Abstract
Direct targeting of critical DNA-binding elements of a repressor by its cognate antirepressor is an effective means to sequester the repressor and remove a transcription initiation block. Structural descriptions for this, though often proposed for bacterial and phage repressor–antirepressor systems, are unavailable. Here, we describe the structural and functional basis of how the Myxococcus xanthus CarS antirepressor recognizes and neutralizes its cognate repressors to turn on a photo-inducible promoter. CarA and CarH repress the carB operon in the dark. CarS, produced in the light, physically interacts with the MerR-type winged-helix DNA-binding domain of these repressors leading to activation of carB. The NMR structure of CarS1, a functional CarS variant, reveals a five-stranded, antiparallel β-sheet fold resembling SH3 domains, protein–protein interaction modules prevalent in eukaryotes but rare in prokaryotes. NMR studies and analysis of site-directed mutants in vivo and in vitro unveil a solvent-exposed hydrophobic pocket lined by acidic residues in CarS, where the CarA DNA recognition helix docks with high affinity in an atypical ligand-recognition mode for SH3 domains. Our findings uncover an unprecedented use of the SH3 domain-like fold for protein–protein recognition whereby an antirepressor mimics operator DNA in sequestering the repressor DNA recognition helix to activate transcription.
INTRODUCTION
A classical mechanism for negative regulation of transcription initiation is to sterically block promoter access to RNA polymerase by a repressor bound at an operator site that overlaps with promoter elements (1–3). This transcription block is removed under appropriate conditions by disrupting the operator–repressor complex in a variety of ways, such as by the repressor binding to small molecule inducers or to other protein factors—the antirepressors (4). Non-covalent union to an antirepressor can inactivate a repressor by altering its conformation, oligomeric state, susceptibility to proteolysis or aggregation, or intracellular localization (5–9); or it may occlude DNA-binding elements of the repressor (10). Structural descriptions are available for how an antirepressor binds to a repressor and alters the latter’s conformation, oligomeric state or proteolytic susceptibility to thwart operator-binding (5,6,9). By contrast, structural details for the direct interaction of an antirepressor with a specific, crucial DNA-binding repressor element have, to our knowledge, not been reported, even though this mechanism of action has been proposed for many bacterial and phage antirepressors. Here, we describe the structural and functional basis of how the CarS antirepressor of the bacterium Myxococcus xanthus recognizes and neutralizes cognate repressors to turn on a photo-inducible promoter.
Blue light induces carotenogenesis in M. xanthus, where all but one of the structural genes involved are encoded by the light-inducible carB operon (11). carB expression is driven by promoter PB, and its photo-induction is regulated by the CarA–CarS repressor–antirepressor pair (12,13). In the dark, RNA polymerase access to PB is blocked by CarA binding cooperatively to a bipartite operator, of which one part overlaps with the −35 promoter region (14). Blue light causes expression of the carQRS operon to produce CarS (11). Physical interaction of CarS with CarA then dismantles the CarA–operator complex to derepress PB. A parallel pathway for regulation of PB also exists. It involves CarS and the CarH repressor, which shares the two-domain architecture of CarA. Both repressors have an N-terminal, MerR-type, winged-helix DNA-binding domain that recognizes the same operator as well as CarS, linked to a C-terminal dimerization domain with a vitamin B12-binding motif (10,15). However, only CarH requires B12 for repressor activity (15).
The DNA recognition helix of CarA is crucial in mediating interactions with both operator DNA and CarS (10). Does CarS then have structural features that resemble operator DNA? In this study, we demonstrate that CarS adopts a fold characteristic of an SH3 (Src homology 3) domain and that the CarA DNA recognition helix is, by itself, sufficient for high-affinity binding to CarS. SH3 domains are protein–protein interaction modules frequently encountered in proteins acting in signal transduction, endocytic and cytoskeletal machineries in eukaryotes, but which are much less common in prokaryotes (16–18). The molecular details of how CarS recognizes CarA differ, however, from those of typical SH3 domains. Our structural and functional analyses reveal an apolar solvent-exposed pocket in CarS, bordered by negatively charged residues, where the CarA recognition helix can dock and, thereby, be occluded from operator-binding. Thus, this work provides structural–functional insights into an elegant molecular mechanism to turn on transcription, in which a bacterial antirepressor with an SH3 domain fold mimics operator DNA to sequester a repressor.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains, plasmids and growth conditions
Supplementary Table S1 lists the M. xanthus strains and plasmids used in this study. Myxococcus xanthus was grown in casitone–Tris (CTT) rich medium with or without blue light exposure (10). Escherichia coli strain DH5α, used in plasmid constructions, and BL21(DE3), employed for protein overexpression, were grown in Luria broth or a modified M9 minimal medium containing 15NH4Cl with and without 13C-glucose to express 15N, 13C-labeled and 15N-labeled H6CarS1, respectively.
Site-directed mutagenesis
Specific mutations to Ala in CarS were generated by PCR using the required construct containing wild-type carS as template and two complementary primers bearing the given mutation either by the overlap extension method (19), or the Quikchange mutagenesis kit (Stratagene). The presence of the desired mutation was confirmed by DNA sequencing.
Proteins and peptides
H6-tagged CarS, CarS1, CarANt and CarHNt were overexpressed from constructs in pET15b, purified and the H6-tag removed by thrombin cleavage as described elsewhere (10,15). CarS variants, generated as described above, were overexpressed using pET15b and purified as described for CarS. 15N-labeled and 15N, 13C-labeled H6CarS1 were overexpressed and purified as reported previously (20). Synthetic N-acetylated, C-amidated peptides were purchased from Caslo Laboratory, Denmark. Protein and peptide concentrations were determined using the BioRad protein assay kit or the absorbance at 280 nm. ε280 (in M−1cm−1). Extinction coefficients at 280 nm used were (10,15): 9540 (CarANt); 6990 (CarS and variants); 1490 (CarS1); 11 460 (CarHNt); 6990 (P01, P02, CHP01, TtP01); 5500 (P03).
NMR
NMR data were acquired in Bruker DMX600 and AV-800 US2 spectrometers equipped with a z-shielded gradient triple resonance cryoprobe. 1H, 15N and 13C NMR chemical shifts of CarS1 assigned using standard triple resonance methods have been deposited in BioMagResBank (ref. no. 15770; http://www.bmrb.wisc.edu/; 20). Structures were calculated with the program CYANA version 1.0 (21) using distance constraints from NOE data (from 15N-edited and simultaneous 15N and 13C-edited NOESY HSQC data for τm = 80 ms), and torsion angle constraints determined using TALOS (22). The best structures from CYANA were refined with the SANDER module of the AMBER 7.0 package (23), and analyzed using PROCHECK (24), VADAR (25) and MOLMOL (26). Surface potential calculations with MOLMOL used an ionic strength of 150 mM and default values for the dielectric constants of solute and solvent. Amide 1H exchange data were obtained at 25°C by adding 100% D2O to 1H-15N H6CarS1 lyophilized in 100 mM NaCl, 50 mM phosphate buffer (pH 6.6), and recording 1H-15N HSQC spectra consecutively every 45 min. Peak intensities were fit to a single exponential decay to determine the exchange rate constants, and thereby protein stability parameters (27). Heteronuclear 1H-15N NOEs were determined using 15N-labeled H6CarS1 at 25°C, pH 6.6, with 1H saturation (3s pulse applied just prior to the first heteronuclear pulse) during the preparation time with or without NOE. The pulse sequence began with direct 15N excitation and subsequent magnetization transfer using INEPT (28) to the corresponding 1H, with long waiting times between each pulse cycle for complete relaxation. Heteronuclear 1H-15N NOEs were measured from the ratio of cross-peak intensities (using SPARKY 3; Goddard, T.D., and Kneller, D.G., San Francisco, University of California) with and without 1H saturation. NMR chemical shift mapping was carried out at 25°C or 45°C by titrating 15N, 13C-H6CarS1 at 0.10–0.25 mM with 0.25, 0.50, 0.75, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0 and 4.0 equivalents of unlabeled CarANt or peptides P01 or P02, and recording 1H-15N and 1H-13C HSQC spectra after each addition. Chemical shift perturbations (Δδ were calculated from the shifts in the backbone amide 1H (δH) and 15N (δN) signals using 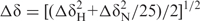 (29).
(29).
Yeast two-hybrid analysis
We have previously described the constructs pEG202-carA to express N-terminal fusions of CarA to the LexA DNA-binding domain, and pJG4-5-carS for CarS fusions to the B42 transcriptional activation domain (12). Each carS variant, carS* (generated as described above) was also cloned into pJG4-5 (Supplementary Table S1). The recipient EGY48 yeast strain bearing the reporter plasmid pSH18-34 was transformed by the lithium acetate method with pEG202-carA and carS or carS* in pJG4-5. Ten microliters from cultures of equal cell densities were spotted on galactose (Gal) or glucose (Glu) plates supplemented with leucine, incubated for 1 day at 30°C, then overlaid with X-Gal (5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-beta-D-galacto pyranoside) agarose and incubated for a further 2–3 h (Gal) or ≥7 h (Glu). CarA–CarS interaction was assessed from the blue color that developed on plates.
