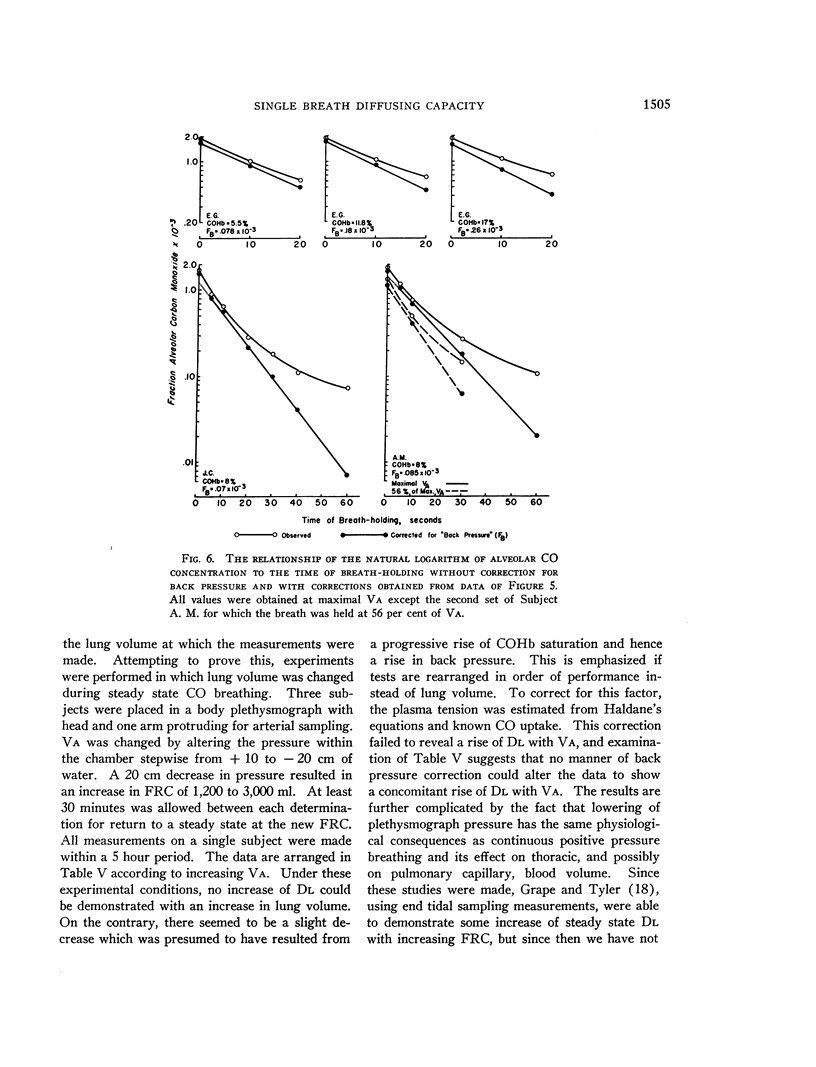
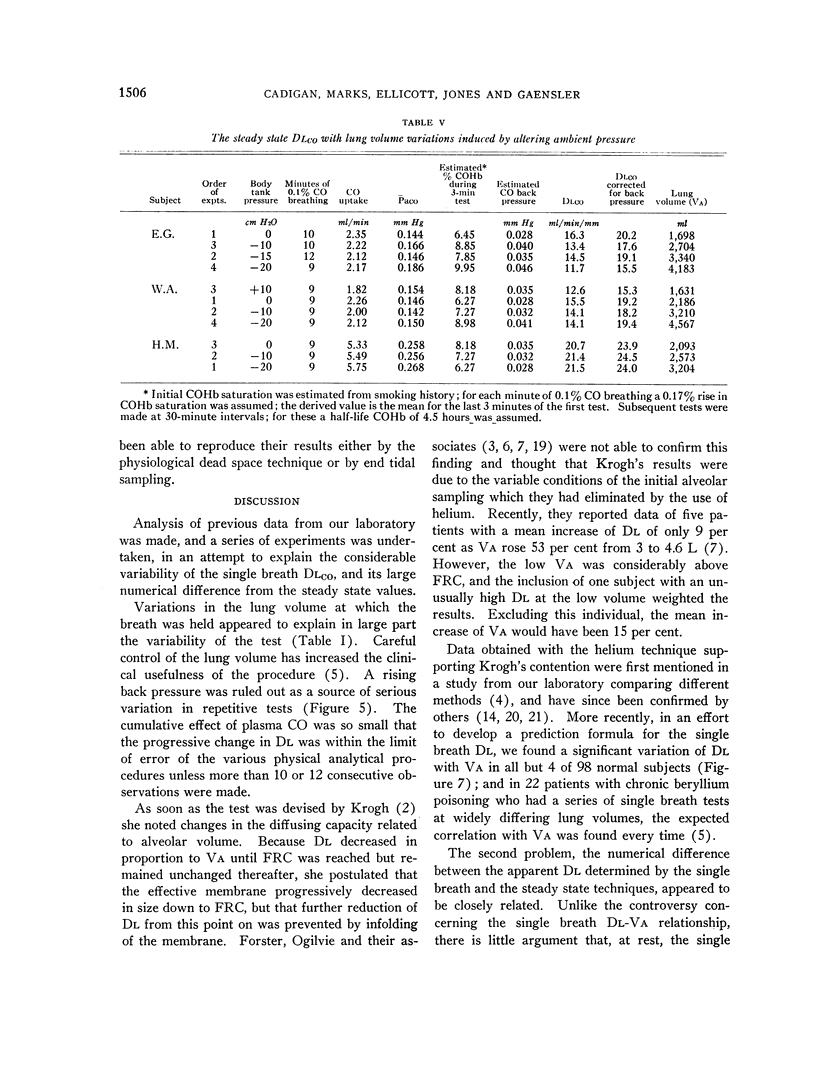
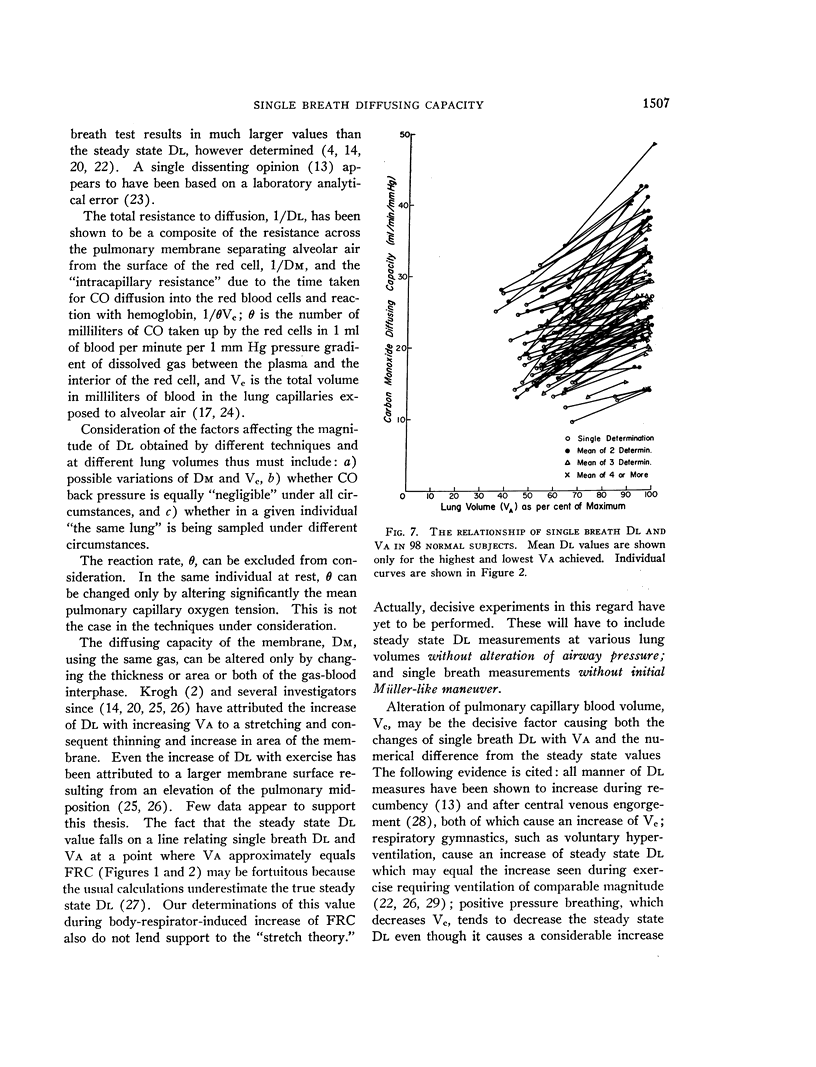
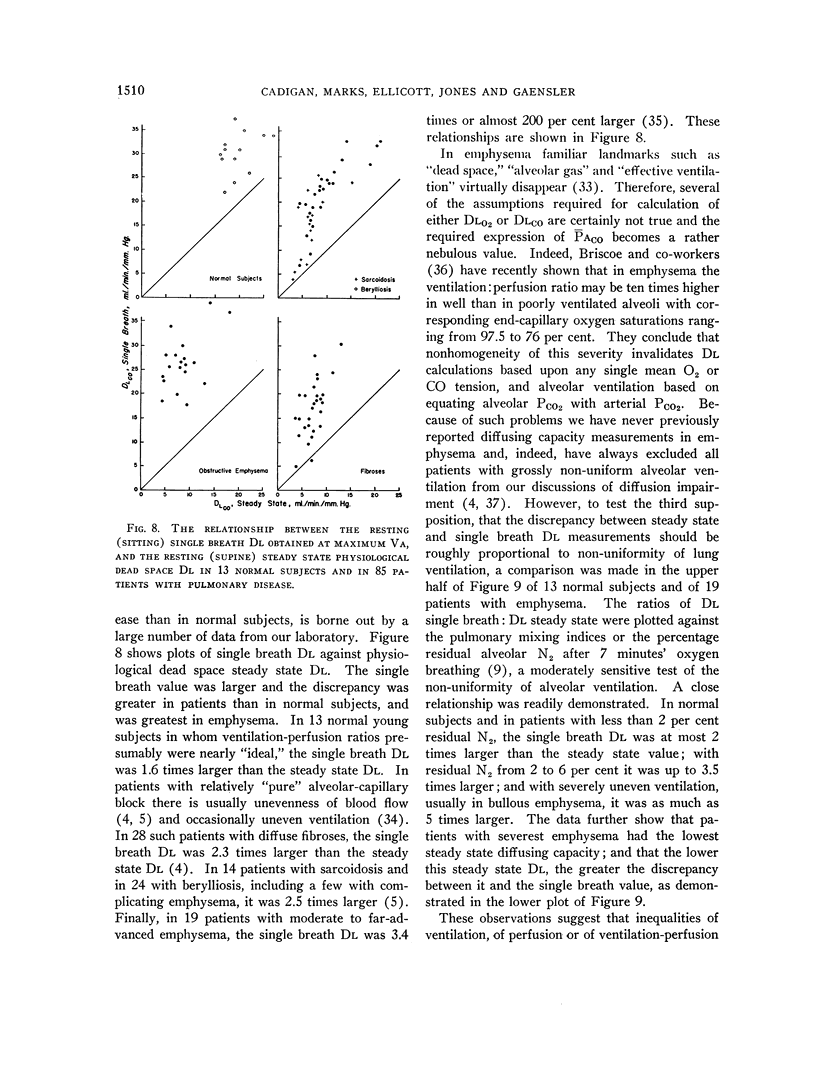
Full text
PDF

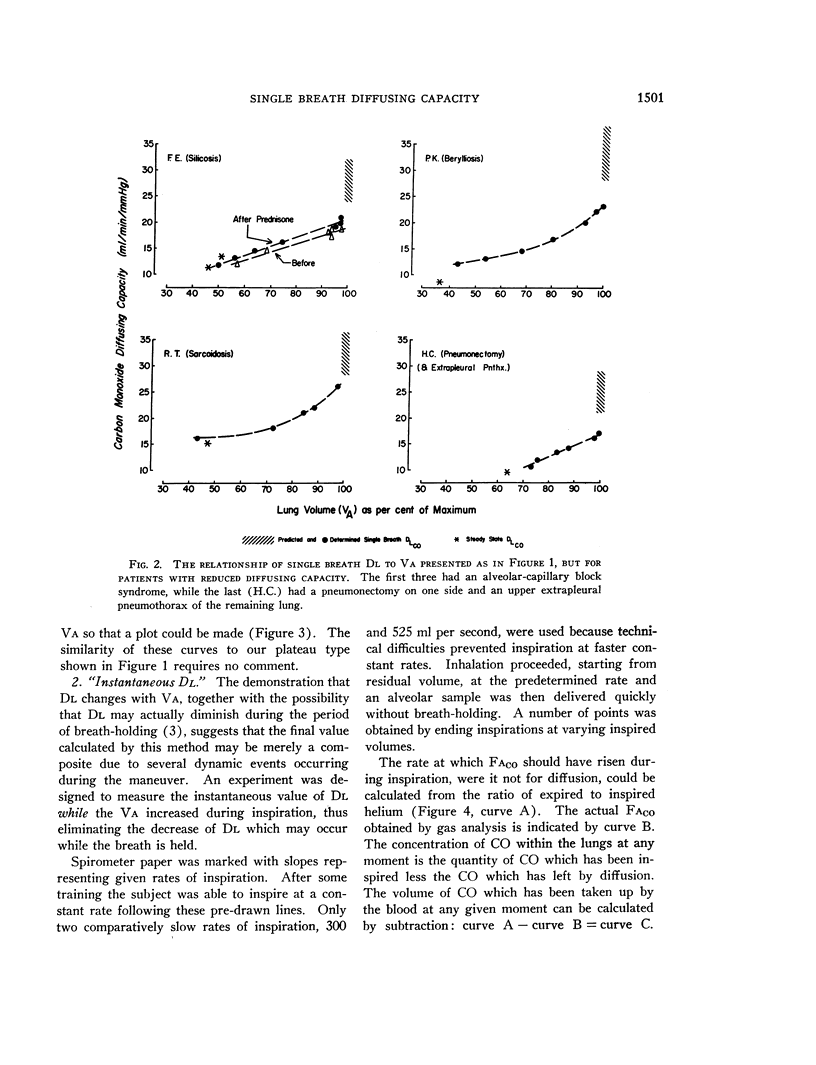
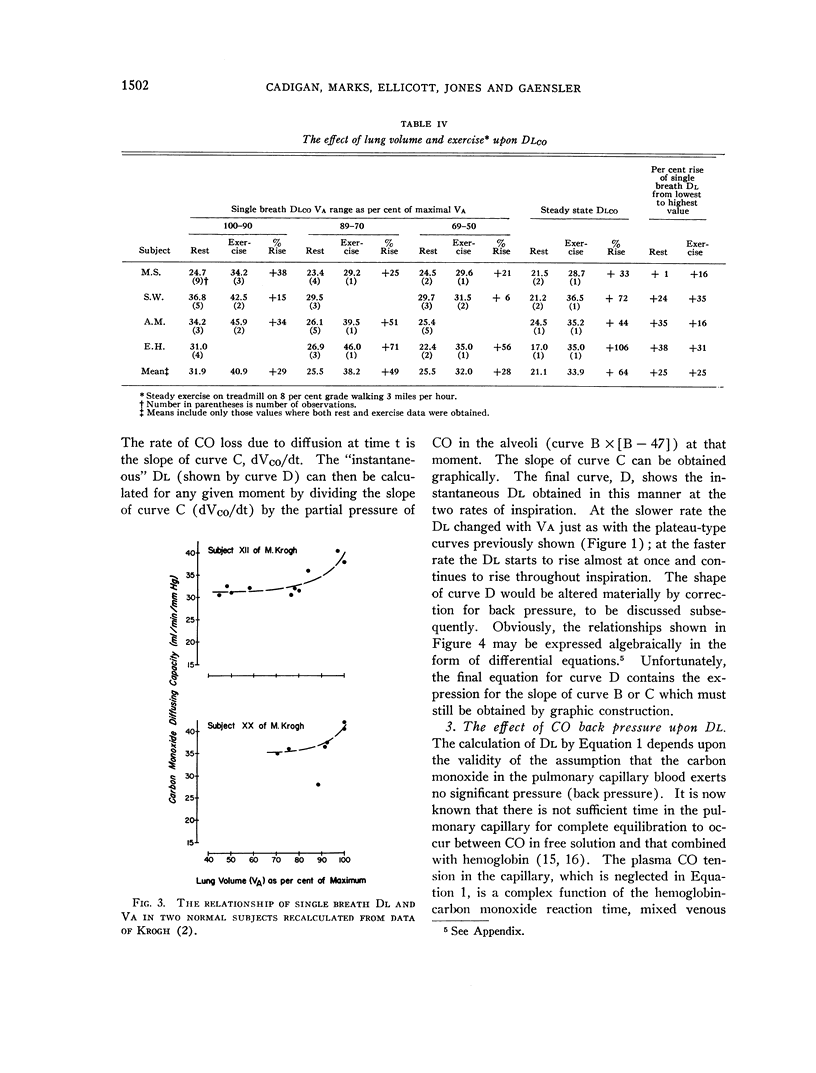
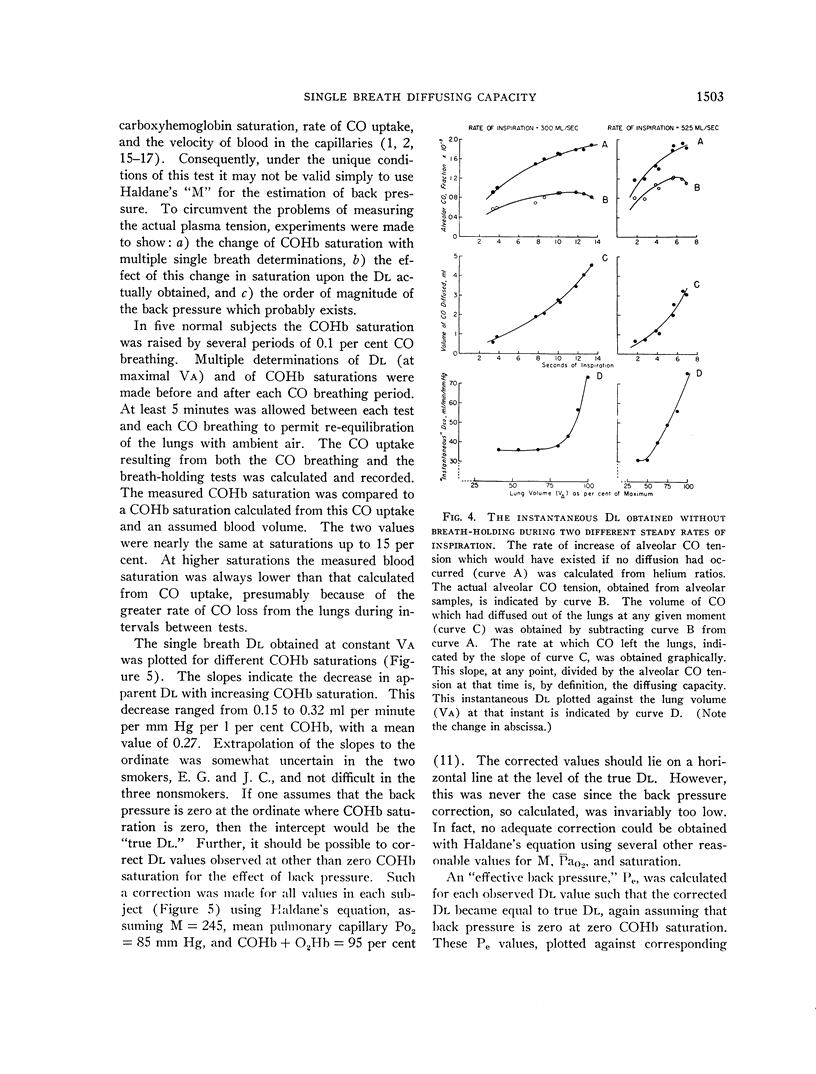
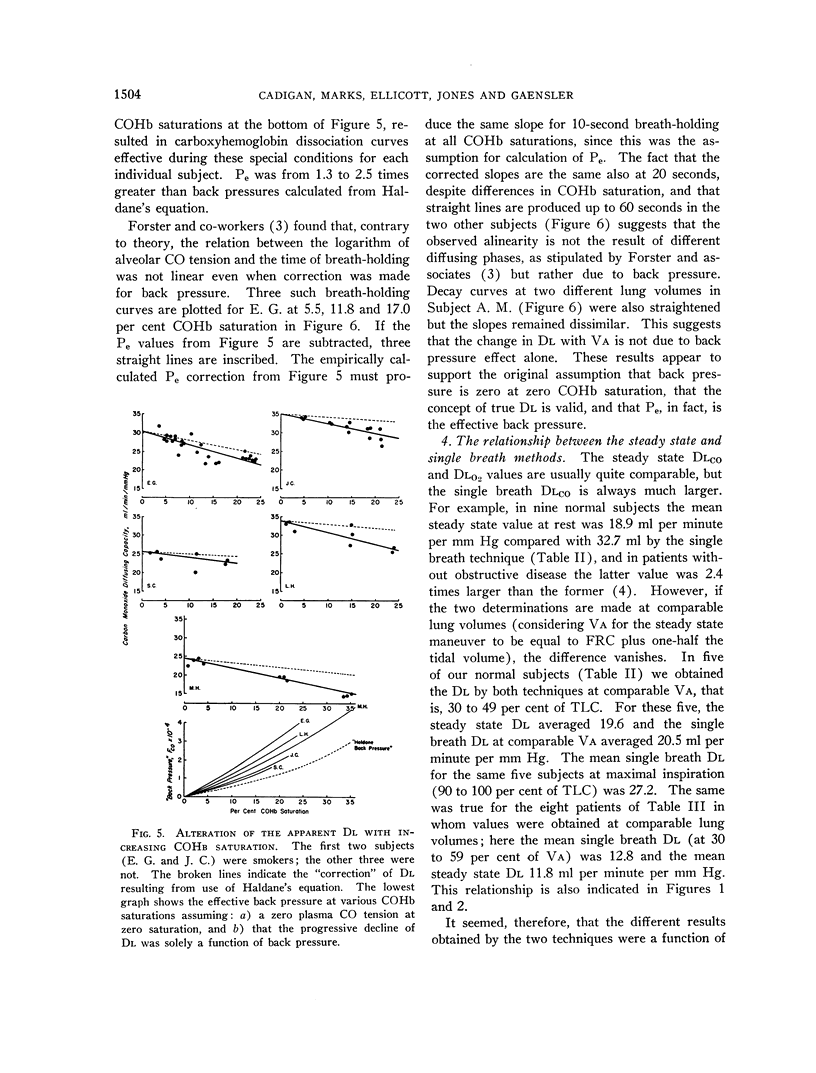





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BADGER T. L., CUGELL D. W., ELLICOTT M. F., GAENSLER E. A., MARKS A. Carbon monoxide diffusing capacity during steady exercise. Am Rev Tuberc. 1956 Sep;74(3):317–342. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1956.74.3.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BATES D. V., PEARCE J. F. The pulmonary diffusing capacity; a comparison of methods of measurement and a study of the effect of body position. J Physiol. 1956 Apr 27;132(1):232–238. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLAKEMORE W. S., FORSTER R. E., MORTON J. W., OGILVIE C. M. A standardized breath holding technique for the clinical measurement of the diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide. J Clin Invest. 