Abstract
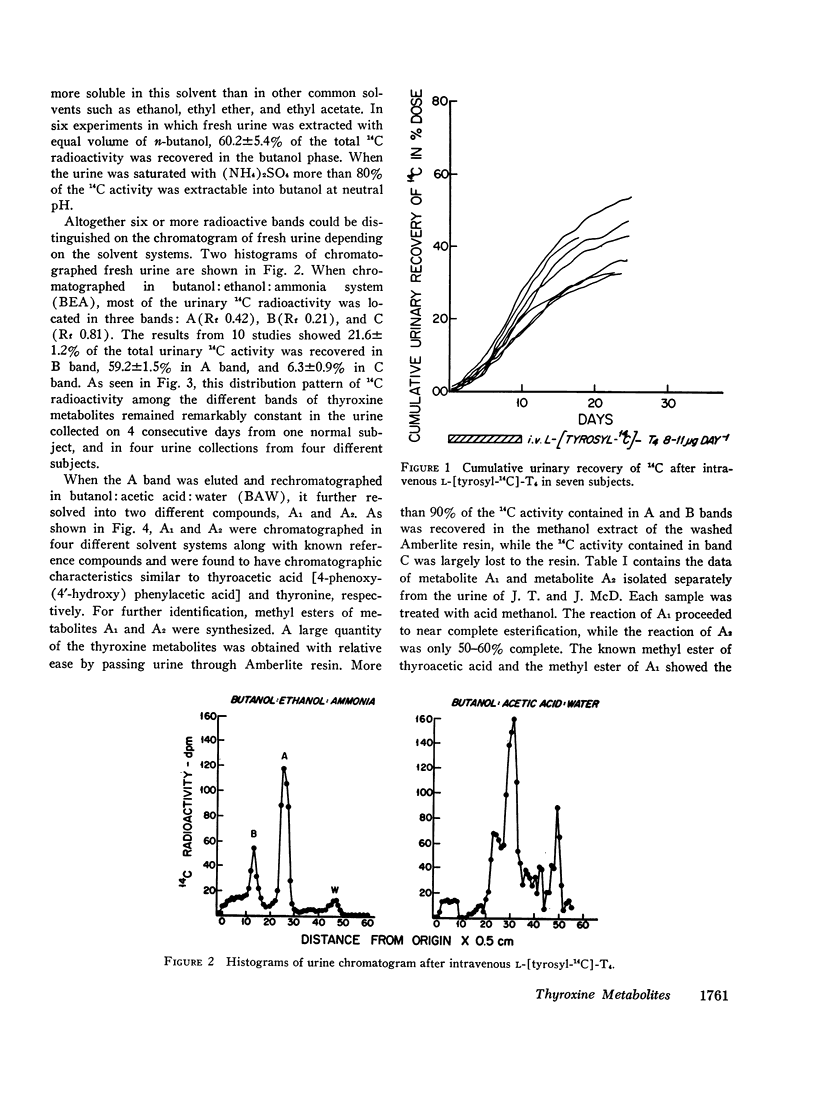
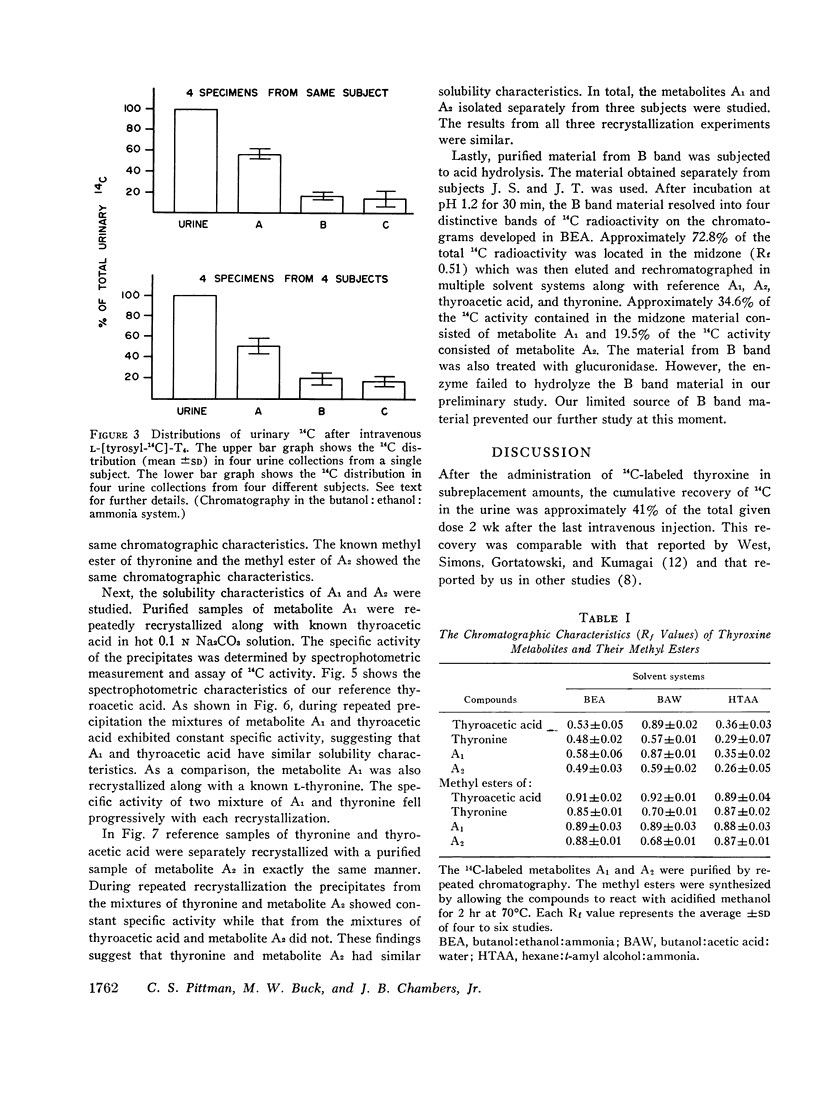
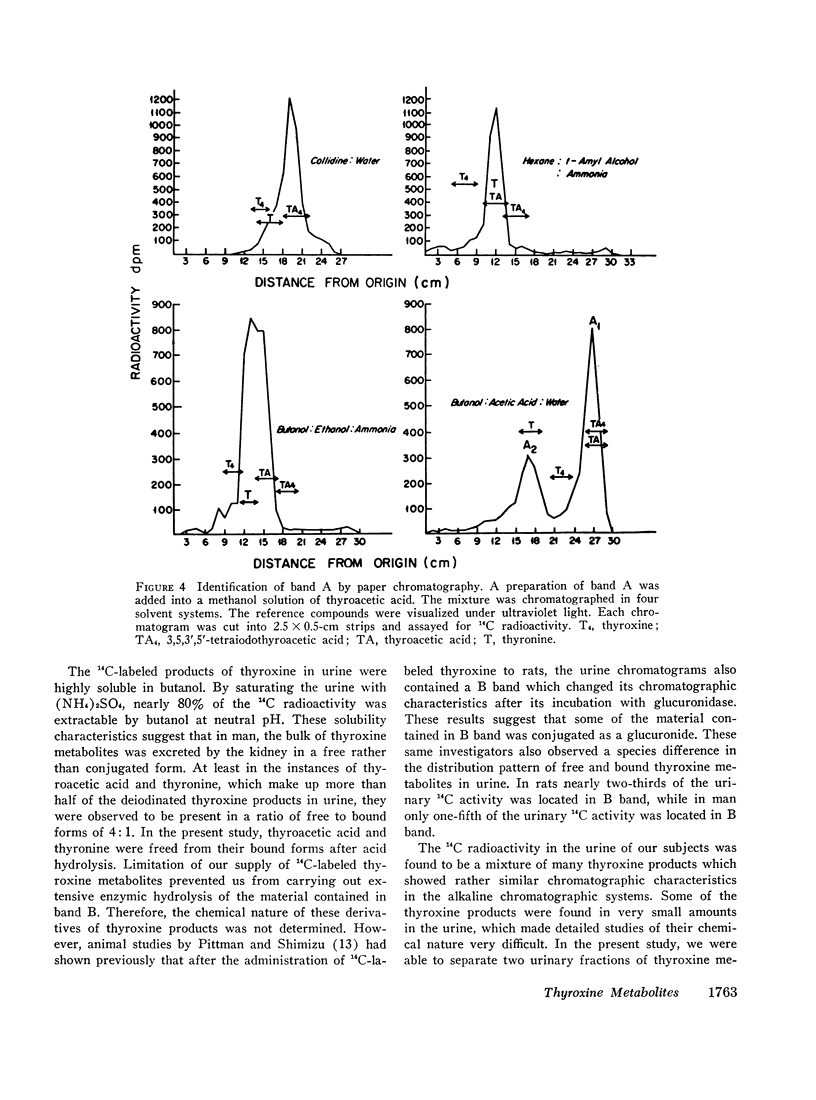
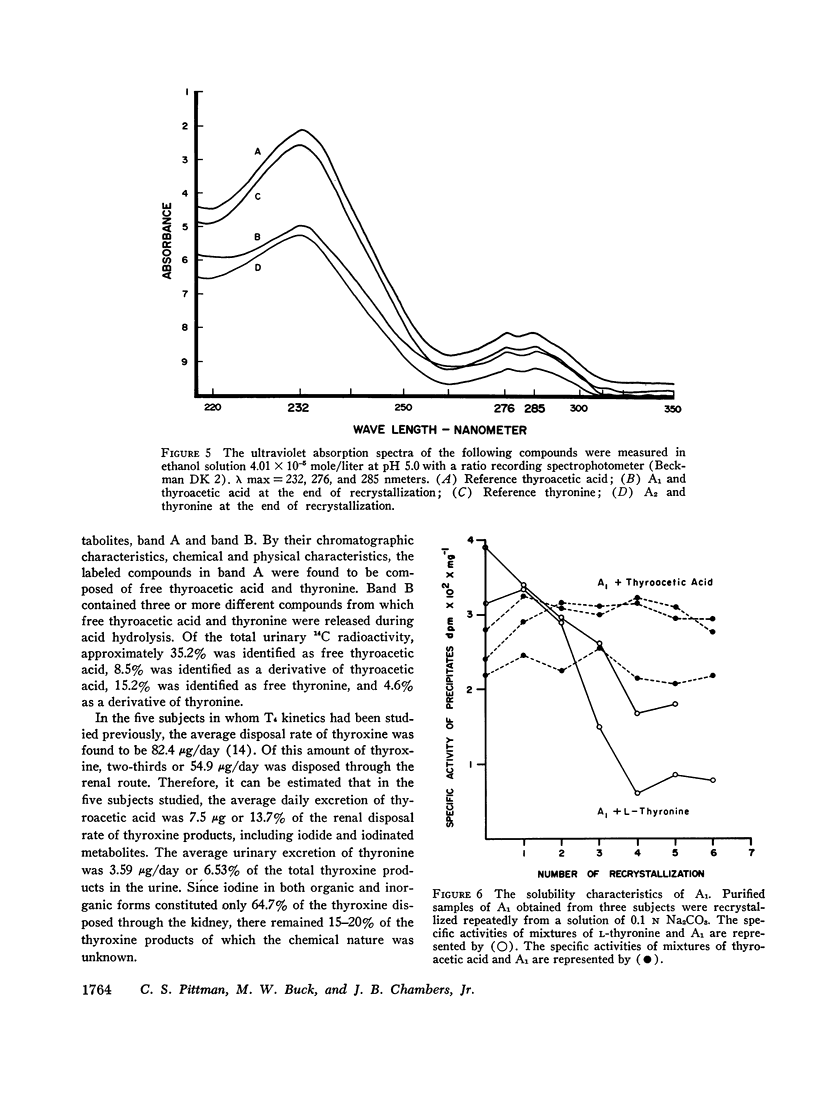
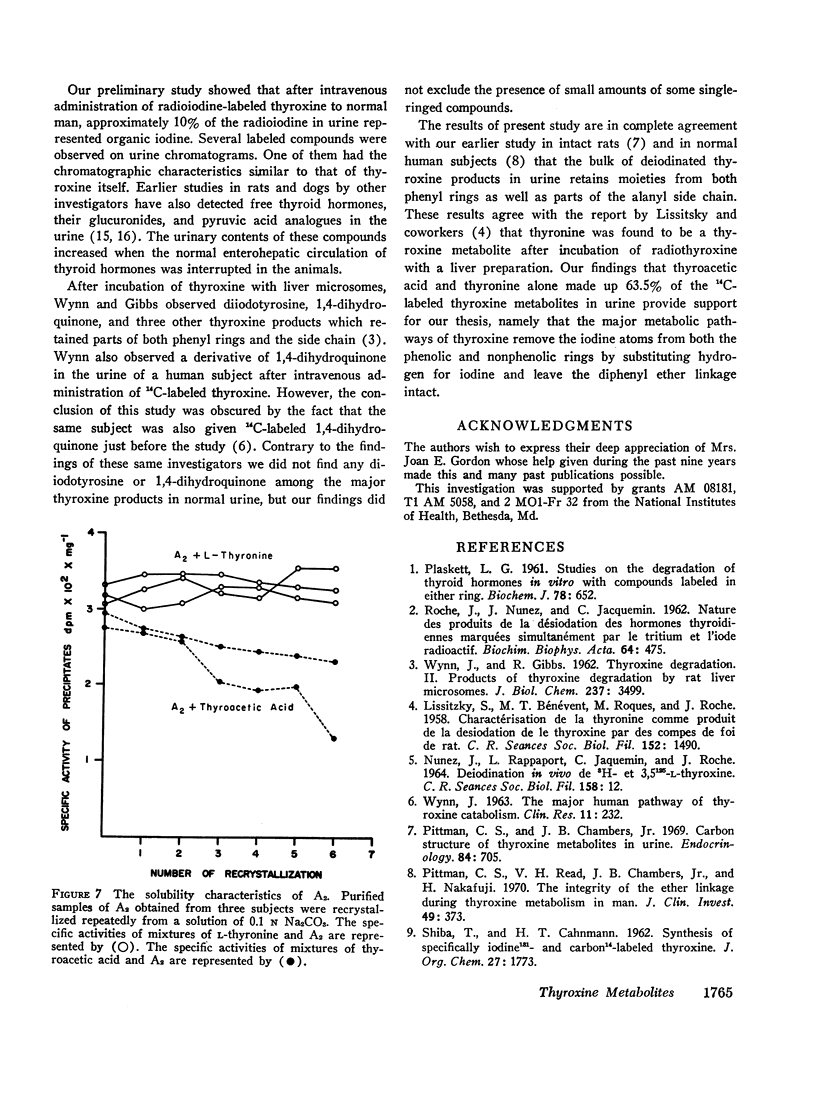
Studies were carried out to determine the chemical structures of thyroxine metabolites after total deiodination. Normal subjects were given thyroxine labeled with 14C on the nonphenolic ring and the alanine side chain, 8-11 μg/day for 10 days. By paper chromatography of fresh urine, six or more 14C-labeled compounds were separated. The 14C-labeled metabolites were concentrated by passing the urine through a nonionic polymeric adsorbent. Two major thyroxine metabolites were identified. The identification was made by three different methods: (a) chromatography, (b) synthesis of derivatives, and (c) recrystallization to constant specific activity. One 14C-labeled metabolite was identified as thyroacetic acid or 4-phenoxy-(4′-hydroxy) phenyl-acetic acid. Another one was identified as thyronine. Of the total urinary 14C radioactivity, 43.7% was recovered as thyroacetic acid and 19.8% was recovered as thyronine. Approximately one-fifth of