Myxococcus xanthus strain construction and western blot analysis
Plasmid pMR3184 (Supplementary Table S1) contains an in-frame deletion of essentially all of the carS coding sequence (327 out of 336 bp). The deleted allele consists of the first 4 bp of carS (as they include the TGA stop codon of carR) separated from its last 5 bp by an EcoRI site. When expressed and translated in M. xanthus, this deleted allele would render a four-residue peptide with the sequence MRIQ. To construct pMR3184, regions flanking the carS region to be deleted were first PCR-amplified from genomic DNA: (i) an upstream DNA fragment of ∼1.2 kb with a 5′ KpnI site and a 3′ EcoRI site; (ii) a downstream DNA fragment of ∼1 kb with a 5′ EcoRI site and a 3′ PstI site. The two fragments were ligated at the EcoRI site and then introduced into the KpnI–PstI sites of plasmid pMAR975. pMR3184, which also bears a kanamycin (Km) resistance marker for positive selection and a Gal sensitivity gene for negative selection, was then electroporated into the wild-type DK1050 M. xanthus strain, where plasmid integration into the chromosome by homologous recombination yields KmR merodiploids containing the wild-type as well as the deleted carS (ΔcarS) allele. To obtain a haploid strain bearing the ΔcarS allele alone, a merodiploid was grown for several generations in the absence of Km, and then plated on CTT plates with 10 mg/ml Gal to select for the loss of the vector GalS marker together with one of the carS alleles by intramolecular recombination events. Haploid colonies with the ΔcarS allele, easily identified by their inability to turn red from yellow in blue light (Car− phenotype), were verified for the presence of the deletion by PCR analysis of the corresponding chromosomal DNA region.
To introduce a mutant carS allele into M. xanthus, a PCR-amplified fragment corresponding to the carS coding sequence (without the initiator codon) bearing the specific mutation (carS*) was ligated into the EcoRI site of pMR3184. As a result of the construction, the CarS* protein expressed once introduced into M. xanthus would have, besides the mutation, an additional three-residue, N-terminal sequence (R-I-L) separating the initiator M from the I that is the second residue in native CarS. A plasmid with wild-type carS (without the initiator codon) introduced at the EcoRI site of pMR3184 was also generated for use as a positive control. The resulting constructs (Supplementary Table S1) were independently electroporated into the M. xanthus ΔcarS strain MR1776 and plasmid integration into the chromosome by homologous recombination was selected for on CTT/Km plates. KmR colonies would be Car+ (yellow in the dark, red in the light) or Car− (yellow in the dark and in the light, like the ΔcarS strain) depending on whether the incoming carS allele retains or lacks CarS activity. To assay the color phenotypes, 8-µl cell droplets of exponentially growing cultures (OD550 = 0.8) were spotted on CTT plates and grown for 2 days in the dark or in the light. The absence of CarS in the ΔcarS strain (MR1776) and the stable in vivo expression of each CarS variant in the respective M. xanthus strain were confirmed by western blot analysis of the corresponding whole cell extracts (obtained after cell growth in the light) with mouse monoclonal anti-CarS antibodies. The total protein concentrations of the extracts were estimated and equivalent amounts of protein were loaded for analysis. Antibody production and immunoblot analysis of whole cell extracts were carried out as described previously (30).
CD spectroscopy
Far-UV CD spectra were recorded in an Applied Photophysics (UK) Pistar apparatus coupled to a Peltier temperature control device and a Neslab RTE-70 water bath, and calibrated with (+)-10-camphorsulfonic acid. Data were collected in 0.2-nm steps in the adaptive sampling mode at 25°C with 10–20 µM protein, peptides, or 1:1 mixtures in 100 mM KF, 7.5 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.5), 1 mM path length, 2-nm slit width and averaged over three scans.
Calorimetry
Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) was carried out in a MicroCal (Northampton, MA) VP-ITC system. Protein samples were dialyzed against ITC buffer (100 mM NaCl, 50 mM phosphate buffer pH 7.5, 2 mM β-mercaptoethanol, 0.05% sodium azide). Peptides were dissolved in the ITC buffer. All samples were degassed prior to ITC, and at least two independent titrations were carried out for each condition. An amount of 1.44 ml of 20 µM CarANt or peptide in the ITC cell was titrated with 30 injections of 8 µl of 0.22 mM CarS, CarS1, or CarS* at a given temperature with stirring at 300 rpm. Control titrations with buffer alone in the ITC cell or the injector syringe were used to correct for the heat of dilution of the titrant. The average heat of the final four or five values in a titration with peptide solutions was used to correct for the heat changes on mixing due to any slight differences in the pH between the two solutions. Corrected data were fit to a single-site binding model using the MicroCal Origin software to determine the binding stoichiometry (N), binding enthalpy (ΔH) and entropy (ΔS), and equilibrium association constants (Ka).
Analytical gel filtration and EMSA
CarS, CarS1, or CarS* complex formation with CarNt or CarHNt was analyzed in vitro using a Superdex200 analytical size-exclusion HPLC column. The column was equilibrated with 50 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.5) containing 2 mM β-mercaptoethanol and the required NaCl concentration. The calibration curve [obtained as in (10), and essentially the same at 0.15 M and 1.0 M NaCl] was log Mr = 7.64 – 0.209 Ve, where Mr is the apparent molecular weight and Ve, the elution volume. One hundred-microliter samples of 10–50 µM pure protein or mixtures of CarNt or CarHNt, and CarS or CarS* at equivalent concentrations were eluted at a flow rate of 0.4 ml/min and tracked by absorbances at 280, 235 and 220 nm. Each peak fraction was collected, protein identities were verified by SDS–PAGE, and Mr was estimated from the corresponding Ve.
EMSA (electrophoretic mobility shift assays) were carried out using a PCR-amplified, 130-bp DNA probe containing the CarA operator and PB promoter, which was 32P-labeled at the 5′-end as described elsewhere (12). A 20-µl reaction volume containing the DNA probe (1.2 nM, ∼13 000 cpm), CarANt with or without CarS or CarS* (final concentrations as indicated), 100 mM KCl, 25 mM Tris, pH 8, 1 mM dithiothreitol, 10% glycerol, 200 ng/µl bovine serum albumin and 1 µg of sheared salmon sperm DNA as non-specific competitor was incubated at 37°C for 30 min. Samples were electrophoresed for 1–1.5 h at 200 V, 10°C in an 8% non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel (37.5:1 acrylamide:bisacrylamide) that was pre-run for 30 min in 0.5× TBE buffer (45 mM Tris base, 45 mM boric acid, 1 mM EDTA). Gels were vacuum-dried and analyzed by autoradiography. Band intensities were estimated using a Gel Logic200 Imaging System and Kodak 1D ImageAnalysis Software V3.6.
Docking using HADDOCK
Starting with the average energy-minimized NMR structures determined for the free proteins, CarANt was docked onto CarS1 using the high-ambiguity-driven protein–protein docking program HADDOCK (31). Experimentally derived data from chemical shift perturbations and site-directed mutagenesis (this study; 10) were translated into the ambiguous interaction restraints for the docking. Surface accessible residues (ASA ≥ 25%) defined as ‘active’ included: T34, D52, D53, L75, F77 and E79 in CarS1; R10, R20, E23, R24, R25 and L32 in CarANt. The neighbouring ‘passive’ residues were: S30, E31, I35, P54 and Q57 in CarS1; R6, M11, E16 and Y26 in CarANt. Residues 48–65 and 73–82 in CarS1, and 2–12, 15–28 and 32–43 in CarANt were treated as semi-flexible. The docking involved randomization and rigid body energy minimization, semi-flexible simulated annealing and flexible explicit solvent refinement to minimize structural changes during docking. Of the initial 200 rigid-body docked structures generated, the best 20 were refined first by semi-flexible simulated annealing, then in water solvent, and clustered using a 3.0 Å RMSD cut-off criteria. The resulting 20 complex models presented essentially the same structure. The complex with the lowest energy was selected as the most representative and submitted to molecular dynamics refinement with AMBER (23). The complex structure with ∼5000 water molecules was submitted to a standard equilibration protocol described previously (32), and then to a long run of 1 ns of an unconstrained molecular dynamics calculation using the AMBER-98 force field (33) for the solute, the TIP3P model to simulate water molecules (34), and the Particle mesh Ewald method to evaluate long-range electrostatic interactions (35). The last 25 ps of the trajectory were averaged and the resulting structure was analyzed using MOLMOL (26).