1957 Jan;36(1 Pt 1):1–17. doi: 10.1172/JCI103402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CADIGAN J. B., CUGELL D. W., GAENSLER E. A., MARKS A. Clinical determination of the diffusion capacity of the lungs; comparison of methods in normal subjects and patients with alveolar-capillary block syndrome. Am J Med. 1957 Jan;22(1):51–73. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(57)90337-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COTES J. E., SNIDAL D. P., SHEPARD R. H. Effect of negative intra-alveolar pressure on pulmonary diffusing capacity. J Appl Physiol. 1960 May;15:372–376. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1960.15.3.372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darling R. C., Cournand A., Richards D. W. STUDIES ON THE INTRAPULMONARY MIXTURE OF GASES. III. AN OPEN CIRCUIT METHOD FOR MEASURING RESIDUAL AIR. J Clin Invest. 1940 Jul;19(4):609–618. doi: 10.1172/JCI101163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FILLEY G. F., MACINTOSH D. J., WRIGHT G. W. Carbon monoxide uptake and pulmonary diffusing capacity in normal subjects at rest and during exercise. J Clin Invest. 1954 Apr;33(4):530–539. doi: 10.1172/JCI102923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORSTER R. E. Exchange of gases between alveolar air and pulmonary capillary blood: pulmonary diffusing capacity. Physiol Rev. 1957 Oct;37(4):391–452. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1957.37.4.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORSTER R. E., FOWLER W. S., BATES D. V. Considerations on the uptake of carbon monoxide by the lungs. J Clin Invest. 1954 Aug;33(8):1128–1134. doi: 10.1172/JCI102986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORSTER R. E., FOWLER W. S., BATES D. V., VAN LINGEN B. The absorption of carbon monoxide by the lungs during breath-holding. J Clin Invest. 1954 Aug;33(8):1135–1145. doi: 10.1172/JCI102987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAENSLER E. A., CADIGAN J. B., Jr, ELLICOTT M. F., JONES R. H., MARKS A. A new method for rapid precise determination of carbon monoxide in blood. J Lab Clin Med. 1957 Jun;49(6):945–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAENSLER E. A., CUGELL D. W. Bronchospirometry differential residual volume determination. J