intercellular spaces were closed when the perfusing and bathing solutions were, respectively, hypotonic and isotonic; in the presence of ADH, the cells swelled and the intercellular spaces dilated. These data suggest that ADH increased the water permeability of the luminal membranes of the tubules.
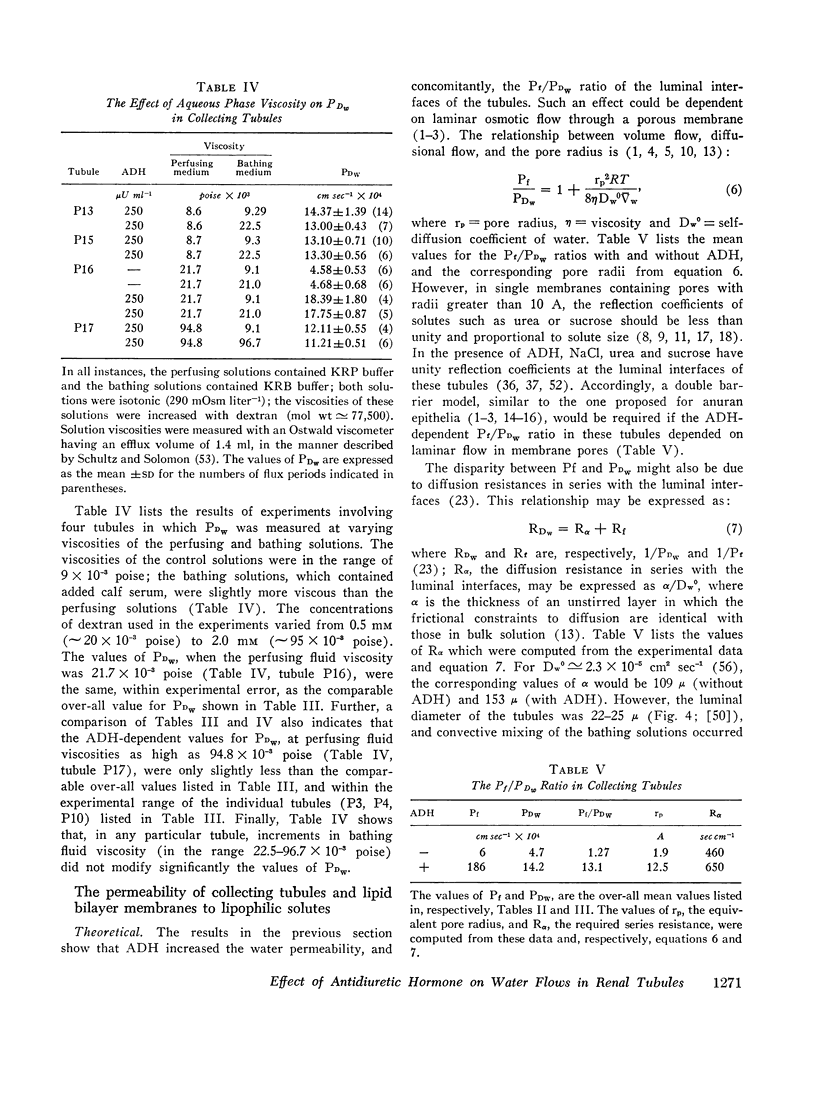
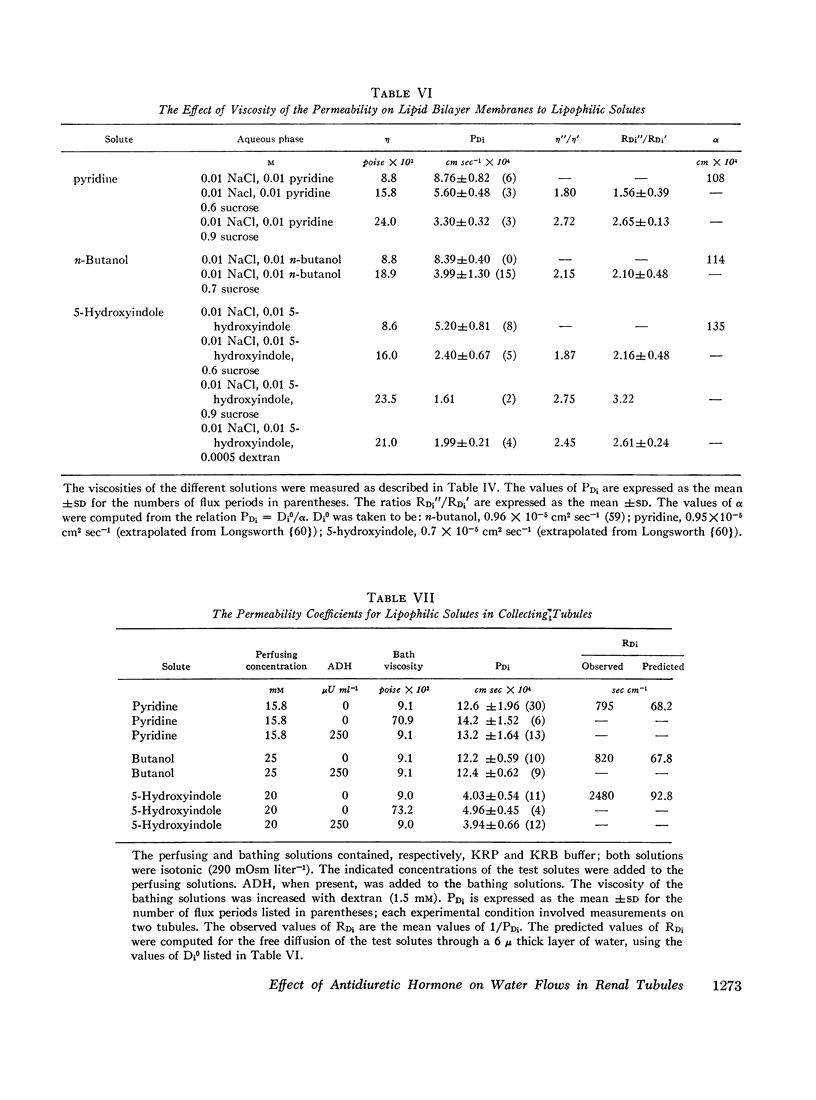
It was possible that the ADH-dependent Pf/PDW ratio was referable to the resistance of the epithelial cell layer (exclusive of luminal membranes) to water diffusion (RDW, sec cm-1). Such a possibility required that RDW be ∼ 650, i.e., approximately 25-fold greater than in an equivalent thickness of water. To test this view, it was assumed that RDi values for lipophilic solutes in lipid bilayer membranes and in luminal membranes were comparable. In lipid bilayer membranes, RDi was substantially less than 90 sec cm-1 for pyridine, n-butanol, and 5-hydroxyindole. In renal tubules, RDi for these solutes ranged from 795 to 2480 with and without ADH. It was assumed that, in the tubules, RDi was referable to cellular constraints to diffusion; for these solutes, the latter were 12-25 times greater than in water. Accordingly, it is possible that the ADH-dependent Pf/PDW ratio was also due to cellular constraints to diffusion.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSEN B., USSING H. H. Solvent drag on non-electrolytes during osmotic flow through isolated toad skin and its response to antidiuretic hormone. Acta Physiol Scand. 1957 Jun 8;39(2-3):228–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1957.tb01425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreoli T. E., Dennis V. W., Weigl A. M. The effect of amphotericin B on the water and nonelectrolyte permeability of thin lipid membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Feb;53(2):133–156. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.2.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreoli T. E., Monahan M. The interaction of polyene antibiotics with thin lipid membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Aug;52(2):300–325. doi: 10.1085/jgp.52.2.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreoli T. E., Schafer J. A., Troutman S. L. Coupling of solute and solvent flows in porous lipid bilayer membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Apr;57(4):479–493. doi: 10.1085/jgp.57.4.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreoli T. E., Troutman S. L. An analysis of unstirred layers in series with "tight" and "porous" lipid bilayer membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Apr;57(4):464–478. doi: 10.1085/jgp.57.4.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry P. H., Hope A. B. Electroosmosis in membranes: effects of unstirred layers and transport numbers. I. Theory. Biophys J. 1969 May;9(5):700–728. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86413-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry P. H., Hope A. B. Electroosmosis in membranes: effects of unstirred layers and transport numbers. II. Experimental. Biophys J. 1969 May;9(5):729–757. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86414-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean R. C., Shepherd W. C., Chan H. Permeability of lipid bilayer membranes to organic solutes. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Sep;52(3):495–508. doi: 10.1085/jgp.52.3.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M. B., Orloff J. Control of fluid absorption in the renal proximal tubule. J Clin Invest. 1968 Sep;47(9):2016–2024. doi: 10.1172/JCI105888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M., Grantham J., Abramow M., Orloff J. Preparation and study of fragments of single rabbit nephrons. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jun;210(6):1293–1298. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.6.1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cass A., Finkelstein A. Water permeability of thin lipid membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Jul;50(6):1765–1784. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.6.1765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIAMOND J. M. THE MECHANISM OF ISOTONIC WATER TRANSPORT. J Gen Physiol. 1964 Sep;48:15–42. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DURBIN R. P., FRANK H., SOLOMON A. K. Water flow through frog gastric mucosa. J Gen Physiol. 1956 Mar 20;39(4):535–551. doi: 10.1085/jgp.39.4.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DURBIN R. P. Osmotic flow of water across permeable cellulose membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1960 Nov;44:315–326. doi: 10.1085/jgp.44.2.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. M., Bossert W. H. Standing-gradient osmotic flow. A mechanism for coupling of water and solute transport in epithelia. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Sep;50(8):2061–2083. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.8.2061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick D. A. The permeability coefficient of water in the cell membrane and the diffusion coefficient in the cell interior. J Theor Biol. 1964 Nov;7(3):504–531. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(64)90019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everitt C. T., Redwood W. R., Haydon D. A. Problem of boundary layers in the exchange diffusion of water across bimolecular lipid membranes. J Theor Biol. 1969 Jan;22(1):20–32. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(69)90077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINZBURG B. Z., KATCHALSKY A. THE FRICTIONAL COEFFICIENTS OF THE FLOWS OF NON-ELECTROLYTES THROUGH ARTIFICIAL MEMBRANES. J Gen Physiol. 1963 Nov;47:403–418. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganote C. E., Grantham J. J., Moses H. L., Burg M. B., Orloff J. Ultrastructural studies of vasopressin effect on isolated perfused renal collecting tubules of the rabbit. J Cell Biol. 1968 Feb;36(2):355–367. doi: 10.1083/jcb.36.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. C., Jr, Karnovsky M. J. Glomerular permeability. Ultrastructural cytochemical studies using peroxidases as protein tracers. J Exp Med. 1966 Dec 1;124(6):1123–1134. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.6.1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham J. J., Burg M. B. Effect of vasopressin and cyclic AMP on permeability of isolated collecting tubules. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jul;211(1):255–259. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.1.