RESULTS
Solution structure of CarS1 reveals a fold resembling SH3 domains
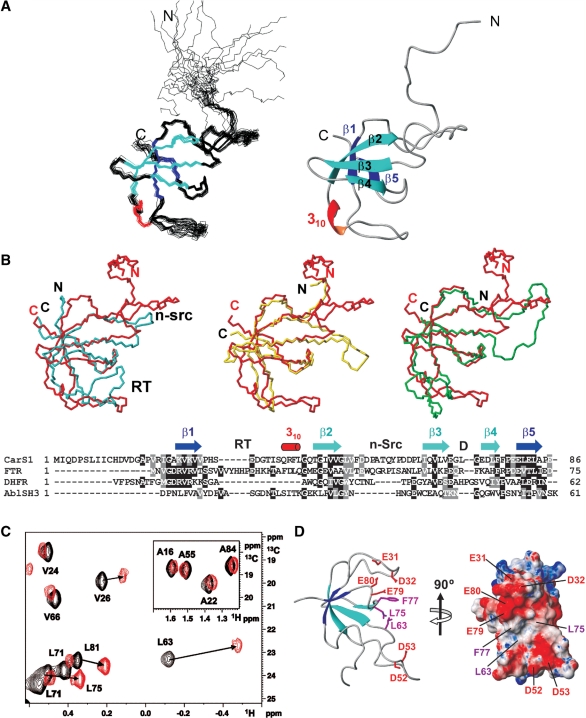
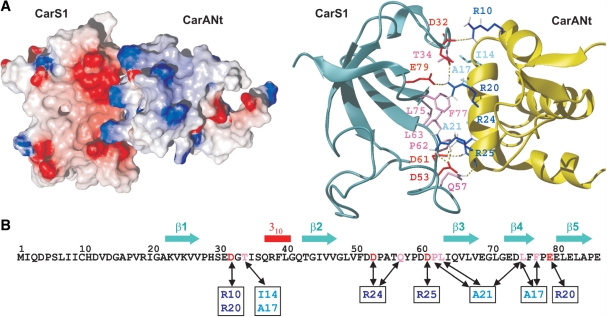
CarS1 is a functional, truncated form of CarS (lacking the last 25 residues) that, like CarS, forms a 1:1 complex with the CarA or CarH N-terminal domain (10,15,36). Given its excellent spectral dispersion and overall quality, NMR studies were carried out with CarS1. 1H, 15N and 13C resonances were assigned using standard triple resonance methods (20). The ensemble of the 20 lowest-energy structures calculated using experimental constraints (Supplementary Table S2) revealed a disordered nine-residue N-terminal segment, a relatively well-defined loop with two arms (residues 10–13 and 17–19) in extended conformations, a 310 helix (residues 37–39) and a five-stranded β-sheet (Figure 1A and Supplementary Figure S1). The β3–β4 hairpin is orthogonal to the β5–β1–β2 sheet, and long loops connect β1 to β2 and β2 to β3. Pairwise root mean square deviations (rmsd) for the superposition of the final structures, excluding the disordered, nine-residue N-terminal segment, were 0.8 ± 0.1 Å and 1.4 ± 0.3 Å for the backbone and heavy atoms, respectively (Supplementary Table S2). Steady-state, backbone 15N-{1H} heteronuclear NOEs of ≤0.65 for several non-P residues in the β1–β2 loop suggest flexibility with large amplitude motions on the subnanosecond timescale (Supplementary Figure S1C). Twenty-five residues mostly in strands β1 to β5 and involved in H-bonds showed the slowest amide 1H exchange with solvent (three to four orders of magnitude slower than random-coil values; Supplementary Figure S1A). The total solvent-accessible surface area (ASA) in native CarS1 is 6360 Å2, and its hydrophobic core is composed of 13 non-polar residues. Of the eight P in CarS1, only P59 is in the cis form and is stabilized by stacking interactions with Y58. With nine D and seven E but only two each of R, K and H, CarS1 is highly acidic (theoretical pI = 4.1). Basic residues lie on one face of the protein surface, while regions of high negative electrostatic potential are on two other adjoining faces (Supplementary Figure S1D). These latter are likely regions for interaction with CarANt, the highly basic and autonomously folded N-terminal DNA-binding domain of CarA.
Figure 1.
CarS1 structure and interactions with CarANt from NMR. (A) Superposition of the backbone traces for the 20 final NMR structures (left) and ribbon diagram of the average structure. (B) Cα-based overlay of the Abl tyrosine kinase SH3 domain (blue; PDB ID: 1JU5), R67-plasmid DHFR (yellow; PDB ID: 1VIE), or chloroplast FTR subunit B (green; PDB ID: 1DJ7) onto CarS1 (red). The respective DALI Z-score/rmsd (Å)/sequence identity (%)/number of superimposed residues are: Abl SH3 domain: 3.4/2.6/6/50; DHFR: 5/1.6/20/49; FTR B: 5.2/2.7/21/57. Below is a structure-based sequence alignment showing secondary structural elements and the RT, n-Src and distal (D) loops as denoted in SH3 domains. Residues are shaded black if identical in at least two sequences and gray if similar. (C) Portion of the 1H-13C HSQC spectrum of 13C, 15N-labeled H6CarS1 (0.24 mM) showing methyl crosspeaks perturbed by a 1.5-fold excess of unlabeled CarANt (red) compared to no CarANt added (black). Inset shows negligible perturbation of labeled Ala methyl crosspeaks for comparison. (D) Ribbon and electrostatic surface models of CarS1 showing residues that interact with CarANt from NMR data. Interacting side chains are depicted as magenta sticks with neighbouring acidic residues in red in the ribbon model.
A DALI search of the structure database (37) matched the five-stranded β-sheet in CarS1 to the characteristic fold of SH3 domains, small and diverse protein–protein interaction modules typically involved in signal transduction pathways. The best matches (Z-scores ≥ 5) of CarS1, a monomer, were to the bacterial R67-plasmid dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR), which exists as homodimers or tetramers (38), and to subunit B of the chloroplast ferredoxin thioredoxin reductase (FTR) heterodimer (39). Figure 1B shows an overlay of the CarS1 β-sheet backbone onto DHFR, the FTR subunit B, or the prototypal Abl tyrosine kinase SH3 domain and the corresponding structure-based sequence alignment. The CarS1 backbone fold differs from the prototypal SH3 domain fold primarily in the length of the ‘n-Src’ loop, in having a 310 helix between β2 and β3 rather than between β4 and β5, and in the presence of an additional N-terminal loop.
CarS1 residues contacting CarA mapped by NMR
CarS1 residues that contact CarA can be inferred from NMR chemical shift perturbations on titrating 15N, 13C-labeled H6CarS1 with unlabeled CarANt. However, in such titrations at 25°C, exchange-broadening effects caused disappearance of the 1H-15N and 1H-13C HSQC crosspeaks. Similar problems on titrating 1H, 15N-labeled CarANt with unlabeled CarS1 were partly alleviated by using higher temperature (45°C) and adding 50 mM arginine and glutamate in the buffer for improved solubility (10). While these conditions also reduced exchange broadening in titrations of 13C, 15N-labeled H6CarS1 with unlabeled CarANt, we could not unambiguously assign the perturbed 1H-15N peaks. Nonetheless, 1H-13C HSQC spectra indicated significant perturbations for the methyl cross-peaks of V26, L63, L75, L81 (Figure 1C) and I64. Of these, only L63 and L75 are sufficiently solvent-exposed (ASA: 15 and 32%, respectively; others <1%) to likely be part of a contact surface. Since L63 is in the proximity of the solvent-exposed F77 (ASA = 34%; Figure 1D), any interaction with CarANt involving F77 that reorients its aromatic side-chain could also perturb the L63 methyl crosspeaks. Thus, NMR mapping suggests that L63, L75 and, possibly, F77 in CarS1 may interact with CarA.
CarS-binding surface probed by site-directed mutagenesis
To assess the functional importance of CarA-interacting residues of CarS inferred from NMR, we examined the consequences of mutating L63, L75, or F77 to A. The role of the acidic residues in CarS was also assessed, as some of these could be important in the interaction with CarA, given that mutating the basic residues R24 and R25 in the latter abolished binding to CarS (10). Moreover, E31, D32, D52, D53, E79 and E80 lie in the vicinity of L63, L75 and F77 in CarS, hinting that some or all of these may be involved in contacts with CarA (Figure 1D). We therefore examined the consequences of mutating these, as well as other acidic residues, in CarS. Specifically, we generated single mutations to A of D4, E69, E82 and E86; or double mutations to A of D12/D14, E31/D32, D52/D53, D60/D61, E73/D74 and E79/E80.
