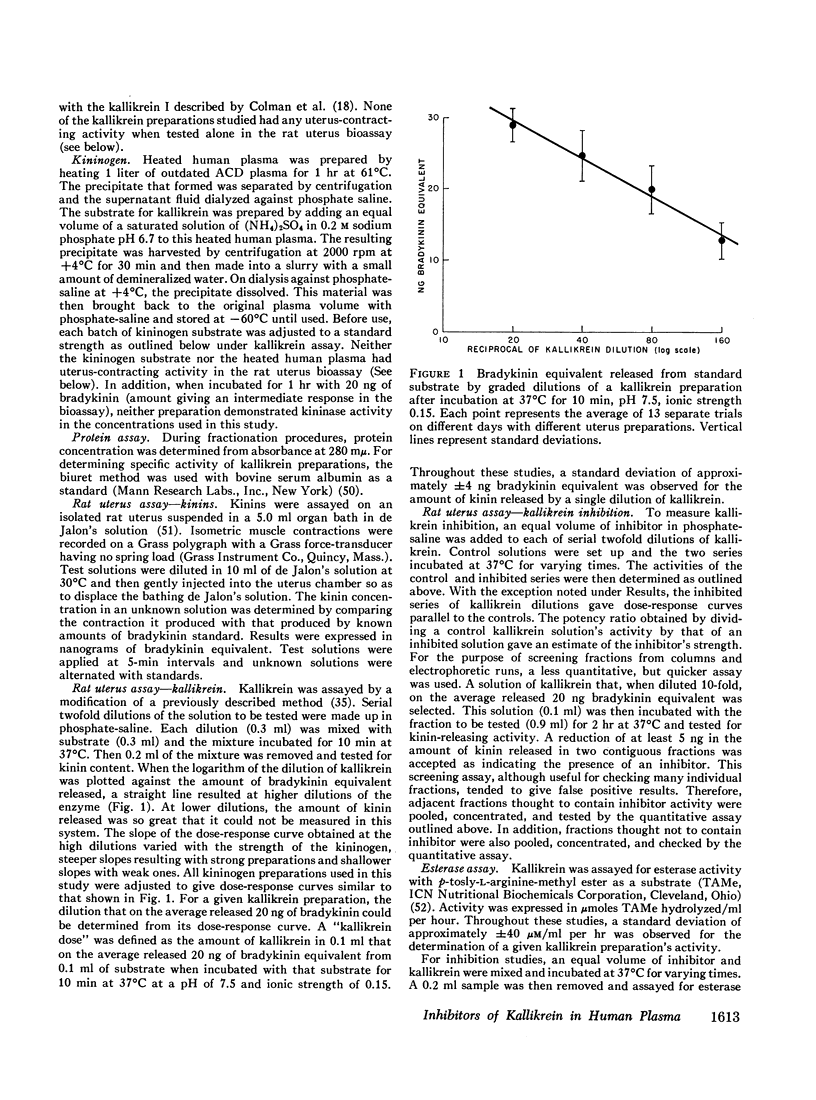
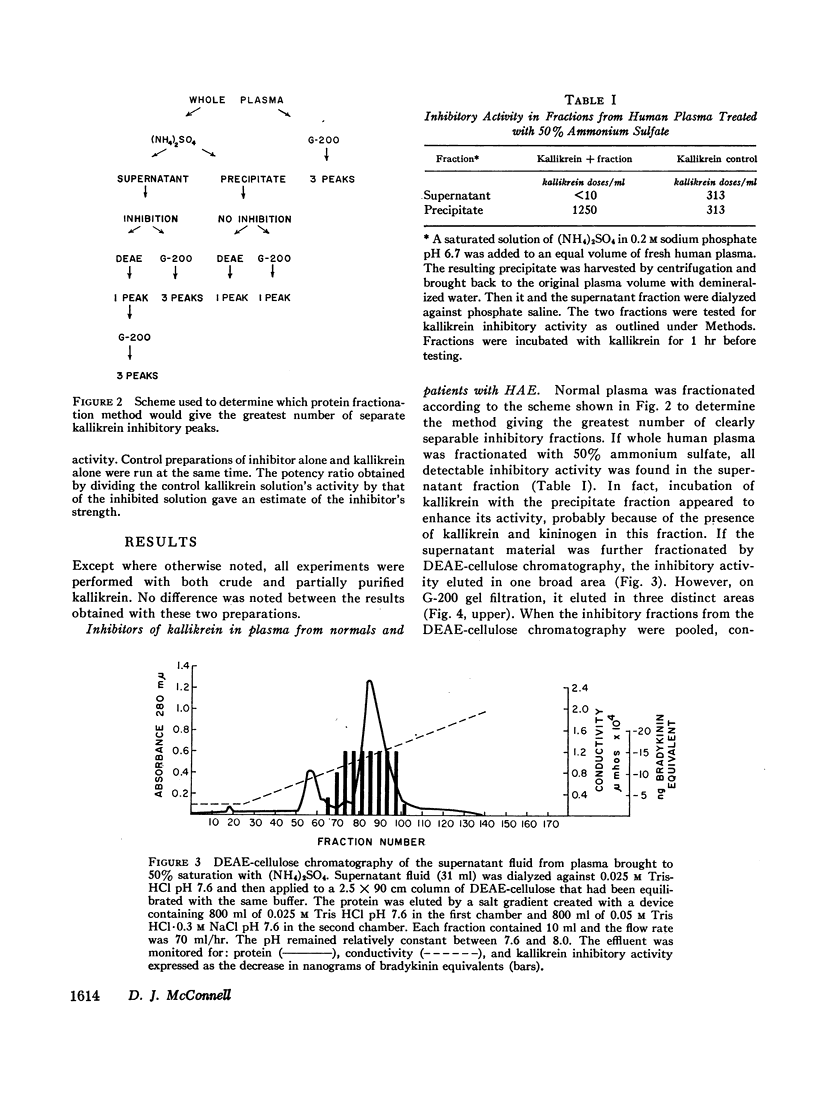
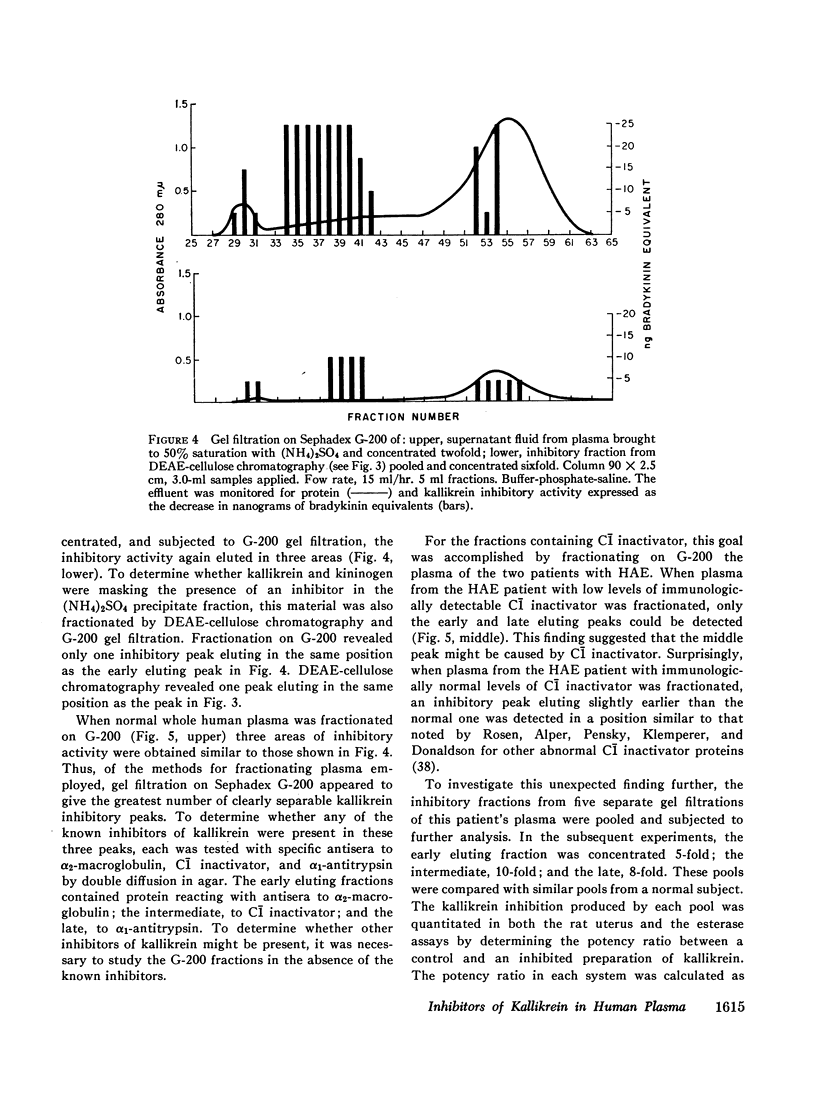
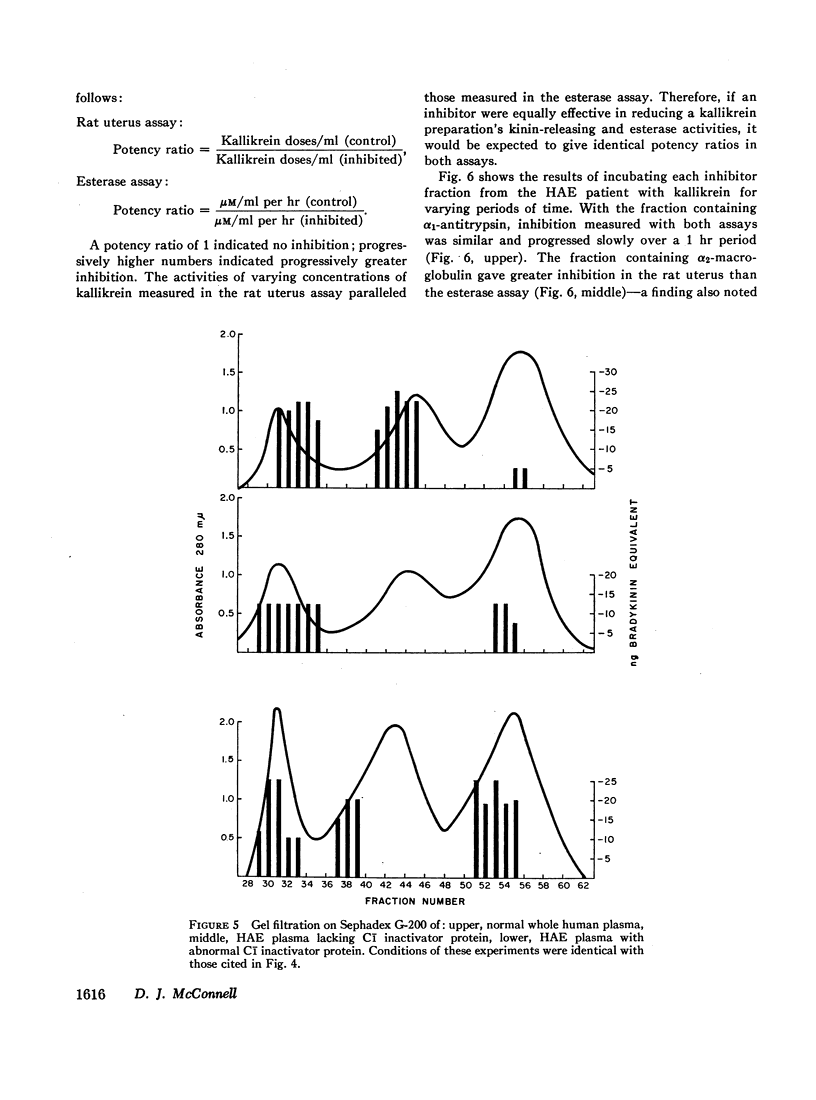
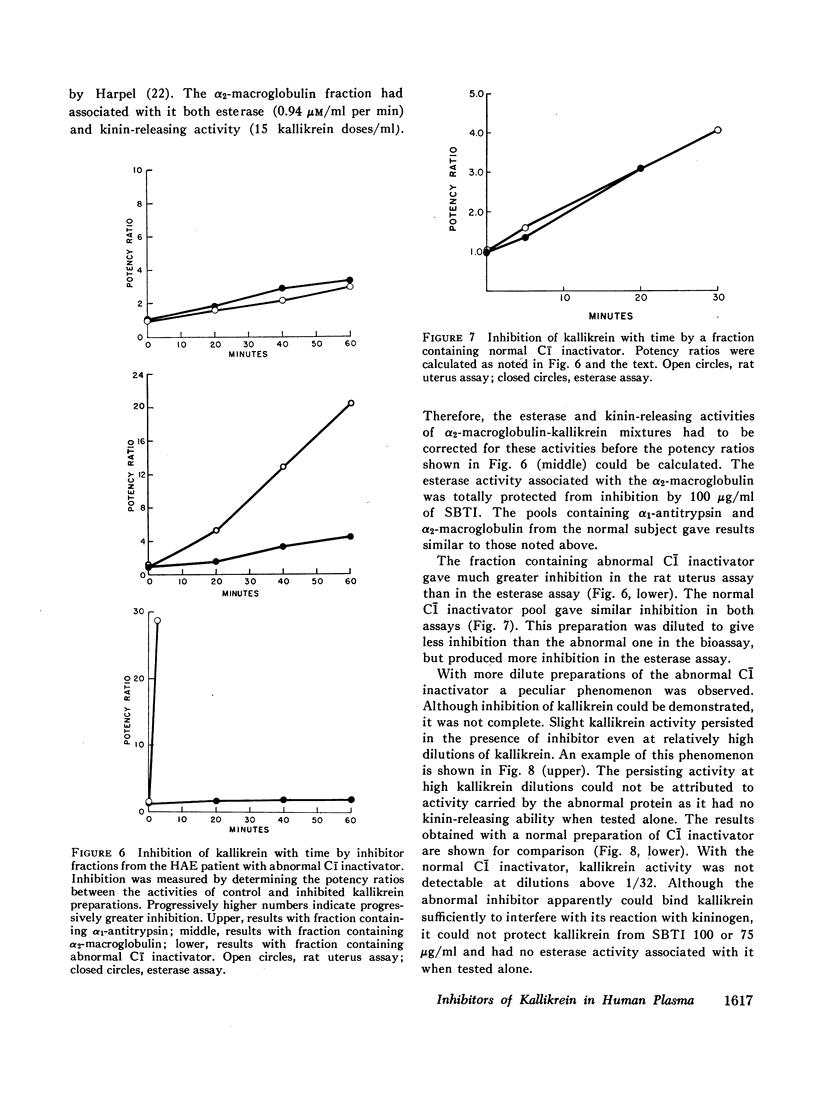
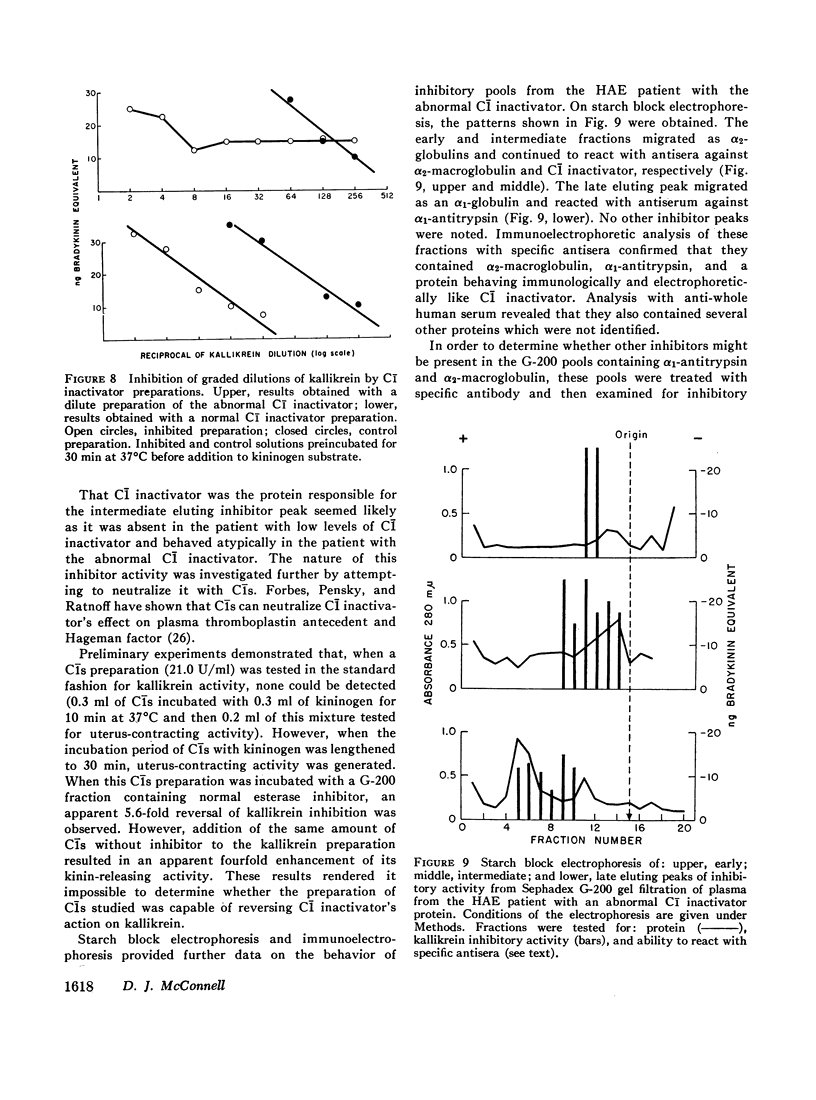
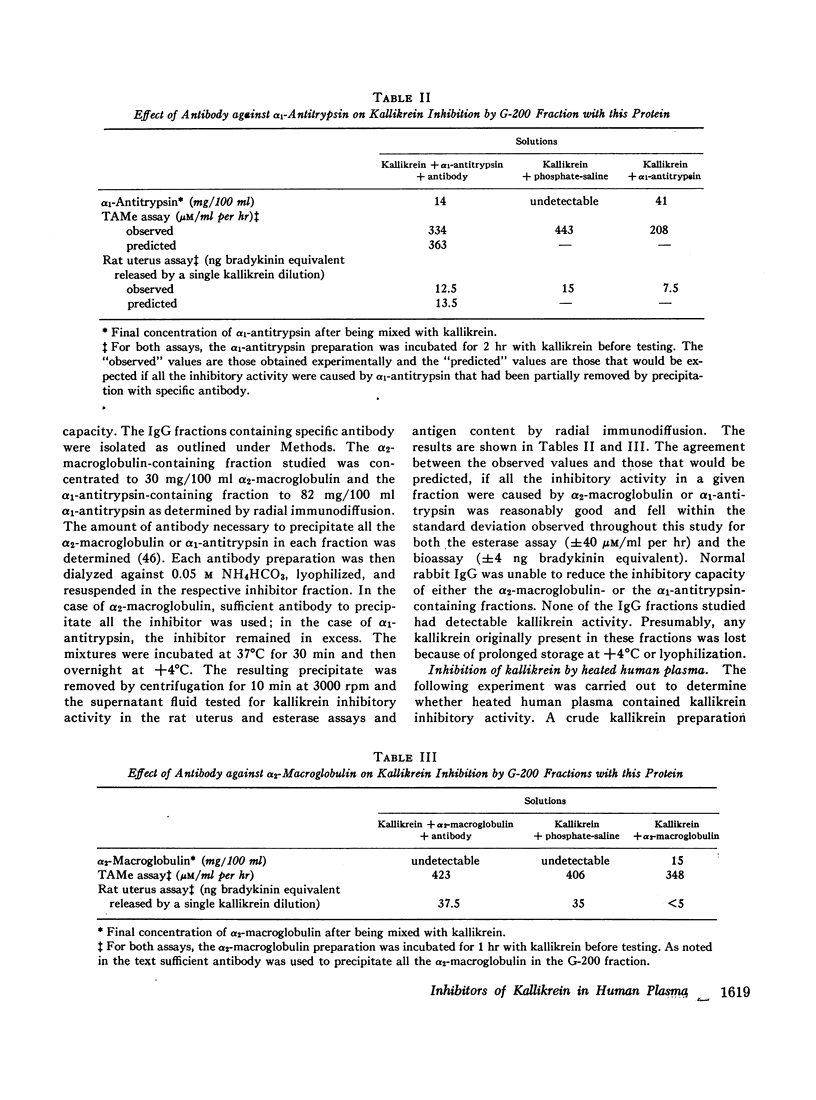
Abstract
Human plasma was fractionated by ammonium sulfate precipitation, DEAE-cellulose chromatography, and Sephadex G-200 gel filtration to determine which method would give the greatest number of clearly separable kallikrein inhibitory peaks. With G-200 gel filtration three peaks could be separated which were demonstrated to contain α2-macroglobulin, C1̄ inactivator, and α1-antitrypsin. No other kallikrein inhibitors could be identified. The fractions containing C1̄ inactivator and α2-macroglobulin appeared to be more effective against kallikrein than that containing α1-antitrypsin. A patient with hereditary angioneurotic edema was shown to have an abnormal C1̄ inactivator protein capable of interfering with kallikrein's biologic, but not its esterolytic activity. Heat-treated human plasma, a commonly used source of kininogen for experiments with kallikrein, was shown to have kallikrein inhibitory activity.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BECKER E. L., KAGEN L. THE PERMEABILITY GLOBULINS OF HUMAN SERUM AND THE BIOCHEMICAL MECHANISM OF HEREDITARY ANGIONEUROTIC EDEMA. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Aug 27;116:866–873. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb52552.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W., Mattler L., Sherry S. Studies on the prekallikrein (kallikreinogen)--kallikrein enzyme system of human plasma. I. Isolation and purification of plasma kallikreins. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jan;48(1):11–22. doi: 10.1172/JCI105959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson V. H., Rosen F. S. Hereditary angioneurotic edema: a clinical survey. Pediatrics. 1966 Jun;37(6):1017–1027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen V., Glanville K. L. Separation of kinin-forming factors in human plasma. Br J Exp Pathol. 1969 Oct;50(5):427–437. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes C. D., Pensky J., Ratnoff O. D. Inhibition of activated Hageman factor and activated plasma thromboplastin antecedent by purified serum C1 inactivator. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Nov;76(5):809–815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz H., Brey B., Schmal A., Werle E. Zur Identität des Progressiv-Antikallikreins mit alpha1-Antitrypsin aus Humanserum. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1969 Dec;350(12):1551–1555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganrot P. O. Inhibition of plasmin activity by alpha-2-macroglobulin. Clin Chim Acta. 1967 May;16(2):328–329. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(67)90201-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganrot P. O., Laurell C. B., Ohlsson K. Concentration of trypsin inhibitors of different molecular size and of albumin and haptoglobin in blood and in lymph of various organs in the dog. Acta Physiol Scand. 1970 Jun;79(2):280–286. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1970.tb04727.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gans H., Tan B. H. Alpha-1-antitrypsin, an inhibitor for thrombin and plasmin. Clin Chim Acta. 1967 Jul;17(1):111–117. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(67)90104-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAINES A. L., LEPOW I. H. STUDIES ON HUMAN C'1-ESTERASE. I. PURIFICATION AND ENZYMATIC PROPERTIES. J Immunol. 1964 Mar;92:456–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann E. Inhibitors of kallikrein and other proteinases from animal blood. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1968 Jun 28;146(2):479–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1968.tb20308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C. A sensitive colorimetric method for the measurement of serum C1 inactivator using the substrate N-alpha-acetyl-L-lysine methyl ester. J Immunol. 