Abstract
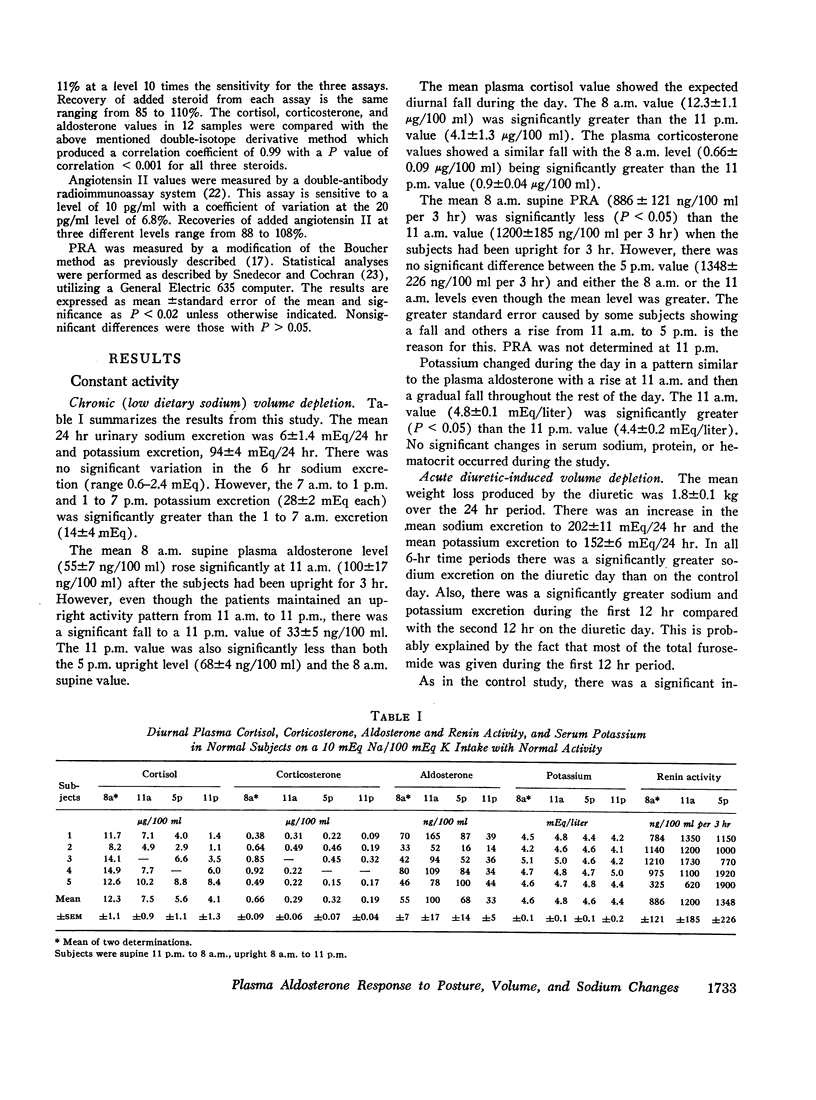
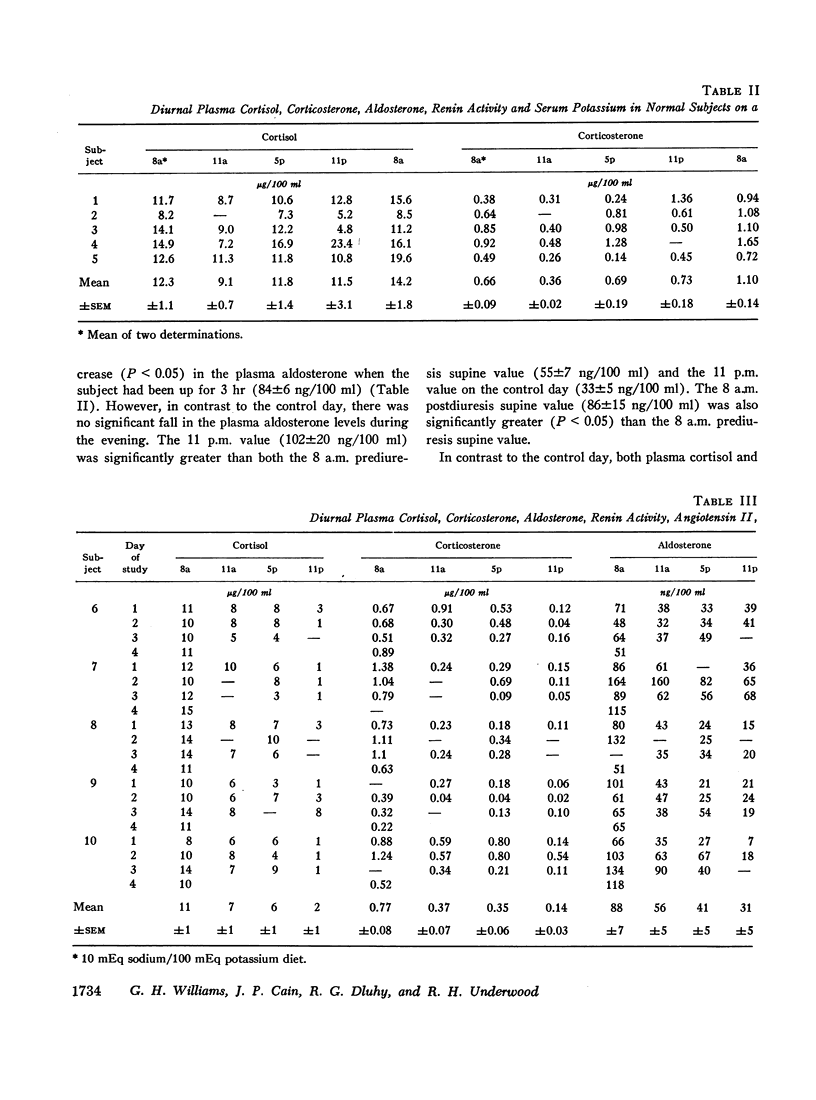
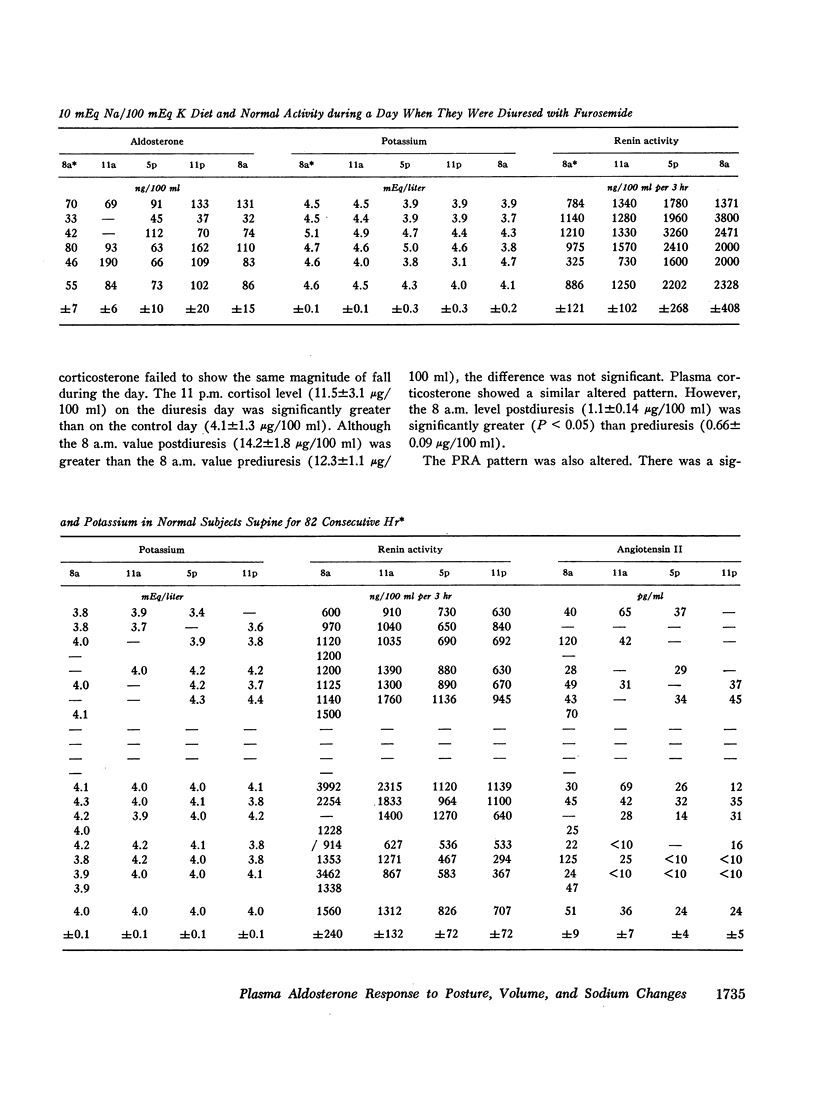
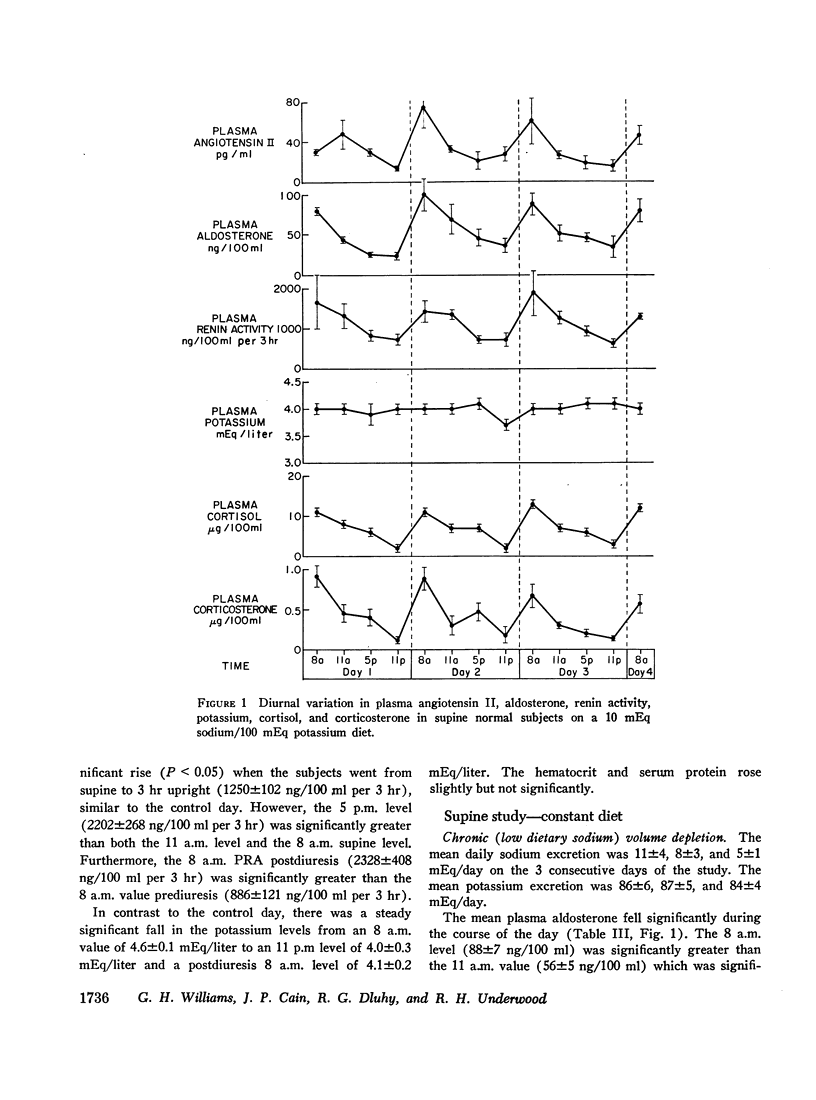
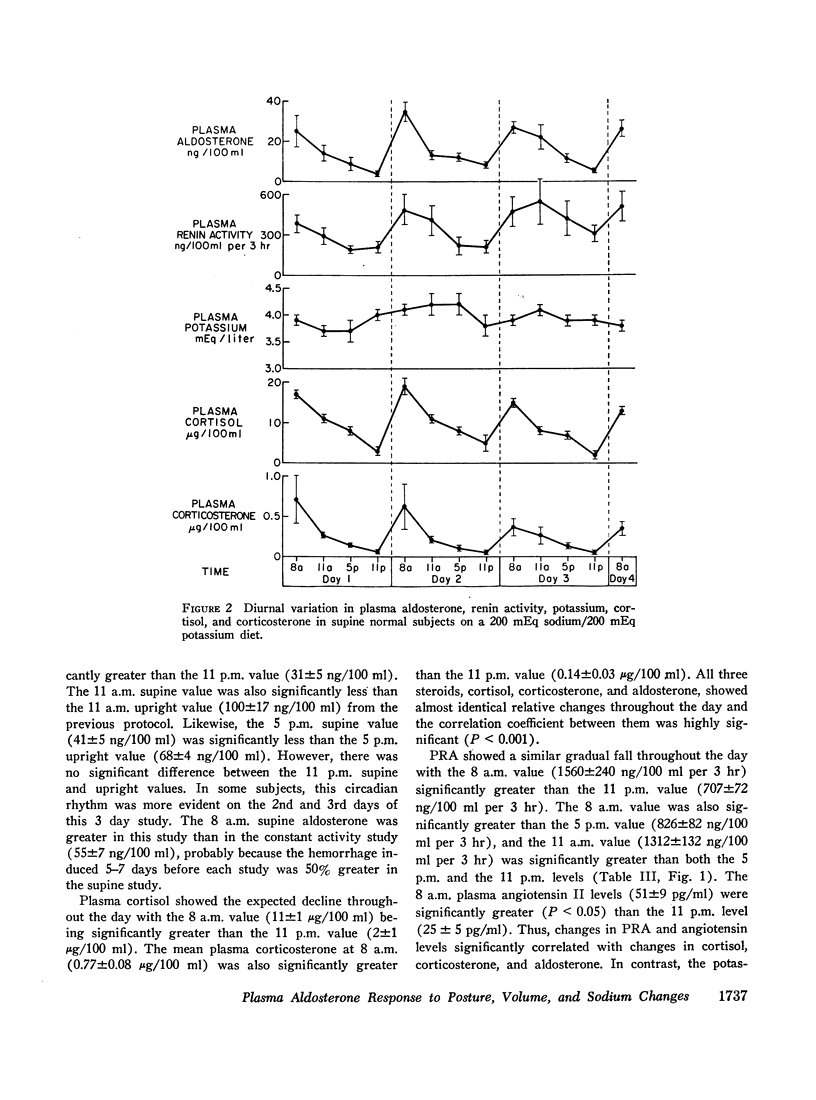
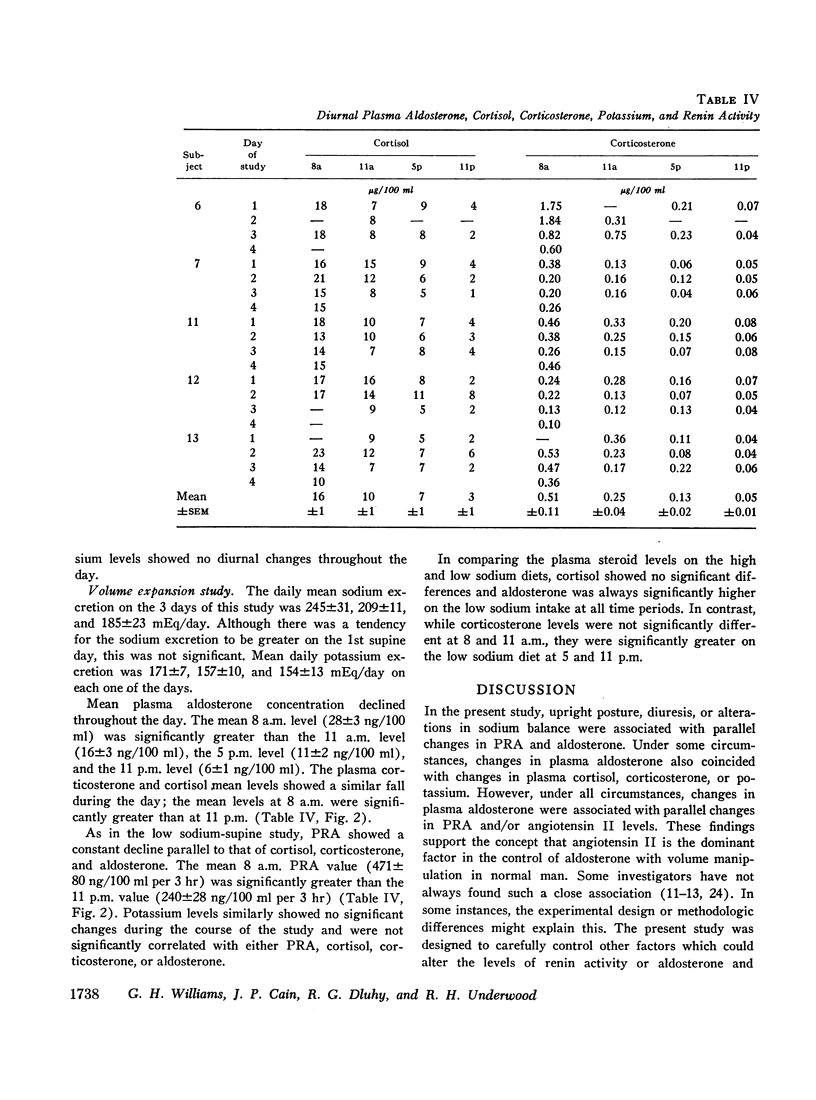
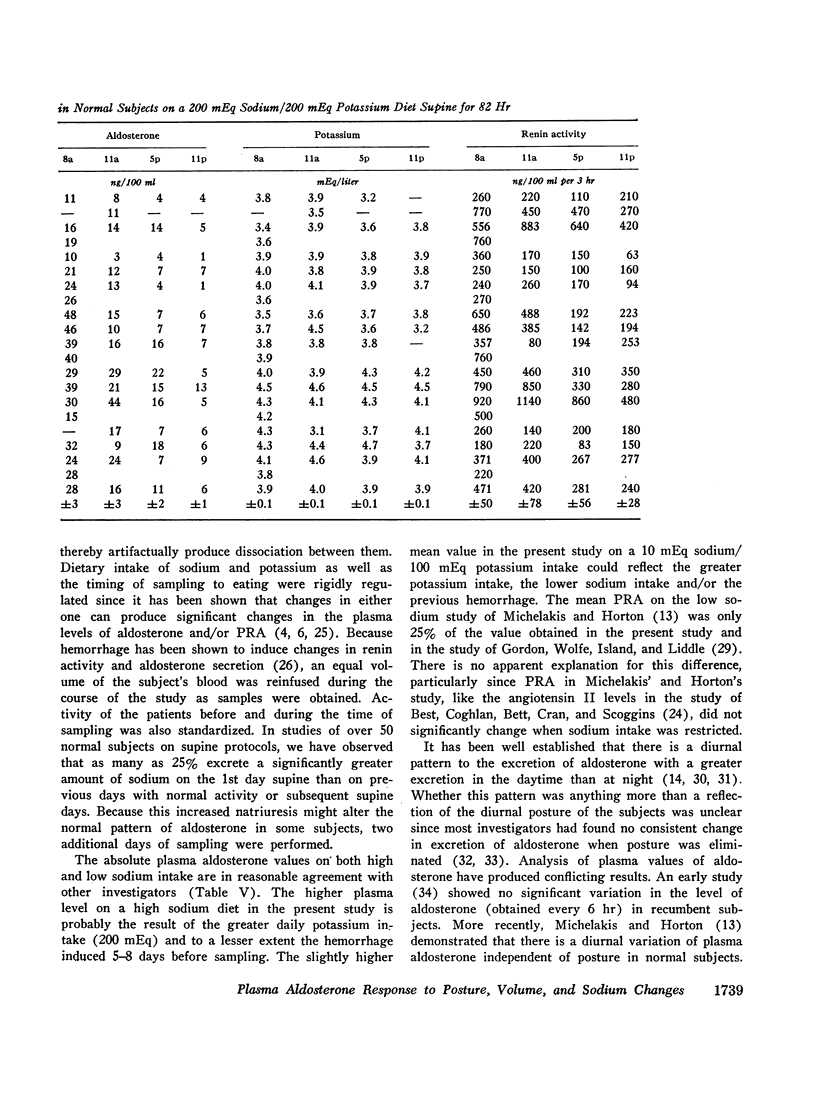
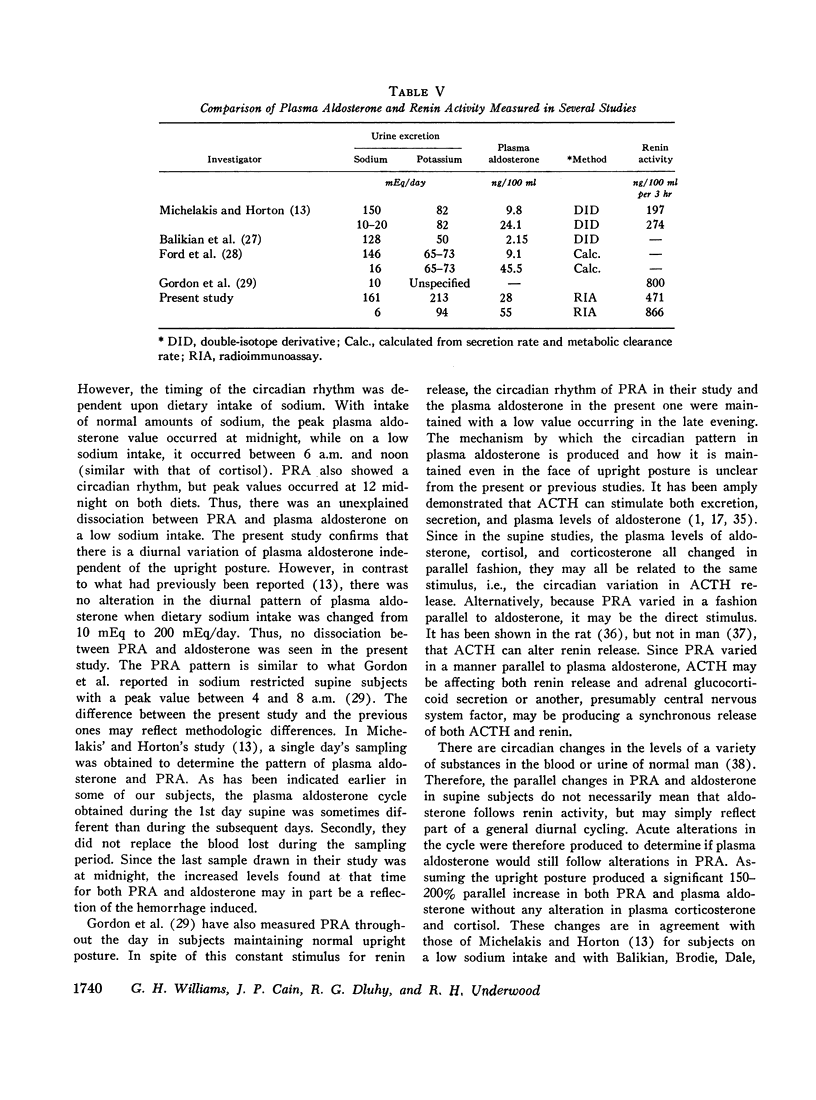
The peripheral plasma levels of aldosterone, renin activity (PRA), potassium, corticosterone, cortisol, and in some cases angiotensin II, were measured in normal subjects undergoing postural changes, acute diuretic-induced volume depletion, and alterations in dietary sodium. On a 10 mEq sodium/100 mEq potassium intake, subjects supine for 3 consecutive days had identical diurnal patterns of PRA, angiotensin II, aldosterone, cortisol, and corticosterone, with peaks at 8 a.m. and nadirs at 11 p.m. With an increase in sodium intake to 200 mEq, plasma levels of aldosterone and PRA fell to one-third their previous levels but the diurnal pattern in supine subjects was unchanged and again parallel to that of cortisol and corticosterone. There was no diurnal variation of plasma potassium on either sodium intake in the supine subjects. On a 10 mEq sodium/100 mEq potassium intake, supine 8 a.m. plasma aldosterone (55±7 ng/100 ml) and PRA (886±121 ng/100 ml per 3 hr) increased by 150-200% after subjects were upright for 3 hr. However, even though the patients maintained an upright activity pattern, there was a significant fall in plasma aldosterone to 33±5 ng/100 ml at 11 p.m. Potassium levels varied in a fashion parallel to aldosterone and PRA. Plasma cortisol and