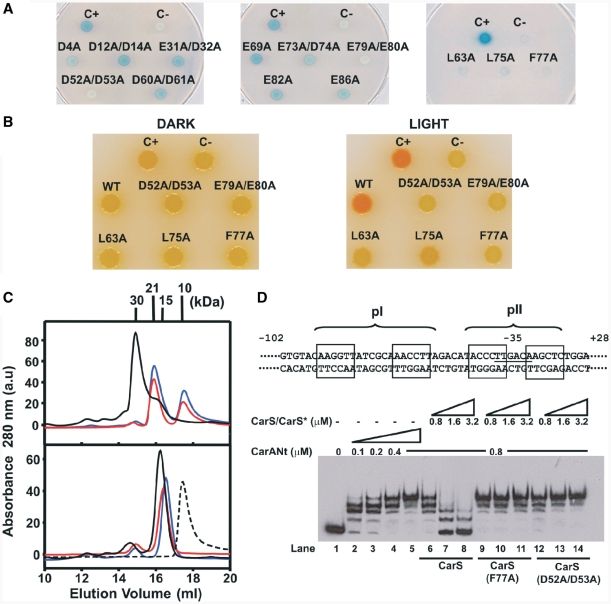
First, we monitored the effects of these CarS mutations on interactions with CarA by yeast two-hybrid analysis. In the system employed, the LexA DNA-binding domain fused to the N-terminus of CarA (LexA–CarA) served as ‘bait’, and CarS or any of its mutant forms (CarS*) fused to the C-terminus of the B42 transcriptional activation domain as ‘prey’. The B42–CarS hybrids were thus expressed from the GAL1 promoter, which is strongly activated by galactose and repressed by glucose. Physical interaction activates the reporter lacZ gene supplied in the yeast host employed. Control cells producing only one hybrid protein remained white on galactose plates even 24 h after the X-gal overlay. By contrast, cells producing LexA–CarA and B42–CarS turned blue within two hours, as also did cells expressing LexA–CarA and the other B42–CarS* fusions (Supplementary Figure S2A). Hence, under these conditions, no differences in interactions with CarA could be discerned between wild-type and any of the CarS* forms. However, on glucose plates, where the B42-fusions are expressed at basal levels, relative to the blue color of cells expressing LexA–CarA and B42–CarS, those expressing LexA–CarA and B42 fusions to the D52A/D53A, E79A/E80A, L63A, L75A or F77A CarS* were either white (like the negative control) or a very pale blue even after a prolonged (7–24 h) incubation with X-gal (Figure 2A). These CarS* are thus likely to be impaired in interactions with CarA. If this were indeed the case, introducing these mutations in M. xanthus could result in loss of light-induced carotenogenesis. Hence, this was examined next.
Figure 2.
CarS residues interacting with CarA identified by site-directed mutagenesis. (A) Yeast two-hybrid analysis of the interactions of each CarS mutant (CarS*) with CarA on glucose plates. C+: LexA–CarA and B42–CarS; C−: LexA–CarA only; others: LexA–CarA and the indicated B42–CarS*. (B) Color phenotypes for carotenogenesis in M. xanthus strains bearing the indicated carS allele. C+: wild-type; C−: ΔcarS; others are derived from introducing the indicated allele into the ΔcarS strain. (C) Elution profiles off a Superdex-200 analytical gel filtration column for the pure proteins (bottom) and CarANt mixed with CarS or CarS* (top). Dashed line is for pure CarANt; black, blue and red lines are for CarS, CarS* (F77A) and CarS* (D52A/D53A), respectively, with or without CarANt. Mr (in kDa) for each peak maximum is shown. (D) Top: schematic of the 130-bp EMSA probe spanning the carB promoter region, relative to the transcription start site (+1). The operator pI (–64 to −47) and pII (−40 to −26) sites are shown with their palindromic halves boxed. Bottom: EMSA for CarANt-binding to the 130-bp probe alone (lanes 2–5) or with increasing levels of CarS or CarS* added, as indicated.
We first generated a ΔcarS strain bearing an in-frame deletion of carS as described in ‘Materials and Methods’ section. Wild-type M. xanthus cells are yellow in the dark and turn a deep red in the light due to photo-induced carotenogenesis (Car+ phenotype), whereas the ΔcarS strain remains yellow even in the light (Car−) because there is no CarS to derepress carB. We then introduced into the ΔcarS strain a carS* allele (or wild-type carS as a positive control), and then checked for rescue or otherwise of the Car+ phenotype. Western blots using monoclonal anti-CarS antibodies of the corresponding whole-cell extracts obtained after growth in the light confirmed stable expression of each CarS* in vivo (Supplementary Figure S2B). In contrast to cells expressing wild-type CarS, those producing the L63A, L75A, F77A, D52A/D53A or E79A/E80A CarS* were Car−, like the ΔcarS strain (Figure 2B). The inability to restore the Car+ phenotype thus accords with impaired interaction of these CarS* with CarA inferred from two-hybrid analysis.
F77A and D52A/D53A CarS* were chosen as representative of non-polar and charged residues, respectively, whose mutation affected interactions with CarA. These were analyzed in vitro using analytical gel filtration, ITC and EMSA. Pure CarS and the two variants eluted off a Superdex200 analytical gel filtration column with Mr of 15.1 ± 0.8 kDa, compared to calculated monomer values of around 12.5 kDa; Mr is 9.6 kDa for pure CarANt, whose calculated value is 9.5 kDa (Figure 2C). When mixed with CarANt, CarS formed a stable 1:1 complex eluting at Mr of 30 ± 2 kDa, and no free CarANt peak was detected under the conditions used. In the presence of CarANt, either CarS variant produced a peak with Mr of 20.9 ± 0.3 kDa, considerably lower than for the CarA–CarS complex, and the free CarANt peak persisted at significant levels (Figure 2C). Thus, consistent with in vivo data, F77A and D52A/D53A CarS* form less tight complexes with CarANt. This was also confirmed by ITC data: CarANt formed a 1:1, high affinity (the dissociation constant, KD = 12 nM) complex with wild-type CarS, but its binding to the two CarS variants could not be detected under similar conditions (Table 1).
Table 1.
ITC data for the binding of CarS and CarS1 to CarANt or α2 peptidesa
| CarS/CarS1 | CarANt/peptide | Temperature (°C) | N | ΔH (kcalmol−1) | KD (nM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CarS | CarANt | 25 | 0.94 ± 0.01 | −9.24 ± 0.02 | 12 ± 3 |
| CarS | P01 | 25 | 0.93 ± 0.03 | −11.69 ± 0.30 | 150 ± 40 |
| CarS | P02 | 25 | 1.07 ± 0.01 | −12.03 ± 0.22 | 300 ± 50 |
| CarS | CHP01 | 25 | 0.91 ± 0.01 | −7.15 ± 0.17 | 690 ± 140 |
| CarS1b | P01 | 25 | 0.92 ± 0.02 | −8.46 ± 0.13 | 150 ± 18 |
| CarS1b | P01 | 20 | 0.93 ± 0.01 | −5.70 ± 0.05 | 175 ± 19 |
| CarS1b | P01 | 30 | 0.89 ± 0.01 | −10.88 ± 0.07 | 200 ± 17 |
| CarS1b | P01 | 35 | 0.89 ± 0.01 | −14.39 ± 0.11 | 270 ± 22 |
| CarS1 | P02 | 25 | 0.97 ± 0.02 | −7.60 ± 0.10 | 490 ± 90 |
aHeat changes were negligible or undetected for the following titrations: (i) CarANt or P01 with CarS(F77A) or CarS(D52A/D53A); (ii) P03 with CarS or CarS1; (iii) TtP01 with CarS (for details on peptides P01, P02, P03, CHP01 and TtP01, see Figures 3A and 4A, and text).
bTemperature dependence of ΔH for these titrations was used to estimate ΔCP = −0.57 ± 0.03 kcal mol−1 K−1. Values represent the average of at least two independent titrations.
Weakened CarA–CarS interactions would be expected to favor CarA–operator binding. Hence, we also compared the effect of F77A or D52A/D53A CarS* versus CarS on CarANt–operator binding in vitro using EMSA. For this, we used a 130-bp DNA probe containing both sites of the bipartite CarA operator: the high affinity pI site, located upstream of the promoter region, and the low affinity pII site that straddles the −35 promoter element (Figure 2D). CarANt binds to this probe in a step-wise manner, first to each half-site of pI and then to each half-site of pII, as is manifested by the progressive appearance of a ladder-like pattern of retarded bands with increasing CarANt amounts that gradually disappear as excess CarS is added (lanes 1–8, Figure 2D). By contrast, CarANt–operator complexes were disrupted neither by F77A nor by D52A/D53A CarS* (lanes 9–14, Figure 2D), consistent with their weaker interactions with CarANt and their observed in vivo effects on light-induced carotenogenesis.
The CarA operator recognition helix is sufficient for tight interaction with CarS
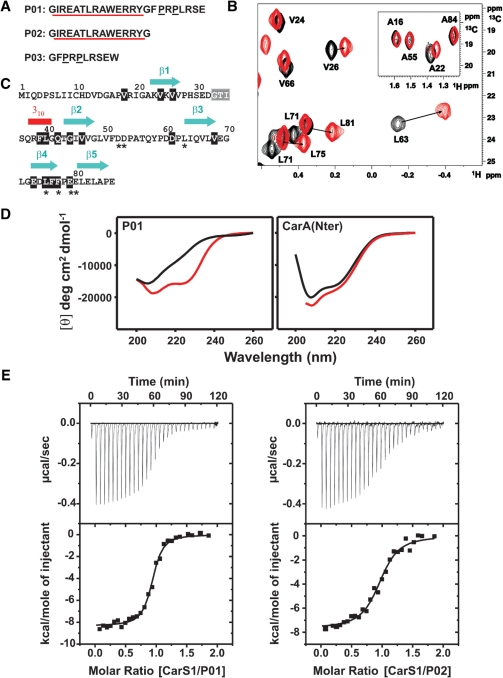
Two residues in the CarA DNA recognition helix α2 (R24, R25) have been shown to be crucial in the interactions with CarS, as noted earlier. Whether α2 alone can be targeted by CarS was checked using synthetic peptides that span CarA α2 (Figure 3A). P01 spans the α2 segment plus the subsequent eight C-terminal residues containing two P reminiscent of P-rich domains recognized by many SH3 domains (16,18); P02 corresponds only to α2. Interactions of P01 and P02 with CarS1 were probed by NMR, CD spectroscopy and ITC.