Lab Clin Med. 1952 Oct;40(4):558–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAENSLER E. A., VERSTRAETEN J. M., WEIL W. B., CUGELL D. W., MARKS A., CADIGAN J. B., Jr, JONES R. H., ELLICOTT M. F. Respiratory pathophysiology in chronic beryllium disease; review of thirty cases with some observations after long-term steroid therapy. AMA Arch Ind Health. 1959 Feb;19(2):132–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON R. L., Jr, SPICER W. S., BISHOP J. M., FORSTER R. E. Pulmonary capillary blood volume, flow and diffusing capacity during exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1960 Sep;15:893–902. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1960.15.5.893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES R. H., ELLICOTT M. F., CADIGAN J. B., GAENSLER E. A. The relationship between alveolar and blood carbon monoxide concentrations during breathholding; simple estimation of COHb saturation. J Lab Clin Med. 1958 Apr;51(4):553–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRUHØFFER P. Studies on the lung diffusion coefficient for carbon monoxide in normal human subjects by means of C14O. Acta Physiol Scand. 1954 Nov;32(2-3):106–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1954.tb01160.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogh M. The diffusion of gases through the lungs of man. J Physiol. 1915 May 12;49(4):271–300. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1915.sp001710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDERHOLM H. On the significance of CO tension in pulmonary capillary blood for determination of pulmonary diffusing capacity with the steady state CO method. Acta Med Scand. 1957 Feb 2;156(6):413–427. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1957.tb00098.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACNAMARA J., PRIME F. J., SINCLAIR J. D. An assessment of the steady-state carbon monoxide method of estimating pulmonary diffusing capacity. Thorax. 1959 Jun;14:166–175. doi: 10.1136/thx.14.2.166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSHALL R. A comparison of methods of measuring the diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide; investigation by fractional analysis of the alveolar air. J Clin Invest. 