1970 Apr;104(4):1024–1030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C. C1 inactivator inhibition by plasmin. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):568–575. doi: 10.1172/JCI106267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C. Human plasma alpha 2-macroglobulin. An inhibitor of plasma kallikrein. J Exp Med. 1970 Aug 1;132(2):329–352. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahrreiss R., Habermann E. On the endogenous mechanism of kinin release. I. Attempts at discriminating kallikreins. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmakol. 1971;269(1):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF01422018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P., Austen K. F. A pre-albumin activator of prekallikrein. J Immunol. 1970 Oct;105(4):802–811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P., Austen K. F. A prealbumin activator of prekallikrein. II. Derivation of activators of prekallikrein from active Hageman factor by digestion with plasmin. J Exp Med. 1971 Apr 1;133(4):696–712. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.4.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P., Kay A. B., Austen K. F. A prealbumin activator of prekallikrein. 3. Appearance of chemotactic activity for human neutrophils by the conversion of human prekallikrein to kallikrein. J Exp Med. 1972 Jan;135(1):81–97. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato H., Nagasawa S., Suzuki T. Studies on the structure of bovine kininogen: cleavages of disulfide bonds and of methionyl bonds in kininogen-II. J Biochem. 1970 Feb;67(2):313–323. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanchantin G. F., Plesset M. L., Friedmann J. A., Hart D. W. Dissociation of esterolytic and clotting activities of thrombin by trypsin-binding macroglobulin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Feb;121(2):444–449. doi: 10.3181/00379727-121-30800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEHL J. W., O'CONNELL W., DEGROOT J. MACROGLOBULIN FROM HUMAN PLASMA WHICH FORMS AN ENZYMATICALLY ACTIVE COMPOUND WITH TRYPSIN. Science. 1964 Aug 21;145(3634):821–822. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3634.821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnell D. J., Mason B. The isolation of human plasma prekallikrein. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 May;38(3):490–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb10591.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa S., Takahashi H., Koida M., Suzuki T., Schoenmakers J. G. Partial purification of bovine plasma kallikreinogen, its activation by the Hageman factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Aug 21;32(4):644–649. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pensky J., Schwick H. G. Human serum inhibitor of C'1 esterase: identity with alpha-2-neuraminoglycoprotein. Science. 1969 Feb 14;163(3868):698–699. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3868.698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATNOFF O. D., MILES A. A. THE INDUCTION OF PERMEABILITY-INCREASING ACTIVITY IN HUMAN PLASMA BY ACTIVATED HAGEMAN FACTOR. Br J Exp Pathol. 1964 Jun;45:328–345. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnoff O. D., Pensky J., Ogston D., Naff G. B. The inhibition of plasmin, plasma kallikrein, plasma permeability factor, and the C'1r subcomponent of the first component of complement by serum C'1 esterase inhibitor. J Exp Med. 1969 Feb 1;129(2):315–331. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.2.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen F. S., Alper C. A., Pensky J., Klemperer M. R., Donaldson V. H. Genetically determined heterogeneity of the C1 esterase inhibitor in patients with hereditary angioneurotic edema. J Clin Invest. 1971 Oct;50(10):2143–2149. doi: 10.1172/JCI106708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIEGELMAN A. M., CARLSON A. S., ROBERTSON T. Investigation of serum trypsin and related substances. I. The quantitative demonstration of trypsinlike activity in human blood serum by a micromethod. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Apr;97:159–163. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(62)90058-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spragg J., Haber E., Austen K. F. The preparation of human kininogen and the elicitation of antibody for use in a radial immuno-diffusion assay. J Immunol. 1970 Jun;104(6):1348–1354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WU F. C., LASKOWSKI M. Crystalline acid-labile trypsin inhibitor from bovine blood plasma. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jun;235:1680–1685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster M. E. Human plasma kallikrein, its activation and pathological role. Fed Proc. 1968 Jan-Feb;27(1):84–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuepper K. D., Cochrane C. G. Plasma prekallikrein: isolation, characterization, and mechanism of activation. J Exp Med. 1972 Jan;135(1):1–20. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano M., Nagasawa S., Suzuki T. Partial purification and some properties of high molecular weight kininogen, bovine kininogen-I. J Biochem. 1971 Mar;69(3):471–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