Figure 3.
CarA α2 peptides interact with CarS or CarS1. (A) CarA α2 peptide sequences. The α2 segment is underlined in red and the two P in black. P03 has a non-native W for concentration determination. (B) Methyl 1H-13C HSQC crosspeaks of 13C, 15N-labeled H6CarS1 perturbed by a 1.5-fold excess of unlabeled P02. Details are as in Figure 1C. (C) CarS1 sequence indicating residues for which the 1H-15N HSQC crosspeaks shifted [shaded black; Δδ(1H,15N ≥ 0.05 ppm)] or disappeared (shaded gray) on titrating with P01 or P02. Other residues were unchanged or could not be assigned. An asterisk below indicates interaction with CarA from mutagenesis data. (D) Far-UV CD spectra of P01 and CarANt in the absence and presence of CarS1. Black curves: P01 (18 µM) or CarANt (11 µM) alone; red curves: molar ellipticity difference between the spectrum of CarS1 mixed with P01 or CarANt (1:1 molar ratio) and that of CarS1 alone. (E) ITC of 20 µM P01 or P02 with CarS1 (216 µM) at 25°C. The heat change with each injection (top panels) and the corresponding integrated heat normalized and corrected for the heat of dilution versus molar ratio (bottom panels) are shown. The line is a best fit of data to a single-site binding model for the parameters in Table 1.
P01 or P02 produced significant CarS1 chemical shift perturbations demonstrating that they are sufficient for interaction. Moreover, 1H-13C HSQC methyl crosspeaks of 13C, 15N-labeled H6CarS1 perturbed by P01 or P02 matched those caused by CarANt (compare Figure 3B with Figure 1C), suggesting that P01 and P02 maintain many of the same specific contacts as CarANt in interacting with CarS1. In addition, we could identify significant perturbation of the P62 δCH and the E73 αCH 1H-13C crosspeaks, and of a number of 1H-15N HSQC crosspeaks (Figure 3C) including those corresponding to residues shown to be functionally important in the previous section. 1Hα, 13Cα and 13Cβ chemical shift deviations from random coil values and medium range NOEs characteristic of helical conformation observed for the free peptides at 5°C suggest an intrinsic helical propensity in the stretch equivalent to the CarANt α2 segment (Supplementary Figure S3). 1Hα deviations were, however, smaller than for the same residues in native CarANt, especially at 25°C. This is consistent with lower peptide helix content, as was confirmed by the far-UV CD spectra of the isolated peptides. By comparison, the helix content (directly related to −[θ]222, the molar residue ellipticity at 222 nm in degrees cm2 dmol−1) of P01 is markedly enhanced by the presence of a molar equivalent of CarS1 (red curve, Figure 3D, left panel), with discernible minima at 222 nm and 208 nm in the far-UV CD spectra characteristic of α-helical conformation (40,41). CarS1 produced similar effects in the far-UV CD spectra of P02 (not shown). On the other hand, the presence of CarS1 caused no significant change in the far-UV CD spectrum of native CarANt, whose helices, notably α2, are stably formed (Figure 3D, right panel). CarS affected the far-UV CD of P01 and CarANt in a manner similar to CarS1.
ITC data confirmed that P01 and P02 bind to CarS1 or CarS (but not to F77A or D52A/D53A CarS*). Binding occurred with a 1:1 stoichiometry and high affinity (KD in the nM range), and was driven by favorable enthalpy (ΔH), whose temperature dependence yielded a heat capacity change on binding (ΔCP) of −0.57 kcalmol−1K−1, consistent with a net burial of solvent-accessible surface (Figure 3E; Table 1). KD for P01 was 2- to 3-fold lower than for P02. This suggests small, if any, contributions to binding from the P-rich segment C-terminal to α2 in P01. Thus, a peptide (P03) corresponding to this segment alone did not bind to CarS1 or CarS under similar conditions (Table 1). Both P01 and P02 bind with lower affinities than CarANt (whose KD is over an order of magnitude lower). This likely reflects the energetic cost of inducing α-helix formation in the peptides on binding to CarS/CarS1, in contrast to the stably folded α2 in CarANt (41,42), although it cannot be ruled out that some interactions of CarANt with CarS are absent with the peptides. In sum, our data indicate that P01 and P02 do interact tightly with CarS1 (or CarS), and do so as α-helices whose formation is enhanced upon binding. Thus, CarA α2 alone is sufficient for tight binding to CarS.
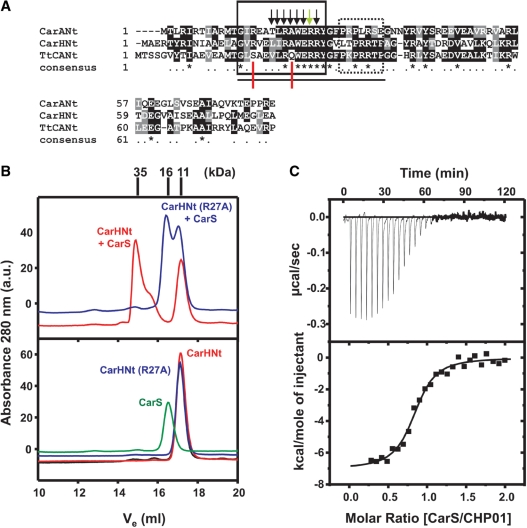
CarS binds the CarH DNA recognition helix
CarS, as noted earlier, also binds to the CarH N-terminal DNA-binding domain, CarHNt (15). Furthermore, the latter has a segment closely matching CarANt α2 and an adjacent, less-conserved C-terminal stretch with two P (Figure 4A). We have previously shown that, like R40 in CarANt, R42 in CarHNt is critical for operator-binding (15). A crucial determinant for CarS-binding is R24 in CarANt (10), and mutating the corresponding R27 in CarHNt to A also destabilizes complex formation with CarS, as monitored by analytical gel filtration (Figure 4B). Thus, CarHNt conserves at least two key CarANt residues involved in binding to operator and CarS, respectively. We therefore examined using ITC if CHP01, a CarHNt peptide equivalent to P01, also binds to CarS with high affinity. We found that CHP01 can indeed bind tightly to CarS, but with a KD somewhat higher than for P01 (Figure 4C and Table 1). Thus, the CarHNt segment equivalent to CarANt α2 is also sufficient for interaction with CarS.
Figure 4.
Analysis of CarS interactions with CarHNt. (A) Sequence alignment of CarANt, CarHNt and TtCANt, the N-terminal domain of the T. thermophilus CarA/CarH-like protein (NCBI accession codes: CAA79964, CAA79965 and NP_967879, respectively). Identical residues are shaded black and marked with an asterisk in the line corresponding to ‘consensus’; similar residues are shaded gray. Shown boxed are the α2 segment (solid lines) and the P-rich part C-terminal to α2 (dotted lines). Black arrows indicate CarA α2 residues contacting CarS from NMR or site-directed mutagenesis data (10), and the green arrow that this residue in CarH is also implicated in CarS-binding, as inferred from site-directed mutagenesis (B). The line at the bottom spans the stretch corresponding to peptides P01 in CarANt, CHP01 in CarHNt and TtP01 in TtCANt. Red lines point to residues conserved in P01 and CHP01, but not in TtP01. (B) Elution profiles off a Superdex200 analytical gel filtration column for the pure proteins (bottom) or mixtures (top) as labeled, with Mr (in kDa) for each peak maximum marked on top. The top panel shows that CarS forms a 1:1 complex (Mr ≈ 35 kDa) with CarHNt (red), but not its R27A mutant (blue). Yeast two-hybrid analysis confirmed the lack of interaction with CarS of the R27A variant of whole CarH (not shown). (C) ITC of 20 µM CHP01 titrated with 216 µM CarS shown as in Figure 3E. The line is the best fit of data to a single-site binding model for the parameters in Table 1.
A segment similar to CarA/CarH α2 is conserved in several proteins of unknown functions with a CarA/CarH-like domain architecture that have been identified from bacterial genome data (15). The N-terminal region of one such protein (from Thermus thermophilus) is shown in Figure 4A. A peptide derived from the latter, TtP01, the counterpart of P01 or CHP01, did not bind CarS when monitored by ITC (Table 1). TtP01 does not conserve CarANt R15 nor A21 (in CarHNt, these are R18 and A24, respectively; Figure 4A). Since CarS-binding was not impaired on mutating CarA R15 to A (10), the A21 to Q change in TtP01 probably explains why this peptide did not bind CarS.
