Abstract
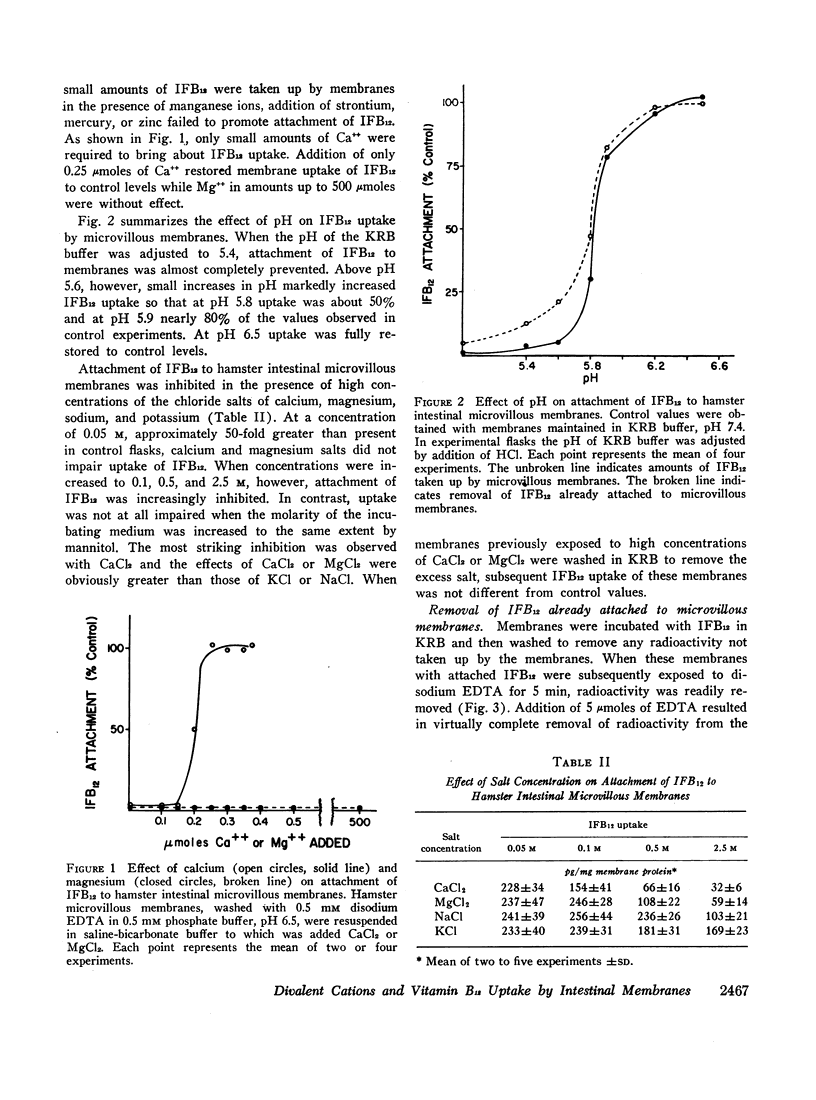
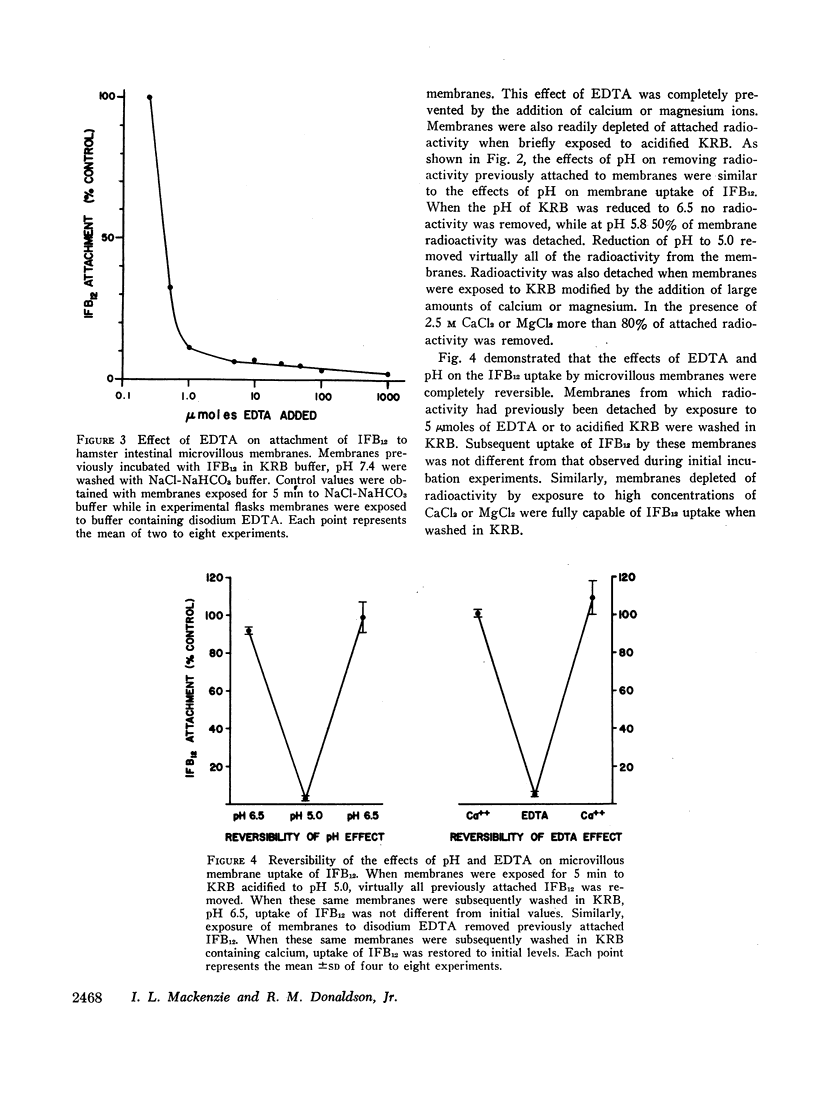
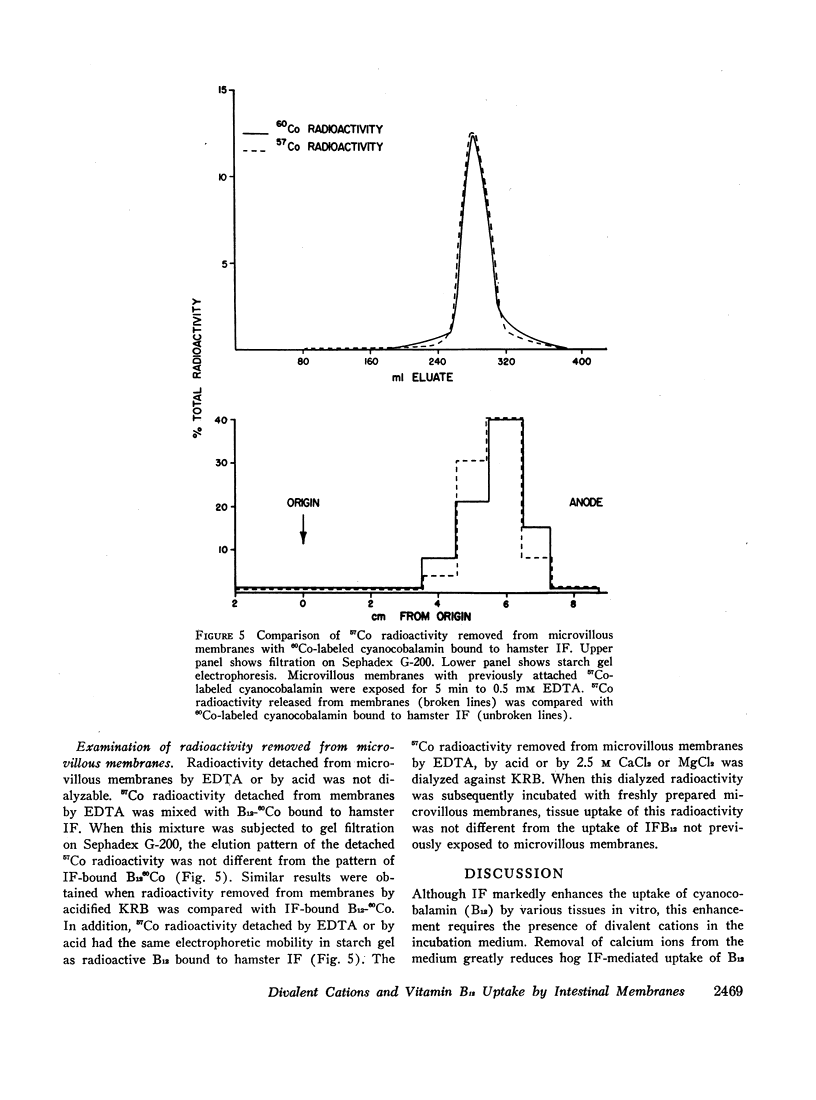
Calcium, but not other divalent cations, is required for optimal uptake of intrinsic factor-bound 57Co-labeled cyanocobalamin (IFB12) by microvillous membranes isolated from hamster ileal-absorptive cells. Chelation of divalent cations by disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetate (EDTA) promptly removes IFB12 previously attached to microvillous membranes. High concentrations of CaCl2 or MgCl2 also markedly inhibit membrane uptake of IFB12 and rapidly remove previously attached IFB12. Similarly, reduction of pH to below 5.4 prevents membrane attachment of IFB12 and removes virtually all IFB12 already bound to microvillous membranes. The effects of calcium depletion, increased salt concentrations, and acidification on membrane uptake of IFB12 were completely reversible. These findings are consistent with the concept that the formation of calcium salt bridges is essential for attachment of IFB12 to the ileal-absorptive surface.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CASTLE W. B., NIEWEG H. O., SHEN S. C. Mechanism of intrinsic factor action in the gastrectomized rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Jan;94(1):223–230. doi: 10.3181/00379727-94-22907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER B. A., CASTLE W. B. Sequential mechanisms in the enhanced absorption of vitamin B12 by intrinsic factor in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jan;39:199–214. doi: 10.1172/JCI104019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER B. A., PARANCHYCH W., LOWENSTEIN L. Studies on the absorption by guinea pig intestine of cyanocobalamin incubated with intrinsic factor. J Clin Invest. 