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham J. J., Ganote C. E., Burg M. B., Orloff J. Paths of transtubular water flow in isolated renal collecting tubules. J Cell Biol. 1969 May;41(2):562–576. doi: 10.1083/jcb.41.2.562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham J. J., Kurg M. B., Obloff J. The nature of transtubular Na and K transport in isolated rabbit renal collecting tubules. J Clin Invest. 1970 Oct;49(10):1815–1826. doi: 10.1172/JCI106399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham J. J., Orloff J. Effect of prostaglandin E1 on the permeability response of the isolated collecting tubule to vasopressin, adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate, and theophylline. J Clin Invest. 1968 May;47(5):1154–1161. doi: 10.1172/JCI105804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutknecht J. Membranes of Valonia ventricosa: apparent absence of water-filled pores. Science. 1967 Nov 10;158(3802):787–788. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3802.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYS R. M., LEAF A. Studies on the movement of water through the isolated toad bladder and its modification by vasopressin. J Gen Physiol. 1962 May;45:905–919. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.5.905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hays R. M., Franki N., Soberman R. Activation energy for water diffusion across the toad bladder: evidence against the pore enlargement hypothesis. J Clin Invest. 1971 May;50(5):1016–1018. doi: 10.1172/JCI106572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henn F. A., Thompson T. E. Properties of lipid bilayer membranes separating two aqueous phases: composition studies. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jan 28;31(2):227–235. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90441-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyer E., Cass A., Mauro A. A demonstration of the effect of permeant and impermeant solutes, and unstirred boundary layers on osmoti flow. Yale J Biol Med. 1969 Dec;42(3-4):139–153. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz R., Finkelstein A. The water and nonelectrolyte permeability induced in thin lipid membranes by the polyene antibiotics nystatin and amphotericin B. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jul;56(1):125–145. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEDEM O., KATCHALSKY A. A physical interpretation of the phenomenological coefficients of membrane permeability. J Gen Physiol. 1961 Sep;45:143–179. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEDEM O., KATCHALSKY A. Thermodynamic analysis of the permeability of biological membranes to non-electrolytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Feb;27(2):229–246. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90330-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOEFOED-JOHNSEN V., USSING H. H. The contributions of diffusion and flow to the passage of D2O through living membranes; effect of neurohypophyseal hormone on isolated anuran skin. Acta Physiol Scand. 1953 Mar 31;28(1):60–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1953.tb00959.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEAF A., HAYS R. M. Permeability of the isolated toad bladder to solutes and its modification by vasopressin. J Gen Physiol. 1962 May;45:921–932. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.5.