Model of the CarS1–CarANt complex and comparison with that of operator–CarANt
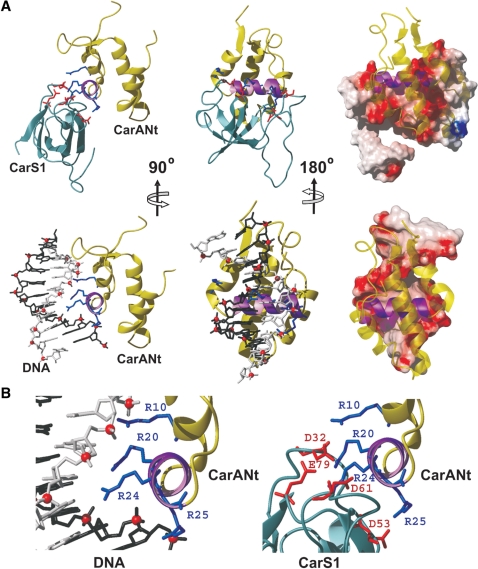
A structural model of the CarS1–CarANt complex was generated using HADDOCK as described in ‘Materials and Methods’ section (Figure 5A). In this model, CarANt docked via α2 in a unique orientation on CarS1, the resulting interface burying ∼1322 Å2 of surface area. The free protein structures were largely maintained in the complex, except for a flexible segment in the CarS1 β2–β3 loop (residues 50–60), whose exclusion in a superposition of the free and the bound structures reduced backbone RMSD from 2.5 to 1.5 Å. Thus, the pocket for housing α2 appears to pre-exist in CarS1. The shape and electrostatic complementarity of the contact surfaces are apparent in Figure 5A, where a positively charged ridge on CarA α2 nestles into a hydrophobic pocket with a negatively charged rim in CarS1. The importance of electrostatic effects is evident from the dependence of stable complex formation on ionic strength (Supplementary Figure S4). Besides L63, L75 and F77, whose functional importance has been demonstrated here, the model implicates T34 and P62 of CarS1, and I14′, A17′ and A21′ of CarA α2 (prime indicates CarA residue) in hydrophobic contacts at the interface. I14′ and A21′ are conserved as V and A, respectively, but A17′ is E in the equivalent CarH α2 segment, which binds to CarS (Table 1 and Figure 4). That A21′, conserved in both CarA and CarH, is important is reinforced by the observation that TtP01, where Q replaces A21′, does not bind to CarS. The docking suggests salt-bridge interactions involving charged residues R24′, R25′, D53 and E79, whose functional significance was established by site-directed mutagenesis. In the model, R20′ participates in charge interactions with E79 and D32, and in cation–π interactions with F77. The finding that mutating R20′ to A produced no apparent impairment in interactions with CarS (10) may be due to this change being accompanied by compensatory interactions and/or local structural readjustments.
Figure 5.
Model of the CarS1–CarANt complex. (A) Electrostatic surface and ribbon representations of CarS1–CarANt complex illustrating charge and shape complementarity of the interacting surfaces. In the ribbon model, side chains at the interface are depicted as sticks in red (E or D) or pink (uncharged residues) for CarS1, and dark (R) or pale blue (uncharged) for CarANt. Dotted lines are possible H-bonds. (B) CarS1 sequence with residues interacting with those in CarANt (boxed) linked by double-headed arrows and colored as in (A).
Determinants necessary for tight binding to CarS1 as well as to operator DNA reside in the basic α2 (theoretical pI = 10.7). Hence, we compared α2 contacts with CarS1 versus those with DNA (Figure 6). CarANt conserves the winged-helix topology and most of the crucial DNA contacts of MerR-family proteins and, like the latter, operator-binding bends the DNA about the central dinucleotide (10). In our model of the complex, α2 occupies the major groove of this bent operator half-site, with its axis nearly perpendicular to that of DNA and burying 1150 Å2 of surface area at the interface. The operator and CarS1 surfaces that contact α2 are both polar and similar in size, and the relative locations and trajectories of negatively charged groups involved in the interactions are comparable (Figure 6). This is consistent with a critical role for electrostatic interactions in both cases, with complex formation being salt-sensitive and crucially dependent on specific charged residues. Thus, three out of the four R in α2 determine operator binding and their mutation relieves carB repression, while the fourth (R24′) has a marginal though observable effect (10). At least two of these (R24′ and R25′) are also critical in the binding to CarS1, as are specific D and E residues in the latter.
Figure 6.
Comparison of CarA α2 contacting CarS1 and DNA. (A) Top: CarS1-CarNt complex as ribbon models (left and centre) or with CarS1 in electrostatic surface representation (right). Charged side chains at the interface are shown as sticks and CarANt α2 is in purple. Bottom: CarANt in complex with the distorted pI half-site of operator DNA (10). CarANt is shown as in the models above. DNA is represented as a stick model with one strand in black, the other in gray, and phosphates as red spheres (left and centre), or by the electrostatic surface (right). (B) Close-up view of the CarANt α2-binding site in operator DNA (left) and in CarS1 (right). Charged side chains at the interface are displayed as sticks with α2 oriented as in the ribbon models on the left in (A).
DISCUSSION
CarS and SH3 domains
This study provides a high-resolution structural description of the CarS antirepressor and its mode of action in activating a photo-inducible transcriptional switch. The structure reveals a β-barrel fold akin to that in SH3 domains. However, it diverges from the typical SH3 domain fold in the lengths and conformations of the connecting loops, notably those equivalent to the n-Src and RT loops, the location of a 310 helix, and the presence of a long N-terminal extension. Also, although the molecular activity of CarS is in protein–protein interactions, like SH3 domains, CarS is a novel variant of this domain superfamily in its ligand binding mode and specificity, as discussed next.
SH3 domains typically bind to P-rich domains, whose specificity and affinity is often increased by basic R or K engaging acidic E or D of the SH3 domain (16,18). P-rich domains bind as a poly-proline type II (PPII) helix to two hydrophobic grooves and a pocket formed by the RT and n-Src loops in the SH3 domain, the affinities for the enthalpically-driven association characterized by KD of usually 1–200 µM, and ΔCP of −0.15 to −0.35 kcalmol−1K−1 (16,18,43). Besides the conventional union to a P-rich domain, the more exceptional Pex13p SH3 domain and p67phox use a distinct surface to simultaneously bind an α-helix or a helix-turn-helix, respectively (44,45). Thus, the p67phox SH3 domain binds to both a P-rich domain and a contiguous C-terminal helix-turn-helix with an affinity (KD = 24 nM) far greater than to each of the two segments separately (KD = 10–20 µM). Some SH3 domains employ the same hydrophobic groove to bind not only canonical P-rich domains but also ubiquitin or ubiquitin-like domains with comparable affinities (46,47). The few ‘SH3 domain-like’ units known in bacteria are modules of larger proteins engaged in oligomerization via surfaces distinct from those in eukaryotic SH3 domains (38,48), and only for that in the DtxR repressor is there evidence of binding to a P-rich motif (49).
For specific, high-affinity interaction with CarS the operator DNA recognition helix α2 in CarA or CarH is sufficient, and a P-rich segment C-terminal to α2 contributes little, if at all. The CarS interaction surface, encompassing residues in the β2–β3 loop and the β4–β5 stretch, also differs from the pockets used by other SH3 domains to bind P-rich domains, ubiquitin, or α-helices. Tight association is achieved by hydrophobic contacts of large non-polar side chains and from interactions involving charged R in the basic α2 and D/E in the acidic CarS. The α-helical conformation, as already existing in native CarA, is required for binding to CarS. Even isolated α2 peptides with low helix contents bind as an α-helix and, despite the energetic cost for this induced folding, have affinities (KD = 150–500 nM) and ΔCP (−0.57 kcal mol−1K−1) that exceed those reported for typical SH3 domains and their ligands. Our results thus indicate an unprecedented mode for protein–protein recognition by an SH3 domain-like fold that is employed in transcriptional regulation.
CarS acts as an operator DNA mimic
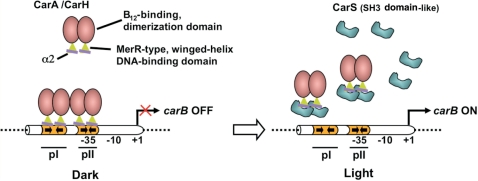
A way to dismantle operator–repressor complexes is, as noted earlier, non-covalent union to an antirepressor. Direct targeting of critical DNA-recognition elements to sequester them and neutralize repressor activity is the strategy resorted to by the CarS antirepressor. CarA binds in a cooperative, stepwise manner to its bipartite operator (Figure 7) (14). Disrupting the pre-bound CarA–DNA complex would be determined by its dissociation kinetics, and by CarS trapping the freed CarA so as to hinder it from binding again to operator. This would be favored if the union of CarS and CarA is tight enough to compete effectively against operator, and if CarS amounts far exceed the single operator site per cell. The affinity for operator remains to be precisely quantified, but available in vitro data suggest that CarANt binds to the operator pI site with KD in the 100–200 nM range (10). Affinity for the pII site would then be much lower; yet mutating it is sufficient to abolish repression by CarA (14). That CarS binds CarANt with high affinity is evident from the KD (∼10 nM) estimated in this study, while high intracellular CarS levels are ensured by its light-induced expression (50). Together, these rationalize how CarS can compete effectively against operator to trap the CarA DNA-binding domain and enable antirepression (Figure 7).