1958 Mar;37(3):394–408. doi: 10.1172/JCI103619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEAD J., LINDGREN I., GAENSLER E. A. The mechanical properties of the lungs in emphysema. J Clin Invest. 1955 Jul;34(7 Pt 1):1005–1016. doi: 10.1172/JCI103150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- READ J., WILLIAMS R. S. Pulmonary ventilation; blood flow relationships in intersititial disease of the lungs. Am J Med. 1959 Oct;27:545–550. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(59)90039-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENBERG E., FORSTER R. E. Changes in diffusing capacity of isolated cat lungs with blood pressure and flow. J Appl Physiol. 1960 Sep;15:883–892. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1960.15.5.883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSS J. C., FRAYSER R., HICKAM J. B. A study of the mechanism by which exercise increases the pulmonary diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide. J Clin Invest. 1959 Jun;38(6):916–932. doi: 10.1172/JCI103874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSS J. C., LORD T. H., LEY G. D. Effect of pressure-suit inflation on pulmonary-diffusing capacity. J Appl Physiol. 1960 Sep;15:843–848. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1960.15.5.843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROUGHTON F. J., FORSTER R. E. Relative importance of diffusion and chemical reaction rates in determining rate of exchange of gases in the human lung, with special reference to true diffusing capacity of pulmonary membrane and volume of blood in the lung capillaries. J Appl Physiol. 1957 Sep;11(2):290–302. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1957.11.2.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEPHARD R. J. Breath-holding measurement of carbon monoxide diffusing capacity; comparison of a field test with steady-state and other methods of measurement. J Physiol. 1958 May 28;141(3):408–419. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURINO G. M., BRANDFONBRENER M., FISHMAN A. P. The effect of changes in ventilation and pulmonary blood flow on the diffusing capacity of the lung. J Clin Invest. 1959 Jul;38(7):1186–1201. doi: 10.1172/JCI103894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