corticosterone had a diurnal pattern similar to that found in supine subjects. In response to acute diuretic-induced volume depletion, the nocturnal fall in aldosterone levels did not occur. The 11 p.m. value (102±20 ng/100 ml) and the 8 a.m. value postdiuresis (86±15 ng/100 ml) were both significantly greater than the prediuresis levels. PRA showed a similar altered pattern while potassium levels fell throughout the day. In some but not all studies, changes in plasma aldosterone coincided with changes in plasma cortisol, corticosterone, and/or potassium. However, in all studies, changes in plasma aldosterone were invariably associated with parallel changes in plasma renin activity and/or angiotensin II levels. These findings support the concept that PRA is the dominant factor in the control of aldosterone when volume and/or dietary sodium is altered in normal man.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTTER F. C., DELEA C. S. A map of blood and urinary changes related to circadian variations in adrenal cortical function in normal subjects. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1962 Oct 30;98:969–983. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1962.tb30612.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTTER F. C., DUNCAN L. E., Jr, LIDDLE G. W. Dual mechanism regulating adrenocortical function in man. Am J Med. 1956 Sep;21(3):380–386. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(56)90038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BINNION P. F., DAVIS J. O., BROWN T. C., OLICHNEY M. J. MECHANISMS REGULATING ALDOSTERONE SECRETION DURING SODIUM DEPLETION. Am J Physiol. 