Figure 7.
Model for the control of carB expression by CarA/CarH-CarS repressor–antirepressor pairs highlighting known details of the domains, their structures and interactions. CarA and CarH dimerize via their C-terminal B12-binding domains (pink oval) and bind to the bipartite operator (orange) via their N-terminal, MerR-type winged-helix domain (green triangle; the purple line represents the DNA recognition helix α2) to repress carB in the dark. The SH3 domain-like CarS (cyan) produced in the light binds tightly to α2 to sequester CarA and CarH, prevent their binding to operator DNA and activate carB expression.
Our finding that CarS binds tightly to the CarA α2 peptide emphasizes that the specific targeting and sequestering of α2, the critical DNA-recognition element, underlies antirepression by CarS. In directly targeting several residues in α2 that also contact DNA, and in its highly acidic nature and use of negatively charged residues for key interactions, CarS acts as an operator DNA mimic. While its overall negative charge may facilitate complex formation, the shape and charge complementarity already sculpted on the SH3 domain-like scaffold of CarS underpins its ability to bind α2 with high specificity and affinity. By contrast, operator-binding via α2 must incur an additional energetic cost as it is accompanied by DNA distortion. Indeed, it is the bent or distorted conformation of the specific DNA site rather than the normal B form that is imitated by protein mimics of DNA to sequester their target DNA-binding proteins (51,52). The small number of reported protein DNA mimics are typically very acidic (theoretical pI: 3.8–5.5) like CarS1 (pI = 4.1) or CarS (pI = 4.8), and their targets include restriction enzymes (53,54), DNA repair enzymes (55,56), DNA gyrase (57), and histones or prokaryotic histone-like proteins (58,59). In transcription regulation, the one structurally well-characterized example of a DNA mimic is the N-terminal subdomain (TAND1) of eukaryotic TAF||230, which binds to TBP, the TATA-binding protein (60). TBP binds DNA using an extended, concave surface constituted by a ten-stranded, antiparallel β-sheet. TAND1 is intrinsically disordered. To insert itself into the concave TBP DNA-binding surface to shut down transcription, TAND1 adopts a defined structure that precisely imitates the bend and distortion of the partially unwound minor groove of the TATA-box target site. By comparison, the stably folded CarS mirrors the distorted major groove of the operator to lock on to CarA (or CarH) α2, a much smaller target, and turn on transcription.
Until recently, CarA and CarH were the only transcriptional regulators known with a MerR-type DNA-binding domain linked to a vitamin B12-binding domain. Genome data now reveal that several other bacteria also contain proteins with this domain architecture, but whose functions are unknown (15). Interestingly, although one of the most highly conserved regions in these is that corresponding to CarA/CarH α2, BLAST analysis indicates that a protein similar to CarS in sequence does not exist in any of these bacteria (except Stigmatella aurantiaca, a myxobacterium very closely related to M. xanthus; Supplementary Figure S5). The question therefore arises as to how the activities of CarA/CarH-like proteins in these other bacteria are modulated, and whether it involves factors that, despite no overall sequence similarity, resemble CarS functionally and possibly structurally. Future work addressing these issues, as well as the design of proteins tailored to target specific DNA-binding proteins, can clearly draw upon the structural and mechanistic details emerging from our studies on CarA, CarH and CarS function in M. xanthus.
COORDINATES
Coordinates for the 20 final NMR structures of CarS1 have been deposited in the Protein Data Bank with accession code 2KSS. These were deposited earlier for CarANt (PDB accession code 2JML). Coordinates for the HADDOCK-generated model of the CarANt–CarS1 complex are available upon request.
ACCESSION NUMBER
PDB Accession code 2KSS.
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
Supplementary Data are available at NAR Online.
FUNDING
Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación-Spain [Grants BFU2006-14524 and BFU2009-12445-C02-01 to M.E.-A.; BFU2008-00911 and BFU2009-12445-C02-02 to S.P.; CTQ2008-00080 to M.A.J.; CTQ2007-68014-C02-02 to C.G.; Ph.D. fellowships to E.L. and G.N.-A.; and a CSIC-I3P contract to C.M.S.]; Fundación Séneca-Murcia [08748/PI/08 to F.J.M.]. Funding for open access charge: Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación-Spain.
Conflict of interest statement. None declared.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors thank J.A. Madrid for technical assistance.
REFERENCES
- 1.Browning DF, Busby SJ. The regulation of bacterial transcription initiation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004;2:57–65. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Rojo F. Mechanisms of transcriptional repression. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2001;4:145–151. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5274(00)00180-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Schlax PJ, Capp MW, Record MT., Jr Inhibition of transcription initiation by lac repressor. J. Mol. Biol. 1995;245:331–350. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.0028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Oppenheim AB, Neubauer Z, Calef E. The antirepressor: a new element in the regulation of protein synthesis. Nature. 1970;226:31–32. doi: 10.1038/226031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lewis RJ, Brannigan JA, Offen WA, Smith I, Wilkinson AJ. An evolutionary link between sporulation and prophage induction in the structure of a repressor:anti-repressor complex. J. Mol. Biol. 1998;283:907–912. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1998.2163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Luo Y, Pfuetzner RA, Mosimann S, Paetzel M, Frey EA, Cherney M, Kim B, Little JW, Strynadka NCJ. Crystal structure of LexA: a conformational switch for regulation of self-cleavage. Cell. 2001;106:585–594. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00479-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Davis BM, Kimsey HH, Kane AV, Waldor MK. A satellite phage-encoded antirepressor induces repressor aggregation and cholera toxin gene transfer. EMBO J. 2002;21:4240–4249. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdf427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Masuda S, Bauer CE. AppA is a blue light photoreceptor that antirepresses photosynthesis gene expression in Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Cell. 2002;110:613–623. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00876-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wilke MS, Heller M, Creagh AL, Haynes CA, McIntosh LP, Poole K, Strynadka NC. The crystal structure of MexR from Pseudomonas aeruginosa in complex with its ArmR. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2008;105:14832–14837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0805489105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Navarro-Avilés G, Jiménez MA, Pérez-Marín MC, González C, Rico M, Murillo FJ, Elías-Arnanz M, Padmanabhan S. Structural basis for operator and antirepressor recognition by Myxococcus xanthus CarA repressor. Mol. Microbiol. 2007;63:980–994. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05567.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Elías-Arnanz M, Fontes M, Padmanabhan S. Carotenogenesis in Myxococcus xanthus: a complex regulatory network. In: Whitworth DE, editor. Myxobacteria: Multicellularity and Differentiation. Washington, DC: ASM Press; 2008. pp. 211–225. [Google Scholar]
- 12.López-Rubio JJ, Elías-Arnanz M, Padmanabhan S, Murillo FJ. A repressor-antirepressor pair links two loci controlling light-induced carotenogenesis in Myxococcus xanthus. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:7262–7270. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110351200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Whitworth DE, Hodgson DA. Light-induced carotenogenesis in Myxococcus xanthus: evidence that CarS acts as an anti-repressor of CarA. Mol. Microbiol. 2001;42:809–819. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02679.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.López-Rubio JJ, Padmanabhan S, Lázaro JM, Salas M, Murillo FJ, Elías-Arnanz M. Operator design and mechanism for CarA repressor-mediated downregulation of the photo-inducible carB operon in Myxococcus xanthus. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:28945–28953. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M403459200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Pérez-Marín MC, Padmanabhan S, Polanco MC, Murillo FJ, Elías-Arnanz M. Vitamin B12 partners the CarH repressor to downregulate a photoinducible promoter in Myxococcus xanthus. Mol. Microbiol. 2008;67:804–819. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.06086.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kuriyan J, Cowburn D. Modular peptide recognition domains in eukaryotic signaling. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1997;26:259–288. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.26.1.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.D'Aquino JA, Ringe D. Determinants of the Src homology domain 3-like fold. J. Bacteriol. 2003;185:4081–4086. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.14.4081-4086.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Li SS. Specificity and versatility of SH3 and other proline-recognition domains: structural basis and implications for cellular signal transduction. Biochem. J. 2005;390:641–653. doi: 10.1042/BJ20050411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ho SN, Hunt HD, Horton RM, Pullen JK, Pease LR. Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene. 1989;77:51–59. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90358-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.León E, González C, Elías-Arnanz M, Padmanabhan S, Jiménez MA. 1H, 13C and 15N backbone and side chain resonance assignments of a Myxococcus xanthus antirepressor with no known sequence homologues. Biomol. NMR Assign. 2009;3:37–40. doi: 10.1007/s12104-008-9136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Guntert P. Automated NMR structure calculation with CYANA. Methods Mol. Biol. 2004;278:353–378. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-809-9:353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Cornilescu G, Delaglio F, Bax A. Protein backbone angle restraints from searching a database for chemical shift and sequence homology. J. Biomol. NMR. 1999;13:289–302. doi: 10.1023/a:1008392405740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Case DA, Perlman DA, Caldwell JW, Cheatham III TE, Wang J, Ross WS, Simmerling C, Darden T, Merz KM, Stanton RV, et al. AMBER 7. San Francisco: University of California; 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Laskowski RA, Rullmannn JA, MacArthur MW, Kaptein R, Thornton JM. AQUA and PROCHECK-NMR: programs for checking the quality of protein structures solved by NMR. J. Biomol. NMR. 1996;8:477–486. doi: 10.1007/BF00228148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Willard L, Ranjan A, Zhang H, Monzavi H, Boyko RF, Sykes BD, Wishart DS. VADAR: a web server for quantitative evaluation of protein structure quality. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31:3316–3319. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Koradi R, Billeter M, Wüthrich K. MOLMOL: a program for display and analysis of macromolecular structures. J. Mol. Graph. 1996;14:51–58. doi: 10.1016/0263-7855(96)00009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bai Y, Milne JS, Mayne L, Englander SW. Protein stability parameters measured by hydrogen exchange. Proteins. 1994;20:4–14. doi: 10.1002/prot.340200103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Morris GA, Freeman R. Enhancement of nuclear magnetic resonance signals by polarization transfer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1979;101:760–762. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Grzesiek S, Stahl SJ, Wingfield PT, Bax A. The CD4 determinant for down-regulation by HIV-1 Nef directly binds to Nef. Mapping of the Nef binding surface by NMR. Biochemistry. 1996;35:10256–10261. doi: 10.1021/bi9611164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Peñalver-Mellado M, García-Heras F, Padmanabhan S, García-Moreno D, Murillo FJ, Elías-Arnanz M. Recruitment of a novel zinc-bound transcriptional factor by a bacterial HMGA-type protein is required for regulating multiple processes in Myxococcus xanthus. Mol. Microbiol. 2006;61:910–926. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Dominguez C, Boelens R, Bonvin AM. HADDOCK: a protein–protein docking approach based on biochemical or biophysical information. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003;125:1731–1737. doi: 10.1021/ja026939x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Soliva R, Monaco V, Gómez-Pinto I, Meeuwenoord NJ, Marel GA, Boom JH, González C, Orozco M. Solution structure of a DNA duplex with a chiral alkyl phosphonate moiety. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001;29:2973–2985. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.14.2973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Cornell WD, Cieplak P, Bayly CI, Gould IR, Merz K, Ferguson DM, Spellmeyer DC, Fox T, Caldwell JW, Kollman PA. A second generation force field for the simulation of proteins, nucleic acids, and organic molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995;117:5179–5197. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Jorgensen WL, Chandrasekhar J, Madura JD, Impey RW, Klein ML. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983;79:926–935. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Darden TE, York D, Pedersen L. Particle mesh Ewald: An N·log(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993;98:10089–10092. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Pérez-Marín MC, López-Rubio JJ, Murillo FJ, Elías-Arnanz M, Padmanabhan S. The N-terminus of M. xanthus CarA repressor is an autonomously folding domain that mediates physical and functional interactions with both operator DNA and antirepressor protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:33093–33103. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M405225200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Holm L, Sander C. Protein structure comparison by alignment of distance matrices. J. Mol. Biol. 1993;233:23–38. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Narayana N, Matthews DA, Howell EE, Nguyen-huu X. A plasmid-encoded dihydrofolate reductase from trimethoprim-resistant bacteria has a novel D2-symmetric active site. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1995;2:1018–1025. doi: 10.1038/nsb1195-1018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Dai S, Schwendtmayer C, Schürmann P, Ramaswamy S, Eklund H. Redox signaling in chloroplasts: cleavage of disulfides by an iron-sulfur cluster. Science. 2000;287:655–658. doi: 10.1126/science.287.5453.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Padmanabhan S, Marqusee S, Ridgeway T, Laue TM, Baldwin RL. Relative helix-forming tendencies of nonpolar amino acids. Nature. 1989;344:268–270. doi: 10.1038/344268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Padmanabhan S, Zhang W, Capp MW, Anderson CF, Record MT., Jr Binding of cationic (+4) alanine- and glycine-containing oligopeptides to double-stranded DNA: thermodynamic analysis of effects of coulombic interactions and alpha-helix induction. Biochemistry. 1997;36:5193–5206. doi: 10.1021/bi962927a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Spolar RS, Record MT., Jr Coupling of local folding to site-specific binding of proteins to DNA. Science. 1994;263:777–784. doi: 10.1126/science.8303294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Demers JP, Mittermaier A. Binding mechanism of an SH3 domain studied by NMR and ITC. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009;131:4355–4367. doi: 10.1021/ja808255d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Douangamath A, Filipp FV, Klein AT, Barnett P, Zou P, Voorn-Brouwer T, Vega MC, Mayans OM, Sattler M, Distel B, et al. Topography for independent binding of alpha-helical and PPII-helical ligands to a peroxisomal SH3 domain. Mol. Cell. 2002;10:1007–1017. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00749-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Kami K, Takeya R, Sumimoto H, Kohda D. Diverse recognition of non-PxxP peptide ligands by the SH3 domains from p67(phox), Grb2 and Pex13p. EMBO J. 2002;21:4268–4276. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdf428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Stamenova SD, French ME, He Y, Francis SA, Kramer ZB, Hicke L. Ubiquitin binds to and regulates a subset of SH3 domains. Mol. Cell. 2007;25:273–284. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.12.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Trempe J-F, Chen CX-Q, Grenier K, Camacho EM, Kozlov G, McPherson PS, Gehring K, Fon EA. SH3 domains from a subset of BAR proteins define a Ubl-binding domain and implicate parkin in synaptic ubiquitination. Mol. Cell. 2009;36:1034–1047. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.11.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Delbrück H, Ziegelin G, Lanka E, Heinemann U. An Src homology 3-like domain is responsible for dimerization of the repressor protein KorB encoded by the promiscuous IncP plasmid RP4. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:4191–4198. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110103200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Wang G, Wylie GP, Twigg PD, Caspar DL, Murphy JR, Logan TM. Solution structure and peptide binding studies of the C-terminal src homology 3-like domain of the diphtheria toxin repressor protein. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 1999;96:6119–6124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.11.6119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Hodgson DA. Light-induced carotenogenesis in Myxococcus xanthus: genetic analysis of the carR region. Mol. Microbiol. 1993;7:471–488. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01138.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Putnam CD, Tainer JA. Protein mimicry of DNA and pathway regulation. DNA Repair. 2005;4:1410–1420. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2005.08.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Dryden DTF. DNA mimicry by proteins and the control of enzymatic activity on DNA. Trends Biotechnol. 2006;4:378–382. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2006.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Walkinshaw MD, Taylor P, Sturrock SS, Atanasiu C, Berge T, Henderson RM, Edwardson JM, Dryden DTF. Structure of Ocr from bacteriophage T7, a protein that mimics B-form DNA. Mol. Cell. 2002;9:187–194. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00435-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.McMahon SA, Roberts GA, Johnson KA, Cooper LP, Liu H, White JH, Carter LG, Sanghvi B, Oke M, Walkinshaw MD, et al. Extensive DNA mimicry by the ArdA anti-restriction protein and its role in the spread of antibiotic resistance. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37:4887–4897. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Mol CD, Arvai AS, Sanderson RJ, Slupphaug G, Kavli B, Krokan HE, Mosbaugh DW, Tainer JA. Crystal structure of human uracil-DNA glycosylase in complex with a protein inhibitor: protein mimicry of DNA. Cell. 1995;82:701–708. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90467-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Serrano-Heras G, Ruiz-Masó JA, del Solar G, Espinosa M, Bravo A, Salas M. Protein p56 from the Bacillus subtilis phage ϕ29 inhibits DNA-binding ability of uracil-DNA glycosylase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35:5393–5401. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Hegde SS, Vetting MW, Roderick SL, Mitchenall LA, Maxwell A, Takiff HE, Blanchard JS. A fluoroquinolone resistance protein from Mycobacterium tuberculosis that mimics DNA. Science. 2005;308:1480–1483. doi: 10.1126/science.1110699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Parsons LM, Liu F, Orban J. HU-alpha binds to the putative double-stranded DNA mimic HI1450 from Haemophilus influenzae. Protein Sci. 2005;14:1684–1687. doi: 10.1110/ps.041275705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Wang HC, Wang HC, Ko TP, Lee YM, Leu JH, Ho CH, Huang WP, Lo CF, Wang AH. White spot syndrome virus protein ICP11: A histone-binding DNA mimic that disrupts nucleosome assembly. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2008;105:20758–20763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0811233106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Liu D, Ishima R, Tong KI, Bagby S, Kokubo T, Muhandiram DR, Kay LE, Nakatani Y, Ikura M. Solution structure of a TBP–TAF||230 complex: protein mimicry of the minor groove surface of the TATA box unwound by TBP. Cell. 1998;94:573–583. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81599-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.