Abstract
This study documents the development of alkalosis in patients returning to caloric intake after a period of starvation and investigates the mechanisms responsible for this metabolic alteration. We studied the acid-base status, bicarbonate reabsorption, acid excretion, and sodium metabolism during fasting and glucose refeeding in 19 patients receiving sodium supplements.
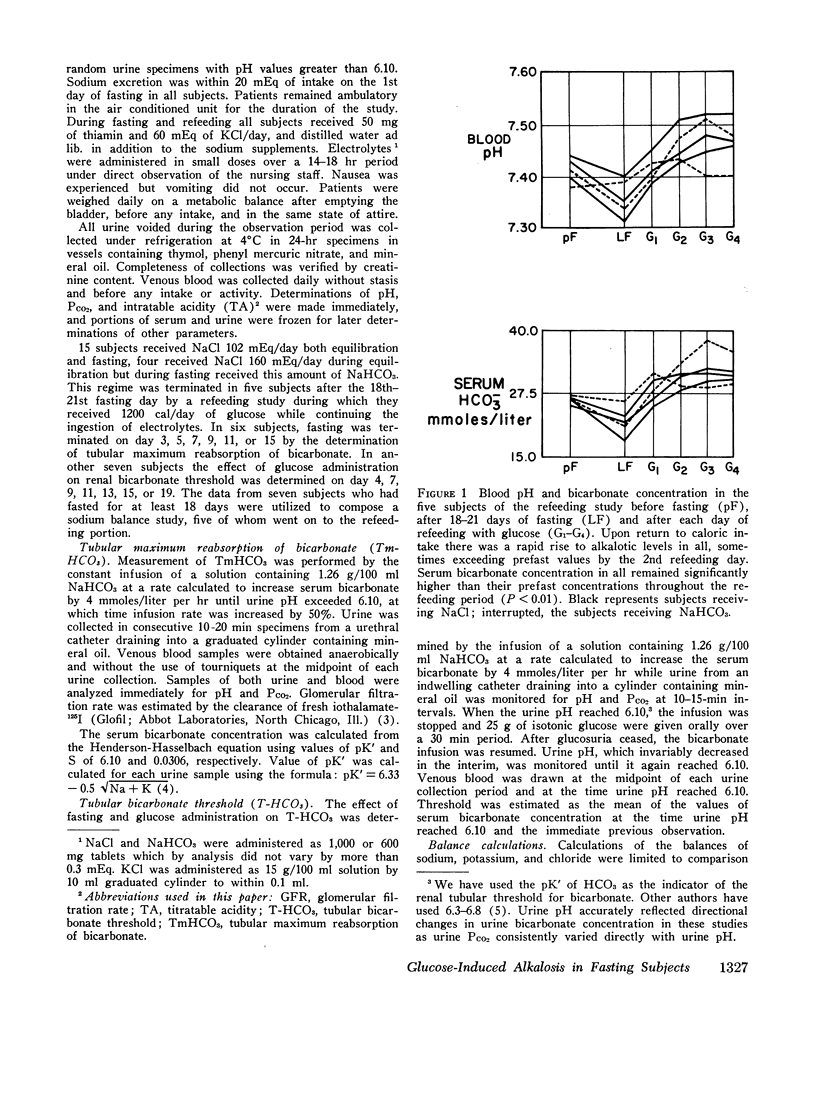
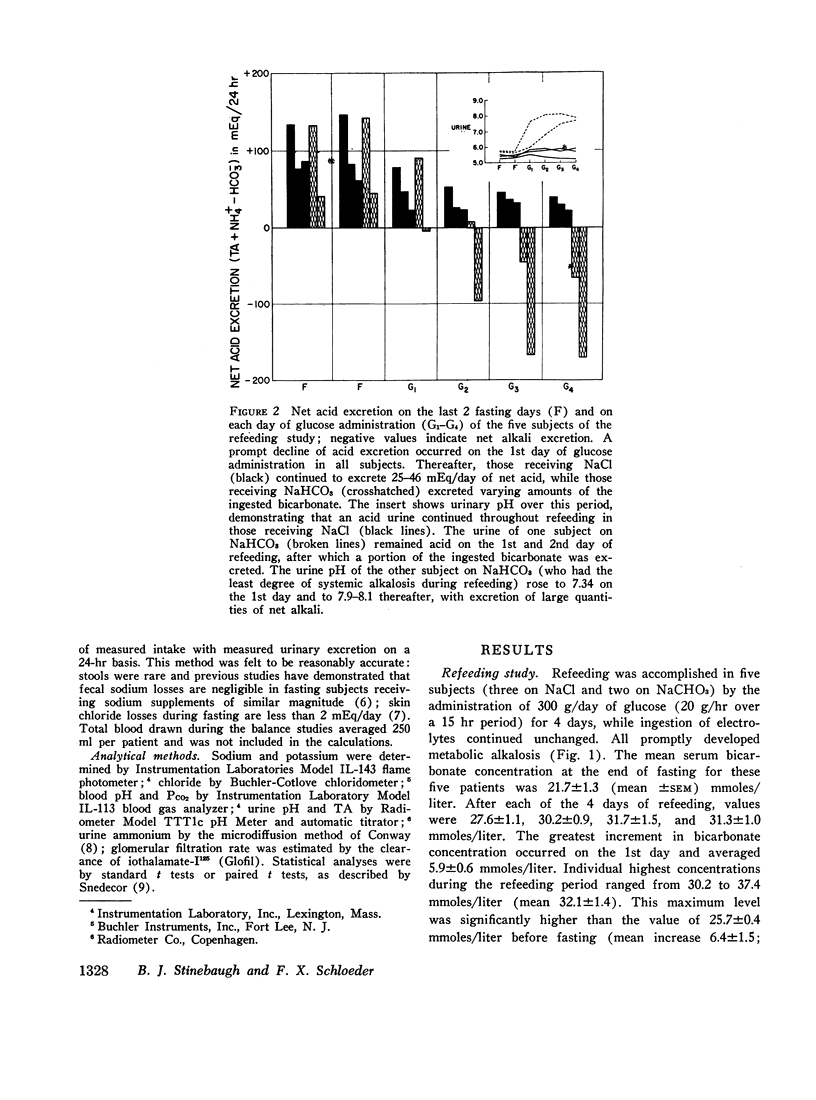
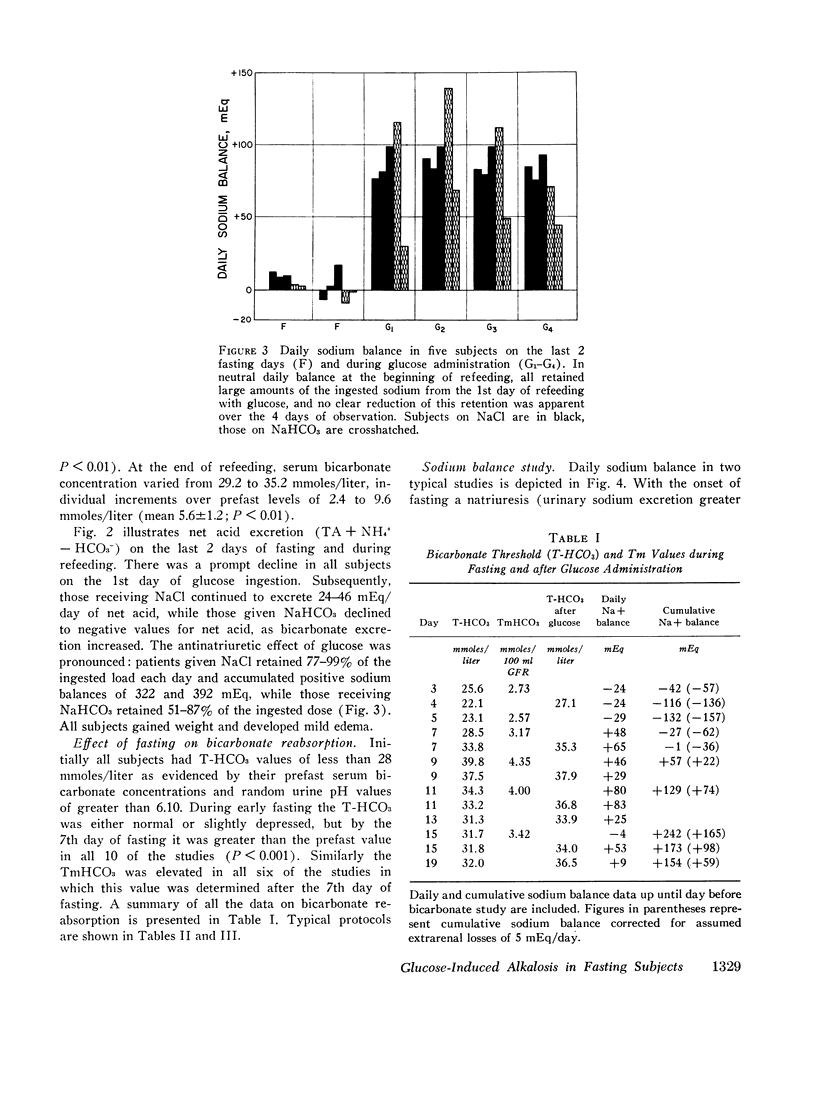
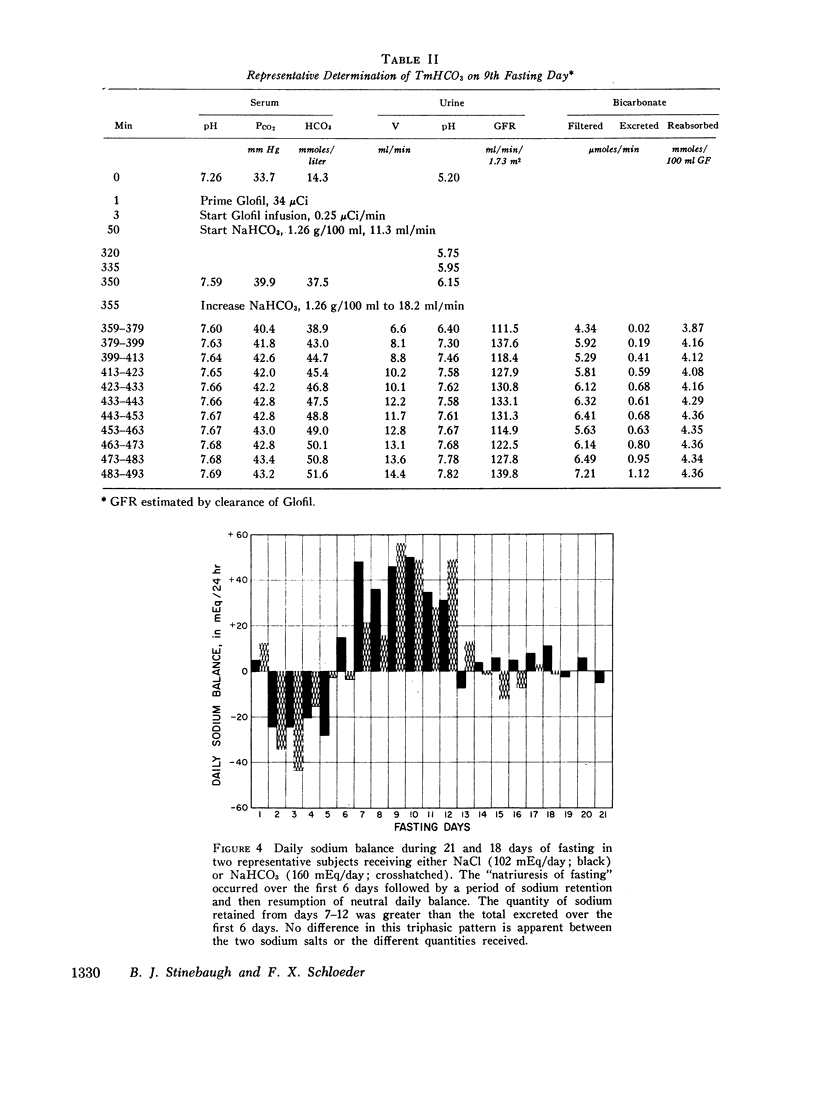
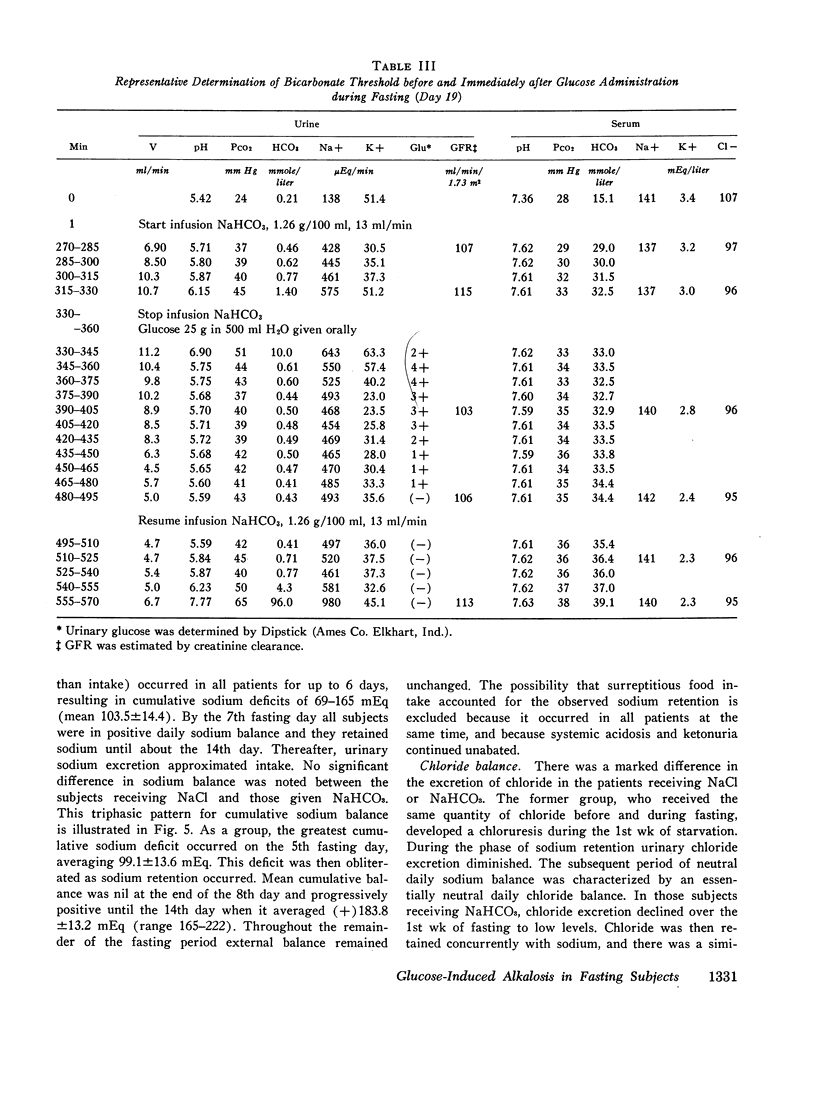
Metabolic alkalosis developed promptly in all of the subjects who terminated an 18 day fast with 300 g of glucose daily for 4 days. Tubular maximum reabsorptive capacity for bicarbonate and renal bicarbonate threshold determinations were performed at varying intervals in six and seven subjects, respectively, who had fasted for 3-18 days. The results demonstrated that bicarbonate reabsorptive capacity was normal or low during early fasting, markedly elevated during the 2nd wk; and moderately elevated during the 3rd wk of fasting. Glucose administration at all stages of fasting caused a further increase in bicarbonate threshold.