1965 Apr;208:655–661. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.208.4.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balikian H. M., Brodie A. H., Dale S. L., Melby J. C., Tait J. F. Effect of posture on the metabolic clearance rate, plasma concentration and blood production rate of aldosterone in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Nov;28(11):1630–1640. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-11-1630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best J. B., Coghlan J. P., Bett J. H., Cran E. J., Scoggins B. A. Circulating angiotensin-II and aldosterone levels during dietary sodium restriction. Lancet. 1971 Dec 18;2(7738):1353–1354. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92366-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodie A. H., Shimizu N., Tait S. A., Tait J. F. A method for the measurement of aldosterone in peripheral plasma using 3H-acetic anhydride. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Jul;27(7):997–1011. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-7-997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinn R. H., Brown J. J., Fraser R., Heron S. M., Lever A. F., Murchison L., Robertson J. I. The natriuresis of fasting: relationship to changes in plasma renin and plasma aldosterone concentrations. Clin Sci. 1970 Sep;39(3):437–455. doi: 10.1042/cs0390437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christlieb A. R., Hickler R. B., Lauler D. P., Williams G. H. Hypertension with inappropriate aldosterone stimulation. N Engl J Med. 1969 Jul 17;281(3):128–131. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196907172810304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins R. D., Weinberger M. H., Dowdy A. J., Nokes G. W., Gonzales C. M., Luetscher J. A. Abnormally sustained aldosterone secretion during salt loading in patients with various forms of benign hypertension; relation to plasma renin activity. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jul;49(7):1415–1426. doi: 10.1172/JCI106359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DYRENFURTH I., GIROUD C. J., VENNING E. H. Aldosterone excretion in healthy persons. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1956 Oct;16(10):1326–1332. doi: 10.1210/jcem-16-10-1326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dluhy R. G., Underwood R. H., Williams G. H. Influence of dietary potassium on plasma renin activity in normal man. J Appl Physiol. 1970 Mar;28(3):299–302. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1970.28.3.299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espiner E. A., Tucci J. R., Jagger P. I., Pauk G. L., Lauler D. P. The effect of acute diuretic-induced extracellular volume depletion on aldosterone secretion in normal man. Clin Sci. 1967 Aug;33(1):125–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford H. C., Pieters H. P., Bailey R. E. Aldosterone and sodium conservation: the effect of acute dietary sodium deprivation on the plasma concentration, the metabolic clearance and the secretion and excretion rates of aldosterone in normal subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Apr;28(4):451–459. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-4-451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganong W. F., Biglieri E. G., Mulrow P. J. Mechanisms regulating adrenocortical secretion of aldosterone and glucocorticoids. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1966;22:381–430. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4831-9825-5.50013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon R. D., Wolfe L. K., Island D. P., Liddle G. W. A diurnal rhythm in plasma renin activity in man. J Clin Invest. 1966 Oct;45(10):1587–1592. doi: 10.1172/JCI105464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauger-Klevene J. H., Brown H., Fleischer N. ACTH stimulation and glucocorticoid inhibition of renin release in the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jun;131(2):539–542. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-33920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton R. Stimulation and suppression of aldosterone in plasma of normal man and in primary aldosteronism. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jul;48(7):1230–1236. doi: 10.1172/JCI106087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLIMAN B., PETERSON R. E. Double isotope derivative assay of aldosterone in biological extracts. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jun;235:1639–1648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARAGH J. H., STOERK H. C. A study of the mechanism of secretion of the sodium-retaining hormone (aldosterone). J Clin Invest. 1957 Mar;36(3):383–392. doi: 10.1172/JCI103434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUETSCHER J. A., Jr, LIEBERMAN A. H. Aldosterone. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1958 Aug;102(2):314–330. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1958.00260200142012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luetscher J. A., Weinberger M. H., Dowdy A. J., Nokes G. W., Balikian H., Brodie A., Willoughby S. Effects of sodium loading, sodium depletion and posture on plasma aldosterone concentration and renin activity in hypertensive patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Oct;29(10):1310–1318. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-10-1310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULLER A. F., MANNING E. L., RIONDEL A. M. Influence of position and activity on the secretion of aldosterone. Lancet. 1958 Apr 5;1(7023):711–713. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(58)91137-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelakis A. M., Horton R. The relationship between plasma renin and aldosterone in normal man. Circ Res. 1970 Jul;27(1 Suppl 1):185–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. N. Human circadian rhythms. Physiol Rev. 1966 Jan;46(1):128–171. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1966.46.1.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra S., Genuth S. M., Berman L. B., Vertes V. Aldosterone secretion in anephric patients. N Engl J Med. 1972 Jan 13;286(2):61–64. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197201132860204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller J., Ziegler W. H. Stimulation of aldosterone biosynthesis in vitro by serotonin. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1968 Sep;59(1):23–35. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0590023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton M. A., Laragh J. H. Effect of corticotropin on aldosterone excretion and plasma renin in normal subjects, in essential hypertension and in primary aldosteronism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Jul;28(7):1006–1013. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-7-1006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nugent C. A., Mayes D. M. Plasma corticosteroids determined by use of corticosteroid-binding globulin and dextran-coated charcoal. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1966 Oct;26(10):1116–1122. doi: 10.1210/jcem-26-10-1116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal J., Boucher R., Nowaczynski W., Genest J. Acute changes in plasma volume, renin activity, and free aldosterone levels in healthy subjects following Fursemide administration. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1968 Jan;46(1):85–91. doi: 10.1139/y68-015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skillman J. J., Lauler D. P., Hickler R. B., Lyons J. H., Olson J. E., Ball M. R., Moore F. D. Hemorrhage in normal man: effect on renin, cortisol, aldosterone, and urine composition. Ann Surg. 1967 Dec;166(6):865–885. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196712000-00001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underwood R. H., Williams G. H. The simultaneous measurement of aldosterone, cortisol, and corticosterone in human peripheral plasma by displacement analysis. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 May;79(5):848–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VENNING E. H., DYRENFURTH I., DOSSETOR J. B., BECK J. C. Influence of alterations in sodium intake on urinary aldosterone response to corticotropin in normal individuals and patients with essential hypertension. Metabolism. 1962 Feb;11:254–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFF H. P., TORBICA M. Determination of plasma-aldosterone. Lancet. 1963 Jun 22;1(7295):1346–1348. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)91925-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. H., Dluhy R. G., Underwood R. H. The relationship of dietary potassium intake to the aldosterone stimulating properties of ACTH. Clin Sci. 1970 Oct;39(4):489–496. doi: 10.1042/cs0390489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. H., Rose L. I., Dluhy R. G., McCaughn D., Jagger P. I., Hickler R. B., Lauler D. P. Abnormal responsiveness of the renin aldosterone system to acute stimulation in patients with essential hypertension. Ann Intern Med. 1970 Mar;72(3):317–326. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-72-3-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe L. K., Gordon R. D., Island D. P., Liddle G. W. An analysis of factors determining the circadian pattern of aldosterone excretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1966 Nov;26(11):1261–1266. doi: 10.1210/jcem-26-11-1261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