1962 Feb;41:370–377. doi: 10.1172/JCI104491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER B. A. THE UPTAKE OF CO57-LABELED VITAMIN B12 BY EVERTED SACS OF INTESTINE IN VITRO. Medicine (Baltimore) 1964 Nov;43:689–696. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196411000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson R. M., Jr, Mackenzie I. L., Trier J. S. Intrinsic factor-mediated attachment of vitamin B12 to brush borders and microvillous membranes of hamster intestine. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jul;46(7):1215–1228. doi: 10.1172/JCI105615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRASBECK R., NYBERG W. Inhibition of radiovitamin B12 absorption by ethylenediaminetetraacetate (EDTA) and its reversal by calcium ions. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1958;10(4):448–448. doi: 10.3109/00365515809051257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERBERT V., CASTLE W. B. Divalent cation and pH dependence of rat intrinsic factor action in everted sacs and mucosal homogenates of rat small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1961 Nov;40:1978–1983. doi: 10.1172/JCI104423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERBERT V. Studies of the mechanism of the effect of hog intrinsic factor concentrate on the uptake of vitamin B12 by rat liver slices. J Clin Invest. 1958 May;37(5):646–650. doi: 10.1172/JCI103648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERBERT V. Studies on the role of intrinsic factor in vitamin B12 absorption, transport, and storage. Am J Clin Nutr. 1959 Jul-Aug;7:433–443. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/7.4.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie I. L., Donaldson R. M., Jr, Schilling R. F. Radioiodination of human intrinsic factor. J Clin Invest. 