each of these metabolites was present in the urine in bound form which released the free metabolites during acid hydrolysis. The average daily excretion of thyroacetic acid was 13.7% of the renal disposal rate of thyroxine, or approximately 7.5 μg/day. The average daily excretion of thyronine was 6.5% of the renal disposal rate of thyroxine or approximately 3.9 μg/day while the urinary iodide made up 64.7% of the renal disposal rate of thyroxine. Our findings provide the needed proof that the major metabolic pathways of thyroxine remove the iodine atoms by substituting hydrogen for iodine and leave the diphenyl ether nucleus intact.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FLOCK E. V., BOLLMAN J. L., GRINDLAY J. H., McKENZIE B. F. Metabolites of radioactive L-thyroxine and L-triiodothyronine. Endocrinology. 1957 Oct;61(4):461–473. doi: 10.1210/endo-61-4-461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LISSITZKY S., BENEVENT M. T., ROQUES M., ROCHE J. Caractérisation de la thyronine comme produit de la désiodation de la thyroxine par des coupes de foie de rat. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1958;152(11):1490–1491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NUNEZ J., RAPPAPORT L., JACQUEMIN C., ROCHE J. D'ESIODATION IN VIVO DE H-3- ET 3,5-I-125-THYROXINE. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1964;158:12–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLASKETT L. G. Studies on the degradation of thyroid hormones in vitro with compounds labelled in either ring. Biochem J. 1961 Mar;78:652–657. doi: 10.1042/bj0780652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman C. S., Chambers J. B., Jr, Read V. H. The extrathyroidal conversion rate of thyroxine to triiodothyronine in normal man. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1187–1196. doi: 10.1172/JCI106596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman C. S., Chambers J. B., Jr The carbon structure of thyroxine metabolites in urine. Endocrinology. 1969 Apr;84(4):705–710. doi: 10.1210/endo-84-4-705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman C. S., Shimizu C. Metabolism of 131-I- and 14-C-labeled thyroxines. Endocrinology. 1966 Dec;79(6):1109–1116. doi: 10.1210/endo-79-6-1109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROCHE J., MICHEL R., TATA J. Sur la nature des combinaisons iodées excrétées par le foie et le rein après administration de L-thyroxine et de L-3:5:3'-triiodothyronine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1954 Dec;15(4):500–507. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(54)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROCHE J., NUNEZ J., JACQUEMIN C. [Nature of the deiodination products of thyroid hormones labelled simultaneously with tritium and radioactive iodiine]. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Nov 5;64:475–486. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90305-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEST C. D., SIMONS E. L., GORTATOWSKI M. J., KUMAGAI L. F. The metabolism of ring-labeled L-thyroxine-C14 in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1963 Jul;42:1134–1141. doi: 10.1172/JCI104798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WYNN J., GIBBS R. Thyroxine degradation. II. Products of thyroxine degradation by rat liver microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1962 Nov;237:3499–3505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