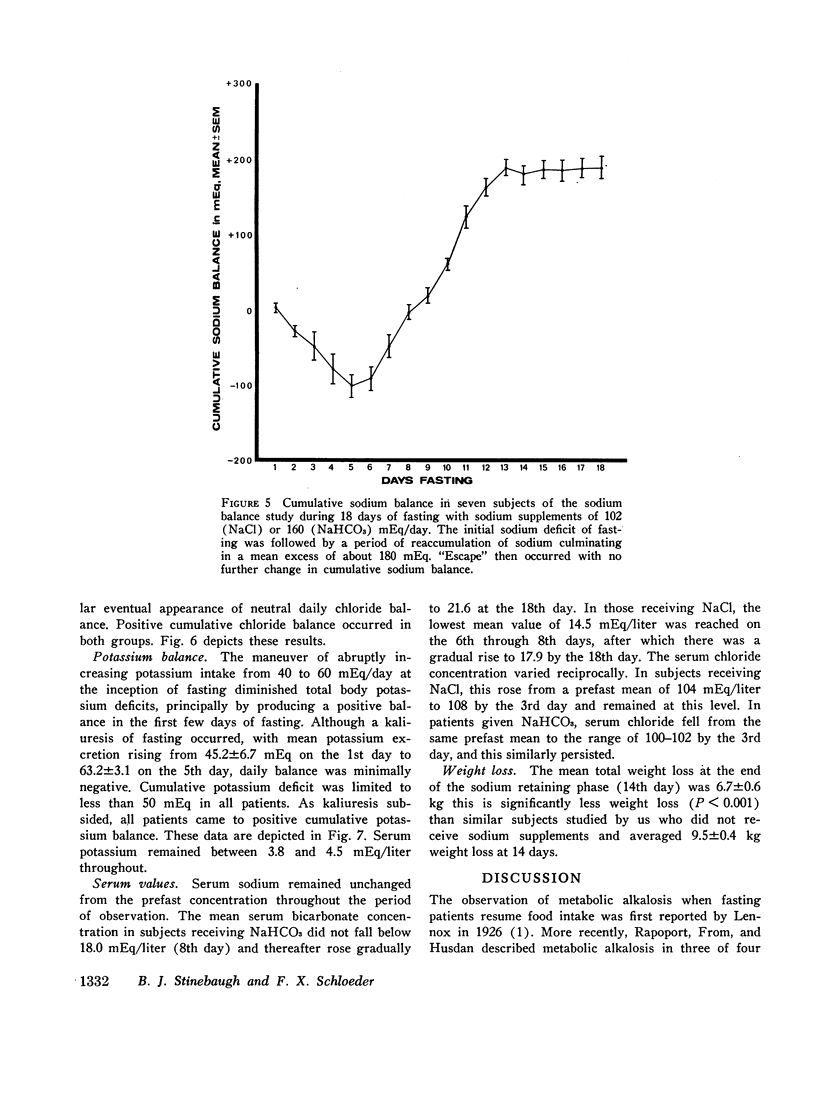
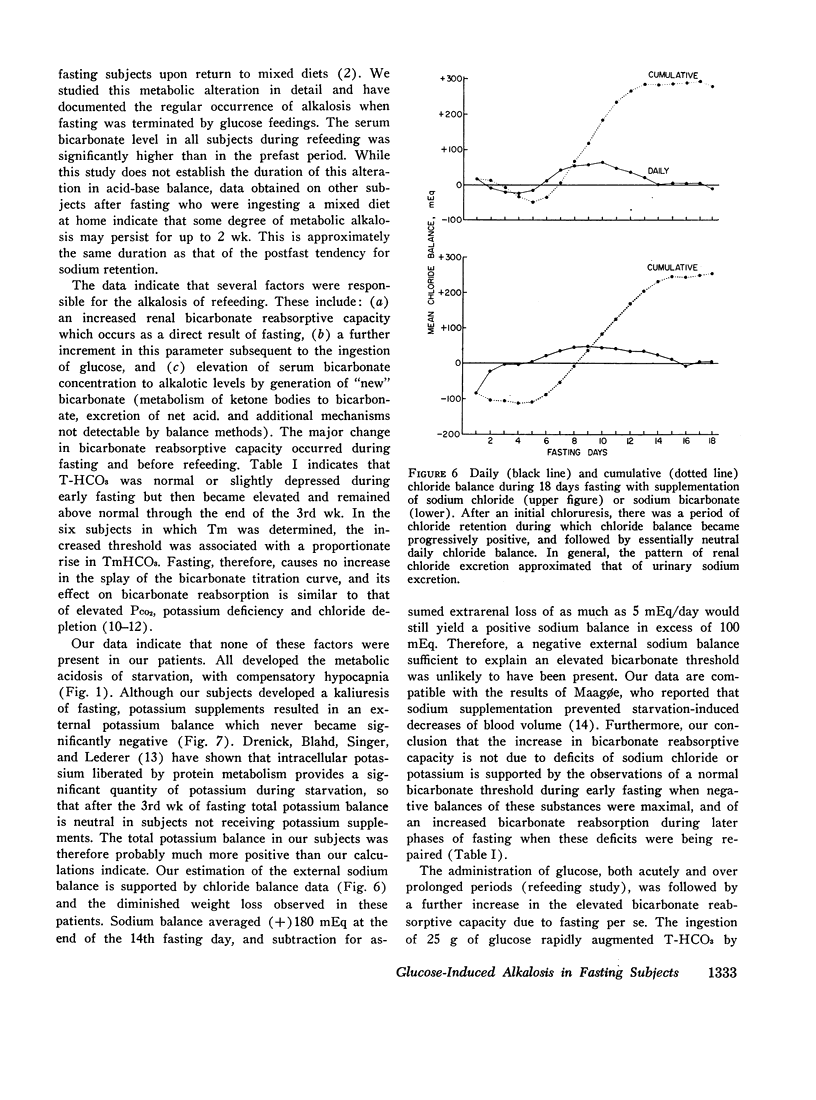
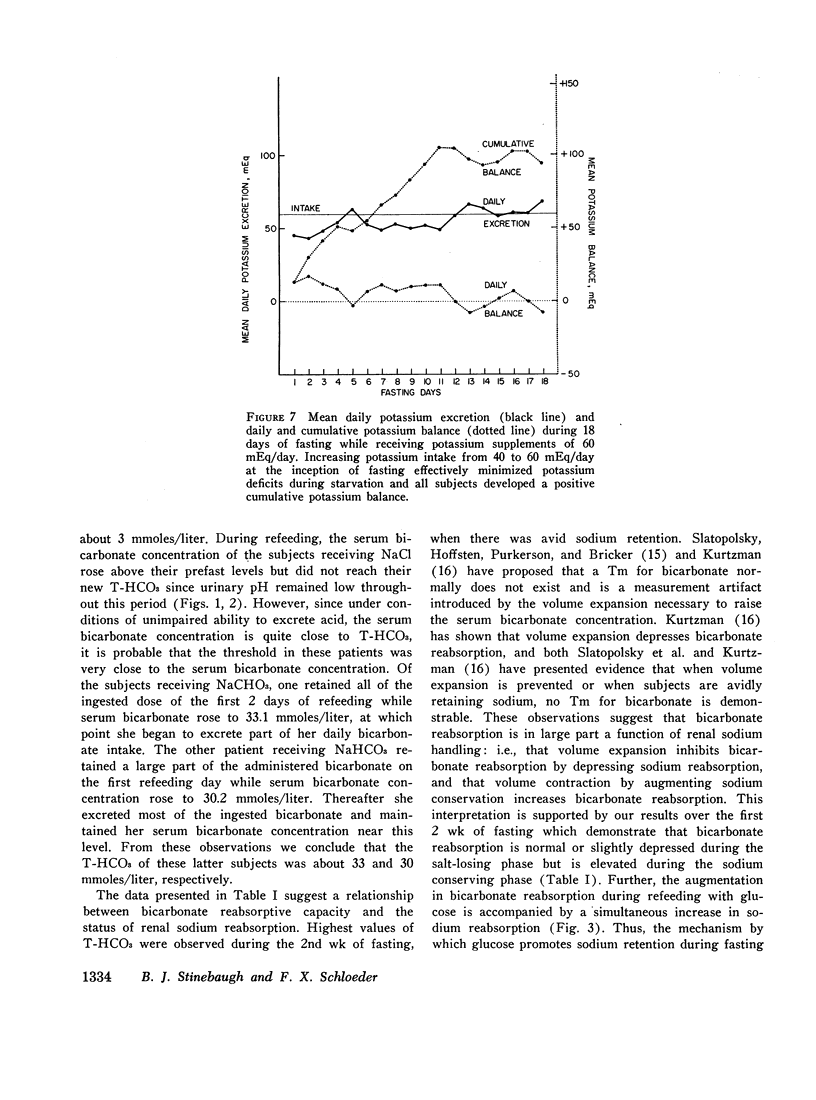
Sodium balance during fasting with sodium supplements was found to follow a triphasic pattern, with the occurrence of a natriuresis during the 1st wk followed by a period of sodium retention after which neutral daily sodium balance was reestablished. Correlation of bicarbonate reabsorption with sodium homeostasis indicated a slight decrease in renal bicarbonate threshold during the natriuretic phase, a marked increase in bicarbonate reabsorption during the period of sodium retention, and a continued moderate elevation of threshold after sodium balance was reestablished. This relationship was interpreted to indicate that changes in bicarbonate reabsorption during fasting and refeeding may be secondary to alterations in the renal reabsorption of sodium.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cahill G. F., Jr, Herrera M. G., Morgan A. P., Soeldner J. S., Steinke J., Levy P. L., Reichard G. A., Jr, Kipnis D. M. Hormone-fuel interrelationships during fasting. J Clin Invest. 1966 Nov;45(11):1751–1769. doi: 10.1172/JCI105481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. J., Chazan J. A., Garella S. The interrelationship between ECF volume and ECF anion composition in the regulation of sodium excretion. Clin Sci. 1970 Oct;39(4):475–487. doi: 10.1042/cs0390475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. B., Walter M. J., Murdaugh H. V., Jr Renal response to graded saline challenge. Am J Physiol. 1969 Dec;217(6):1604–1607. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.6.1604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drenick E. J., Blahd W. H., Singer F. R., Lederer M. Body potassium content in obese subjects and potassium depletion during prolonged fasting. Am J Clin Nutr. 1966 Apr;18(4):278–285. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/18.4.278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GULYASSY P. F., VAN YPERSELE DE STRIHOU C., SCHWARTZ W. B. On the mechanism of nitrate-induced alkalosis. The possible role of selective chloride depletion in acid-base regulation. J Clin Invest. 1962 Oct;41:1850–1862. doi: 10.1172/JCI104642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garella S., Chazan J. A., Cohen J. J. Saline-resistant metabolic alkalosis or "chloride-wasting nephropathy". Report of four patients with severe potassium depletion. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Jul;73(1):31–38. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-73-1-31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGGINS B. A., NASSIM J. R., COLLINS J., HILB A. THE EFFECT OF BENDROFLUAZIDE ON URINE CALCIUM EXCRETION. Clin Sci. 1964 Dec;27:457–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haag B. L., Reidenberg M. M., Shuman C. R., Channick B. J. Aldosterone, 17-hydroxycorticosteroid, 17-ketosteroid, and fluid and electrolyte responses to starvation and selective refeeding. Am J Med Sci. 1967 Nov;254(5):652–658. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196711000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howards S. S., Davis B. B., Knox F. G., Wright F. S., Berliner R. W. Depression of fractional sodium reabsorption by the proximal tubule of the dog without sodium diuresis. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jul;47(7):1561–1572. doi: 10.1172/JCI105848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassirer J. P., Schwartz W. B. The response of normal man to selective depletion of hydrochloric acid. Factors in the genesis of persistent gastric alkalosis. Am J Med. 1966 Jan;40(1):10–18. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(66)90182-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzman N. A. Regulation of renal bicarbonate reabsorption by extracellular volume. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):586–595. doi: 10.1172/JCI106269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maagoe H. Changes in blood volume during absolute fasting with and without sodium chloride administration. Metabolism. 1968 Feb;17(2):133–138. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(68)90139-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RECTOR F. C., Jr, SELDIN D. W., ROBERTS A. D., Jr, SMITH J. S. The role of plasma CO2 tension and carbonic anhydrase activity in the renal reabsorption of bicarbonate. J Clin Invest. 1960 Nov;39:1706–1721. doi: 10.1172/JCI104193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosin J. M., Katz M. A., Rector F. C., Jr, Seldin D. W. Acetazolamide in studying sodium reabsorption in diluting segment. Am J Physiol. 1970 Dec;219(6):1731–1738. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.6.1731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schloeder F. X., Stinebaugh B. J. Renal tubular sites of natriuresis of fasting and glucose-induced sodium conservation. Metabolism. 1970 Dec;19(12):1119–1128. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(70)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slatopolsky E., Hoffsten P., Purkerson M., Bricker N. S. On the influence of extracellular fluid volume expansion and of uremia on bicarbonate reabsorption in man. J Clin Invest. 1970 May;49(5):988–998. doi: 10.1172/JCI106318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano J. R., Boichis H., Edelmann C. M., Jr Bicarbonate reabsorption and hydrogen ion excretion in children with renal tubular acidosis. J Pediatr. 1967 Dec;71(6):802–813. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(67)80005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suki W. N., Schwettmann R. S., Rector F. C., Jr, Seldin D. W. Effect of chronic mineralocorticoid administration on calcium excretion in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1968 Jul;215(1):71–74. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