1969 Mar;48(3):516–524. doi: 10.1172/JCI106009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda K., Sasayama K. Effects of ethylenediaminetetraacetate and metal ions in intestinal absorption of vitamin B 12 in man and rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Oct;120(1):17–20. doi: 10.3181/00379727-120-30431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITHIES O. Zone electrophoresis in starch gels: group variations in the serum proteins of normal human adults. Biochem J. 1955 Dec;61(4):629–641. doi: 10.1042/bj0610629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SULLIVAN L. W., HERBERT V., CASTLE W. B. IN VITRO ASSAY FOR HUMAN INTRINSIC FACTOR. J Clin Invest. 1963 Sep;42:1443–1458. doi: 10.1172/JCI104829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUMMERSKILL W. H. Malabsorption and jejunal ulceration due to gastric hypersecretion with pancreatic islet-cell hyperplasia. Lancet. 1959 Jan 17;1(7064):120–123. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)90003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimoda S. S., Saunders D. R., Rubin C. E. The Zollinger-Ellison syndrome with steatorrhea. II. The mechanism of fat and vitamin B 12 malabsorption. Gastroenterology. 1968 Dec;55(6):705–723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOWNLEY R. R., CASS M. H., ANDERSON C. M. SMALL INTESTINAL MUCOSAL PATTERNS OF COELIAC DISEASE AND IDIOPATHIC STEATORRHOEA SEEN IN OTHER SITUATIONS. Gut. 1964 Feb;5:51–55. doi: 10.1136/gut.5.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VEEGER W., ABELS J., HELLEMANS N., NIEWEG H. O. Effect of sodium bicarbonate and pancreatin on the absorption of vitamin B12 and fat in pancreatic insufficiency. N Engl J Med. 1962 Dec 27;267:1341–1344. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196212272672604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisberg H., Rhodin J. Relation of calcium to mucosal structure and vitamin B12 absorption in the canine intestine. Am J Pathol. 1970 Nov;61(2):141–160. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