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LICHTENSTEIN N. S., LEAF A. EFFECT OF AMPHOTERICIN B ON THE PERMEABILITY OF THE TOAD BLADDER. J Clin Invest. 1965 Aug;44:1328–1342. doi: 10.1172/JCI105238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein N. S., Leaf A. Evidence for a double series permeability barrier at the mucosal surface of the toad bladder. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jul 14;137(2):556–565. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb50181.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan T., Berliner R. W. Permeability of the loop of Henle, vasa recta, and collecting duct to water, urea, and sodium. Am J Physiol. 1968 Jul;215(1):108–115. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.1.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAGANELLI C. V., SOLOMON A. K. The rate of exchange of tritiated water across the human red cell membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1957 Nov 20;41(2):259–277. doi: 10.1085/jgp.41.2.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPPENHEIMER J. R. Passage of molecules through capillary wals. Physiol Rev. 1953 Jul;33(3):387–423. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1953.33.3.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPPENHEIMER J. R., RENKIN E. M., BORRERO L. M. Filtration, diffusion and molecular sieving through peripheral capillary membranes; a contribution to the pore theory of capillary permeability. Am J Physiol. 1951 Oct;167(1):13–46. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.167.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson E. Water permeability in rat distal tubules. Acta Physiol Scand. 1970 Mar;78(3):364–375. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1970.tb04672.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RENKIN E. M. Filtration, diffusion, and molecular sieving through porous cellulose membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1954 Nov 20;38(2):225–243. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS E., MAURO A. Experimental study of the independence of diffusion and hydrodynamic permeability coefficients in collodion membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1960 Jan;43:523–532. doi: 10.1085/jgp.43.3.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULTZ S. G., SOLOMON A. K. Determination of the effective hydrodynamic radii of small molecules by viscometry. J Gen Physiol. 1961 Jul;44:1189–1199. doi: 10.1085/jgp.44.6.1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer J. A., Andreoli T. E. The effect of antidiuretic hormone on solute flows in mammalian collecting tubules. J Clin Invest. 1972 May;51(5):1279–1286. doi: 10.1172/JCI106922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ULLRICH K. J., RUMRICH G., FUCHS G. WASSERPERMEABILITAET UND TRANDTUBULAERER WASSERFLUSS CORTICALER NEPHRONABSCHNITTE BEI VERSCHIEDENEN DIURESEZUSTAENDEN. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1964 Jul 1;280:99–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright E. M., Diamond J. M. Patterns of non-electrolyte permeability. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1969 Mar 18;171(1028):227–271. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1969.0021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]